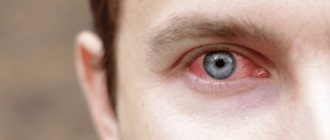
The human eye is a unique tool for perceiving the world around us. They use 65% of the brain's resources and process 36 thousand pieces of information per hour. At the same time, the eyes are one of the most sensitive and fragile organs of the body. Any, even minor, damage can lead to discomfort and vision problems.
You can injure the eye in different ways - from a banal nail or finger getting into the eye, to exposure to sharp objects (knife, wire, glass, needle). Carrying out repair, construction and welding work, interaction with aggressive substances - all this can also lead to serious injuries if you do not take care of protecting your eyes and face in advance.
Causes of eye injury
Eye injuries occur for several reasons. Among them are:
- chemical substances;
- mechanical damage;
- exposure to temperature;
- ultraviolet radiation.
Eye injuries can be superficial, occurring when the eyelids, cornea, and conjunctiva are damaged. Similar injuries occur when using contact lenses, nails, branches, or clothing.
If there is a blow to the eyeball, blunt trauma occurs. Penetrating or shrapnel wounds are also possible.
Compress
The most famous way to reduce inflammation of the eyeball. Tea – contains vitamin P, which helps remove free radicals from cells and restores the structure of damaged tissues.
Tea strengthens capillaries, reduces eye inflammation and normalizes internal blood flow. When preparing tea compresses, you need to remember some nuances: The tea leaves are not very strong and opaque.
Compresses are made from cotton swabs or disks. A separate compress is applied to each eye. The temperature of the liquid should be 2-3 °C higher than the human body temperature. Tampons or discs are soaked in tea and wrung out.
They are kept for no more than 5 minutes until the tampon or disc has completely cooled.
Symptoms of eye injury
Eye injury is characterized by swelling of the eyelids and damage to blood vessels. With such lesions, hemorrhage into the iris or orbital fracture is possible. Contusion of the organ leads to dilation of the pupils, they stop responding to light. Subsequently, patients report photophobia and blurred vision. As a result of paresis of the ciliary muscle, a disturbance in the accommodation of the eye is observed.
Due to severe trauma to the eye, the iris may be torn off with damage to its vessels. As a result of pathology, blood accumulates in the anterior chamber of the eye. There is also a risk of lens damage with luxation into the anterior chamber, vitreous, or subconjunctiva. Since this type of injury complicates the outflow of moisture, secondary glaucoma is possible. Headache and double vision are signs that require immediate medical attention.
Hemorrhage into the vitreous body is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- retinal detachment;
- retinal tear;
- drooping eyelids;
- swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva;
- scleral rupture;
- inflammation of the iris;
- decreased intraocular pressure;
- destruction of the optic nerve;
- displacement of the eyeball.
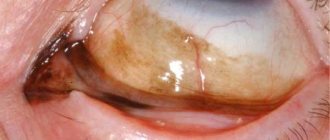
Superficial damage to the eye is accompanied by severe pain in the organ, swelling of the eyelids, lacrimation, and photophobia. When examining the cornea, erosion is noticeable. If foreign objects get into the eye, the patient may develop a scar or cataract. As a result of penetrating injury, clouding of the lens and changes in the shape of the pupil are observed.
Symptoms of damage to the eye orbit are:
- retraction or protrusion of the eyeball;
- deterioration of eye mobility;
- hemorrhage.
Patients with this injury report blurred vision, loss of visual fields, and severe intraocular pain. The pathology, if left untreated, leads to blindness, which may be irreversible due to destruction of the optic nerve and rupture of the internal membranes.
When the eye is burned, the patient experiences burning pain, accompanied by lacrimation and sensitivity to light. Glaucoma develops when exposed to alkalis and concentrated acids. The patient is more likely to develop a cataract.
