The eye is a complex organ, consisting of various types of tissues and performing specific tasks. “Eye cold” is usually called a combination of various inflammatory reactions that can be localized in any part of the organ, including those around the eye. There are several main foci of damage to the organs of vision, which can occur in:
- century;
- eye socket;
- ocular vessels;
- conjunctiva;
- cornea.
If a person says that he has a cold in his eye, one should distinguish between true inflammation and irritation of the mucous membrane, which can be provoked by any irritants: cold air, dust, light, etc.
It should be noted that irritation of the mucous membrane is the optimal conditions for the penetration of bacterial, viral or fungal pathogens into the organ, which should be taken into account.
Why does inflammation occur in the eyes?
Is it possible to get a cold in your eye? Like any other organ, the eye is susceptible to the influence of negative mediators of infectious and non-infectious origin. The following reasons can provoke the occurrence of foci of inflammation:
- infectious (bacteria, unicellular organisms, fungi, viruses);
- traumatic (impacts, exposure to acids or alkalis);
- allergic (reaction to medications, cosmetics).
If your eye is cold, what should you do? First of all, it is necessary to find out the main reason for the malfunction of the organ. The following types of eye diseases can provoke the appearance of lesions:
- blepharitis and keratitis;
- corneal ulcer and stye;
- phlegmon and tenonitis;
- boil and iritis;
- conjunctivitis and exophthalmos;
- dacryocystitis and neuritis;
- eyelid abscess and canaliculitis.
All of the above diseases, to one degree or another, provoke inflammatory reactions in the organ. To understand what kind of disease could lead to failures, let's look at the most common of them in more detail.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is a disease characterized by inflammation in the outer lining of the eye. The main causes of the disease include:
- poor nutrition;
- hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- allergic reaction;
- decreased immunity;
- diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, runny nose).
- The main symptoms of a cold eye will be:
- pain and burning;
- lacrimation;
- feeling of "sand";
- eye fatigue;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- photophobia.
Depending on the type of causative agent of the disease, conjunctivitis can be:
- bacterial – provoked by bacteria, in particular streptococci and staphylococci;
- allergic – occurs as a reaction to the action of medications, dust and other allergens;
- adenoviral – a post-influenza complication that appears after infection of the upper respiratory tract with adenoviruses;
- hemorrhagic – develops with a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels, therefore it is characterized by hemorrhages in the eyeball;
- atopic – a seasonal disease, which is often accompanied by acute rhinitis;
- fungal - provoked by a fungus, the source of which can be a sick person or animal, dirty fruits and household items.
Optic neuritis
Neuritis is a disease accompanied by inflammation of the peripheral nerves, which leads to malfunctions of the visual organs. Optic neuritis can be acute or chronic. In the first case, complete or partial loss of vision occurs within 2 days, and in the second - within a month or more. The causes of neuralgia include:
- inflammation of the brain;
- infectious diseases (flu, sore throat, otitis media);
- post-traumatic complications;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hypothermia;
- diabetes and gout.
If a person has a cold in the optic nerve, the symptoms of the disease will be:
- loss of vision;
- decreased perception of shapes and colors;
- deterioration of peripheral vision;
- pain during eye movement;
- presence of a blind spot in the field of vision;
- increased pain with physical activity.
Neuritis is one of the most severe eye diseases and therefore requires immediate treatment.
If a person has double vision due to a cold in the optic nerve, this may indicate destruction of the outer sheath of the nerve. Untimely treatment can lead to complications and complete loss of vision.
Blown eye - what to do and how to treat
Often, inflammation occurs under the influence of external factors on the external structures of the eyes.
When visiting a doctor, patients describe the condition as a “blown eye.”
The reason may be many factors that the doctor finds out through the use of instrumental and laboratory research methods. He can guess the diagnosis based on the symptoms that appear in the first two days after the onset of the disease.
