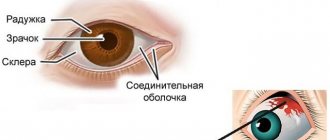
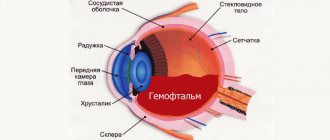
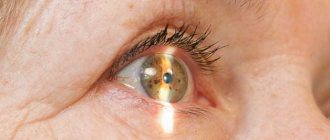
Herpes on the eyes (ophthalmoherpes) is a clinically complex phenomenon. It has several forms with their own symptoms. Therefore, self-medication is strictly not recommended, since it is necessary to treat herpes on the eye only after correct diagnosis, which we will discuss below. Herpes can affect both the mucous membrane of the eyes and the eyelids or skin around the eyes. Below we discuss all the features of the herpes virus getting into the eyes.
Causes and methods of infection
- The activity of the virus and its manifestation in the eye area can be provoked by: treatment with cytostatic drugs, pregnancy, or taking immunosuppressants.
- External factors of infection can be: eye injuries; infection of the eyes with a virus during the active stage of a cold on the lips, when the bladder is damaged and the contents interact with the eye tissues.
- Infection of the eye area with ophthalmoherpes is possible through household contact, through hygiene items. Let's say, wiping yourself with a towel that was used by someone infected in the active stage of herpes on the lips. When applying makeup, for example, using a common infected attribute, transferring herpes to the upper eyelid.
If there is a frequent recurrence of herpes in the eye area, this is usually due to a weakened immune system. Even if there was a clinical recovery, the herpes virus will remain (inactive) inside the body for a long time. And with reduced immunity, it will make itself felt, affecting the previous areas.
Diagnostics
The disease is detected during an initial examination by a doctor, who, if necessary, will prescribe additional tests.
Often a cold on the organs of vision is determined during the initial examination by a doctor. To complete the picture, consultations with other specialists are possible: allergist, dermatologist, cosmetologist, immunologist, therapist. If the eye has a cold and other symptoms are vague, the doctor prescribes eye biomicroscopy, non-contact tonometry, ultrasound, gonioscopy, visometry, and ophthalmoscopy. To confirm the diagnosis of barley, the excreted liquid is analyzed for culture to determine the type of microbe and its resistance to antibiotics. The patient's immune system is also examined. If conjunctivitis is suspected, the laboratory examines a cytological scraping, a smear of the mucous membrane, and tests for the presence of Demodex mites.
Common symptoms of herpes on the eyes
The symptoms and signs of ophthalmic herpes are very similar to many eye diseases. Especially if we talk about general symptoms, they can easily be confused with conjunctivitis, keratitis and other bacterial inflammations.
As a rule, eye herpes and some other eye diseases have common symptoms:
- Soreness and tearing;
- Reaction to bright light;
- Impaired vision clarity (especially in the dark);
- Redness of the eyelid;
- Redness of the eye;
- Possible nausea and headache;
- Lymph nodes may be enlarged.
There are symptoms that can distinguish ophthalmoherpes from other eye diseases: pronounced blisters, the same as with herpes on the lips, as well as severe itching in the eyelid area.
Upon visual examination, several areas affected by the ocular herpes virus can be identified:
- Herpes around the eyes - not only the eyelids are affected, but also areas of skin on the left and right sides of the eyes;
- Herpes above the eye - damage to the upper eyelid;
- Herpes on the lower eyelid - the same blistering rashes;
- Damage to the mucous membrane of the eye;
- Herpes under the eye - the rash extends beyond the lower eyelid.
Preventing eye infections
To prevent the development of eye infections, attention should be paid to prevention. First of all, these are the rules of eye hygiene:
- do not touch your eyes, especially with unwashed hands;
- during a cold, avoid touching the eye area even more carefully;
- do not use the towel of a person with a cold;
- do not use someone else’s decorative cosmetics (eye and lip pencils, lipsticks, etc.) - a person can leave viruses and bacteria with microparticles of saliva on them;
- do not test cosmetic products presented for review by customers (testers); you can test them on the skin of your hands, and purchase an unused, sealed product;
- When you have a runny nose, blow your nose carefully to avoid introducing bacteria through the nasolacrimal duct.
