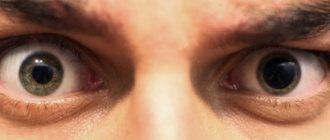
Some people may notice that one pupil is larger than the other. Is this normal or pathological? In what cases should you consult a doctor? We will consider these and other questions in this article.
Anisocoria is a pathological condition in which a person's pupils become different sizes. As a rule, in this case, one eye behaves normally (i.e., it narrows and widens depending on the degree of illumination), while the second does not change its size and remains motionless. The causes of this disease in adults and children are practically the same, but we will talk about each of them separately.
Causes
Reducing light levels
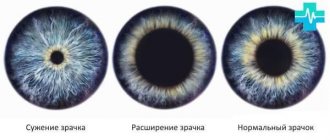
Expansion in the dark is a normal reaction. The eye tries to catch a little light so that a person can better navigate in a poorly lit room.
This is not a pathology. After moving to a bright room, the pupil remains dilated for some time.
Strong emotions and their effect on the eyes
Experiences, fear, joy or surprise cause the release of hormones into the blood. For this reason, the pupils automatically become larger. This is the norm. They can change size depending on their mental state. Sometimes the increase is one-sided.
Interest in a particular subject
They expand in an attempt to see something interesting. This is the psychological response of the pupils. Both or one may increase, depending on what a person is thinking about, what emotions he experiences while looking at an object (after all, different hemispheres are responsible for some).
Use of certain drugs (pharmaceutical mydriasis)
Abuse of psychotropic medications, narcotic drugs and solutions containing alcohol can lead to different diameters. Asymmetry is observed in exceptional cases, most often a bilateral increase.
Headaches with autonomic disorders
The symptom being studied is the cause of autonomic disorders, in which headaches and migraines are observed.
Asymmetry is accompanied by redness, blurred vision and vomiting.
Hereditary factors in the development of pathology
The occurrence factor is the pathology of the iris and other anomalies in the development of the visual organs. Causes:
- anisocoria;
- lagophthalmos;
- ptosis;
- intraocular hemorrhage;
- hypoplasia;
- malformations of the vascular tract of the eyes.
Compression of the oculomotor nerve
One pupil is more dilated as a result of loss of reaction to light, which causes sphincter paralysis. Compression of the nerve trunk may be the cause. This sign is often the first symptom, ahead of other manifestations, indicating damage to the 3rd pair of cranial nerves due to dislocation of the brain stem.
After a traumatic injury, aberrant regeneration develops. When looking up or down, the hole in the iris narrows. With a microinfarction of the nerve, this sign is not present, this refutes its presence.
Brain or eye injury with iris damage
If one of the pupils does not react to light, the doctor makes a diagnosis of severe damage to one of the brain hemispheres. If there is a reaction, but it is weak, the patient has a mild concussion.
Horner's syndrome
Develops with concomitant pathological conditions of the neck, head and lungs. It is caused by damage to the part of the nervous system that regulates breathing, digestion and blood circulation.
Horner's syndrome is characterized by a decrease in pupil size. Ptosis occurs, intraocular pressure decreases, and accommodation increases. The reaction to light and fixation of the gaze at a close point changes.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine as a cause in adults
The cervical region contains arteries that supply the brain. Due to wear of the intervertebral discs, they are compressed, that is, cerebral circulation is disrupted.
Because of this, different parts of the brain suffer, and the eyes may also suffer. There is a weak reaction to light, an enlargement of the hole in the iris.
Holmes-Eydie syndrome
Diagnosed if the pupil remains dilated for a month, but responds poorly to light signals. This is paralysis of the eye muscles.
Holmes-Eydie syndrome is characterized by an oval pupil and segmental damage to the iris. It slowly returns to its original size.
The syndrome can be congenital or acquired. The difference between the pupils is not noticeable; it increases by about 1.5 mm.
Nerve palsy as a consequence of stroke or malignant brain tumors
Malignant or benign formations of the central nervous system or brain affect visual functions. Cancer or an abscess, increasing in size, increases IOP, hence tissue compression and asymmetry.
Symptoms and course of the disease
Why is one testicle larger than the other in a child - the norm and deviations
Since different pupil sizes in infants are not a disease as such, but either a symptom or a variant of the norm, it is not possible to unambiguously describe the symptoms and course of the disease.
Effect on vision
According to the famous doctor Komarovsky, anisocoria in a child in the absence of concomitant pathological symptoms and with normal general health of the baby will not affect vision in any way in the foreseeable or distant future. In this case, neither drug treatment nor corrective measures aimed at visual impairment are required.
If the baby feels unwell, is capricious and shows other symptoms of ill health, it would be a good idea to show him to an ophthalmologist. Perhaps during the examination, the doctor will give referrals to other specialized specialists, whose joint efforts will make a final accurate diagnosis and develop treatment tactics, if necessary.
