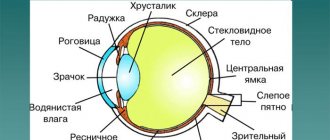
Electrophysiological testing of the visual organs is a series of procedures used to study the functioning of the optic nerve, retina, and visual areas in the cerebral cortex. The methods are based on recording visual reactions to specific stimuli and are highly informative.
EPI is contraindicated if pathological activity of the nervous system is observed, accompanied by attacks of epilepsy. The procedure cannot be performed if there are pathological processes on the skin at the examination site, severe angina or hypertension. The examination is not performed on patients with pacemakers.
Indications for EPI
EPI has a wide range of indications:
- genetic diseases of the retina (pathological genes are identified);
- pathological childbirth complicated by fetal hypoxia/hypotrophy and prematurity;
- congenital anomalies of the development of visual systems;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- amblyopia of any degree;
- herpetic keratitis (will show signs of damage to retinal ganglion cells and optic nerve fibers);
- contusions of the eyeball;
- metallosis;
- congenital or acquired myopia;
- demyelinating diseases of the nervous system;
- opaque optical media (vitreous fibrosis, hemophthalmos, hyphema, traumatic cataract).
An electrophysiological procedure is carried out when the visual analyzer is injured, to determine the functioning of the retina and optic nerve. The procedure is performed for unexpected vision loss, including psychiatric disorders.
Types of EPI
EPI of the visual organs includes 4 types of studies:
- Electrooculography (EOG) is a diagnostic method that allows you to determine the difference in potentials when the eyeballs move.
- Electroretinography (ERG) is based on graphic recording of the activity of retinal cells, which occurs against the background of light irritation.
- Multifocal electroretinography (MERG). Using this research, a three-dimensional map is built. Based on the results obtained, doctors determine the light sensitivity of the central part of the retina, which is the most important part of the fundus of the eye. Detects small areas of damage to the central part of the retina.
- Method of visually evoked potentials (VEP). The study involves identifying visual pathways all the way from the retina to the visual cortex. Used for multiple sclerosis, ocular hypertension, diabetes, optic tract tumors. VEP is the best method for detecting retinal functionality.
Types of procedure
There are 4 types of eye EPI.
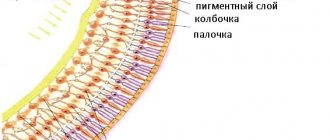
Electrooculography. This method allows you to record changes in the constant potential of the corneal-retinal area of the eye during lateral movement. EOG depends on the degree of preservation of the pigment epithelium. Changes in the electrooculogram indicate the presence of diseases that are localized in Bruch's membrane, the choriocapillaris layer of the retina, as well as in the pigment epithelium. Electroretinography. The method allows you to obtain a graphic image of the electrical activity of the retina, which occurs in response to light stimulation. The ERG shows the activity of most cells in the retina, which depends on the number of healthy neurons and photoreceptors. Each layer of cells is displayed separately on the electroretinogram as a curve graph. By assessing the cells' response to certain stimuli, the doctor determines how these groups of cells function. Multifocal electroretinography method. MERG builds a three-dimensional map showing the light sensitivity of the most important area of the retina in terms of functionality - the central one. In addition, the method detects small lesions in this area of the retina. Visually evoked potentials. EEP is the reaction of the optic nerves of the cortex in the occipital region of the brain to light stimulation of the eyes (cortical fields 17–19 according to Brodmann). The above potentials are recorded in the form of an electroencephalogram, which demonstrates the functional state of the visual analyzer sections. That is why EPI examination of the eyes using the EVP method plays an important role in the topical diagnosis of developing pathology. The stimulus can be flashes or structured stimuli (alternating black and white cells of different sizes), which depends on the visual acuity of the subject and the objectives of the study.
An ophthalmologist and a doctor-researcher who uses EPI eye examination work closely with each other to set the task and decide on the type of examination and choose early or differential diagnosis. The electrophysiologist selects a research plan to obtain an answer from those retinal cells that are involved in pathological processes. EPI of the eyes gives objective results, being decisive in making a diagnosis.
Preparation for the procedure
You need to prepare for the procedure. Before conducting an electrophysiological study, you need to wash your hair the day before. Do not use hairsprays, gels or other chemicals. Immediately before the procedure, remove your earrings and braid your hair so that there is a parting at the back of your head.
If you have a refractive error (myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism), take contact lenses or glasses with you. For SCL and LCL, bring a container and disinfectant solution with you.
When performing the visual evoked potential method, the day before the procedure, stop taking vascular drugs and tranquilizers. These medications distort the results; the VEP will have to be repeated.