Degrees of eyeball contusion according to medical classification
The disease in question is divided into 3 degrees according to the severity of the consequences and the characteristics of its course:
- Degree I. Due to its “humane” consequences, it is called mild. During the inspection
The victim has no rupture of the eyelid structure. The area around the injury is swollen and bluish. If the external impact was large, the retina may be damaged: it will be bruised. Visually, this will manifest itself as a cloudy color of the retina. When checking the contused area, you can actually see a cloud-like cloudiness that has a light gray, white color. This phenomenon occurs a couple of hours after the incident and disappears within 4-11 days. Transformations are possible in the aspect of the lens: it is capable of partially losing its transparency due to the emergence of a pigment spot on it. The events listed above cannot affect visual acuity when eliminating the disease in question; - Degree II. Often, with this degree of destruction, they involve the cornea, but are limited by swelling of the latter. If the victim closes his eyes during injury, errors in the structure of the cornea will be complemented by damage to the eyelid. Due to severe swelling, the patient cannot always open the shell-shocked eye. Examination of such an injury may show the presence of hemorrhage, varying in volume and shape. After the bruise resolves, lesions may appear in parallel, which will have a negative impact on visual acuity. It is possible to restore it with surgical intervention.
- Degree III. In various medical literature it has a different name. Some call it severe, others call it very severe. Some experts divide the disease in question into 4 stages, classifying very severe exacerbations as a separate group. Within the framework of this article, all severe, very severe consequences are grouped into the third degree of concussion. The retina of a shell-shocked eye can be destroyed under the influence of a huge blow. The form of the rupture varies; the fact itself may not occur immediately during the injury, but after a certain time. Massive ruptures of this component of the eye can provoke its dissection. Over time, purulent masses will accumulate in the retinal area. The lens is radically transformed - there is no reaction of the pupil to light. The integrity of the eyelid membrane is compromised: a torn structure can be visualized. The vision of the victim with the specified degree of concussion will drop by at least 50%. If the optic nerve is ruptured during injury, its loss is 100% guaranteed. If this nerve is damaged, it may swell and atrophy over time - this is due to the lack of the necessary blood supply.
If a girl hurts her eye, what should she do? First of all, it is necessary to determine the severity of the injury. There are four of them in total, each of which is characterized in its own way.
First degree bruise:
- the pain is not very strong, tolerable;
- the perception of the surrounding world deteriorates slightly;
- presence of small bruises;
- swelling of the cornea of the eye;
- pupil reduction, poor reaction to light;
- the retina takes on a grayish tint.
Second degree contusion:
- well felt impulsive pain;
- fear of light;
- excessive tearing;
- vision noticeably deteriorates;
- the eye is completely covered with hemorrhages;
- the damaged conjunctiva is destroyed;
- mucous membrane is susceptible to erosion;
- the pupils are dilated and do not respond to light stimuli;
Third degree contusion:
- the pain is obvious, very strong;
- fear of light rays;
- tearfulness;
- vision decreases so much that it is almost completely lost.
- the fundus of the eye is completely filled with blood;
- There may be a dislocation of the lens.
Fourth degree contusion:
- complete destruction of the eye structure;
- the optic nerve is severed;
- the lens is dislocated;
- vision is lost.
Types of eye injury
Eye injuries are classified according to where they occur. They can be domestic or industrial. There are also agricultural eye injuries that occur as a result of mechanical damage. Their appearance is associated with the ingress of dirt or dust, as well as metal shavings.
Eye burns can be chemical, thermal, or caused by ultraviolet radiation. They are classified according to the degree of damage:
- In the first degree, the eyelids and surface of the cornea are affected.
- A 2nd degree eye burn is manifested by clouding of the cornea and the formation of blisters on the eyelids.
- Deeper damage to the cornea affecting the conjunctiva is typical for grade 3. With such damage, scabs are visible on the eyelids.
- With a 4th degree eye burn, the victim’s cornea is completely destroyed, the lens and vitreous body are affected.
Diagnosis of eye injury
If your eye is injured, you must visit an ophthalmologist and describe the symptoms that appear. The doctor examines the eyelids, cornea and fundus of the eye, determines the degree of damage to the retina and optic nerve. This diagnosis shows how likely the patient is to lose vision. If necessary, the patient's eye is instilled with a dye, which will help detect a grain of sand and a small wound.
