The causes of circles before the eyes can be varied. Sometimes such visual abnormalities occur after prolonged exposure to bright light, as a result of friction or pressure on the eyeballs. In this case, the circles before the eyes do not last long and most often do not require medical intervention.
In other situations, the visual phenomenon is associated with taking medications, injuries, disorders of the vascular system, a deficiency in the body of substances that maintain the visual apparatus in good shape, and the entry of aggressive chemical compounds into the organs of vision. In some patients, the appearance of circles before the eyes is caused by certain diseases.
Pathology can occur both in people with ophthalmological disorders and in people with neurological or psychiatric disorders.
Ophthalmic diseases
Most often, rainbow circles are a concomitant symptom of the following ophthalmological pathologies:
- glaucoma;
- cataracts.
Glaucoma leads to gradual atrophy of the optic nerve, significant deterioration and even complete disappearance of vision. Bright and iridescent circles present before the eyes are most characteristic of the acute stage of the disease. Near the lighting they acquire a purple color, closer to the edge they become red. There can be a wide variety of shades within the circle. Simultaneously with the appearance of rounded colored figures, patients often experience pain in the eyeballs.
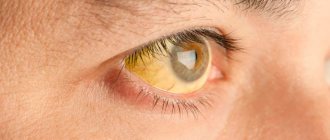
Cataracts cause clouding of the lens and mainly occur in older people. In persons with this diagnosis, circles before the eyes may be present already at the initial stage of the development of the disease. In addition to them, the patient often sees colored and black flies and a foggy haze in the field of view.
An unpleasant symptom sometimes occurs with conjunctivitis. In the presence of such a disease, the circles are not constantly present and disappear after clearing the eyes of accumulated mucus.
Neurological and psychiatric disorders
Among neurological pathologies, the following can provoke the appearance of rounded figures in the field of vision:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- pinched nerve;
- damage to brain stem structures;
- exacerbation of migraine.
Sometimes a visual anomaly is a symptom of mental disorders (primarily schizophrenia). In this case, it is considered as a hallucination. Additionally, the patient may experience delusional ideas and paralogical judgments.
The pathology may be of concern to patients with hypertension. Representatives of certain professions (welders) also periodically observe circles before their eyes.
In what cases is it necessary to consult an ophthalmologist?
If the problem is constantly bothering you, and no visible reasons for its development can be established, you should immediately visit a doctor. The main specialists who will help establish the cause of the pathology and select effective treatment will be an ophthalmologist and a therapist.
Doctors traditionally consider rainbow circles before the eyes not as an independent disease, but as a symptom of a certain pathology. In this regard, medical measures prescribed to the patient will be aimed at eliminating the provoking disorder.
Why do you see different patterns when you close your eyes?
The eyes transmit information to the brain about what kind of light falls on them. If the eyes are tightly closed, no light reaches the retina and we should not see anything. Why is it that when we close our eyes, we sometimes still see colored spots and even patterns?
This is a side effect of the brain recognizing the colors and brightness of points in the visual field. The lighting conditions around us are constantly changing, but we must correctly determine the colors when it’s day outside, and when it’s night, and when we walk through a green forest, and when we swim underwater, and even if we find ourselves in a disco and everything around is illuminated by multi-colored spotlights . If you take photographs of the same object under such different conditions, the object will appear in different colors in all the photographs. And yet we will always correctly determine the color of an object in a variety of circumstances, unless among us there are color blind people. How do we do this?
Different retinal cells called cones react to light of different colors. Some of them react most strongly to red light, others to blue light, and others to green light. The cones send the brain information about the color of each point in the visual field, and the brain figures out how to interpret it. If the brain interpreted information from cones in a straightforward manner, we would often identify colors incorrectly. For example, if we were in a room illuminated by red light, then all the objects in it would seem red to us, because the cones responsible for the color red would send the strongest signals to the brain. But in fact, after a few minutes in such a room, our eyes will adapt, and we will begin to correctly determine the colors of objects.
This will happen because the brain will change its idea of what “zero red” is. In a room with red lighting it is definitely higher than in the more common white or yellow light. After a few minutes in a red-lit room, the brain will begin to “subtract” this excess redness from the colors of all objects, and we will begin to perceive their colors correctly (although the cones will still receive mostly red signals).
How does the brain know exactly how much red to subtract? This happens naturally because the cells that normally detect redness will work too hard in the red room and begin to get tired. Their activity will quickly return to normal levels, but it will correspond to greater redness than before.
In fact, such an adjustment of neurons that recognize colors occurs even under ordinary lighting. In the same way, we adapt to the brightness of light. If a color is too bright or something is very brightly lit, the brain automatically subtracts the excess brightness or excess color. We sometimes see areas where adjustment has taken place when we close our eyes. It turns out something like a negative that we “see” for some time, even when we close our eyes. And we can see patterns because we tend to look for order even where there is none. Including spots that can be visible when we close our eyes.