- 1 Symptoms
- 2 Reasons
- 3 Treatment
- 4 Prevention
- 5
Symptoms
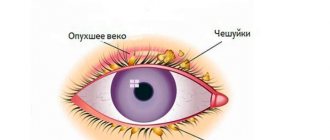
Since the development of an infectious-inflammatory disease in the eye area, the following clinical symptoms appear:
- redness of the conjunctiva and skin surfaces around the eyeball;
- discomfort that turns into acute pain;
- itching, burning, irritation;
- sensation of a foreign object under the eyelids;
- increased production of tear fluid;
- discharge from the inner corner of the eyes, which has a white, green, yellow, brown tint (the brighter the color, the more active the reproduction of pathogenic microflora in the secret);
- formation of acute pain when exposed to bright colors;
- swelling of the skin surfaces around the eyeball, possible formation of seals;
- elevated body temperature rarely occurs if an infectious-inflammatory condition causes complications;
- blurred vision, double vision, decreased visual acuity up to complete blindness;
- The lymph nodes in the head area become dense and can be easily palpated.
Based on the clinical symptoms that appear, the doctor can assume the viral or infectious nature of the disease.
Causes
The causes of blowing eyes are the following conditions and diseases:
- severe viral infection, in which the discharge from the inner corner of the eyes is transparent, and bright redness of the conjunctiva of the eyes is observed;
- bacterial infection, which is formed during the proliferation of opportunistic microflora, the main symptom will be the release of purulent contents from the inner corner.
Doctors identify the following types of diseases that form when exposed to strong winds:
- meibomitis (hordeolum) is an inflammatory condition that develops in the eyelash bulbs and glands located on the eyelid;
- conjunctivitis is an inflammatory condition of the conjunctival sac, which causes severe redness and pus discharge from the corner of the eyes;
- blepharitis is an inflammatory condition of the internal structure of the eyelids:
- dacryocystitis is an inflammatory disease of the lacrimal canal, gland and sac, which reduces the production of tear fluid and forms conjunctivitis as a complication.
It is important for the doctor to identify the first symptoms of the disease in time and determine the cause. The eyes are a very delicate structure through which infection quickly spreads. If it has penetrated into the internal sections, treatment will be more difficult.
Treatment
Treatment of infectious and inflammatory conditions of the outer surface of the eye should be carried out comprehensively. Several techniques are used to reduce the risk of developing complications when a pathogenic microorganism moves into the internal structure of the eyes:
- Antiviral agent. The most commonly used systemic drug is prescribed in tablet form. Viral eye diseases occur due to decreased immune function. Most often, this condition occurs due to herpes, which is constantly in the blood. It is activated when the immune function decreases and the negative impact of environmental factors. This condition cannot be completely cured; the virus can be eliminated temporarily.
- Antibacterial therapy. Most often, ophthalmologists prescribe broad-spectrum drugs. But for greater effect, it is recommended to initially undergo an analysis to identify the pathogen and the sensitivity of antibacterial drugs. Using this method, you can prescribe not a broad-spectrum drug, but a more narrow-profile drug. This reduces the risk of developing resistance in pathogenic microflora.
- Moisturizers. During infectious and inflammatory diseases of the eyes, the mucous membrane becomes very dry. This is due to decreased production of tear fluid. If the mucous membrane is dry for a long time, this forms microtraumas and cracks in the cornea. Through them, the infectious focus can quickly pass into the internal structure of the eyes. Moisturizing drops promote prolonged presence of tear fluid on the mucous membrane.
- Creams and ointments to enhance tissue regeneration. Such agents are used at the healing stage. They are applied under the upper or lower eyelid. Creams are used before bedtime, since after their application visual acuity is temporarily reduced. Such products include Korneregel, Solcoseryl. Increased production of new cells is achieved by improving metabolic rate.
- Vasoconstrictors. They are used for excessive redness of the conjunctival membrane. When used, swelling decreases. These products are indicated for use for no more than 4 days, since after this time an addiction to the active substance develops.