You should avoid hypothermia, treat ARVI in a timely manner and strengthen your immune system - eat well, exercise, and often be in the fresh air. This will help you prevent not only eye colds, but also other colds.
Correct diagnosis of ophthalmoherpes
Based on the above clinical forms of ocular herpes and their similar symptoms, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis. After diagnosing the disease, treatment will be carried out by an ophthalmologist. Below we will describe methods for diagnosing the disease, which can be carried out in herpetic centers or clinics that provide services for the following types of diagnostics and tests.
- Slit lamp. This method is mandatory when diagnosing herpetic eye lesions. When examined with a lamp, damage to the cornea is revealed with pronounced symptoms that occur with a herpetic infection. These include: inflamed eye vessels, focal opacities, etc.
- Immunofluorescence analysis (IFA). To examine the biomaterial under a fluorescent microscope, cells from the affected area are collected and treated with antibodies (labeled with fluorochrome) to herpes viruses. Then, when analyzed under an ultraviolet lamp, herpesvirus cells are highlighted due to glow. If they are not present, then the analysis is negative. This is one of the most accurate types of diagnosis of ophthalmoherpes today.
- Linked immunosorbent assay. It is carried out in particularly severe cases of ocular herpes, or when other types of diagnostics are questionable. With a herpetic eye infection, immunoglobulins M are usually present. When examined in two stages (an interval of 2-3 weeks), the presence of ophthalmoherpes is indicated by a 4-fold increase in the IgG titer, and low-avidity IgG can also indicate the nature of the disease.
Do not forget that for a better and more accurate diagnosis of the disease, it is advisable to take biomaterial at an early stage of symptoms. And also timely contact with a specialist will avoid complications.
Treatment of herpes virus infection
How to treat a herpes virus cold on the eye? The gold standard in the fight against herpes is the antiviral substance acyclovir. To treat ocular forms of herpes, acyclovir is used in the form of drops. In severe cases, acyclovir is also taken orally (acyclovir is available in tablet form).
For eyelid herpes, you can also use antiviral ointments based on acyclovir. These include drugs such as Gerpevir, Acyclovir, Zovirax and others. You can use the ointment several times a day, lubricating the surface of damaged skin with it.
Treatment
How to treat herpes on the eye depends on the clinical form, which is why correct diagnosis is necessary. For forms with damage to the upper tissues, drugs are usually used to relieve symptoms, which makes it possible to suppress the activity of the virus.
There are 4 groups of medications that are usually taken in combination when treating ophthalmoherpes:
- Medicines to relieve symptoms (anti-edema drugs, painkillers, etc.).
- Immunomodulators.
- Antiviral agents.
- Antiherpetic vaccine.
When herpes penetrates into the deep tissues of the eyes, surgical treatment is used:
- removal of affected areas;
- laser coagulation (radiation exposure).
Immunomodulators
Most often, eye herpes manifests itself when the virus is activated, which occurs when the immune system decreases, so the doctor, as a rule, prescribes immunoglobulins and interferon inducers for immunocorrection of the body:
- Interlock. Drops based on donor blood cells. Leukocyte interferons modify cell membranes, which makes it possible to create a protective blockade to the cell against the penetration of the virus.
- Reaferon. Drops that also contain human interferons. They are used in two ways: a) dripped into the eyes, b) administered as injections in the affected area.
- Interferon inducers: Amisksin, Cycloferon, Timalin, etc. They are used both in the form of tablets and by injection. Unlike immunoglobulins, interferon inducers practically do not cause allergic reactions and have a minimal list of side effects.