(In addition to the negative effect that occurs due to the adjustment of the visual system, spots and lines before the eyes may appear due to disruptions in its functioning. Most often, such disturbances occur due to spasms of the vessels of the retina or brain. The spots that appear have nothing to do with what we look at, and can be visible with both open and closed eyes. Vascular spasms occur due to overwork, lack of sleep or nervous tension. So if you see spots and patterns that do not resemble anything, this is not a very good sign .)
False visual sensations can also occur due to mechanical effects on the eyes - for example, if you rub a closed eye. In addition, they can be induced artificially by affecting the areas of the brain responsible for vision. False visual sensations that occur without the influence of light are called phosphenes.
You can make sure that the brain adjusts our sense of color using these pictures:
Focus on the cross in the middle of one of the circles on the left for 20 seconds, and then move your gaze to the cross in the middle of the gray square on the left. You will see a circle of the opposite color (for example, if you initially looked at the red circle, and then look at the gray background, you will see a green circle). Gray is a neutral color, so against its background you see the opposite color to what your eyes have become accustomed to.
It is interesting that with the help of such tricks you can learn to see even “impossible” colors - objects in the real world cannot have such colors, but thanks to the properties of our visual system, it is possible to see them. To do this, you need to get used to a certain bright color, and then move your gaze to the background of the opposite color. For example, get used to red and look at the green background. As the brain gets used to the color red, it will subtract redness from everything the eyes see. But green is already the antipode of red, and if you subtract redness from it, you get something like “super green”. You won’t be able to print a picture of this color, so experiment with your color vision yourself.
You can read more about color recognition and “impossible” colors in the article Chimerical Colors: Some Phenomenological Predictions from Cognitive Neuroscience.
Answered by: Yulia Kondratenko
Diagnostics
Treatment of pathology is preceded by a diagnostic examination, consisting of several stages:
- Taking anamnesis. The doctor asks whether the visual apparatus has been injured, what medications the patient has taken, and asks the patient about the health status of his relatives and whether they have neurological or mental disorders.
- General inspection. The doctor assesses the condition of reflexes, skin and mucous membranes, studies the surface structures of the organs of vision for the presence of uncharacteristic signs.
- Ophthalmoscopy, which consists of determining the condition of the fundus. The procedure is carried out using mydriatics; it also helps to examine the cornea, lens, eye chambers, retina, and vitreous body.
- Computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging (CT. MRI). These methods provide layer-by-layer images of visual structures, help clarify the condition of blood vessels, nervous tissue, and identify bleeding and tumors.
Among the laboratory tests, general and biochemical blood tests and urine donation are required. These procedures help detect signs of systemic disorders that directly affect the condition of the visual organs.
The type of disease that caused the visual defect is also indicated by the color of the circles before the eyes. Thus, pink or purple figures appear in the field of vision of patients suffering from cataracts or glaucoma, taking antidepressants, drugs for the treatment of cardiovascular pathologies. Dark circles can appear with hypertension, spasms of the eye muscles, or retinal detachment.
In addition to an ophthalmologist and a therapist, the patient may be recommended to be examined by a psychiatrist, which will help confirm or refute pathological phenomena in the psyche.
“Floaters” before the eyes, flashes and vision of a rainbow halo
Description
And more minor visual impairments can cause anxiety in the patient.
The doctor is required to be able to distinguish those visual disorders for which specialist consultation is needed from those for which it is not necessary. "Floaters" before the eyes
.
This is the appearance of small black dots in the field of vision, especially noticeable against a dark background. These points move when the eyeball moves, but with some slowdown. The reason for this phenomenon
is the formation of opacities in the vitreous body. The bulk of floating bodies (floaters) consists of particles of degeneratively altered vitreous body of the eye. They are quite common in people with myopia, but also appear after injury. These flying “flies” irritate a person, but they are completely harmless, and over time this phenomenon goes away on its own. The sudden appearance of a whole shower of such “floaters” in one eye, often accompanied by flashing lights, is caused by blood entering the vitreous body. In such cases, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist, as the cause may be retinal detachment.
Flashing lights before your eyes
. This phenomenon may be associated with intraocular pathology or migraine. In such cases, you need to ask the patient whether he is experiencing severe headaches with nausea and whether he is suffering from migraines.
A slight separation of the somewhat compressed vitreous from the retina (which occurs more often in people with myopia) may be accompanied by the appearance of black spots and flashes in the field of vision. In 5% of cases this is a retinal rupture and detachment. Retinal damage usually occurs in the periphery and is difficult to notice; in such a case, you must immediately contact your ophthalmologist.
Appearance of a rainbow halo in the field of view
. The appearance of even colored circles around a light source is a diffraction phenomenon that can be observed at night when a source of ordinary white light is behind fogged glass; This is how street lights are seen if you look at them at night through a foggy car window. Scratched glasses can also produce similar effects.
