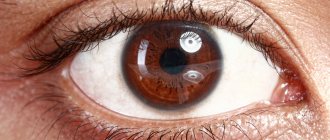
The central part of the retina (macula, or macula) is represented by nerve fibers and a thin layer of cells that are sensitive to light and color (the concentration zone of cone photoreceptors, which form central vision). Thanks to the presence of cones, a person sees during the day and distinguishes colors. Because the cells of the macula contain yellow pigment, it is also called the “yellow spot.” Patients suffering from diabetes mellitus and other general diseases develop macular edema. It leads to a decrease in visual acuity or loss of vision, including complete blindness.
Fig. 1 Retina of a healthy eye and macular edema against the background of diabetic retinopathy
Causes
Retinal edema can be caused by a wide variety of reasons, including:
- Angiopathy. As a result of untreated diabetic angiopathy, a disturbance in the blood supply to the retina occurs, which leads to edema. The pathological process can involve the entire retina or be localized only in the macular area responsible for color vision.
- Trauma. With traumatic damage to the eyeball or with traumatic brain injury, venous congestion occurs in the vessels of the retina.
- Damage to the vitreous body. With changes in the vitreous, which include traction and episcleral membranes, retinal edema develops.
- Surgery. During invasive operations, blood flow through the vessels of the retina is disrupted, which often results in cell swelling.
- Inflammation of the eye. The cause of retinal edema is often uveitis, which develops due to inflammation of the choroid.
- Vein thrombosis. If blood flow through the retinal veins stops, blood stagnation and swelling occur.
Retinal angiopathy - treatment with drops
Angiopathy is a pathology of retinal vessels caused by various negative factors (hypertension, diabetes mellitus). In order to eliminate its manifestations, an ophthalmologist in the early stages of the disease or as part of complex therapy prescribes certain eye drops to patients.
The goal of such therapy is to activate the metabolic processes of the organ of vision, stimulate the speed of local blood flow, and improve the process of tissue nutrition. Eye drops are becoming one of the components of therapy for symptomatic treatment. Eye drops are becoming one of the components of therapy for symptomatic treatment. Read below what medications are prescribed.
Eye drops are convenient, but not very effective.
Taufon
The main component of the solution is taurine. Apply the solution 1-2 drops in each eye three times a day for a long time. The drug is produced in bottles of 5 and 10 ml.
Indications for use of Taufon:
- Moderate retinal angiopathy.
- Corneal injuries.
- Early stage cataract.
- Dystrophic changes in the retina and cornea.
- Open angle glaucoma.
Expected effect:
- Stabilization of cell membranes.
- Acceleration of the regeneration process of traumatic corneal injuries.
- Activation of metabolic and energy processes.
- Normalization of IOP.
Emoxipin
This is a synthetically produced antioxidant, a solution of which is instilled daily, three times a day, 1-2 drops in each eye. Treatment lasts several days or for a long time - as prescribed by a doctor. The drug is not prescribed to pregnant women, as well as to persons with allergies to the components of the solution.
Indications for use:
- Diabetic retinal angiopathy.
- Cerebral circulation disorders.
- Various origins of hemorrhage in the eye.
- Corneal burns.
- Complicated myopathy and glaucoma.
Expected effect:
- Resorption of small hemorrhages on the retina.
- Protects the mesh shell from bright light.
- Strengthening the walls of blood vessels, reducing their permeability.
- Stimulation of local blood flow.
Emoxipine and Taufon (taurine) are the most popular eye drops for retinal diseases
Quinax*
Expected effect:
- Stimulation of metabolic processes in tissues.
- Activation of antioxidants.
- Increased lens transparency.
*At the moment, the drug is no longer available.
Aisotin
Able to increase and restore visual acuity in case of eye diseases. Available in 10 ml bottles. It is instilled three times a day, 1-2 drops, for 2-3 months.
Indications for use:
- Diabetic angiopathy.
- Restoring visual function after eye surgery.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Eye burns.
- Redness of the eyes.
- Glaucoma.
It is better to discuss the use of any medications with your attending ophthalmologist.
Emoxy optic
Substitute for Emoxipine at a lower cost.
- Indications for use:
- Eye burn.
- Bleeding in the eye.
- Progressive myopia.
- Inflammatory processes of the organ of vision.