If the wound is penetrating, the patient is referred for x-rays and ultrasound to detect a foreign body.
First aid for eye injury
In case of injury to the organ of vision, you should:
- Cover the injured eye with a sterile bandage, through which the sun's rays will not penetrate. The victim is not recommended to perform any physical activity or bending during this period. The situation can be aggravated by sudden head movements. It is recommended to cover both eyes, since the movement of a healthy organ causes movement of the damaged one.
- If chemicals come into contact with the eye, rinse it with cold water for 40 minutes. After this, apply a cool compress.
- If quicklime gets into your eye, you cannot wash it off, because when exposed to water, heat begins to be released, which intensifies the burn. In this case, it is necessary to mechanically remove particles of the specified substance.
- If a grain of sand gets into the eye, remove it with a sterile napkin, moving from the temple to the nose. You can't rub your eyes while doing this. After removing the foreign body, the eye is washed well with running water and instilled with drops. After this, you should consult a doctor, even if the injury is minor.
- If a large foreign body gets into the eye, it is recommended to close it and immediately go to the doctor. Blinking in this case will lead to increased irritation.
- If the eye is injured by ultraviolet radiation, it is necessary to darken the room and apply antibacterial ointment.
What to do at home
Shell shock
Do not rub or press hard on the shells.
- rub or press hard on the shells;
- try to remove a foreign object yourself;
- use lavage if there is a risk of penetrating injury (unless the mucous membranes are damaged by chemicals);
- in case of a chemical burn, do not wash the eye with another reagent to neutralize the effect;
- use a bandage of cotton wool and gauze so as not to introduce additional villi and further injure the mucous membranes (with the exception of heavy bleeding).
After visiting an ophthalmologist, the patient can be transferred either to inpatient treatment or sent home.
Therapy must necessarily include procedures recommended by the attending physician, in compliance with the timing of taking medications.
And in general, as far as vision is concerned, without consulting an ophthalmologist, only first aid can be provided to the victim.
What not to do if you have an eye injury
If a speck of debris that gets into your eye does not change its position when you blink, you should not remove it yourself to prevent infection. Apparently, it has penetrated the eye membrane and must be removed by a doctor. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the eye patch does not compress the organ.
Blinking when pieces of glass, metal and wood enter the eye worsens the prognosis for recovery, since the organ is further injured.
If your eye is injured, it is strictly forbidden to perform the following actions:
- rub the eye;
- touching the eye with dirty hands;
- apply a non-sterile bandage to the eye;
- wash the eye with a penetrating wound;
- trying to get an object sticking out of the eye;
- independently remove foreign objects from the iris and pupil;
- treat your eyes with alcohol.
When providing assistance to the victim, it is necessary to take into account that when applying a bandage to the eye, it is prohibited to use cotton wool. If the eye is exposed to chemicals, other drugs cannot be used to neutralize them.
It is forbidden to remove blood clots coming out of the eye, since the fallen membranes can be removed along with them.
Physical exercises and sudden head movements can aggravate eye injury, so their implementation is categorically not recommended, even with minor damage to the organ of vision.
Perforated wounds: classification
An eye injury is an unpleasant accident.
Huge variations in the prognosis of penetrating lesions are determined not only by the nature and circumstances of the current injury, but also by the location, shape of the injury to the apple and depth.
Depending on the depth of such a lesion, injuries can be divided into:
- A penetrating wound to the eye, in which the wound channel passes through the sclera or cornea and extends to varying depths into the eye cavity, but does not have an exit hole;
- Wounds to the eye are through, in which the wound channel passes through the membranes of the eye and has both an inlet and an outlet;
- Destruction of the eyeball, in which damage is accompanied by destruction of the eyeball, this injury will be accompanied by irreversible and complete loss of visual functions of the damaged eye.
Based on the location of the injury, eye injuries can be divided into:
- Corneal - with this injury, the cornea of the eyeball is damaged;
- Corneal-scleral - the wound channel affects both the cornea and sclera;
- Scleral - the wound channel passes only through the sclera.
