Content
- Characteristics of Virgan 0.15% eye gel 5g
- Delivery of Virgan eye
- Release form, composition and packaging
- pharmachologic effect
- Pharmacokinetics
- Indications for use
- Dosage regimen
- Side effect
- Contraindications for use
- Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Use for renal impairment
- Use in children
- special instructions
- Drug interactions
When the organs of vision are damaged due to herpetic infections, special external medications are used, namely ophthalmic forms with a certain concentration of active substances.
The drug Virgan meets these characteristics.
The components of the product contribute to prolonged contact of the drug with the surface of the eye.
The active ingredient of the drug, Ganciclovir, has antiviral properties and, when entering directly into the eye cell affected by the virus, it makes it possible to influence the herpes pathogen.
Application and dosage.
Virgan gel is prescribed for keratitis due to the influence of herpes infection.
Virgan is offered as a lightweight eye gel with a convenient tip for dosed instillation.
It is used by introducing the gel directly into the eye, namely into the lower conjunctival sac, drop by drop up to five times a day, gradually reducing the frequency of administration.
The duration of use of the gel does not exceed three weeks.
Before use, it is advisable to study the recommendations for use in detail.
It is important to know.
Virgan gel is considered a safe and effective antiviral drug, which further prevents the development of relapse.
It is advisable to buy Virgan gel only after the recommendations of an ophthalmologist.
Effect of the drug
The gel is quickly absorbed and begins to affect the virus. Its effect is felt immediately after use and lasts for three hours.
The ophthalmic agent has an active effect on the viral cell. Its active substance completely changes the metabolic processes in the microorganism, which helps the eyes get rid of pathological symptoms.
The medicine interrupts the synthesis of enzymes in the affected cell without affecting healthy tissue.
In addition, the medication has the ability to change the chromosomal apparatus of the virus, preventing its reproduction. The pathogen loses its strength and soon dies.
pharmachologic effect
Antiviral agent. It is a synthetic analogue of guanine. Its chemical structure is similar to acyclovir.
Inside the cell, ganciclovir is sequentially metabolized into its monophosphate form by cellular deoxyguanosine kinase and then into active ganciclovir triphosphate. Acting as a substrate and being incorporated into DNA, ganciclovir triphosphate competitively inhibits viral DNA synthesis. This leads to suppression of DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA chain elongation. Ganciclovir inhibits viral DNA polymerase more actively than cellular polymerase.
Active against cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, Varicella zoster, Epstein-Barr virus. Clinical studies were conducted only for CMV infection.
Main components and their pharmacological action
Antiviral agent. It is a synthetic analogue of guanine. Its chemical structure is similar to acyclovir.
Inside the cell, ganciclovir is sequentially metabolized into its monophosphate form by cellular deoxyguanosine kinase and then into active ganciclovir triphosphate. Acting as a substrate and being incorporated into DNA, ganciclovir triphosphate competitively inhibits viral DNA synthesis. This leads to suppression of DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA chain elongation. Ganciclovir inhibits viral DNA polymerase more actively than cellular polymerase.
Active against cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, Varicella zoster, Epstein-Barr virus. Clinical studies were conducted only for CMV infection.
neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, eosinophilia.
obsessive states or nightmares, ataxia, coma, confusion, insomnia, dizziness, headache, nervousness, paresthesia, psychosis, seizures.
nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea, flatulence, changes in laboratory parameters of liver function.
arrhythmia, arterial hypertension or hypotension.
fever, skin rash, itching, urticaria.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:EPdHvnJU8wY
hematuria, increased creatinine and urea in the blood plasma, increased urea nitrogen in the blood.
inflammation, pain, phlebitis at the injection site; from the organ of vision - blurred vision, eye irritation, pinpoint keratitis, conjunctival hyperemia.
hypoglycemia, dyspnea, alopecia.
Probenecid and other drugs that inhibit renal tubular secretion or reabsorption may reduce the clearance of ganciclovir and increase its half-life.
With simultaneous use of ganciclovir with dapsone, pentamidine, fluorocytosine, vincristine, vinblastine, adriamycin, amphotericin B, combinations of trimethoprim with sulfonamides, additive toxicity may develop.
Concomitant use of zidovudine and ganciclovir increases the risk of developing neutropenia.
With the simultaneous use of ganciclovir and a combination of imipenem and cilastatin, generalized seizures are observed.
The use of the drug Virgan very often causes side effects in the form of local reactions: superficial mottled keratitis, visual disturbances, allergic reactions, eye irritation. The most common reactions include a tingling or burning sensation, which usually goes away quickly and on its own.
If the above or any other side effects occur, consult your doctor.
Pharmacokinetics
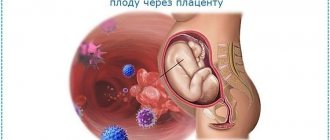
After oral administration, it is slightly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability is 6-9%. Cmax in blood plasma after oral administration is achieved after 1.8 hours, with intravenous administration - within 1 hour. Distributed in all tissues, passes through the placenta. Vd is 0.74 l/kg. Plasma protein binding - 1-2%. Excreted in urine. T1/2 after oral administration is 3.1-5.5 hours, with intravenous administration - 2.9 hours.
After instillation of ganciclovir in the appropriate dosage form into the eye 5 times a day for 11-15 days for the treatment of superficial herpetic keratitis, plasma concentrations of ganciclovir were very low:
on average 0.013 μg/ml (0=0.037).
Possible side effects
Virgan eye gel may cause unpleasant symptoms. Instructions and patient reviews show that the most common disturbing phenomena during therapy may be the following:
- burning at the time of insertion and a few minutes after manipulation;
- redness of the eyelid and eyes.