Today we will talk about what EPI , or electrophysiological study of the eyes, is. In Moscow it can be done, in particular, at the Scientific and Practical Center named after. V.F. Voino-Yasenetsky in Solntsevo, at the Morozov Children's Clinical Hospital, at the Children's City Clinical Hospital named after. BEHIND. Bashlyaeva, at the Moscow Research Institute of Eye Diseases named after. Helmholtz and a number of other clinics. This study is prescribed no earlier than 12 months; it should not be done earlier. Before a child is one year old, both the eye itself and the nerve pathways are not yet sufficiently formed, and the data obtained are not informative. Even if you want to do a study as soon as possible and obtain some data, you will need to repeat this type of diagnosis due to the fact that by the age of one year the neuronal system of the eye will have clearly expressed large compensatory capabilities.
Why do this?
The most important thing in this study is that based on its data (if the result is below 28%), a visual disability is issued. Often, even with severe violations of refraction (the process of refraction of light rays in the optical system of the eyes), for example, myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism or the absence of a lens, the disability commission is limited to prescribing glasses, and does not give a disability. The study shows how damaged the nerve pathways are, even if everything is fine with refraction. This is especially true for children with cerebral palsy and organic damage to the central nervous system due to hypoxia or IVH : if there are neurological abnormalities, they will also be reflected in the study. If the doctor detects damage to the nerve tracts (the result is below 50% of the norm for a 12-month-old child), he prescribes conservative treatment - trophic drugs (there must be no contraindications from the epileptologist to eliminate the risks of provoking epilepsy!). This treatment can improve conductivity and thus the ability to see.
The research takes place in two stages. The first one studies the ability to distinguish between light and dark, the second one studies the percentage of preserved vision. For this, two methods are practiced: visually evoked potentials (VEPs) and pattern-evoked visual potentials (PEVPs). In the first case, visual pathways are examined all the way from the retina to the visual cortex. Readings are taken from both eyes. This type of research has been carried out for a long time and is the most common; equipment is available in many hospitals. It allows you to determine whether the child distinguishes between light and dark. With the PVEP method, a black and white picture is shown, and the device records the moment when the child ceases to distinguish gradually decreasing black and white squares. Thanks to this, we can objectively assess the approximate visual acuity and visual functions that the child has at the time of the examination. Some doctors use the term baby flash. This means that the examination is carried out with optical correction - glasses or contact lenses - and the device first takes readings from one eye, then from the second, while the eyes are wearing special glasses, which eliminates diagnostic errors if the child is not fixating the monitor. But such devices are not yet available everywhere.
It is important to note that the EPI examination of the eyes must be carried out with optical correction (glasses or contact lenses) in order to exclude problems with the optics of the eye, which can be diagnosed in a child at 12 months. With incorrectly corrected optics, the EPI of the eyes may not be informative, since the machine can take into account problems associated with the optics of the eye in the failure of the visual impulse, which is generally perceived in the visual center, passing through the optical and neuronal portion of the visual analyzer (eye).
It is very advisable to do this study on all premature children, especially those with hypoxic lesions, at the age of one year, in order to understand how the child actually sees, even when it seems to us that he sees very well (10% of visual functions are enough to collect crumbs on table to get behind the wheel of a car - you will need more than 60% of visual functions). an ultrasound every year and look at the ratio of their size to the age norm, so that it is possible to objectively monitor the development of myopia, which often occurs in premature babies.
We have repeatedly received questions about the drug Alloplant (a biological substance with which the body can restore the functions of various organs). We are communicating with parents about this, but at the moment we do not have a single case in which it has improved visual functions. In this case, the administration of the drug must be carried out under general anesthesia, which every time negatively affects the overall development of the child and his health in general. If you nevertheless decide to have Alloplant administered, we recommend that you first undergo eye EPI at an independent center in order to be able to objectively assess the dynamics of visual functions during Alloplant administration.
How does EFI work?
Before the ERG, the patient undergoes dark adaptation for 20 minutes. Then the work of all retinal cells is examined. The doctor gives bright flash stimuli to which the cells begin to respond. Then drops are instilled to dilate the pupil and oscillatory potentials are examined.
After this, the eyes are illuminated for 10 minutes and measurements are taken again. This procedure measures the action of photoreceptors.
Method of conducting EOG:
- Electrodes are placed on opposite corners of the eye;
- the patient must rotate the eyeballs in different directions;
- installed electrodes read information.
The procedure does not take more than 7 seconds. Does not cause discomfort. There are no strict standards for the time of electrooculography; if necessary, the doctor repeats the examination.
The visual evoked potential method is the sum response of large populations of neurons in the visual cortex. The results of the study are provided in the form of an electroencephalogram.
The manipulation is painless. It is even performed on newborns. It does not contain manipulations associated with the penetration of foreign objects inside. Method:
- the doctor applies several electrodes to the head;
- one eye is closed with an occluder or shield;
- the doctor tells you what needs to be done during the study.
Sometimes you need to close both eyes. Using this method, the prognosis of visual impairment in pathological conditions such as optic nerve injury, diabetes, and glaucoma is determined.
Multifocal electroretinography is performed in a similar way to ERG. The research is rarely carried out because it is at the stage of study and testing. Only scientists who are developing this research can conduct it. Multifocal electroretinography is not used in ophthalmology clinics.