Antiviral drugs
| A drug | Description |
Topical preparations | |
| Acyclovir (ointment) 5% or 3% |
|
| Fenistil-pencivir (cream). |
|
| Oftalmoferon (drops). |
|
Medicines in tablets | |
Tablets with Valaciclovir base:
|
|
Tablets with Famciclovir base:
|
|
| Acyclovir or Zovirax tablets. |
|
HSV vaccine for ocular herpes
For herpes in the eyes, vaccination can be carried out only in the absence of an acute form of the disease. Repeated vaccination can be done after 6 months. In this case, we are talking about a vaccine, the creation of which used HSV types 1 and 2.
There are several herpetic vaccines. Vitagerpavak of Russian origin is popular. Placed in the forearm area, the course includes 5 injections with an interval of 7 days if the drug is well tolerated. Then it is recommended to repeat the vaccination after six months.
Do not forget that for herpes on the eye, treatment can only be prescribed by an ophthalmologist after correct diagnosis. Self-medication of this type of herpes is highly discouraged. Incorrect therapy can lead to vision loss. At the first manifestations of the disease, consult a specialist!
Prevention
Prevention of herpetic rashes on the upper eyelid, first of all, begins with strengthening the immune system.
- Determining the state of the immune system - identifying and correcting immunodeficiencies.
- Detection and timely treatment of acute and chronic diseases.
- Proper nutrition - the body must receive a sufficient amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, microelements, and vitamins. It is necessary to exclude fatty, fried foods and baked goods from the diet. Preference should be given to vegetables, lean meat, fish and cereals.
- Weekly physical activity helps oxygenate the body and strengthen the immune system. This could be exercise in the gym, jogging outside, swimming or daily gymnastics.
- Eyelid hygiene also helps prevent the development of herpetic rashes. All you need to do is wash your face twice a day and remove makeup from the eye area before going to bed.
- Timely treatment of any infectious pathologies of the eyelids and conjunctiva.
- Taking vitamin preparations in spring and autumn. It is at these times of the year that vegetables and fruits do not contain enough microelements to satisfy the needs of the human body. Taking vitamins during this period helps strengthen the immune system.
Prevention of the spread of infection to the lower and upper eyelid also includes timely treatment of herpesvirus infection on the lips and genitals.
Ophthalmoherpes in a child
The causes of herpes in front of children can be:
- Vaccinations;
- Overheating (including in the sun);
- Hormonal changes;
- Minor damage, eye injuries;
- Cold or hypothermia;
- Decreased immunity.
- Features of symptoms in children. In addition to itching in the eyelid area, watery eyes, sensation of a foreign body in the eye and redness, in children, herpes in the eye area is usually accompanied by a cold on the lips, pay special attention to this. Before you contact a specialist, your child can be given symptomatic treatment with Ophthalmoferon drops as first aid. Don't forget that children may be more susceptible to illness if they are infected with chickenpox.
- Features of treatment in young children. To treat herpes on the eye in babies and newborns, a combination of drugs is most often used: Acyclovir (3% ointment), Viferon suppositories and Ophthalmoferon drops. But more detailed treatment can be selected only by knowing the degree of damage and the form of ophthalmoherpes.
Types, causes and symptoms of colds
A cold on the eyelid is not an acute respiratory viral infection, as is commonly believed among people without medical education. This discomfort in the visual area is mainly caused by bacteria and viruses. The causes of the pathology are ophthalmoherpes, barley, conjunctivitis. The appearance and development of diseases is provoked by the following factors:
- weak immune system;
- avitaminosis;
- hypothermia or drafts;
- infectious diseases of ENT organs.
Ophthalmoherpes
A cold on the eye caused by herpes is dangerous due to its consequences. Untimely or unqualified treatment of ophthalmoherpes can provoke the development of keratitis, iridocyclitis or acute retinal necrosis. Such pathologies often lead to partial or complete loss of vision. In every body there is a herpes virus in a dormant state. Unfavorable factors help it activate: stress, pregnancy, decreased immunity, mucosal injuries, long-term use of antibiotics, unbalanced nutrition.