Treatment
Table. Treatment methods depending on the cause of enlargement of one pupil
| Cause | Treatment |
| Use of certain drugs (pharmaceutical mydriasis) | For the treatment of short-term mydriasis, no treatment is required. Once the medication is stopped, everything returns to normal. |
| Headache | If one pupil is dilated and the other is not due to a unilateral headache affecting the visual system, then therapy will be based on medication. In chronic cases, it is important to maintain a work and rest schedule, undergo balneotherapy, and kinesiotherapy. |
| Holmes-Eydie syndrome | The neurological disorder does not have a specific treatment regimen. If the left pupil is larger than the right, the use of Pilocarpine is indicated. Conventional therapy consists of wearing reading glasses. |
| Oculomotor nerve damage | In most cases, anticonvulsants are used. Physiotherapeutic procedures will be required. |
| Implanted lens | The apple of the eye is specially expanded before preparing for surgery. After it is carried out, mydriasis lasts for some time. More often than not, no treatment is required. |
| Brain or eye injury | If you have a brain injury, it is important to stay in bed for at least 2-3 days. You cannot watch TV or listen to loud music. Treatment consists of antiseptic, antibacterial, anticonvulsant drugs. If necessary, analgesics and glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. For eye injuries involving the iris, hemostatic therapy is prescribed. If necessary, surgical intervention is performed. |
| Brain swelling caused by meningitis or encephalitis | Treatment consists of using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and reducing intracranial pressure. Detoxification treatment is performed and glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. |
| Congenital Horner's syndrome | It is necessary to force the nerves and muscles to work fully, and the asymmetry of the pupils will disappear. For this purpose, kinesiotherapy with neurostimulation is used. |
| Osteochondrosis | To eliminate visual impairment and restore pupil diameter, you will need electrophoresis, massage of the collar area, and a course of exercise therapy for the spine. Measures aimed at prevention are also considered measures to prevent anisocoria. |
| Stroke | The shape of the appendage becomes oval-horizontal. This indicates insufficient blood supply to the brain, which will need to be restored. Treatment includes vasodilators, medications to prevent blood clotting, and medications that lower cholesterol levels. The diet will help improve blood circulation in the brain. |
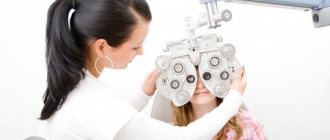
Diagnostics
Determination of the child’s condition and well-being is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist and ophthalmologist. To do this, they conduct several diagnostic tests:
- Interview with the child's parents. He finds out whether the child has had mechanical damage, injuries, or falls. Determines when symptoms first began before discrepancy in pupil size is detected.
- Examination of the child by a doctor. He pays attention to the condition of the eyeballs, the color and quality of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Testing neurological reflexes. The most important thing is to check the quality of eye accommodation. The doctor shines a flashlight into the child's eyes. Normally, each of the pupils should decrease in size.
- Fundus examination. To do this, Atropine or similar agents are instilled into the child's eyes. The patient's pupils dilate greatly. Using a slit lamp, the doctor evaluates the contents of the eyeball.
- Biomicroscopy. The doctor can evaluate the condition of the cells in the surface structures of the child's eyeballs. This is an intravital study for which there is no need to remove a piece of tissue.
- Removal of cerebrospinal fluid with bacteriological analysis to detect the pathogen in the presence of symptoms of meningitis. The laboratory technician will determine not only the microorganisms that caused the inflammation, but also a broad-spectrum antibiotic to which he is sensitive.
- PCR. For the method, venous blood sampling is sufficient. Viral pathogens always spread through the blood, causing symptoms of the disease. Using the method, you can determine the exact type of virus.
- Determination of visual acuity using diagnostic tables. The technique is applicable if the child is over 5 years old. To do this, use tables that depict pictures or letters. The more symbols a child sees, the better his visual acuity.
- MRI, CT. This is a basic examination that allows you to see a layer-by-layer image of the brain and eyeballs. The doctor can assess the condition of blood vessels, nervous tissue, and the presence of inflammatory processes.
Having carried out all the diagnostic tests, the doctor can identify the true cause of the child’s condition, only after this the treatment methods begin.
How to constrict your pupils
If one pupil is slightly larger, narrow it with drops. Pilocarpine, Carbachol, Physostigmine, Aceclidine, Pilotimol, Phosphacol are suitable.
To narrow the pupil, perform gymnastics. This is an excellent method when there are no miotic agents. Here is one of the exercises:
- focus your gaze on an object above your head;
- watch 2–5 seconds;
- sharply lower your eyes down without tilting your head.
The exercise is done ten times.
There are also folk methods of narrowing if one pupil is slightly larger. To stabilize them, blueberries and raspberry leaves are suitable. Decoctions are prepared from the ingredients and taken 4 times a day.
How to dilate your pupils
If one pupil is severely constricted, you can restore its normal diameter with medications and exercises.
It is enough to look into the distance or concentrate your gaze on a distant object. In this case, the eye automatically becomes wider. This leads to muscle tissue relaxation.
An unusual way is to tense the abdominal muscles. You need to pull it in so hard that the muscles tense. The blood flow will begin to flow to the desired area where there is no tension. Accordingly, it will allow them to recover.
Mydriatics are used for expansion. It is important to consult a physician before use. Mydriatics include the following medications:
- Atropine;
- Cyclomed;
- Mydriacyl;
- Tropicamide;
- Irifrin.
general information
A pathology in which one pupil is larger than the other has a scientific name - anisocoria. This unusual condition can occur in both adults and children. The pupil is a round hole in the center of the iris of the eye.
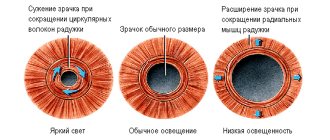
When exposed to light, it has the ability to change its size with the help of muscles. If a person has a pathological condition in the body or directly in the eye apparatus, the pupils can change dramatically: the left one can be narrowed, and the right one can be very dilated.
With a sharp expansion, they can become huge or, conversely, small.
Return