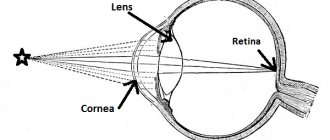
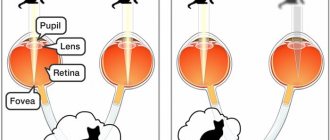
Human vision in some nuances (viewing angle, light sensitivity, etc.) differs from the vision of animals. However, for all higher beings on Earth it is built according to the binocular principle: two eyes are the most economical way of stereoscopic, three-dimensional perception of the surrounding three-dimensional space. Only in some mollusks and insects, in particular arachnids, evolution decided not to save money and went along the path of multi-eyedness.
However, minimalism has a downside: having only two eyes, you can no longer say - they say, the eye is larger, the eye is smaller... And if for some reason one eye is not able to transmit a sufficiently clear image to the visual zone of the cerebral cortex, it is suitable when merging with the second signal, for constructing a stereoscopic image, is that the central nervous system perceives such an eye as a distorting interference and, for protective purposes, begins to ignore it, gradually “disconnecting” it from the sensory-analytical process. In such an unemployed organ of vision, amblyopia develops, or “lazy eye” syndrome (literal translation from Greek) - degradation of visual functions as a result of lack of load. Vision, to some extent, retains sharpness - it is determined by the refractive status of the healthy, used eye - but becomes monocular, flat.
One of the main problems is that developing amblyopia is usually difficult or impossible to diagnose on your own. Sometimes it is detected by chance by the patient himself, sometimes it is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist during a routine examination or at an appointment for other reasons. At the same time, the key factor in therapy is early diagnosis and possibly earlier treatment, before amblyopic changes become irreversible.
What is amblyopia
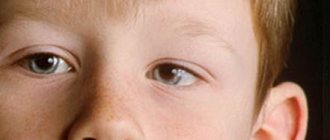
Amblyopia is often called lazy eye syndrome. This is a condition in which one eye is completely or almost not involved in the visual process. As a rule, amblyopia develops in children when the flow of information from one eye is sharply reduced or the pictures from different eyes are too different. It becomes difficult for the brain to perceive such contrast, and it blocks the image from the affected eye.
One of the most severe complications of amblyopia is the loss of binocular vision (merging images from different eyes into one picture). Without it, it is difficult for a person to analyze the volume of objects and distances; the world loses depth and three-dimensionality.
Due to the fact that a functional imbalance develops, the neurons of the visual cortex of the brain atrophy. If this happens during the period of development of the visual analyzer (up to 12 years), in the future it will be almost impossible to restore normal vision.
The eye that sees better becomes the leading one. The work of the second is suppressed due to insufficient participation in the visual process. Over time, the eye ceases to see, the muscles atrophy and it deviates to the side, and strabismus develops.
At risk are prematurely born children (especially with severe prematurity), patients with mental retardation or a burdened perinatal history. Vision control should be carried out for people who have a family history of amblyopia or strabismus. Lazy eye syndrome can be a sign of Kaufman and Benche syndromes, ophthalmoplegia (paralysis of the eye muscles).
Gamma program, Rainbow kit: treatment of binocular vision disorders
The simulators are designed to conduct training exercises in order to restore binocular vision, as well as to consolidate the correct eye position achieved during conservative treatment or as a result of operations to eliminate strabismus. The work is based on the separation of images into visual branches using glasses with red-blue filters. Their design allows you to choose the eye (right or left) looking through the red filter, and also to wear them over the patient's own glasses. The Gamma program is a computer synoptophore with centering and merging exercises, complemented by dynamic animation, patterns and statistics of results.
The Rainbow kit is similar to a bivisiotrainer : we observe the object with the “blue” eye, and the result of drawing with the “red” eye. The presence of common objects (for the right and left eyes) ensures fusion (fusion) of the visual fields. The patient draws with a felt-tip pen on a laminated album sheet, which can then be reused by washing off the drawing.
Classification of amblyopia in adults and children
Based on the time of occurrence, primary and secondary pathologies are distinguished. Congenital cases of amblyopia are considered primary.
