- Features of keratoplasty
- Advantages of treatment at the International Health Center
The cornea is the part of the eyeball located in front. It is a convex and transparent shell and is one of the light-refracting media of the visual apparatus. It performs important functions:
- eye protection due to the strength of the cornea and its ability to quickly recover;
- light refraction - being part of the optical system of the eye apparatus, it conducts and refracts light rays due to transparency and sphericity;
- maintaining the shape of the eyeball, participating in intraocular metabolism.
The cornea consists of 5 layers:
- superficial – lined with squamous epithelial cells and continues the conjunctiva, characterized by high vulnerability;
- border anterior plate - when damaged, it does not recover, but becomes cloudy, and tends to quickly tear away;
- stroma - the thickest part, containing approximately 200 layers of collagen fibrils, between which is located mucoprotein - a connecting component;
- Descemet's membrane - covers the stroma from the inside and is a derivative of the endothelium, from which all corneal cells are formed;
- endothelium - the inner part, prevents the stroma from becoming permeated with intraocular fluid.
Any pathologies occurring in this membrane contribute to a decrease in visual acuity and even loss of vision. All kinds of inflammations easily begin and continue for a long time, which is why it is important not to delay a visit to an ophthalmologist if suspicious symptoms appear.
Cornea of the eye - functions
The cornea is the anterior portion of the eye sclera, which is endowed with a high refractive index. This transparent film is located in an uncovered space and is therefore most often subject to various damages. Any damage to the ocular cornea requires an immediate response, since it is very difficult to judge the severity of the injury by external signs and delay in treatment may cost the visual functions of the eye.
The cornea consists of collagen fibers and a transparent matrix, which are covered with stratified epithelium. This protective hemisphere with a diameter of 10 mm separates the anterior eye chamber from external influences. An interesting feature: the cornea in the central part of the hemisphere, which is most susceptible to external attacks, is two times thinner than at the edges. Therefore, the eyes should be greatly protected from foreign bodies that cause damage to the cornea precisely in these potentially weak areas.
The functional purpose of the cornea is to refract light with a power of 40 diopters and keep the eyes in good shape. If the cornea is injured, it will not be able to perform its functions fully. And this can cause significant damage to the visual capabilities of the eye.
Drops for cataracts
The modern pharmaceutical market offers hundreds of drugs for a variety of pathologies of the visual system, and cataracts are no exception. Typically, doctors prescribe drops only to relieve symptoms, since there is no sufficiently effective remedy on the market to resolve opacities.
For cataracts, Vitafacol, Quinax, Vitaiodurol, Taufon and Oftan-catachrome are often prescribed. However, replacement therapy (drugs with substances, the deficiency of which presumably causes cataracts) is ineffective for the traumatic nature of opacification. The eye may be completely healthy before the injury and not need additional “nutrition.”
Notably, most cataract drugs are not independently tested. The manufacturer himself organizes an effectiveness study, the results of which are not always reliable. Therefore, the effectiveness of numerous drugs for cataracts has not been scientifically proven, and therefore their use may be inappropriate.
Separately, it is worth mentioning Quinax drops. Only this drug has shown real, albeit insignificant, effectiveness in the treatment of senile, diabetic and other forms of cataracts. This drug is unique in its kind: its active substances are able to activate enzymes in the intraocular fluid and enhance the process of resorption of lens proteins. To achieve results, you need to use drops for years, which is unacceptable if the disease progresses quickly.
Cataract drops can only be effective at the initial stage of the disease. Existing dense opacities can be completely cured only with surgery, so you should not postpone surgical treatment.
Causes
The reasons why corneal damage can occur are varied, there are many of them, but you should be aware of them. These include:
- mechanical injury from a foreign body;
- infectious disorders;
- metabolic disease;
- drying of the cornea;
- congenital collagen defect;
- strong ultraviolet or radioactive healing;
- mechanical clogging: dust, midges, specks, etc.;
- ingress of chemical and thermal agents.
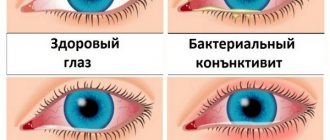
Signs of illness
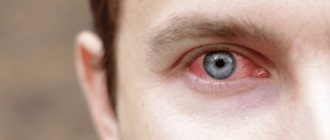
Symptoms indicating that damage to the cornea has occurred are expressed in profuse lacrimation, redness of the injury site, photophobia, reflex closure of the eyelids - blepharospasm. In addition, you may experience:
- epithelial layer defects;
- dilation of conjunctival vessels;
- feeling of sand;
- eye pain and headaches;
- redness of the eyelids.
