Prednisolone drops are an eye suspension with anti-inflammatory and antiallergic properties from the group of glucocorticosteroids. It is mainly prescribed by ophthalmologists for the treatment of scleritis, keratitis and uveitis and similar eye diseases, and is included in the therapeutic regimen after operations on the organ of vision. Can be used as an adjuvant in the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis and to eliminate long-term irritations of the visual organ.
Prednisolone drops are an eye suspension with anti-inflammatory and antiallergic properties from the group of glucocorticosteroids.
Pharmacological properties of Prednisolone drops
Ophthalmic drops have a more pronounced antiallergic effect than the similar drug Hydrocortisone. Within 15-20 minutes after application, the area of inflammation decreases by stopping the release of exudate and reducing the permeability of cell membranes. Additional properties - eliminates itching and redness.
Pharmacodynamics
The immunosuppressive effect of Prednisolone has not been fully described. It is indicated that after administration the number of monocytes, T-lymphocytes and acidophilic granulocytes decreases, which inhibits the formation of immunological complexes. Long-term use reduces the production of androgens and corticosteroids by the adrenal cortex, enhances protein catabolism, and stimulates the production of enzymes that participate in the metabolic process of amino acids.
Using a solution in the form of eye drops helps quickly eliminate eye inflammation by reducing capillary permeability. Itching and irritation disappear, redness of the eyelids disappears. The production of histamine is blocked, the manifestation of autoimmune reactions is reduced. The drug can be used at all stages of the disease.
Using a solution in the form of eye drops helps quickly eliminate eye inflammation by reducing capillary permeability.
Pharmacokinetics
The action develops 5-15 minutes after application. The effect lasts from 12 to 36 hours. The drug substance is metabolized in the liver, the half-life is on average 3 hours. It is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Composition and release form
The main active ingredient of the drug is prednisolone (in Latin - Prednisolone). Also, each dosage form has its own auxiliary components.
Today there are 4 forms of release of the drug. These include:
- Tablet form. The concentration of the active substance is 1 or 5 mg, and the auxiliary components are lactose monohydrate, talc, corn and potato starch, octadecanoic acid and colloidal silicon dioxide.
- Ampoules. The injection solution contains 30 mg/ml prednisolone. The composition also includes distilled water, sodium metabisulfite, caustic soda, niacin amide and disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid as additional elements.
- Eye drops. 5 or 10 mg of active ingredient.
- Ointment. In addition to 0.05 mg of the active substance, the external form of release includes glycerin, emulsifiers Cremofor A25 and A6, octadecanoic acid, as well as preservatives E216 and E218.
Tablets are sold in quantities of 20, 30, 50 and 60 pieces in cardboard packages and polymer jars, as well as 100 pieces in polypropylene bottles. Injection solutions are produced in ampoules; one cardboard package contains 3, 5 or 10 dark glass ampoules. Ointment - in aluminum tubes of 10, 15 and 20 g, and eye drops 0.5% - in bottles of 10 ml.
It is necessary to store drugs of any release form out of the reach of children, protected from direct sunlight at a temperature of 18 to 25 degrees. The shelf life of eye drops and ointments is 3 years. After opening the bottle or tube, the drug must be used within a month.
The injection solution can be stored for 2 years, and after opening at low temperature - for 24 hours. The tablets have a shelf life of 5 years from the date of manufacture.
Indications for use
Prednisolone is a broad-spectrum drug. It is prescribed for the treatment of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, dermatological diseases of various etiologies, to eliminate keloid scars, for allergies, no matter what caused them, autoimmune reactions, against the background of acute inflammatory processes.
In ophthalmology the medicine is used:
- with keratitis - inflammation of the cornea that occurs without damaging the integrity of the epithelium;
- for allergic blepharoconjunctivitis - for a chronic course;
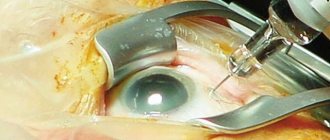
- after injuries and operations of the organ of vision or irritation of the eyeball;
- for diseases of the anterior ocular region - scleritis, uveitis, episcleritis.
Drops are introduced into the therapeutic regimen for the treatment of seasonal hay fever or the development of acute allergic reactions, if they cannot be relieved by other methods.
For hemorrhoids
When treating this pathology, tampons with drops are not used, but ointment is used. Application quickly relieves the symptoms of the inflammatory process: itching, irritation, swelling. The intensity of exudation decreases, the wound stops getting wet. Regeneration of the mucous membrane and skin is accelerated.
Pharmacological properties
The drug belongs to hormonal drugs (weakly active glucocorticosteroids of the 1st group). Prednisolone, being a more active dehydrogenated analogue of hydrocortisone or cortisol, inhibits the enzyme phospholipase A2, which accelerates the synthesis of prostaglandins e1 and e2.