Forms of secondary amblyopia:
- Strabismatic (dysbinocular). This form of amblyopia is caused by prolonged inactivity of one eye, resulting in a disorder of binocular vision. Dysbinocular pathology can be central (fixation occurs in the central region of the retina) and non-central (fixation area is located outside the center of the retina). This is the most common form of amblyopia, occurring in 75% of patients.
- Obscuration (deprivation). This form develops due to clouding of the optical media of the eye (lens, cornea). The obscuration form of amblyopia is diagnosed if, even after eliminating the opacities, vision is not restored. It is also necessary to take into account structural changes in the posterior parts of the eye.
- Refractive. The form differs in that it accompanies any refractive pathology. Refractive errors occur when a blurred image is projected onto the retina for a long time.
- Anisometropic. Amblyopia develops due to unequal refraction of the eyes (the size of the image on the retina of different eyes is different). With anisometropic amblyopia, the visual system cannot form a single visual image.
- Hysterical. This form is rare and occurs against the background of severe distress. Depending on the strength of the affect, vision loss can be complete or partial.
- Mixed. Due to several reasons at once.
Despite this division, the mechanism of development of amblyopia is always due to deprivation of formal vision or pathology of binocular connections, which impairs central vision. Amblyopia can be weak (0.4-0.8), as well as moderate (0.2-0.3), high (0.05-0.1) and very high (below 0.04). Pathology can be unilateral or bilateral.
Treatment and methods of correction
The disease has one specific feature, namely the disappearance of all symptoms when one eye is closed. This is explained by the characteristic of anisometropia, since the main cause of the pathology is different eye diopter readings.
Treatment
The most common form is the congenital form, which can be detected already during a medical examination of the child a year. But often low-grade anisometropia is ignored by doctors and patients due to the lack of complaints, until they appear in adulthood.
Congenital develops during the first few months of life. It affects both eyes and is expressed through chaotic horizontal movements. It appears when a child is born with a visual impairment.
Nystagmus is a common condition. It is characterized by uncontrolled oscillatory movements of the eyeballs. The pathology is often accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system or inner ear.
Causes of different forms of amblyopia
Different types of amblyopia can be caused by multiple factors. Dysbinocular pathology is a consequence of concomitant strabismus, when the affected eye “falls out” of the visual process. In strabismus, amblyopia affects the squinting eye. The severity of this condition is due to the fact that strabismus causes amblyopia, and the progression of the syndrome aggravates strabismus.
Dysbinocular amblyopia can also be a complication of nystagmus. This pathology disrupts binocular vision and provokes constant inhibition of the functions of central vision of the eyes. To avoid double vision, the brain begins to suppress the image coming from the diseased eye. The conduction of impulses from the retina to the visual cortex gradually stops.
One of the causes of lazy eye syndrome is inhibition of perception in the cerebral cortex. This is possible if there is a significant difference in the refraction of light in the optical systems of different eyes. Amblyopia is often combined with a high degree of myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism.
Deprivation (obscuration) amblyopia develops when there is insufficient light supply to the retina. This occurs when the optical media are clouded due to cataracts, in the presence of corneal cataracts and gross defects of the vitreous body. The light is also blocked in cases of retinopathy in prematurity and ptosis of the upper eyelid.
Anisometropic amblyopia is a complication of uncorrected anisometropia. This pathology occurs with a high degree of myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism. In this case, the syndrome develops in an eye with severe refractive error.
Refractive amblyopia is diagnosed in patients who neglect the correction of myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism. The syndrome develops if the refractive difference between the eyes is 0.5 diopters for farsightedness, 1.5 diopters for astigmatism and 2 diopters for myopia.
Hysterical amblyopia
The influence of psychogenic stimuli cannot be excluded. Hysterical amblyopia can be a consequence of severe hysteria. Such blindness is called psychogenic, when visual acuity suddenly decreases. Hysterical amblyopia is characterized by bilateral impairment and concentric narrowing of the visual fields.
Other disorders of the visual analyzer often appear; color perception may change, photophobia may develop, etc. Hysterical amblyopia occurs when exposed to unfavorable psychogenic factors during hysteria and psychosis.
By medication
Poor treatment results are associated with ignoring recommendations for wearing glasses, the child’s reluctance or fear of visiting a doctor. As a result, time is missed when the optic nerve is not yet formed and can be easily corrected.