Expected effect:
- Normalization of the permeability of vascular walls.
- Stimulation of local blood circulation.
- Resorption of hemorrhages in the eye.
- Elimination of the effects of oxidative stress.
- Increasing tissue resistance to hypoxia.
Diagnostics
Often, retinal edema is asymptomatic or accompanied by nonspecific manifestations. However, pathological changes in the fundus progress steadily and become irreversible.
This is why it is very important to undergo regular examinations with an ophthalmologist. This is especially true for people suffering from diabetes, hypertension, dystrophic changes in the fundus and other ophthalmological pathologies. This group of patients should visit an ophthalmologist twice a year for preventive purposes, other people - once a year.
During a visit to the ophthalmologist, an examination of the fundus of the eye is performed, and, if necessary, other diagnostic measures, including optical coherence tomography. Based on the results of the examination, the optimal treatment method can be determined.
Clinical picture of the manifestation of pathology
Swelling of the retina of the organs of vision is often not accompanied by obvious signs. Excess moisture in the fundus of the eye is detected during a visit to the ophthalmologist's office for a routine examination. Patients have the following complaints:
- Image blur;
- Manifestations of a veil before the eyes;
- Photosensitivity of the eye;
- Impaired perception of colors;
- Distortion of the shape of objects.
| Patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension should be regularly examined by an ophthalmologist, since complications can cause complete loss of vision. |
Conservative therapy
As a medicinal treatment, instillation of various eye drops, tablets, and injection solutions are used to help eliminate cell swelling and improve blood flow through the vessels. Some drugs also have an antioxidant effect, that is, they protect cells from the negative effects of free radicals and reactive oxygen molecules. It is necessary that the drugs used for edema have an anti-inflammatory, neurotrophic and absorbable effect.
If the therapy does not have the desired effect, then glucocorticosteroid treatment is performed, in which hormones are injected into the vitreous area. These hormone analogues, which are secreted by adrenal cells, have a pronounced anti-edematous effect.
How is diabetic retinopathy diagnosed?
Patients with diabetes should visit an ophthalmologist much more often than healthy people, since the risk of developing retinopathy is very high. At the same time, identifying ophthalmopathology is quite simple, based on the patient’s complaints alone. But you will still have to undergo a thorough examination to determine the nature of the damage to the eye structures. The patient is prescribed:
- perimetry;
- tonometry;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the eyeballs;
- OCT.
Other diagnostic methods may also be used. Treatment of diabetic retinopathy is carried out by an ophthalmologist, but since diabetes mellitus is part of the group of endocrine diseases, the patient is also examined by an endocrinologist.
Surgery
Depending on the cause of retinal swelling, your doctor may prescribe the following types of surgeries:
- If the swelling is associated with traction and episcleral membranes, then it is necessary to perform a vitrectomy, in which the vitreous substance is removed. As a result of the operation, the retina is freed from the influence of pathological formations, and blood flow through its vessels is restored.
- For severe diabetic retinopathy, which has led to retinal swelling, laser coagulation is performed. In this case, using a laser device, the microsurgeon creates point adhesions between the retina and the underlying tissues. As a result of the operation, the retina becomes stronger and its trophism improves.
It should be noted that effective treatment for retinal edema largely depends on the correct diagnosis of the disease and the qualifications of the ophthalmologist.
How does diabetic retinopathy affect vision?
The retina is a very thin and sensitive layer of the eyeball. At the same time, it performs the most important functions in ensuring vision. Light rays are collected on it after they are refracted in the cornea and lens. Next, information about what is visible enters the cerebral cortex via the optic nerve. Any damage to the retina affects the quality of vision. With diabetes, visual functions begin to suffer only after a few years, when retinopathy enters the second or third stage. The following symptoms are observed:
- “floaters” in the eyes - floating opacities that are especially noticeable against a light background;
- blurred image, diplopia;
- curvature of straight lines, incorrect perception of the shape and size of objects, their colors, that is, metamorphopsia;
- the appearance of “lightning” in the eyes;
- scotomas, or blind spots in the field of vision.
Some of these signs may indicate retinal detachment, which causes visual impairment to worsen even more rapidly. Let's look at how retinopathy in diabetes is diagnosed and treated.
