Orthokeratology is one of the methods of vision correction without surgical intervention. It is achieved using special hard gas-permeable lenses, which are worn only at night.
This method allows you to do without contact lenses or glasses during the day, while visual acuity remains at a high level. The effect of night lenses is reversible, which means you need to wear them either every night or every other night (this parameter is strictly individual).
Correction range
According to a huge number of studies, the possibility of 100% correction of myopia with night lenses in the range from -1.5 to -4 diopters is reported. But there are also reports of the possibility of correcting myopia in the range of -5 diopters. In very rare cases, with the help of night lenses it is possible to cope with myopia of -6 diopters.
The greatest correction effect is usually achieved with the first use of such lenses. Full correction and further stabilization of results occurs by the seventh to tenth day of using night lenses.
A slight decrease in the effect is observed during the day, since lenses are not worn at this time: up to -0.75 diopters.
In order to use night lenses for vision correction for a long period, you need to use them every night or once every two or three nights. Typically, patients adhere to the regimen every other night.
Night lenses have no age restrictions and are suitable for teenagers and children, which is very relevant, because surgical treatment of myopia cannot be performed until the age of eighteen. Such lenses can also be worn by adults who, for certain reasons, cannot have contact correction or have contraindications to surgical intervention.
Alternative to contact lens solution
If you do not have the opportunity to use professional cleaning products for optical products, it is recommended to choose:
- Saline solution, or pharmaceutical solution of sodium chloride 0.9%. This product was used to store lenses before modern analogues appeared. However, then they had a more rigid structure.
- Table salt solution.
- Eye drops. Eye drops with o . They moisturize and disinfect optical products.
Operating principle
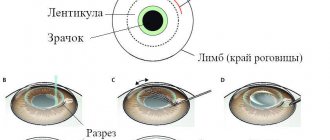
In the presence of myopia, light rays, after passing through the optical medium of the eye, tend to focus directly in front of the retina. In order to shift the focus to the retina, the refraction of rays must be “weakened”.
This is achieved by changing the shape of the cornea, for which it must be made flatter. This principle underlies the vast majority of surgical techniques for vision correction. It is also used in orthokeratology: hard lenses, by pressing the cornea, make it flatter, as they provoke the processes of redistribution of the surface layers of cells. They also have a slightly reduced ability to refract light rays.
As a result, the image is focused on the retina. After the night lenses are removed, the cornea retains its given shape for a certain time and the patient sees perfectly without any correction. However, the cornea gradually straightens out to its original shape, so night lenses have to be put on again.
How it works?
With myopia, light rays passing through the optical media of the eyes tend to focus in front of the retina. In order for the focus to fall on the retina, it is necessary to “weaken” the refraction of the rays. This is achieved by changing the shape of the cornea, which requires making it flatter . By the way, it is this principle that underlies most surgical techniques for vision correction. Orthokeratology also uses it: hard lenses, pressing the cornea, make it flatter, as they provoke a redistribution of the surface layers of cells, which, in turn, refract light rays less easily, and the image is focused on the retina. After removing the night lenses, the cornea can retain its given shape for some time, and the patient sees well without any correction. But gradually the cornea straightens out to its original shape, and OK lenses have to be put on again.
Benefits of using night lenses
Night lenses have a number of specific advantages over other methods of vision correction:
- no need for vision correction during the day, that is, the patient is free from lenses, glasses and other restrictions associated with poor vision. Sometimes correction with glasses or contact lenses is unacceptable due to the patient’s occupation (swimmers, pilots, etc.), and surgical treatment cannot be carried out due to medical contraindications or due to personal reluctance. In these cases, the most rational option is night lenses;
- the cornea of the eye does not suffer from a lack of oxygen, as with constant wearing of contact lenses, because the patient is without them during the day, and therefore the cornea is fully supplied with oxygen. Moreover, corneal hypoxia at night is compensated by excellent access to oxygen during the day plus excellent vision;
- minimal risk of developing dry eye syndrome, which can develop with constant wearing of contact lenses. Since there are no lenses during the daytime, the physiological mechanisms of tear fluid distribution are preserved. Bactericidal and nutrients are supplied with tears, the smallest particles of dust, metabolic products and microorganisms are removed;
- the use of night lenses almost never leads to the development of allergic reactions, the risk of keratitis and conjunctivitis is also significantly reduced;
- with such lenses you can use absolutely any cosmetics and not be afraid of the deposition of its particles on the surface of the contact lenses;
- there is no need to remove lenses while swimming, or swim wearing special safety glasses. Wearing night lenses allows you to ride a bike or car quickly without fear of the lenses “drying out” in the wind;
- There is also no need to purchase a container for lenses, as is the need to use moisturizing drops after communicating with smokers in confined spaces.
If the possibility of surgical correction becomes achievable over time, then wearing night lenses should be stopped.
You need to know and follow this - Okomistin eye drops instructions for use.