Causes of hysterical amblyopia
In the case of diagnosing obscurational amblyopia, surgical removal of the cataract and correction of ptosis is performed. For dysbinocular amblyopia, strabismus correction is necessary, which is also performed surgically.
Amblyopia is a weakening of vision of a secondary nature. It is characteristic of all types of such visual pathology that in adulthood, deterioration in the quality of vision persists after removal of the main problem that caused amblyopia. The diagnosis of amblyopia in medical records may be indicated by a code. There is an International Classification of Diseases (ICD), according to which this or that disease is designated. Currently, the tenth classification is used - MBK-10. According to this classification, amblyopia due to anopsia (visual field defect) is designated by code H53.0
Symptoms of amblyopia in adults and children
Different forms of amblyopia may present in different ways. At the initial stage of development, the disease may be asymptomatic. If a child has strabismus and nystagmus, the visual system should be additionally checked for the presence of amblyopia.
As a rule, the visual analyzer is fully formed by the age of 9-11 years. In young children, the visual system adapts to disturbances by suppressing the image that comes from the diseased eye. And since children cannot understand that they are seeing incorrectly, they do not complain about poor vision.
Pathology can be identified only by the lack of stable gaze fixation and impaired orientation in unfamiliar rooms. Also, while reading, you may notice that the affected eye deviates to the side or closes.
Signs of amblyopia in older children:
- decreased visual acuity that cannot be corrected;
- impaired orientation in unfamiliar places;
- closing one eye when reading and focusing;
- deviation of the affected eye to the side;
- tilting the head when focusing the gaze;
- defects in color perception and dark adaptation.
Adult patients with amblyopia note a sharp decrease in vision, usually after severe emotional shock. The impairment is predominantly bilateral, affecting central and peripheral vision. The deterioration may persist for hours, days, or even months.
The diagnosis is made only after excluding all organic pathologies that can impair vision. Without treatment, the patient develops a persistent and often incurable disorder. Spontaneous improvements are not typical for amblyopia, only for hysterical cases. Visual impairment due to lazy eye syndrome can range from mild to complete blindness.
Current issues
Ë
È
Why is hardware treatment also recommended after surgery?
Surgery for strabismus is primarily a cosmetic remedy, since in itself it rarely restores binocular vision (when the brain combines two images received by the eyes into one). Each eye of a person with normal vision receives slightly different images (you can verify this by closing first one eye and then the other), which the brain combines into one. This does not happen with strabismus. In order for a person to see one picture and not two, surgery alone is not enough. The brain is not used to this kind of work. Therefore, to restore binocular (3D) vision, special exercises are necessary for a long time. At Excimer clinics, complex vision stimulation and hardware treatment help solve this problem.
Ë
È
Can strabismus develop from fright or from a blow?
In the practice of doctors, there are cases where strabismus appears due to fear or injury. There are also cases of strabismus due to influenza and childhood infectious diseases - measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria and others
Ë
È
If a child’s strabismus is not permanent, should it be treated?
Even then, treatment is necessary. Modern complex therapeutic treatment should begin with a comprehensive diagnosis of the visual system to establish the type of strabismus and identify its causes. Most likely, early optical correction (glasses, soft contact lenses) will be required; increasing visual acuity in both eyes (prevention of amblyopia); orthoptic and diploptic treatment (development of binocular vision); consolidation of achieved monocular and binocular functions.
| Ask a Question | All questions |
Sign up for an excimer clinic and learn more about your health!
You can call by phone
Or click the button and fill out the application form and receive a 5% discount on a full vision diagnostic
Make an appointment
Our address: Moscow, st. Marksistskaya, 3, building 1
"Excimer" on the map of the "Excimer" Clinic in other cities
Diagnosis of amblyopia
Lazy eye syndrome can only be identified after a comprehensive ophthalmological examination. The initial examination makes it possible to assess the condition of the eyelids and palpebral fissure, analyze the position of the eyeball and the reaction of the pupils to light stimulation.