- Antihistamines. They can be used systemically for widespread allergies, or topically in the form of drops if there is a small lesion. The drugs relieve swelling, inflammation, and redness. With the help of their action, the immune system has less impact on the penetration of the allergen.
After treatment, it is recommended to be re-examined by an ophthalmologist to reduce the risk of complications or secondary infection.
Prevention
In order to prevent various diseases of the superficial structures of the eye due to exposure to strong winds, the following rules apply:
- annual examination by an ophthalmologist; if a person has a chronic eye disease, it is recommended to visit him more often;
- treatment of viral and infectious systemic diseases to the end, preventing their transition to a chronic form;
- hardening, which is carried out by visiting the pool, walking barefoot at home, drinking cold water (methods strengthen the immune system);
- wearing sunglasses when exposed to strong winds to prevent the penetration of foreign substances into the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- preventive use of moisturizing drops to prevent dryness and clean the surface of foreign objects.
Preventive measures cannot completely eliminate the possibility of exposure to negative environmental factors. But they help strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of developing the disease.
If a person’s eyes are blown out, an inflammatory reaction immediately develops. This is a protective function of the body against the influence of negative environmental factors.
To prevent complications, it is recommended to consult a doctor. If a foreign object gets into the eye, it will remove it.
For therapy, an integrated approach is used to prevent damage to the external structures of the eye.
Was the article helpful?
Source: https://proglazki.ru/bolezni/produlo-glaz/
Inflammation of the eyes in a child
The child's body is characterized by reduced immune reactivity, which is due to the instability of the endocrine system. For this reason, children more often suffer from eye diseases, especially dacryocystitis and conjunctivitis. The first type of disease is especially common in newborns and is characterized by inflammation of the lacrimal sac. The main signs of the development of eye inflammation in children will be:
- lacrimation;
- redness;
- burning and itching;
- swelling of the conjunctiva;
- photophobia;
- painful mobility.
If a child has a cold in the eye, first of all, you should consult a pediatrician. He will be able to accurately determine the etiology of the disease and irritating factors that will have to be eliminated. To treat inflammatory processes in the conjunctiva in children under one year of age, preparations based on herbs are used. They eliminate swelling and inflammation, reducing the activity of viral and bacterial flora in the mucosa.
Causes
Among the reasons that provoke the development of bacterial microflora are:
- Staying a child under an air conditioner with a cold air flow;
- Going outside with poorly dried or wet hair;
- Draft or the baby staying under an open window or balcony;
- Frequent intake of cold foods such as ice cream, popsicles, cold drinks;
- Driving with the windows open or looking out of the window of a moving car.
For a child with a weakened immune system, simply walking outside in windy weather can cause inflammation of the eye organ. Eye colds do not always manifest themselves against the background of viral or infectious flora. It is important to determine the cause of the disease and direct recovery therapy specifically to it. When parents note that their child has a cold eye, this may be a simple lack of vitamins in a growing body.
Principles of treatment
What to do if you have a cold in your eye? The principles of drug therapy are determined by the location of inflammation and the type of pathogen:
- with inflammation of the eyelids. Abscesses and other purulent-inflammatory processes occurring in the periocular areas require oral antibiotics. For local treatment, antiseptic ointments, gels and drops are used;
- with inflammation of the cornea. Depending on the type of causative agent of the disease, foci of inflammation are eliminated with antiviral, antimicrobial, antihistamine and antifungal drugs. In the absence of positive dynamics, intramuscular or intravenous antibiotics are prescribed;
- with inflammation of the conjunctiva. Features of drug treatment depend on the type of pathogen that provoked the development of conjunctivitis. If the disease becomes chronic, ophthalmologists recommend the use of hormonal agents such as hydrocortisone.
Treatment in case of viral infection
In such a situation, it is necessary not only to relieve symptoms, but also to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. It is important to understand that in this case, the active activity of the virus is observed not only on the surface of the eyes, but throughout the body. In this regard, if you have a cold in your eye, your doctor should tell you how to treat the disease if complications arise, based on the results of bacterial culture.