The depth and degree of penetration of a foreign body or wound damage may vary. According to the severity of the injury, corneal erosion and ulcer are distinguished. When injured, the integrity of the eye structure and its functional abilities are disrupted. Injury can occur from a blow from a hard object or from dust or chemicals entering the mucous membrane of the eye. In case of injury, timely treatment of corneal damage is very important.
Symptoms
Injuries to the corneas of the eye are combined with symptoms:
- discomfort;
- feeling of “sand”;
- acute pain and burning with large-scale lesions;
- redness of the eye.
In this case, visual acuity is noticeably reduced, the picture becomes blurry, and there are no contours. The level of visual impairment depends on the area of the lesion. There is profuse lacrimation, intensified by the movement of a foreign object. In some episodes, the victim complains of a headache.
Commonly encountered signs include:
- profuse lacrimation;
- unusual eye sensitivity;
- burning;
- blurred image.
What is prohibited?
Eye damage can be very dangerous. This organ is so easily vulnerable that any injury can be fatal if measures are not taken in time for diagnosis and treatment. Timely treatment of corneal damage significantly reduces the risk of serious consequences. It also increases the chance of a full recovery. If an eye injury occurs, the following things are prohibited:
- rubbing your eyes with your hands - this action can drive the foreign body even deeper into the cornea or damage it by friction, and there is also a high risk of introducing an infection into the resulting wound;
- Trying to remove a foreign object before seeing a doctor can aggravate the existing damage;
- treat and disinfect the resulting wound, with the exception of exposure to chemicals, in which case the first step is to carefully rinse your eyes with plenty of running water;
- Do not treat the cornea with cotton wool, as its particles may remain on the mucous membrane and penetrate into the resulting damage.
When performing eye manipulations, you must wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
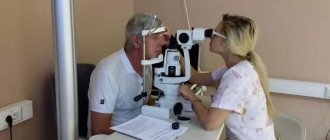
Diagnosis of cataracts and preoperative examination
You need to schedule a visit to the doctor if you notice deterioration in vision and loss of clarity. Only comprehensive diagnostics using special equipment can identify the causes of the violation.
Examination for cataracts includes the following measures:
- visual acuity testing (visometry);
- determination of the degree of refraction of the eyes, measurement of the curvature and refractive power of the cornea (computer keratorefractometry);
- study of the anterior segment of the eye, assessment of the condition of the lens and iris (biomicroscopy);
- checking the angle of the anterior chamber (gonioscopy);
- determination of visual fields (perimetry);
- checking the level of intraocular pressure (tonometry);
- assessment of the condition of the optic nerve and retina (ophthalmoscopy);
- measurement of the thickness of the cornea and lens, the depth of the anterior chamber, assessment of the condition of the vitreous body and retina (ultrasound scanning);
- comprehensive study of the anterior segment, detailed examination of the cornea (keratotopography).
Since cataracts are often treated with the installation of intraocular lenses, during the diagnostic process it is necessary to study the condition of the cornea in detail. The radius of curvature of this shell allows us to calculate the necessary lens parameters. If a traumatic cataract is suspected, it is important to perform a B-mode ultrasound scan. This allows you to find breaks and timely determine the presence of retinal or choroidal detachment.
Before the operation, you should undergo a thorough examination, if necessary, visit other specialists and make sure there are no contraindications. The purpose of ophthalmological diagnosis is to detect or exclude phacodonesis and vitreous hernia, and examine the posterior capsule. Before surgery, it is important to check the condition of the ligaments of Zinn.
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment for damage to the cornea of the eye, it is necessary to perform a visual inspection of the injury. This should be done by a qualified ophthalmologist who can determine the nature of the damage and its severity. To do this, he needs to open and lift his eyelids in order to examine the entire area of the cornea for dirt or sand, as well as other foreign formations. Special drops will help you carry out this manipulation easily and painlessly.
If the cornea is damaged, many ophthalmologists use fluorescein for this purpose, which helps to better see foreign inclusions on the cornea. They act in just a few seconds, during which an experienced doctor is able to see a clear picture of the injuries received. If a child’s cornea is damaged, then these drops cannot be avoided. Especially if this child belongs to a younger age group.