The following tests allow you to fully assess the state of the visual system:
- visometry (determining visual acuity);
- perimetry (study of visual fields);
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye);
- biomicroscopy (analysis of elements of the anterior segment of the eye);
- color test;
- determination of light refraction features;
- fundus examination using a Goldmann lens;
- Ultrasound of the eye (prescribed for opacity of the eyeball media).
It is very important to determine the angle of strabismus using the Hirschberg method and using synaptophore. To exclude refractive error and anisometropia, refractometry and skiascopy are used.
Additional diagnostic measures are tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure) and electroretinography. Additional consultation with a neurologist may be required.
Organizing a trip for an eye examination abroad
For more than 15 years, the tour operator “Treatment Abroad” has been making advanced medical technologies available to Russian-speaking patients. A distinctive feature of the company is its medical approach: the staff consists of certified doctors who speak foreign languages and are in constant contact with foreign clinics. This allows specialists to have a good understanding of the available treatment methods and conduct correspondence consultations with foreign professors, individually selecting the best options for the patient. If you want to get an expert opinion on the possibilities of treating your disease abroad, contact us by phone (toll-free line) or in any other convenient way. The initial consultation with a doctor and analysis of medical documents are carried out free of charge and in compliance with medical confidentiality.
Treatment regimen for amblyopia in children
The main treatment for amblyopia is occlusion - gluing the healthy eye or attaching a plastic occluder to the spectacle frame. Patients often have to wear patches for years to achieve a positive effect. Visual acuity can be improved by stimulating the retina with light and vibration.
Only an individual and comprehensive treatment program can eliminate lazy eye syndrome. It is recommended to start therapy before 6-7 years of age, since patients older than 11-12 rarely experience positive results.
The success of amblyopia correction will depend on treating the cause of the syndrome. In the obscuration form of the pathology, surgical removal of the cataract and correction of ptosis are required. If amblyopia is caused by hemophthalmos, resorption therapy or vitrectomy should be performed.
Refractive and anisometropic forms of pathology can be eliminated using conservative methods. The first step is to prescribe vision correction (glasses and contacts, laser correction for anisometropia).
Spectacle correction must be permanent. It is important to systematically monitor visual acuity and visit a doctor every 2-3 months. Children under one year of age are most often prescribed lenses, since at this age patients cannot wear glasses correctly.
Pleoptic therapy
After three weeks, pleoptic therapy should begin, which allows you to restore the functionality of the diseased eye by suppressing vision in the healthy one. It is possible to use active and passive pleoptics methods.
Passive pleoptics involves taping the healthy eye to make the sick eye work. Active pleoptics methods involve occlusion of the healthy eye with additional stimulation of the retina of the diseased eye. Stimulation is carried out using light and electrical impulses, as well as special programs.
For amblyopia, training on Amblyocor is often prescribed. Hardware methods for correcting the syndrome are common (light-color stimulation, laser, vibration, electrical and electromagnetic stimulation, reflex stimulation and computer methods). To obtain results, pleoptics courses must be repeated 3-4 times a year.
In children under four years of age, penilization is effective. This is a method of targeted suppression of vision in the active eye through overcorrection or instillation of a special solution. Visual acuity in the dominant eye decreases, causing activation of the amblyopic eye.
Lazy eye syndrome can in some cases be cured with physical therapy. Methods such as vibration massage, reflexology, and electrophoresis are effective.
After pleotic therapy, you can begin to restore binocular vision. At this stage, orthoptic treatment is resorted to. Orthoptics is permissible only with visual acuity of at least 0.4 diopters in children over four years of age. Often, orthoptic exercises are performed using a special device - a synoptophore. Looking through its eyepieces, the patient sees separate parts of the image that he needs to connect.
Treatment for amblyopia is considered successful if it achieves equal visual acuity in both eyes. In the hysterical form of the syndrome, sedatives and consultations with a psychotherapist are prescribed.
Brook: accommodation training for refractive error
With progressive myopia, hypermetropia and presbyopia, computer fatigue, it is traditionally recommended to repeat exercises to tense and relax the eyes. For example, consider a stimulus at the near (PP) and far (PR) points of accommodation. However, the expected result will not be achieved if you simply look away from the monitor (60 cm) into the distance: the training range is only 1.7 diopters. Eye training using a mark on the window glass is also ineffective: a child (and an adult) is easily distracted, and there is no way to control the progress of the training. The effectiveness of “mark on glass” exercises increases if:
- objects are presented one by one; at the same time, an automatic switching of attention from the extinguished object to a new one, which has turned on, is ensured.