Depending on the size of the wound, such an injury can be divided into:
- Small (wound up to 3mm in size);
- Medium size (wound ranging from 4 to 6 mm);
- Large (wound larger than 6 mm).
Trauma can be classified based on the form of injury:
- With a fabric defect;
- Star-shaped;
- Chipped;
- Torn;
- Irregular shape;
- Linear.
Also, a wound can occur with adapted edges of the wound channel and with gaping ones. When receiving any injury, at the slightest suspicion of a penetrating blow, the patient must be urgently taken to the appropriate unit so that he can receive full qualified care.
Help for an eye injury with a penetrating wound or suspected such injury:
- Apply pain-relieving drops and apply disinfectant eye drops. Among the painkillers, these may be: 2 percent solution of novocaine, inocaine, alcaine, 0.25 percent solution of dicaine. Among the disinfectants are: a solution of 20 percent sodium sulfacyl, a solution of chloramphenicol 0.25 percent.
- Using a cotton swab, carefully remove foreign bodies from the surface and in the periorbital area, without getting into the wound area itself.
- Apply disinfectant eye drops again and then apply antibacterial ointment. Then apply a sterile bandage to both eyes. You can use the following antibacterial ointment: Floxal ointment, tetracycline 1 percent eye ointment.
- Inject intramuscularly serum or tetanus toxoid, broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- As soon as possible, facilitate the victim’s admission to an ophthalmology clinic to receive further assistance.
Principles of successful treatment:
- Maximum gentle care for the injured eye at the first stage and providing the victim with maximum peace;
- Contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible;
- Start conservative treatment as early as possible (antioxidant therapy, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial);
- The use of surgical treatment strictly at the optimal time, from the point of view of the stages of the wound process;
- Adequate surgical treatment for perforated eye injury using vitreoretinal technology in surgery and all modern diagnostic methods.
Treatment of eye injury
If your eye is injured, you should contact a medical facility. In most cases, the victim is recommended to undergo outpatient treatment and is prescribed eye drops. The most popular are Albucid and Levomycetin. In case of hemorrhage, retinal detachment, penetrating injury and foreign body entry, the patient requires surgical intervention.
Eye bruises are usually treated on an outpatient basis. To restore blood vessels and improve microcirculation in the eye, the patient is prescribed hemostatic agents and angioprotectors. Physiotherapy is also practiced, in particular electrophoresis and UHF. In severe cases, the patient requires a corneal transplant.
For penetrating eye injuries, the patient is prescribed sulfonamides, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antifungal agents.
If foreign objects get into the cornea, the patient may not always be recommended to undergo surgery. You can do without surgery if plastic or glass gets into your eye. When an item quickly oxidizes, it must be removed immediately. If a foreign body gets into the conjunctival sac, it is removed with a special needle or tweezers, after injecting the patient with anesthesia.
If the injury is accompanied by loss of an eye, the victim is given an implant. A patient with an eye injury must be given a tetanus vaccine.
How to treat
The victim must be provided with first aid:
- If the situation requires the removal of a foreign body, then it must be done within the walls of a medical institution;
- Treatment with antibacterial drugs (sodium sulfacyl, chloramphenicol);
- For more serious injuries, this is a solution of diclofenac 0.1% or indoclear 0.1%;
- If hemorrhage occurs, contrical drops will be applied to help resolve the hematoma;
- To relieve pain, inocaine is an eye drop.
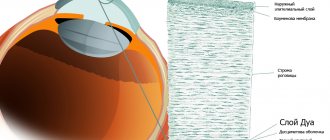
Damage to the cornea of the eye
Injuries to the cornea impair the patient's vision. They occur when exposed to ultraviolet radiation, mechanical particles, and infections. Incorrect growth of eyelashes also leads to injury. Damage to the cornea is caused by excessive drying and lack of collagen. The simplest treatment is prescribed to patients with corneal erosion.
If the corneal epithelium is damaged, the patient requires drug treatment. For this purpose, the following eye drops are prescribed:
- Keratoprotectors . They restore and strengthen the cornea. These include Solcoseryl and Oftagel.