In case of damage to the cornea, a course of antibiotic treatment is carried out to prevent the development of infections and the appearance of secondary infectious diseases. At the treatment stage, antibiotics are usually used in the form of drops and ointments, but in particularly difficult cases, when there is a risk of infection, and after completion of treatment procedures, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibacterial therapy in the form of tablets. In this case, it is important that the patient knows how to take antibiotics correctly. Let us consider further what types of damage from external influences are and what the patient needs to do in a given case.
How does traumatic cataract develop?
With a closed eye injury, cataracts develop in 11% of cases. During injury, the eyeball is subject to impact and counter-impact forces. A strike is a direct force, and a counterstrike is a reflected force. It is the counterblow that damages the lens more strongly. When subjected to mechanical action, the eyeball shortens, the lens capsule ruptures, and the ligaments of zonules are torn off. And everything happens at the same time. The more precise mechanism of damage to the lens capsule during trauma is not clear.
The capsule is able to quickly regenerate (properties of subcapsular epithelium), so damage up to 2 mm is quickly restored. If damage exceeds 3 mm, opacification occurs: rupture of the capsule leads to intraocular fluid entering the lens.
Capsular injuries may suddenly open days or months after the injury. In this case, secondary glaucoma, severe inflammation and cataracts often develop. And although most often traumatic cataracts are not associated with damage to the capsule, this factor cannot be excluded.
In most cases, traumatic cataract occurs due to the fact that at the time of contusion, subcapsular opacities are formed in the cortical layers of the lens. Such opacities have the shape of petals and spokes, diverging radially.
Without treatment, traumatic cataracts can progress to the point that fundus examination becomes difficult. As cataracts mature, vision decreases, intraocular pressure increases, and inflammation recurs.
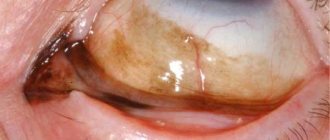
Erosion
Erosion is a mild degree of damage when it is shallow and more superficial. Treatment is performed on an outpatient basis, local anesthetics such as Lidocaine or Dicaine are instilled into the patient's eyes, healing ointments containing antibiotics are applied, and drops based on hyaluronic acid and natural tears are prescribed. Ointments for corneal damage - Actovegin or Solcoseryl eye gel, they are most often prescribed. Corneal erosion epithalizes quickly enough and does not cause any complications.
Corneal wounds are considered complex injuries, especially when the wounds are of a penetrating nature; they are treated inpatiently using techniques intended for use in eye microsurgery. At the same time, antibacterial therapy, systemic enzyme treatment and healing drops are prescribed. If you do not promptly consult a doctor with a penetrating wound, very serious consequences of corneal damage can occur.
Emergency help
Eye injury can occur at different ages. The method of providing first aid to a patient does not depend on the number of years. It should include coherence, urgency in carrying out actions, competence of an eyewitness to the incident and his composure. To be ready to help in an emergency, you need to know the following rules of assistance:
- Active blinking can remove debris from tears. If there is no pain when lightly pressing on the eyelid, it is necessary to perform several movements towards the inner edge;
- rinse the injured eye with an antibacterial drug;
- move back the upper eyelid and cover the lower one, the eyelashes will help pull out the particle;
- move the eyeballs left and right;
- apply anti-inflammatory drops or ointment.
These measures are effective in treating shallow corneal lesions. In case of any episodes of injury, the injured eye is covered with a sterile napkin and fixed.
What not to do:
- rub your eyelids;
- use non-sterile devices;
- touch the eye with fibrous tissue or a cotton swab;
- independently remove a foreign object that has sharp edges or a massive body embedded in the eye.
Burns
Burns can be thermal and chemical; they are treated by using microsurgery, namely excision of the damaged layer of the cornea. In addition, a course of healing treatment with drops and ointments is carried out, as well as antibacterial, enzyme and anti-inflammatory therapy. If the burn is chemical, then you must first remove the substance that caused the injury to the cornea. To do this, you need to tilt your head to the side and hold it under an intense stream of water for about half an hour. But if the burn is caused by lime, it is prohibited to remove it with water, since under the influence of water it generates heat, which can aggravate the degree of damage to the cornea. The lime must first be carefully removed with a napkin, and then rinsing with water begins.
In case of an ultraviolet burn, you need to darken the room, since the patient is very sensitive to bright light, put an antibacterial ointment under the eyelid, for example, “Tetracycline” (1%). You need to apply something cold to the eyelid and ensure that the patient takes an analgesic (Analgin or Nurofen).