- the training range is greater than the initial volume of accommodation;
- observation objects are located not only at the edges of the range, but also at intermediate points to ensure a smooth transition “near-far”;
- over the entire range of distances, the size of the stimulus corresponds to the selected visual acuity (the closer the object, the smaller it is); this is important because objects that are too large will not “turn on” accommodation.
The listed functions are implemented in the TAK-6 (“Rucheyok”) device. Eight objects at different distances are illuminated alternately, providing an accommodation range of up to 7 diopters. In this case, objects (images of optotypes observed through the lens of the device) are actually located between the near zone (up to 15 cm) and infinity (optotype at the focus of the lens). The angular size of switchable optotypes (letters and figures) corresponds to visual acuity V=0.1; 0.2 or 0.4 (smaller ones are not used due to the dynamic nature of the observation). When choosing one of 8 sessions, the duration and algorithm of the training process are set (continuously, with skipping 2-3 intermediate objects, with pauses). The duration of presentation of the object also changes (the object “runs” faster or slower), and the outermost objects of the range glow longer. It is possible to select a color (red or green); There is a vision control table located at the further (PR) point. Working with the table (covered at the beginning and end of the session) is part of the general training process and helps to increase the patient’s motivation.
"Rucheyok" is available in two main modifications: TAK-6.2 and 6.3. The TAK-6.2 version is lightweight (2.2 kg) and compact, convenient for home use. The TAK-6.3 model has a set of 8 interchangeable lenses, which allows you not to use the patient’s own spectacle correction in the refractive range of +2 ... - 6 diopters. The ease of changing lenses is especially convenient for different refractions for the right and left eyes. The screen (in the PR zone) with switchable point light sources is designed for oculomotor exercises (perimetric muscle training ): left-right, up-down, in a circle (in 2 directions). The angular diameter of the training circle is 60°. The choice of session provides either accommodation training, oculomotor exercises or complex training (control, accommodation training, muscle training, control).
Successful treatment of amblyopia in adults
Currently, the method of penalization of the active eye is widely used in the treatment of amblyopia. In this way, it is possible to force the visual cortex to process images that come from the diseased eye. However, penalization does not always guarantee recovery, since it does not take into account binocular visual impairment.
Occlusion therapy is ineffective after the critical period of amblyopia (after 9-12 years). The fact is that the adult brain is not able to adapt to external influences due to insufficient plasticity. Despite this, occlusion is still prescribed to adult patients, since a lack of plasticity does not indicate its absence. In many cases, occlusion therapy helps relieve symptoms.
Recent studies show that antisuppressive therapy in adults can significantly improve visual acuity in amblyopia. Some patients even regained binocular vision. This treatment consists of intensive training of binocular perception (use of virtual reality glasses, tablets with prismatic film).
It can be concluded that the visual cortex of the adult patient's brain can improve visual perception, although to a lesser extent than when treating children. Therefore, more intense training is recommended for adults. The only problem is the need to spend a lot of time on treatment. Often adult patients do not want or cannot devote time and energy to exercise.
Treatment of amblyopia at home
Home therapy for lazy eye syndrome involves performing special exercises. You need to do gymnastics together with your child; it is very important to control the correctness of execution and regularity.
Exercises for amblyopia
- Place the child by the window and close the good eye. You need to bring a sheet of printed text to the sore eye. You need to stop when the child can no longer distinguish the inscriptions, and begin to move it away until the child sees what is printed again.
- Glue a black circle of paper with a diameter of 6-8 mm onto a 60-70 watt light bulb. The child should close his good eye and look at the lamp for 30 seconds. After this, you need to look at the white sheet attached to the wall and look until the image of a circle appears on it.
- On a table lamp with a 100-watt bulb, you need to put on a cap made of black paper with a pronounced hole of 5 mm. Cover the hole with red film, sit the child at a distance of 40 cm and ask to look at the red dot for 3 minutes. An adult should turn the lamp off and on every 2-3 seconds. You should also dim the lighting in the room.