Herpesvirus infection is transmitted by almost all known methods: household, physical contact, airborne droplets.
The disease also occurs after direct contact with the source of infection or when sharing personal hygiene products and utensils. Ophthalmoherpes can affect either one eye or both. In this case, the following symptoms are observed:
- tearfulness;
- swelling, redness;
- photophobia;
- severe burning sensation;
- the appearance of bubbles with clear liquid on the eyelids, which subsequently burst;
- feeling of a foreign body in the eye;
- pain in the pupil and head;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- elevated temperature.
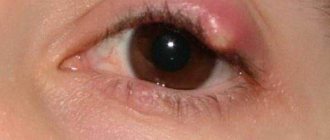
Stye on the eye
Appears as a result of the inflammatory process in the area of the hair follicle. Just like herpes, the causative agent of barley (Staphylococcus aureus) stays in the body for a long time without showing itself in any way. It can be activated by hypothermia, previous viral infections, decreased immune defense, and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. Barley appears as a small abscess, which within 4-7 days develops into an abscess and matures. It is forbidden to open it yourself, as it can cause infection. In addition to these symptoms, there is inflammation, redness, swelling of the eye, general malaise, fever, weakness, and the inability to stay in front of the computer for a long time.
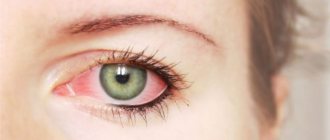
Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye is provoked by infection or may be of an allergic nature.
This is the name for inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva). It can be allergic, viral and bacterial. Accordingly, the cause is an allergic reaction, virus or bacteria. Conjunctivitis is a common disease, most often found in children who attend kindergarten. Main symptoms:
- red eyeball;
- swelling of the eyelid and conjunctiva;
- severe itching and burning;
- purulent discharge;
- fear of bright light;
- in the morning or after a long period of rest, discharge of yellow mucus and sticking of the eyelids;
- crust formation on the eyes;
- temperature increase;
- chills, headache.
Allergic conjunctivitis is caused by exposure to an allergen. It can be seasonal flowering plants, washing powder, food, low-quality clothing and cosmetics, perfume. Bacterial conjunctivitis can be contracted by swimming in dirty water or rubbing your face and eyes with unwashed hands. Viral - most often accompanies ARVI and other colds.
Complications
If treatment for eye herpes is started on time and, after correct diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed, then complications are unlikely. But if the eye infection with herpes was in the deep tissues, then this can affect vision up to the point of blindness.
Incorrect diagnosis, and accordingly incorrectly selected treatment, as well as untimely consultation with a doctor, can lead to the following complications:
- Decreased clarity of vision;
- Constant feeling of dryness in the cornea area;
- Poor eyesight;
- Cyclic eye pain;
- An eye affected by herpes may eventually stop seeing altogether.
With a long course of the disease, the virus can provoke cataracts or glaucoma. Retinal detachment is also possible due to hemorrhages that are typical when it is damaged.
Treatment of conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is a cold of the eye that requires treatment, because infection from the surface of the eyeball can penetrate into its deeper layers. Typically, treatment for this disease includes:
- washing the eyes from purulent plaque with saline solution, brewed black tea (diluted with cold boiled water, without sugar) or a special solution;
- drops with interferon, or with an inducer of your own interferon;
- antibacterial ointment with erythromycyte (optionally with tetracycline).
Typically, treatment of conjunctivitis takes 2-3 days, in more severe cases - up to 10 days.
Prevention and control of relapses
In case of relapse of almost any disease directly related to herpes viruses, the patient can only support the body with the help of constant use of antiviral drugs. Indeed, at the moment there is no vaccine or medicine that can completely rid the body of herpes. Therefore, taking medications is aimed at preventing and combating frequent relapses.
Knowing that ophthalmoherpes is caused by strains of the virus known to us, we can reduce the risk of the disease when vaccinating against chickenpox (Varicella zoster) in children and, accordingly, when vaccinating against herpes zoster (Varicella zoster is also the causative agent) in adults.