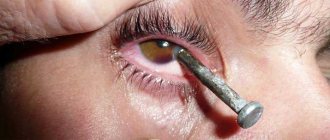
Foreign body. What to do?
The foreign body is removed from the surface of the cornea with a cotton swab. In case of deep penetration, it is removed with special ophthalmic instruments. If these foreign bodies are made of plastic or glass, they are not pulled out of the wound, they themselves move to the surface after some time and can then be easily removed. Healing of the cornea is carried out with the help of drops: “Emoxipin”, “Taurine”, hyaluronic acid, “Natural tears”, and antibiotic ointments, and you can also make injections around the eyeball with these substances.
In some cases, the cornea can be damaged by lenses.
Contact lenses can cause corneal injury in the following cases:
- if a foreign body gets under the lens - mechanical rubbing;
- if you are allergic to components included in lens care products;
- if the rules of lens hygiene are violated, conjunctivitis and other infectious diseases appear;
- when oxygen supply to the cornea is disrupted, which entails swelling and other hypoxic reactions.
Prevention measures
Prevention of eye injuries involves following safety precautions at work, careful use of household chemicals, careful handling of life-threatening objects, and proper wearing of contact lenses.
It is especially important to observe safety precautions in workshops and laboratories. It is also very important to instruct schoolchildren before working in the laboratory and training workshops.
In everyday life, all chemicals should be kept out of the reach of a child. Ammonia, vinegar, glue, cleaning products - all this should be stored in a tightly closed cabinet and taken out only when needed.
One of the causes of corneal damage is the lack of protection of the eyes from exposure to ultraviolet rays. You can reduce the impact of the provoking factor by wearing sunglasses.
When working at a computer for a long time, it is necessary to take periodic breaks and also use special moisturizing drops to reduce the symptom of “dry eye”.
How to use drugs correctly?
When treating injuries to the cornea of the eye, the main focus is initially on getting rid of the object or factor that caused the injury and restoring the original functions of the eye. But infection prevention also plays a big role. And when a doctor prescribes antibacterial tablets, you need to remember how to take them correctly. First of all, patients and their relatives should understand that only a certified doctor of appropriate qualifications can select the drug, dosage, dosage regimen and duration of treatment.
Under no circumstances should you violate the prescribed dose or interrupt treatment without permission. Both a deficiency and an excess of this powerful disinfectant can cause serious deviations in the functioning of human internal organs and systems. Antibiotics are taken strictly according to the schedule, and this must be done at the same time with constant intervals between doses. The minimum treatment period is 7 days, unless otherwise prescribed by a doctor. Sometimes the recovery period extends to 2-3 weeks.
While taking antibiotics, it is prohibited to drink alcohol, smoke, eat smoked meats and other harmful foods; the doctor will give separate recommendations regarding the diet. Antibiotics should be taken with plenty of clean water. You cannot go to the beach or solarium, dye your hair or do perms. Be sure to take probiotics prescribed by your doctor along with the antibiotic to restore the intestinal microflora.
Treatment
Treatment in a medical facility begins with a conversation with a doctor who needs to find out how the injury occurred. In case of damage, drops with a healing effect are prescribed. Lidocaine is used for pain relief. For rapid fusion, specially designed gels are also used. For burns, treatment is similar to conventional techniques used for mechanical damage to the eye.
The doctor’s main goal during treatment is to do everything possible to regenerate or fusion of tissue on the surface of the cornea.
What are the consequences of the injury?
If eye injury is not promptly addressed, serious consequences of damage to the cornea of the eye may occur. The likelihood of complications is very high. These include:
- lens loss;
- development of cataracts or secondary glaucoma;
- retinal detachment;
- formation of a cataract;
- manifestation of hemophthalmos, endophthalmos, panophthalmos.
The severity of the consequences directly depends on the degree of complexity of the injury and the timeliness of the medical care provided.
What are the types of corneal injuries?
All injuries received can be divided into several types: burns, wounds, bruises, foreign bodies.
Burns
Burn injuries are classified as follows:
- Chemicals obtained when acidic or alkaline substances come into contact with the eyes. A chemical burn can be caused by contact with household chemicals, decorative cosmetics, or while working at manufacturing plants.
- Thermal, resulting from exposure to high temperatures. In this case, not only the eye is damaged, but also the tissue adjacent to it.
- Radiation. eyes are affected by ultraviolet or infrared radiation.
Eye burns are also classified according to their severity.