The cause of rainbow circles in the field of vision may also be “foggy” environments of the eye
, as is observed with cataracts or swelling of the cornea. In acute glaucoma, the appearance of iridescent halos is associated with corneal edema, since intraocular pressure increases when the pupil dilates. If the appearance of a rainbow halo is accompanied by pain in the eye, then think about this diagnosis and immediately refer the patient to an ophthalmologist. Rainbow circles with jagged edges that change shape are common in migraines. But be careful with this diagnosis in people over the age of 50 who have not previously suffered from migraines.
—-
Article from the book: The Oxford Handbook for Clinicians | Collier D.A.B., Longmore D.M., Harvey D.G.
Treatment of visual pathology
Treatment tactics are selected taking into account the factor that caused the appearance of rounded figures before the eyes. The main ways to eliminate unwanted visual effects are:
- drug therapy;
- surgical intervention.
Special ophthalmic exercises, as well as traditional medicine, are used as auxiliary methods.
Essential Medicines
The medication course is based on the use of various types of medications. The patient may be prescribed:
- Local preparations with antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal properties. Such pharmacological products are most often used for conjunctivitis.
- Drugs that help normalize intracranial, intraocular, and blood pressure.
- Eye drops that help restore normal transparency of the lens. This type of medication is most relevant at the early stage of cataracts.
- Non-steroidal, nootropic, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs that improve cerebral circulation. These medications are used for confirmed neurological disorders.
- Antidepressants, sedative products addressed to patients with mental pathologies.
Surgical intervention
The need for surgery arises when the medication course is insufficiently effective, or in the presence of severe ophthalmological diseases (primarily cataracts). Experts turn to two main methods of surgical treatment:
- laser correction of visual defects;
- vitrectomy, which consists of removing the vitreous body and filling the vacated space with specific solutions.
Vitrectomy is considered a radical treatment method, used extremely rarely. The procedure can provoke undesirable postoperative effects in the form of hemorrhages, clouding of the lens, and others.
Gymnastics and folk remedies
Special exercises that help eliminate rainbow circles before the eyes are selected together with an ophthalmologist. To obtain a positive result, gymnastics must be combined with the main treatment and performed regularly.
Folk remedies are also used after doctor's approval. The improvement of the general condition of the visual apparatus is facilitated by massage of the eyeballs, compositions with propolis or honey used for eye drops.
Causes
The spot on the white of the eye usually has a different shape and color. It is the color of the spot that is of particular importance in differential diagnosis for identifying a specific pathology. Some diagnostic techniques can be used at home independently. Of course, this will not replace consultation with a specialist, but it can help identify the problem. Timely detection of the disease allows treatment to be prescribed as quickly as possible, which improves its prognosis.
A vision test at home is carried out as follows:
- Cover one eye and look at a point in front of you;
- Assess central and peripheral vision, pay attention to whether there are any disturbances;
- Find out if there are flies or spots in front of the eyes;
- Repeat the same steps for the other eye.
Carrying out such a simple procedure regularly will allow you to maintain good vision for many years, because once you identify violations, you will be able to contact a specialist in time. Regular performance of special exercises designed for the eyes also gives a good effect.
red spot
The reason for the appearance of a red spot in the eye is a ruptured blood vessel. This condition occurs due to injury or ordinary overexertion. If you find a red spot, do not panic or try to eliminate it. Red spots sometimes appear when working at the computer for a long time; in this case, it will go away on its own after a few days. All you need to do is get a good rest, pay attention to your diet and walks outdoors.
True, the reasons for the appearance of red spots can be more serious, those that require treatment. If the spot does not go away within a few days, be sure to see an ophthalmologist.
Black spot
When a floating dark spot appears in the eye, the cause, as a rule, is the destruction of the vitreous body. This condition requires urgent consultation with a specialist. The detection of dark spots, flies or strings before the eyes may indicate clouding of the vitreous body, possible pathology of the nervous or cardiovascular systems, inflammation processes and other conditions.
Scotomas
Scotomas are usually called dark areas in the field of vision, which, however, do not reach its boundaries. At the same time, a person sees dark spots of various sizes and locations before his eyes. Such spots arise as a consequence of diseases that are accompanied by damage to the nerve fibers or vessels of the retina, optic nerve atrophy, and other diseases. Subjectively, patients do not feel scotomas. To identify the cause of their appearance and prescribe adequate treatment, you need to contact an ophthalmologist.
Causes of cataracts
Cataracts most often occur in older people. This is a “senile” cataract. In young people, cataracts are associated with exposure to adverse environmental factors - thermal or radiation radiation, toxic substances, certain medications, or with concomitant diseases of the eyes and the body as a whole, for example, diabetes. Cataracts can also be congenital or traumatic.
The specialists of the Vision Restoration Center have accumulated extensive experience in cataract surgery for the most complex eye complications. The center's surgeons handle the most difficult situations with honor. This has been repeatedly discussed at ophthalmological conferences and symposiums.
The only way to permanently get rid of cataracts is surgery. At our center, we use the best and safest cataract removal techniques.