- Tear replacement drops that relieve irritation. Lacrisify, Visin, Oftolik have these properties.
- Antibacterial. This group of medications is necessary to prevent inflammation and the spread of infection. This includes Floxal, Tsipromed, Tobrex.
- Angiopretectors. They are prescribed to improve the trophism of the organ of vision. The most popular remedy in this group is Emoxipin.
- Vitamin drops. These medications are required to accelerate regeneration and improve metabolism in the eye.
To prevent infection and relieve inflammation, the use of fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides is practiced.
Preventing eye injury
To prevent eye injury, it is necessary to use protective equipment, which includes goggles and a mask. They must be worn when working with power tools, metal, hazardous chemicals, and when welding.
Since traumatic eye injury can occur at any time, it is necessary to ensure that your first aid kit is stocked with dressings and medications.
Athletes involved in team games are susceptible to eye injuries. They are often diagnosed with eye contusions. To avoid them, it is recommended to wear safety glasses.
Children can injure their eyes due to improper handling of objects. The reason may be chemicals located in the access area. To prevent damage to the organ of vision, it is necessary to hide household chemicals, medicines and sharp objects. Children need to be taught that they should not point toy weapons at people or throw any objects in their direction. Adults are required to ensure that explosive and flammable substances are not placed in the hands of children.
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation can cause eye burns. This injury occurs in climbers, skiers, as well as lovers of solariums and sunbathing. Having such hobbies, you should definitely wear safety glasses.
Because the likelihood of injury increases with dry corneas, the use of artificial tears is recommended.
Treatment methods used
These medicinal recipes, which can be prepared at home, will only help in relieving swelling, reducing bruising and eliminating pain. In more complex cases, such methods are no longer sufficient.
1 way
One onion is passed through a meat grinder and a teaspoon of sugar is added to the resulting pulp. Mix and apply to the bruise for twenty minutes. This will reduce swelling and reduce pain.
Method 2
Soda lotions. Prepare a solution - place a teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm water. It should be applied several times a day to relieve bleeding and bruising.
3 way
If there are no bruises, then a mixture of turmeric and ginger in equal proportions is suitable for pain relief. Add a little water to make a paste. It is laid out on the eye and covered with cellophane.
Once the swelling has subsided, any residual effects can be treated with heat. It has a beneficial effect on damaged tissues and promotes their healing.
Cabbage lotion helps very well.
The leaves of fresh cabbage are cored and poured with boiling water for a few minutes. Then applied to the affected area. Do this procedure at least twice a day, keep it for about two hours.
Remember that self-treatment can only make the situation worse. Therefore, it is still worth visiting a doctor and getting his advice.
If the consequences of a severe bruise are not so serious and do not require surgical intervention, then the doctor can prescribe a number of medications that will help cure a severe bruise. The most effective medications are listed below:
- “Diclofenac” - relieves inflammation, reduces temperature, heat and fever, reduces swelling, eliminates pain.
- “Indomethacin” stops the inflammatory process and relieves pain.
- “Suprastin” - reduces the activity of histamine, is a stimulant.
In addition to tablets, eye drops are a good option for severe eye injuries accompanied by complications. They are also discharged after surgery. Typically, the full course of these drugs does not exceed ten days.
- “Ciprofloxacin” is a drug that destroys microbes and bacteria and has low toxicity.
- “Ofloxacin” is a medicine against microbes, has a wide sector of action.
- “Picloxidine” – characterized by antiseptic properties.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Structure and pathologies of the lumbosacral spine
Any injury to the eye is dangerous, because this organ is very fragile, and its health must be treated responsibly. That is why you should not neglect medical care if you are seriously injured.
After delivering the injured person to a medical facility, treatment for an eye injury is prescribed in accordance with the diagnosis, the degree of injury and other factors that can only be determined by an experienced ophthalmologist.