Preventive measures
The development of retinal edema can be prevented by following the following preventive measures:
- control blood sugar levels;
- monitor blood pressure readings;
- eat right, eat more fruits and vegetables;
- get rid of bad habits;
- avoid excessive visual strain;
- avoid eye injuries;
- avoid severe stress and physical overload.
To avoid the appearance of a pathological process that provokes rapid deterioration of vision, it is necessary to regularly visit an ophthalmologist for preventive purposes.
Author of the article: Kvasha Anastasia Pavlovna, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
Causes of retinal detachment
The most common cause directly leading to detachment is a retinal tear. As long as the shell is intact and sealed, it remains motionless. If a gap appears on it, its edges begin to lag further and further behind the choroid. The more extensive the process, the more severe the consequences for the patient, and the more difficult it is for the doctor to restore the patient’s vision.
Among the main causes of the disease are:
- Congenital or acquired myopia (myopia): 40-50% of all cases.
With myopia, the size of the eye changes: this leads to tension in the tissues of the eye and, as a result, thinning of the retina, its fragility and vulnerability. The affected retina easily bursts, which leads to detachment. - Injuries to the organ of vision: 10-20% of all cases.
- Surgical interventions (for example, cataract removal - 30-40% of all cases). It happens that retinal detachment recurs in an eye that has already been operated on for this reason.
- Oncological diseases of the eyes.
- Inflammatory diseases of the retina, degenerative processes in it.
- Hemorrhages, retinopathy, and retinal dystrophy significantly increase the risk of detachment.
- Systemic diseases of the body (endocrinological, hematological, cardiological, vascular).
The risk of the disease increases with intense sports (especially if it is associated with impacts, jumping), as well as pregnancy and childbirth - due to strong tension in pushing. If one eye has already had an episode of retinal detachment, the likelihood of a recurrence in the other increases by 15%. Heredity also influences the possibility of developing the disease.
Treatment of retinopathy with folk remedies
It’s worth noting right away that you can’t put decoctions and infusions of herbs into your eyes. If there is a need for medicinal solutions, the doctor will write a prescription and prescribe the dosage. But at the same time, you can use other folk remedies, which, if they do not help, will not cause harm:
- Nettle. It appears in almost all folk recipes dedicated to the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Soups, decoctions, juices, and salads are made from this plant.
- Aloe. An infusion is prepared from it, which is subsequently taken one spoon 3 times a day.
- Pollen. Traditional medicine specialists suggest eating it, but only in the absence of allergies.
- Calendula. An infusion of it is taken three times a day.
There are other means. They are often recommended to be instilled into the eyes or made using rinsing decoctions, lotions or compresses. But this cannot be done. Moreover, it is useless because diabetic retinopathy affects the internal structures of the eye.
Treatment with folk remedies must be approved by an ophthalmologist. Moreover, it should not replace primary therapy. Diabetics are 25 times more likely to go blind than other people. Taking risks and self-medicating is extremely dangerous. Diabetes mellitus is a complex disease, but if you take a responsible approach to your health, follow all the doctor’s recommendations, adhere to a diet, quit smoking and alcoholic beverages, then you can live a full life even with such a serious pathology.
Types of retinal dystrophy
The disease can have benign (peripheral chorioretinal retinal dystrophies) and low-quality (peripheral vitreochorioretinal retinal dystrophies) variants of the course.
If the disease is benign, laser treatment is not required because the risk is negligible. In order to prevent the disease from passing into a low-quality form in peripheral chorioretinal retinal dystrophies, patients are prescribed outpatient monitoring.
Peripheral vitreochorioretinal dystrophy of the retina is dangerous due to ruptures of thin areas and retinal detachments, so in this case laser coagulation of the affected areas is performed - a quick and effective laser operation to relieve the disease.
Symptoms of retinal detachment
The main symptoms indicating retinal detachment are:
- the appearance of a veil, flies, floating spots before the eyes. The veil is not eliminated when using eye drops; “foreign objects” cannot be removed;
- blurred vision, decreased sharpness;
- “curtain” effect: peripheral vision suddenly disappears, as if part of the field is covered with a gray curtain. The situation improves in the morning: it seems to the patient that the area hidden behind the “curtain” has become smaller. By evening, the viewing area decreases again;
- flashes in the form of lightning or sparks;
- distortion of the objects in question.