There are 4 burn degrees: 1 and 2 are considered mild, 3 – moderate, 4 – severe. With a 1st degree burn, there is a high chance of completely preserving vision; with a 4th degree burn, tissue charring, scleral necrosis and complete death of the cornea occur. Dangerous consequences of burns include damage to the choroid, development of glaucoma or cataracts.
Injuries
Injuries are classified as mechanical injuries, most often caused by a sharp object. Penetrating and non-penetrating wounds are distinguished. Non-penetrating ones slightly damage the upper layer of the cornea.
Penetrating wounds of the cornea are of the following types:
- Deep, passing through the cornea and spreading into the cavity of the eyeball.
- Through, when the wound channel extends beyond the eye.
- Leading to destruction of the eyeball. In this case, loss of the lens, vitreous body or iris, and hemorrhage into the anterior chamber of the eye may occur.
When diagnosing an eye injury, it is necessary to pay attention to the exact location of the wound, its size and shape. The wound may be gaping or have closed edges.
The most common causes of injuries are domestic, industrial, and even sports injuries.
Bruises
A corneal bruise can easily be caused by a blow to the eye. This is one of the most common types of injury. The consequences of a bruise depend on how strong the blow was.
Sometimes the damage is limited to subcutaneous hemorrhage in the tissues around the eye, but in severe cases, corneal rupture may occur. Minor injuries do not require special treatment; in other cases, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
Severe bruises can lead to retinal detachment, optic nerve atrophy, and rupture of the choroid. These pathologies are dangerous due to the prospect of completely losing vision.
Entry of foreign bodies
Once inside the eye, the foreign body remains on the surface of the cornea or penetrates into its mucous membrane to varying depths. The following can act as a foreign body: dust, sand, various grains of sand, small debris.
If the corneal epithelium is damaged, an inflammatory process begins within a few hours and an infiltrate is formed. Consequences may include clouding of the cornea, astigmatism, and decreased visual acuity.
Any damage to the integrity of the cornea is a serious reason for examination by a specialist.
Serious complications after eye injury
In case of unqualified treatment and poor quality treatment of the affected area of the eye, the following complications are possible:
- sepsis - blood poisoning by infectious agents, which threatens to poison the body with toxic waste from bacteria;
- decreased visual function of the eye and even complete loss of vision;
- loss of an eye;
- purulent brain abscess due to the accumulation of pus in the cranial cavity;
- purulent inflammation of the structures and membranes of the eyeball - panophthalmitis;
- sympathetic inflammation of the healthy eye, most often fibroplastic iridocyclitis;
- accumulation of pus in the vitreous with inflammation of internal structures - endophthalmitis;
- the presence of an unaesthetic scar;
- inversion of the eyelids, as well as ptosis and ectropion;
- deformation of facial tissues;
- disturbances in the functioning of the lacrimal glands.
When the patient's immune system is weakened, these complications are especially severe and acute, and a serious disruption of metabolic processes is observed. If the cornea has a normal blood supply, then regeneration will occur in a short time, but if infectious agents enter the affected area, a more severe degree of corneal disease can develop - an ulcer.
Types of traumatic cataracts and their symptoms
Traumatic cataracts can be partial or complete (local and total). There are also semi-resolved cataracts and dense ones.
Types of cataracts according to the position of the lens:
- membranous (normal position);
- subluxation (partial shift);
- luxation (complete shift to the fundus).
Types of cataracts by type of injury:
- contusion (blunt eye injuries);
- toric (damage from chemicals);
- wound (penetrating injuries);
- radiation (damage from ionizing radiation).
Symptoms of traumatic cataracts will depend on the location of the opacities. If there is a posterior subcapsular cataract, symptoms are usually severe and extensive. Cortical and sclerotic opacities add less discomfort to the patient.
The most common type of cataract is contusion cataract. Damage can occur with direct concussion, that is, with a blow with a blunt object, and indirect (to the head). The cause of toxic cataracts is all kinds of burns of the eyeballs with aggressive liquids. In addition, clouding can develop in case of severe poisoning with ergot, nitro dyes, trinitrotoluene and other substances.
Radiation opacities are predominantly ring-shaped. With radiation cataracts, colored spots are visible on the gray background of the lens. This feature is used for differential diagnosis.
Modern medicine offers only surgical methods for treating traumatic cataracts. Such eye injuries, which can cause clouding, often end badly because they damage the structures of the posterior segment of the eye. Patients often develop retinal detachment, macular fibrosis, and optic neuropathy. Sometimes afferent pupillary failure and iridodialysis are also detected.