It is worth noting that such symptoms are often temporary and go away on their own. Basically, all patients claim that the drug is well tolerated even with long-term use.
Side effect
From the hematopoietic system:
neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, eosinophilia.
From the side of the central nervous system:
obsessive states or nightmares, ataxia, coma, confusion, insomnia, dizziness, headache, nervousness, paresthesia, psychosis, seizures.
From the digestive system:
nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea, flatulence, changes in laboratory parameters of liver function.
From the cardiovascular system:
arrhythmia, arterial hypertension or hypotension.
Allergic reactions:
fever, skin rash, itching, urticaria.
From the urinary system:
hematuria, increased creatinine and urea in the blood plasma, increased urea nitrogen in the blood.
Local reactions:
inflammation, pain, phlebitis at the injection site; from the organ of vision - blurred vision, eye irritation, pinpoint keratitis, conjunctival hyperemia.
Other:
hypoglycemia, dyspnea, alopecia.
Similar medicines
A fairly popular drug is “Virgan”. Eye gel has analogues, but they are prescribed as needed:
- if the original caused intolerance;
- or the patient is not satisfied with its cost.
You can find substitutes at the pharmacy, including cheaper ones. Among the most popular and effective medications it is worth noting:
- "Zimaksid";
- "Oksolin";
- "Virolex";
- "Zovirax";
- Oftaquix.
It is worth noting that the use of one or another analogue must be agreed with the attending physician. Despite the similar composition, there are differences in the auxiliary elements. Completely different contraindications and side effects are also possible.
special instructions
Use with caution in patients with impaired renal function. This category of patients requires adjustment of the dosage regimen depending on the value of CC.
During the treatment period, regular monitoring of peripheral blood patterns and renal function is necessary. Depending on the degree of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia, adjustment of the dosage regimen or temporary cessation of treatment is required until signs of hematopoietic recovery appear.
The simultaneous use of ganciclovir with drugs such as dapsone, pentamidine, fluorocytosine, vincristine, vinblastine, adriamycin, amphotericin B, combinations of trimethoprim with sulfonamides is justified only if the expected benefit of therapy outweighs the potential risk.
Ganciclovir should only be administered intravenously, because IM or SC injections cause severe tissue irritation. IV drip administration should be accompanied by an appropriate water load.
In children under 12 years of age, ganciclovir is used in cases where the expected benefit of therapy outweighs the risk of side effects.
When used in high doses, suppression of spermatogenesis in men and fertility in women is possible. Men and women of childbearing age should use reliable methods of contraception during treatment. Men are also recommended to use barrier methods of contraception for 90 days after the end of treatment.
Ganciclovir for topical use in ophthalmology is not intended for the treatment of cytomegalovirus infection of the retina.
Indications and contraindications for use
Virgan gel is used for therapy:
- viral infection of the organs of vision;
- acute superficial keratitis;
- herpes simplex of the eye, etc.
Virgan gel is especially effective in such cases. It works more effectively than any other ophthalmic antiviral agent. A precisely dosed concentration of the main substance allows you to quickly eliminate the symptoms of an infectious disease.
However, despite the great benefits that the medicine can bring to the patient, it must be used with caution. The medication is not used in the presence of severe allergies or individual intolerance to its elements.
It is not recommended to prescribe Virgan gel to women while pregnant or breastfeeding.
It cannot be prescribed to children under 12 years of age.
Drug interactions
Probenecid and other drugs that inhibit renal tubular secretion or reabsorption may reduce the clearance of ganciclovir and increase its half-life.
With simultaneous use of ganciclovir with dapsone, pentamidine, fluorocytosine, vincristine, vinblastine, adriamycin, amphotericin B, combinations of trimethoprim with sulfonamides, additive toxicity may develop.
Concomitant use of zidovudine and ganciclovir increases the risk of developing neutropenia.
With the simultaneous use of ganciclovir and a combination of imipenem and cilastatin, generalized seizures are observed.
Interaction with other drugs
Some medications do not allow simultaneous use with other pharmacological agents. Their mutual influence reduces the overall effect or creates a threat of pronounced negative reactions in the body.
Sometimes medications simply duplicate each other's effects without adding anything to the therapeutic outcome. In such a case, they only place an increased burden on the metabolic processes of the patient’s body.
Virgan gel can be freely combined with most drugs for various internal or external diseases.
But it cannot be prescribed simultaneously with Zidovudine. The difference in their chemical and pharmacological properties can lead to severe changes in the blood picture.
If the drug is used together with cytostatics, there is a cumulation of side effects of both drug groups with the appearance of signs of intoxication of the body.
It should also be taken into account that if the ophthalmologist has prescribed any other drops or ointments, they should be administered only a quarter of an hour after Virgan. The gel must be used last.
Instructions for use
Apply the gel one drop at a time into the conjunctival sac, the number of applications per day is determined by the doctor.
Instructions for use indicate that the product should be dripped 1 drop into the affected eye. It is recommended to use 5 times per day at the beginning of the therapeutic course. Further, the number of injections is reduced according to the doctor’s recommendations, depending on the course of the disease. The duration of treatment is 1 month. The gel should be stored in the refrigerator.
If the patient wears lenses, it is recommended to remove them when instilling them. They can be put on again 20 minutes after the procedure.
Active components and action
The main active ingredient in the gel is ganciclovir. There are also auxiliary components. The action of the drug is based on the fact that the active element penetrates inside the harmful cell, where the reaction occurs, in the process by which the substance is transformed and acquires the ability to destroy the virus. This process is possible only when the drug enters infected cells. The medicine blocks the DNA of the virus so that it can no longer reproduce. Pathological cells die and the recovery process begins.