If you have a viral infection, your doctor may prescribe:
- Drops whose active component is human interferon. This is a specific protein that is synthesized in the body to destroy viruses. Examples of drugs: “Ophthalmoferon”, “Okoferon”, “Aktipol”. As a rule, such drugs are prescribed if the eyes are affected by entero- or adenoviruses. In the first 3 days of treatment it is necessary to apply eye drops every 4 hours. Then the drug can be used 2-3 times a day until the clinical manifestations completely disappear.
- Ointments, the active component of which is intended to combat the herpes virus. In most cases, doctors prescribe Acyclovir. A more expensive analogue is Zovirax. According to the instructions for use, Acyclovir eye ointment can be included in the treatment regimen even for young children. Judging by medical reviews, the drug extremely rarely causes side effects. According to the instructions for use, Acyclovir eye ointment must be squeezed onto your finger. The length of the strip with the product should not exceed 1 cm. Then the drug must be placed behind the conjunctival sac.
It is important to remember that self-medication is unacceptable. The selection of drugs is carried out only on the basis of laboratory diagnostics.
Features of antibacterial therapy
If a person has a cold in the eye, the symptoms of the disease will not take long to appear. In most cases, abscesses indicate the bacterial nature of the infectious agent. To eliminate it, pharmaceutical products such as:
- "Vitabact" - eye drops with antiseptic properties. They help eliminate not only bacteria, but also fungal infections. Used to treat conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis and abscesses of the anterior part of the eye;
- "Tobradex" is a combined action antimicrobial drug that has pronounced anti-inflammatory properties. Used to treat both acute and chronic forms of diseases;
- "Albucid" - antibacterial drops that eliminate abscesses in the cornea and conjunctiva. The components of the product are active against coccal infections;
- "Maxitrol" is a drug with bacteriostatic properties that quickly eliminates infectious and inflammatory processes in the eyeball;
- "Tobrex" is an antibiotic from the aminoglycoside group, which is active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci, enterobacteria and other bacterial pathogens. Used to treat blepharitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, etc.
You can't do without a doctor!
And if the barley still jumped up? For a week, 3–5 times a day, it is necessary to instill an antibiotic prescribed by a specialist into the conjunctival sac. After instillation, apply an anti-inflammatory ointment to the inner surface of the eyelid, which should also be prescribed by your doctor. Do not disturb the sore eye with water procedures, so as not to accidentally squeeze out the stye. After about a week, when the stye opens, remove the pus with a sterile cotton swab, and then treat the wound with an antiseptic (brilliant, alcohol solution). There is no need to apply a bandage or cover the wound with a bactericidal plaster.
Article on the topic
Stye on the eye: why does it “jump up” and how to treat it?
Is your health not improving? Don't put off visiting your doctor. Particular attention should be paid to pain in the depths of the eye, increased temperature, and severe swelling of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes.
If barley pops up one after another, be sure to see an endocrinologist and take blood tests for sugar. Frequently appearing styes may indicate the development of diabetes mellitus. Persistent relapses can also signal a decrease in the body's defenses. In this case, you cannot do without consulting an immunologist.
Treatment of optic neuritis
How to cure a cold eye? Neuritis is characterized by very severe pain, which is provoked by the destruction of the protective sheath of the optic nerve. To eliminate the disease, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, analgesic and anticonvulsant drugs are used:
- Naproxen is a drug based on pionic acid, which has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. A strong lipoxygenase inhibitor that helps inhibit platelet aggregation;
- Nimesulide is a non-steroidal drug with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Inhibits cyclooxygenase, which prevents the synthesis of prostaglandins, which are mediators of edema and tissue inflammation;
- Carbamazepine is an inhibitory and antidepressant drug that has a pronounced anticonvulsant effect. Reduces the frequency of spontaneous contractions of icons.