Find out the causes and treatment methods for pterygium in this publication.
Care for night lenses
Convenient container
Lenses are cleaned every time they are removed with solutions recommended by your ophthalmologist. Do not replace solutions yourself! Before removing OK lenses, it is necessary to fill the container cells with fresh solution. Apply cleaner (shampoo) to the removed lens and rub between your fingertips for 1 minute. Try to treat the entire surface of the lens evenly, especially the inside. During manipulations, do not apply excessive force to the OK lens, as it may break.
Special solutions
Then rinse the OK lens thoroughly with warm water until you feel a “squeak.” Water must comply with drinking GOST standards. Do not use water from open reservoirs. Place the treated lenses in the solution container. When handling lenses, be careful not to lose them. It is best if there is an insert in the opening of your sink that prevents the lens from penetrating into the drain.
note
1. At the beginning of wearing OK lenses, the desired effect is achieved gradually over the course of a week (time frames vary from person to person). These days it is possible: blurred vision, double vision, deterioration of vision at dusk, etc. In the first days, redness of the eyes is possible after sleeping in lenses and discharge.
2. If you do not wear OK lenses at night, the return of myopia or farsightedness will be gradual. You may need weak glasses during this period.
3. Sometimes in the morning, mucous discharge may accumulate in the corners of the eyes.
4. Try not to drop the lenses on hard surfaces or touch them with your fingernails, as this will cause scratches, cracks and chipped edges. Such lenses require replacement with new ones.
5. You cannot wear OK lenses during illnesses accompanied by high fever: acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis, etc., since at this time general and local immunity decreases and the risk of complications increases significantly.
6. If, when putting on the lenses, you feel: noticeable discomfort, excessive tearing, pain, itching, immediately remove the OK lenses and rinse them thoroughly. If symptoms persist, contact lenses should NOT be worn. Show yourself to us soon. If you go to bed with such symptoms, the lenses will quickly stop moving with your eyes closed, the eyes will not feel them, and the lens will cause injury to the cornea. In an unfavorable situation, such an injury can be complicated by infection, resulting in a serious complication - KERATITIS.
7. KERATITIS is accompanied by the following complaints: lacrimation, photophobia, pain, redness of the eyes. Against the background of such symptoms, you should absolutely not wear lenses. It is necessary to contact us by phone as soon as possible.
8. If you have the above complaints, you must immediately begin treatment with two drugs at the same time: Floxal (or Tsipromed, or Oftaquix) instill 1 drop into the affected eye (or eyes) every hour for 1 day. If it is impossible to see a doctor, instill the drug in the following days, 1 drop 6 times a day. And also instill Khilozar-komod (or Hypromelose P, or Hilabak) 1 drop up to 6 times a day.
9. The service life of the container is 3 months, the puller is 6 months. Replace in a timely manner. Do not allow the lenses and container to be in the same condition as in the photo:
Fungus in a container
Plaque on the lens
Benefits of Ok-therapy
Night OK therapy has a number of important advantages compared to other methods of vision correction:
- The first and most important thing is that during the day the patient does not require any correction at all , i.e. he is free from glasses, lenses and any restrictions that are associated with poor vision. It is worth recalling that in some cases, spectacle or contact correction is simply unacceptable due to the patient’s type of activity (pilots, swimmers, hockey players, etc.), and surgical treatment is postponed due to medical indications or personal reluctance. In such cases, the only possible option is night lenses.
- In these lenses, the cornea of the eyes does not suffer from a chronic lack of oxygen, as when wearing contact lenses constantly , because during the day the patient is without them, and oxygen has free access to the cornea. At the same time, we will not deny that at night, with lenses and closed eyelids, hypoxia intensifies. But during the day, nighttime hypoxia is more than compensated by free access to the cornea of air and oxygen. And also excellent eyesight.
- Wearing contact lenses significantly reduces the frequency of blinking movements and impairs tear exchange, which causes dry eye syndrome. OK therapy minimizes the risk of dry eye syndrome , since there are no lenses during the daytime, and the physiological mechanism of tear fluid distribution is preserved. Along with tears, nutrients and bactericidal substances are supplied, and the smallest particles of dust, microorganisms, and metabolic products are removed.
- The use of OK lenses practically does not give impetus to the development of allergic manifestations , in addition, the risk of conjunctivitis and keratitis is reduced.
- With such lenses you can use any cosmetics and not be afraid that its particles will settle on the surface of the contact lenses.
- There is no need to remove lenses when swimming , or swim wearing safety glasses. With OK lenses, you can ride a car or bike at high speed without fear that the lenses will “dry” in the wind.
- There is no need for a lens container , as well as the need to apply moisturizing drops after communicating with smoking friends in a confined space.
If over time the possibility of surgical correction becomes achievable, then you should simply stop wearing OK lenses. After some time, the cornea will return to its original shape and the operation will take place.