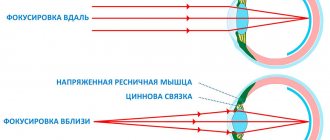
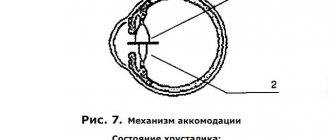
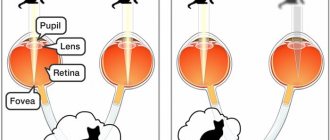
Accommodation is the ability of the eye to rearrange the optical system of the eye so that we can clearly see objects at different distances.
For example: in order to clearly see an object close up, and a second ago you were looking into the distance, many changes must occur in the human eye, which should affect the shape of the lens, so that the image again falls on the retina and we can read or see something. Without these changes, we will have trouble seeing distant or near objects. The mechanism of accommodation is a complex physiological process, the operation of which depends on many factors.
Accommodation is a physiological mechanism that can be compared to switching the low and high beams on a car, but it is much more complex because the human eyes have a complex focusing mechanism and work with hundreds of modes in a very short period of time.
Accommodation mechanism
How does eye accommodation work? When the ciliary muscle contracts, the pupil narrows, the depth of the anterior chamber decreases, and the lens moves slightly anteriorly and downward. At the same time, the tension of the ligaments of Zinn weakens, the radius of curvature of the anterior and posterior surfaces of the lens decreases. This leads to an increase in refractive power and an increase in the dynamic refraction of the eye, which contributes to clear vision at close and medium distances. But when the ciliary muscle relaxes, the curvature of the surface of the anterior and posterior surfaces of the lens increases, and we can see distant objects. All this mechanism is controlled by our autonomic nervous system.
Violation of eye accommodation
- Spasm of accommodation is an acute pathological excessive tone of accommodation, causing a change in the existing refraction of the eye towards myopia (negative refraction) and reducing the maximum corrected (corrected) visual acuity.
- Habitually excessive tension of accommodation (HATS) is a long-term accommodative tone that causes myopization of the existing refraction and does not reduce the maximum corrected visual acuity. This condition is increasingly common among teenagers who are not limited in their communication with a computer, telephone, smartphone, or tablet.
- Paresis or paralysis of accommodation is an acute disorder of accommodation, in which a change in the optical system of the eye to any distance, due to a change in refraction, becomes temporarily impossible.
- Weakness of accommodation is a long-term state of insufficient or unstable accommodation.
- Accommodative asthenopia is a condition of a disorder of the visual system in which the performance of visual work becomes difficult or impossible due to a violation of the refractive and accommodation system.
- Presbyopia is a weakening of accommodation, which physiologically occurs after 40 years.
- Violation of accommodation after refractive surgery. Most often this is a decrease in near vision, rapid fatigue, difficulty in focusing and moving the gaze to a close distance.
What contributes to the disturbance of accommodation?
- Long-term work on a computer, tablet, phone, smartphone, TV.
- Doing homework in the evening.
- Poor workplace lighting.
- Computer games.
- Incorrect seating position at a workstation at home or school.
- Weakness of the neck and back muscles.
- Neglect of sports, exercise, physical education.
- Lack of proper daily routine.
- Abuse of any work at close range.
- Insufficient physical activity.
- Presence of somatic concomitant diseases.
Any work at close range involves constant tension of the accommodative apparatus. In children and young people, a disorder of the accommodative apparatus leads to false myopia. Violation of accommodation in children can aggravate existing visual disorders: myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism and amblyopia.
Violation of eye accommodation, symptoms
- Rapid fatigue when working close.
- The appearance of unpleasant sensations, burning, stinging, redness of the eyes, sometimes watery eyes or, on the contrary, a feeling of dryness.
- The image up close becomes less clear, ripples, pulsates, when you move your gaze into the distance, the image blurs, double vision may appear, and you cannot focus your vision on distant objects.
- Frequent headaches.
- Children get tired faster in school, which contributes to a decline in academic performance.
What could be the reasons?
The picture clearly shows the mechanism of accommodation of the eye in accordance with the distance of the object focused by the eye.
Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs against the background of excessive psycho-emotional stress. The relationship between the occurrence of pathology and metabolic disorders and diabetes mellitus of any type is also noted.
Since this disease is very rare, medical scientists are constantly studying its triggering factors. As a result of this work, the main causes of accommodation paralysis were established. These include:
- Diseases of infectious etiology: botulism, diphtheria, syphilis, influenza.
- Frequent exposure to cycloplegics and mydriatics.
- Traumatic injury to the ciliary muscle.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Eye contusion.
- Brain pathologies: neoplasms, cysts, abscess, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Damage to the ciliary nerves during surgical treatment with a laser.
These causes cause constantly developing paralysis. A temporary paralytic phenomenon can occur against the background of severe alcohol intoxication.
Diagnostics of the accommodative apparatus
Violation of eye accommodation, symptoms
- Violation of accommodation of any kind can only be detected by an ophthalmologist. Very often, accommodation disorders are detected during the selection of spectacle correction and on the basis of the patient’s characteristic complaints.
- Remember, in childhood, disorders of the accommodative apparatus lead to the development of myopia.
- An objective examination consists of: visometry, refractometry, examination of the optical media of the eyes, examination of the fundus, measurement of IOP, determination of the nature of vision, determination of convergence, volume and reserves of accommodation, fusion reserves of both eyes.
Treatment of accommodation
After a thorough diagnosis, ophthalmologists at our clinic “OPTIKA-RADUGA” prescribe the optimal course of treatment, which may consist of several stages:
- Individually selected course (10 – 15 sessions) of hardware procedures: Magnetotherapy;
- Laser stimulation;
- Paraorbital massage;
- Color therapy;
- Classes on the Visotronic 3M ophthalmic simulator.
- In childhood and adolescence, we recommend special spectacle lenses “Perefocal” and “Anlauf”, progressive and, in some cases, bifocal lenses;
Prevention methods
To date, preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of paralysis of accommodation have not been developed. But as preventive measures, ophthalmologists recommend:
- Avoid uncontrolled use of ophthalmic drops.
- Minimize eye and head injury.
- Reduce eye strain by limiting your work with the computer and small print.
- Be examined by an ophthalmologist after suffering from infectious diseases.
The best preventive measure is an annual preventive consultation with an ophthalmologist.
Palsy of accommodation requires timely diagnosis and adequate treatment. To identify the disease at an early stage, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist.
An experienced ophthalmologist will tell you about the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of accommodation spasm in the video:
Prices for diagnostic services and consultation with an ophthalmologist
| Type of medical service | Service price in rubles |
| Complete ophthalmological examination | 1000 |
| Complete ophthalmological examination of children | 1100 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye disease in an adult | 500 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye diseases in children over 3 years of age | 700 |
| Selection of simple glasses with a prescription | 500 |
| Selection of progressive, office glasses with prescription | 700 |
| Selection of contact lenses with training and prescription | 1000 |
| Selection of contact lenses without training | 600 |
| Training in the use of contact lenses | 400 |
Treatment methods
Hardware treatment of eyes in children
Treatment with ophthalmological devices makes it possible to achieve a lasting therapeutic effect in young patients. In some cases, it is possible to completely get rid of pathologies such as amblyopia, impaired binocular vision, and false myopia.
Perifocal
The lenses have a corrective effect for myopia. Perifocal models are aimed at correcting central and peripheral vision, which provides excellent visibility and a pronounced therapeutic effect.
Ophthalmological device "Rucheek": accommodation training
The device is a system in which light emitters are located at different distances from the patient’s eyes. Training is carried out by adjusting the image position and the speed of changing “pictures”.
Ophthalmological device "Cascade"
Impact on the visual function of the eyes with light and color stimuli that dynamically move over a certain distance in a closed tube. Particularly effective for accommodation disorders and restoration of binocular vision.
Ophthalmological treatment device "Visotronic M3"
The ophthalmic myotrainer relaxer has a complex effect on the organ of vision and oculomotor muscles. Particularly effective for eye accommodation disorders, as well as during myopia, hypermetropia and computer syndrome.
This is interesting
Blue light and optical coatings that reduce its transmission
Do I need to correct my vision and why is it so important?