So, you must remember that treatment of herpes in the eyes should take place after it is prescribed by an ophthalmologist, and not at home. Do not forget that it is possible to damage not only external tissues (herpes virus on the upper eyelid, lower and around the eyes), but also deep ones, the symptoms of which are almost impossible to recognize at home. When visiting the clinic, the doctor will tell you in more detail about the symptoms and treatment of a specific form of ophthalmoherpes, conduct a diagnosis and select the correct treatment. If, after reading the article, you find yourself experiencing similar symptoms, we advise you not to delay and make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible.
Barley - symptoms and treatment
Stye is an inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash. In this case, the upper or lower eyelid swells and turns red (see photo of a cold under the eye - stye). After a few days, a yellowish purulent head appears on the surface of the swollen part of the eyelid. Under no circumstances should it be pierced, as this may cause increased inflammation. Within a couple of days the head breaks out on its own, and after this the patient rapidly recovers.
It is known that in more than 90% of cases the causative agent of barley is staphylococcus. This bacterium belongs to the opportunistic microflora. This means that staphylococci are normally present on human skin in small quantities and do not threaten health in any way. But when a person’s immunity is reduced (by hypothermia, viral infection), staphylococcus can cause various diseases, such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis, and, in fact, barley.
Thus, the appearance of barley is a signal of decreased immunity.
Treatment of barley can be carried out independently, at home. To do this, use antibacterial ointments (for example, tetracycline, erythromycin) and antibiotic drops (based on ofloxacin, gentamicin, etc.). You should put drops in your eyes 3-4 times a day (follow the instructions), and put the ointment behind the eyelid and lubricate the outer surface of the eyelid with it 1-2 times a day. It is not recommended to heat barley.
If the stye does not go away within 4-5 days, you should see an ophthalmologist.
Types and clinical forms
There are clinical forms of ophthalmoherpes. Among them:
- eyelid dermatitis;
- keratitis (the cornea becomes inflamed and cloudy, the patient cannot open his eyes);
- stromal keratitis (vascular damage, displacement of the eyeball);
- trophic keratitis (cornea loses sensitivity);
- herpetic corneal ulcer;
- blepharoconjunctivitis (rash on the inside of the eyelids, along the edge and in the corner of the eye);
- herpetic uveitis (the vitreous body of the eye becomes cloudy);
- retinal necrosis (dangerous loss of vision).
There is also a species classification of ocular herpes. Among the most common types:
- epithelial (the disease does not penetrate deep inside);
- tree-like (areas damaged by the virus form convex lines, shaped like a tree);
- geographical (in contrast to the tree-like picture of the lesion is larger, reminiscent of a geographical map);
- disc-shaped (disc-shaped areas of deep infiltration are formed on the cornea).
Inflammation of the eyes in the form of stye
This inflammation is called by different words. It all depends on the severity of the disease. Barley is an inflammation of the inner side of the eyelid, which is expressed in the appearance of an abscess.
If barley appears, you must:
- lubricate the swollen area of the eyelid with warming ointment;
- If possible, refrain from various types of decorative cosmetics;
- put special drops into the eye - Albucid or Tetracycline;
- use traditional medicine - apply a boiled warm egg, which must first be wrapped in a scarf. Make lotions with decoctions of tansy, chamomile, calendula or burdock;
- Make sure your body gets enough vitamins.
If barley occurs, it is important to remember that under no circumstances should the purulent formation be opened. By doing this, you can contribute to the spread of infection and the occurrence of many serious diseases, such as sepsis and meningitis.
As for preventive measures, it is important to remember that one of the causes of this disease is hypothermia. Therefore, especially in cold and damp seasons, it is necessary to dress warmly and protect yourself from cold gusts of wind. In addition, a bacterial infection may be the cause. Therefore, observing the necessary hygiene standards (do not rub your eyes with dirty hands, do not use someone else’s towel or cosmetics) also provides a certain guarantee that you will not have to deal with stye.