Prevention. In most cases, the patient is vaccinated with antitetanus serum to prevent tetanus. To prevent infection from entering the wounded surface of the eye, the patient is prescribed the drugs norsulfazole and sulfadimethoxine orally. In addition, it is advisable to instill a solution of chloramphenicol into the affected eye.
Treatment. After a complete examination using special methods: ophthalmochromoscopy, radiography, tonography and ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor can perform surgical treatment of the injured appendages of the eye. The patient is injected intramuscularly with hemostatic drugs, for example, calcium gluconate, dicinone or ascorutin.
In the future, when acute symptoms have been relieved, it is recommended to use warm baths or alcohol compresses. They help fight swelling and hematomas quite well. Physiotherapeutic procedures also contribute quite effectively to recovery: magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, UHF therapy. Anti-inflammatory drugs, which are recommended to lubricate the bruised area, relieve redness in severe bruises.
Calendula tincture has proven itself well as a remedy. To use it, you need to prepare an alcohol tincture at home and apply it to the affected eye.
If there is a head injury with a large area of injury, then a solution of vodka, vinegar and salt can be applied to the affected areas of the face.
Any bruises to the eye, no matter how minor, should not be ignored. Self-medication in this case often leads to the development of irreversible processes. Only in a specialized ophthalmological institution or in traumatology will you be able to correctly diagnose, assess the real extent of injury and prescribe adequate treatment.
Consequences of eye injury
If you do not see a doctor after an eye injury, complications are possible that also affect the healthy organ. The most favorable prognosis is for corneal edema, which resolves within 7 days. More severe consequences are caused by inflammation of the cornea, called keratitis. A patient with this pathology experiences severe pain and photophobia; he cannot open the injured eye. If erosion or keratitis is not treated, an ulcer develops. This pathology is provoked by the growth of bacterial microflora. If left untreated, the patient experiences pinched iris and optic nerve atrophy.
Consequences of other eye injuries:
- Burns from chemicals, especially meadows, pose a great danger to the eye. They penetrate deep into the tissue, dissolving the protein and destroying the anatomical structures of the eye. The consequences of this process appear after 3 days. Patients are diagnosed with secondary glaucoma, cataract, and atrophy of the eyeball as a complication.
- If, when the organ of vision is injured, the outflow of intraocular fluid is disrupted, the patient's intraocular pressure increases, which leads to glaucoma. This pathology causes nerve death and blindness.
- When the inflammatory process spreads to the tissue of the eyeball, endophthalmitis is diagnosed. This complication leads to loss of vision and subsequently spreads to the meninges, causing meningitis.
- After moderate to severe eye injury, vision deterioration is observed. Complete blindness is also possible.
- If the patient ignores a foreign body in the eye for a long time, his field of vision narrows. After this, retinal detachment and eye atrophy are diagnosed.
An unfavorable prognosis for eye injury is possible in patients who do not consult a doctor in a timely manner. As a result of such actions, a healthy organ also suffers. Medical care allows you to avoid negative consequences for the anatomical structures of the eye and preserve vision.
Eye drops
To treat eyes after injuries, ophthalmologists often prescribe topical medications. Below is a list of the most popular gels and eye drops for eye injuries:
- “Floxal”, “Otaquix”, “Tobrex” are drops containing antibiotics. Help prevent and relieve the inflammatory process.
- “Balarpan-N” - the drops contain natural substances similar to those found in the tissues of the cornea. They have a healing and restorative effect.
- "Vitasik" - drops used for injuries to the inner membranes of the eye. They help restore mucous tissue.
- “Inocaine” – instillation into the eye relieves pain.
- “Defislez” – have a protective, nourishing and moisturizing effect. These eye drops for eye injury promote rapid healing and are endowed with a restorative effect. Particularly effective for corneal burns.
- “Solcoseryl” is a gel that helps speed up metabolic processes, replenishes the lack of minerals and oxygen in tissues. Quickly regenerates and heals damaged tissue areas. Used for burns and mechanical damage to the eyes.
Before using any drops, you should consult your doctor. Only in case of minor damage to the eye is it possible to independently use Albucid to disinfect the mucous membrane.