What diseases can be diagnosed based on the condition of the eyes?
Preserving vision and eye health with Crizal Eyezen lenses
Which spectacle lenses should I choose? Choose your glasses with Crizal Corner
Preventive measures
In order to prevent paralysis of accommodation, it is necessary to follow some recommendations. First of all, it is necessary to have proper lighting for prolonged visual loads. If a table lamp is used, it should be placed on the left; for left-handers it should be on the right. There must be general lighting.
Maintain proper body position. As a rule, when reading, the distance between books should be about forty centimeters. The laptop must be placed so that it is slightly lower than eye level. Watching TV should be at a distance of about five meters. If you read while lying down, this primarily develops myopia.
If a person works for a long time, then he needs to take frequent breaks and rest for about five minutes. Regular physical exercise not only strengthens the body, but also eyesight. It is important that children play sports as they need to lead an active lifestyle. Massage procedures, swimming, and regular walks in the fresh air give positive results.
Proper nutrition is a must. The diet should contain vitamins and minerals. Eat spinach, cabbage, carrots, dried fruits. Be sure to eat fresh fruits and vegetables. If you follow all the recommendations, you can prevent paralysis of accommodation.
As soon as there is a suspicion of the development of pathology, you must immediately visit a doctor. If accommodative paralysis occurs, serious complications can occur. It is best to start treatment in a timely manner. The specialist will conduct a comprehensive examination and prescribe treatment. You should not self-diagnose, as this can lead to irreversible consequences. At the first manifestation of symptoms, you should consult a doctor. It is also important to follow preventive measures to prevent further development of the pathology.
Symptoms
The main symptom of the pathological condition is paralysis of the ciliary muscle. It cannot function properly by changing the curvature of the lens. As a result, the following symptoms appear:
- a person is not able to clearly see objects located at close range;
- nearsighted people cope with the disease more easily than farsighted people (they don’t feel the process of vision deterioration so acutely);
- in patients with hypermetropia, visual perception near and far deteriorates;
- the pupil is enlarged.
As the condition worsens, patients complain of cephalgia, tension, asthenopia at the end of the working day, difficulty reading, and blurred vision. These symptoms indicate that the lens loses its elasticity, and you have to strain your eyesight to perform your usual tasks.
Cycloplegia is especially acute in office workers who, due to their professional activities, are forced to spend a long time in front of a computer screen.
Forecast
The prognosis is favorable if treatment is provided in a timely manner. Cycloplegia can be a harbinger of a serious disease, not necessarily of the visual system.
It may indicate pathologies of the spinal cord, endocrine system, or brain diseases. In each case, the prognosis is determined individually. It depends on the general condition of the patient, the course of the pathology and the speed at which it progresses.
The prognosis depends on the speed of establishing the correct diagnosis, determining the cause, and timely treatment of paralysis of accommodation.
Recommendations
- Watson, Neil W.; Breedlove, S. Mark (2012). The Mind Machine: Foundations of Brain and Behavior
. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates. p. 171. ISBN 978-0-87893-933-6. OCLC 843073456. - Kaufman, Paul L.; Levine, Leonard A.; Alm, Albert (2011). Adler physiology of the eye
. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 508. ISBN 978-0-323-05714-1 - via Google Books. - Bhatnagar, Subhash Chandra (2002). Neuroscience for the Study of Communication Disorders
. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. pp. 185–6. ISBN 978-0-7817-2346-6 - via Google Books. - ^ a b c d e
Dragoy, Valentin.
"Chapter 7: The Ocular Motor System." Neuroscience Online: An Electronic Textbook for Neuroscience
. Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy, University of Texas Medical School at Houston. Archived from the original on November 2, 2012. Retrieved October 24, 2012. - Garg, Ashok; Alio, Jorge L., ed. (2010). "Neuroanatomical basis of accommodation and vergence." Strabismus surgery
. Surgical methods in ophthalmology. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Pub. paragraph 16. ISBN 978-93-80704-24-1. OCLC 754740941. - ^ a b c d
Khurana, AK (September 2008).
"Asthenopia, anomalies of accommodation and convergence." Theory and practice of optics and refraction
(2nd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 98–99. ISBN 978-81-312-1132-8.