- Sit your child upright and ask him to place his hands on his knees. Without blinking, look straight, left and down. The exercise is performed until tears appear. It is allowed to repeat actions no more than once a day.
Improvement can only be achieved with regular exercise for 3 months. There are also simpler exercises. The child may look at the tip of the nose or bridge of the nose and roll his eyes.
Home treatments for amblyopia
- Eat berries (blueberries, black and red currants).
- Soak 50-70 g of medicinal rosemary in a liter of wine. Leave in a dark place for two days, then strain thoroughly. You need to drink the tincture one tablespoon before meals.
- Boil a tablespoon of parsley in a glass of water (2-3 minutes). Drink chilled twice a day.
- For half a liter of water, take a teaspoon of catnip, eyebright, lemon balm, valerian root, blackberry, walnut greens and sweet clover. Cook for 10 minutes, drink ½ glass before meals.
- For two glasses of water, take a teaspoon of eyebright and a tablespoon of hernia. Leave for 2 hours, drink before each meal.
- Drink the juice of young nettles, blueberries and black currants.
- Add homemade currant wine to your diet.
- Instead of tea, drink an infusion of blue cornflower flowers.
- Mix ginseng root powder (4 parts), horsetail (5), carrot roots (10). Take one gram three times a day before meals.
Patients with amblyopia must limit the use of their healthy eye for four months or more. If you have lazy eye syndrome, you can train your eyesight through drawing and embroidery; creating mosaics will be useful.
Additional exercises for amblyopia for adults and children
- assembling puzzles;
- wood carving;
- modeling from clay and plasticine;
- coloring large pictures with transition to images with small details;
- drawing pictures through transparent paper;
- bead weaving;
- cutting and folding patterns;
- embroidery;
- games of checkers, chess, dominoes and cards;
- active ball games, table tennis;
- reading (transition from large text to small text);
- computer games;
- dosed TV watching.
As visual acuity increases in the amblyopic eye, the complexity of the activity must be increased. The greater the visual stress, the sooner the amblyopia will subside. However, you need to adjust the lighting and properly arrange the workplace.
If a child over 6 years of age has serious central vision impairment, comprehensive treatment should not be neglected. Only ophthalmological procedures in specialized rooms will help cure a child.
Prevention and prognosis for amblyopia
The prognosis for lazy eye syndrome will depend on the causes of the pathology and the time of its onset. If amblyopia is corrected early, full recovery can be achieved. The best results are observed in patients who were treated before the age of seven. In adults, amblyopia provokes a persistent and often irreversible decrease in visual acuity.
Prevention of amblyopia involves regular examination of children from birth. If the patient has opacities of the eye, nystagmus, strabismus or ptosis, the defects must be urgently corrected.
A lasting effect is observed only with full treatment and completion of the full course of pleoptic and orthoptic therapy. It is important to follow the ophthalmologist's instructions, wear glasses and tape.
If a child is diagnosed with amblyopia, you need to prepare for long and difficult treatment. You cannot neglect the help of specialists and limit yourself to home therapy. Only through the joint efforts of doctors, parents and the little patient can the defect be overcome and normal vision restored.
Sources used:
- Amblyopia Goncharova S.A., Panteleev G.V., Tyrlovaya E.I. Lugansk, 2006
- Skoromets A. A. Topical diagnosis of diseases of the nervous system: A guide for doctors. — 1st ed. - L.: Medicine, 1989
- D. Hubel. Eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- Volgograd State Medical University
Sets of optotype tables for monitoring visual acuity
A special feature of the tables is the possibility of their use for various observation distances (1, 3, 4 and 5 m), and for near (0.3 m), and for the monitor (0.6 m). The sets are combined into an album (letters, figures, rings, sign E and texts; folded 32x31 cm) or a book (letters, figures for 3 and 4 m, texts; 16x28 cm).
*) Reg. certificate No. FSR 2009/05442, 08/14/2009; Cert. resp. No. ROSS RU.IM32.N00581, 07/29/2015; Decl. resp. No. ROSS RU.IM32.D00682, 07/29/2015; RF Patents No. 2172614, 2172624. Developer and manufacturer NPL Medoptika LLC, Moscow, (916) 059-3591,