The result of this is a significant decrease in the concentration of the main inflammatory mediators (PGs e1 and e2), which leads to a decrease in pain and the severity of inflammatory reactions.
In this case, prednisolone interacts with the cytoplasmic receptors of the body, which leads to the formation of inducing synthesis of vital proteins and enzymes. The anti-inflammatory effect is also achieved by inhibiting the functions of neopterin, inflammatory cytokines (including interferon-beta, interferon-gamma, interleukin-1) and strengthening the molecular structure of proteins and lipids.
The extensive biochemical effect of the drug is also aimed at suppressing the immune system, which leads to a decrease in the number of cells responsible for the inflammatory process (tissue macrophages, lymphocytes, leukocytes).
This immunosuppressive effect occurs due to the specific effect of prednisolone on cellular and other structures, in particular, the occurrence of involution of lymphoreticular tissue, inhibition of the proliferation of beta and T lymphocytes, as well as a decrease in the formation of antibodies.
The effects include the following:
- Increased reabsorption of sodium and water ions in the distal convoluted tubules of the kidneys, which often leads to swelling.
- Increased protein catabolism in the body (decomposition).
- Inducing protein production in the liver.
- Inhibition of bone tissue synthesis, as well as suppression of the production of follicle-stimulating and thyroid-stimulating hormone.
- Increased serum glucose concentration.
- Reduced production of adrenocorticotropic hormone during long-term drug therapy with Prednisolone.
- Reduced absorption of potassium in the intestines, as well as its accelerated removal from the body.
- Redistribution of adipose tissue and fiber, which can contribute to its deposition in the upper body and facial area.
- Increased excitability of the brain.
- Reducing the threshold for convulsive readiness, as well as the risk of convulsive reactions with relatively weak stimuli.
Many of these effects are the basis for the occurrence of negative reactions. If you properly follow the instructions for use of the medicine, as well as if you follow medical recommendations, possible harm from using the drug will be minimized.
One of the advantages of Prednisolone is the speed of its action: the use of the drug is important both in complex therapy and in case of critical situations (to prevent the development of massive edema, relieve spasms of the respiratory tract, etc.).
In addition to relieving inflammatory symptoms and reducing swelling, the drug may have some other effects. These include:
- Relief of shock. Prednisolone restores the sensitivity of adrenergic receptors to vasoconstriction (narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels), to basic catecholamines and an increase in their concentration. In total, this leads to an increase in blood pressure and activation of liver enzymes involved in the metabolism of endobiotics.
- Suppression of tissue proliferation and cell reproduction to prevent the formation of scar thickenings and the appearance of tumors.
- Disappearance or reduction of itching, especially in allergic or inflammatory processes.
- Rapid antihistamine effect, stopping the development of spasms, allergic swelling, rashes.
- Elimination of excessive vascular permeability, which has an anti-exudative effect.
Relief of the allergic reaction occurs due to the reduction of basophilic leukocytes by the active substance and suppression of the release of inflammatory mediators from circulating lgE mast cells. Excessive doses of the drug can stimulate the production of pepsin and hydrochloric acid, leading to the development of peptic ulcers.
Prednisolone has good absorption: after administration, it is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in plasma can be recorded in the range from 60 to 90 minutes. In some cases it could appear after 2 hours. In this case, the onset of the maximum biological effect occurs 4-8 hours after administration.
Eating food can slow down C-max by 1-2 hours, but does not have a strong effect on the therapeutic properties of the drug. The binding rates of prednisolone to transcortin (corticosteroid-binding globulin) are about 90−95%. This percentage also includes binding to plasma albumin. Only 5−10% of the substance remains biologically active.
The main metabolic processes occur in the liver with the formation of prednisone, an active metabolite. About 25% of the substance is excreted unchanged by the kidneys along with urine, 20% is eliminated during the elimination process.
The average half-life from the body is 120−240 minutes. Taking medications that induce hepatic isoenzymes reduces the elimination time. The biological half-life is approximately 18-36 hours.
Application and dosage of Prednisolone drops
When stopping inflammatory processes, the medicine is administered using a dispenser pipette 2 to 4 times a day, 1-2 drops. For traumatic injuries, the frequency of use is 1 time per day. The standard dosage is indicated in the instructions; correction of the therapeutic regimen is carried out based on the clinical picture.
With a pronounced immunological response, additional administration of Prednisolone solution intramuscularly, intravenously or orally in tablet form may be required. To relieve swelling in allergic rhinitis in children, the suspension is dripped into the nose.
To relieve swelling in allergic rhinitis in children, the suspension is dripped into the nose.
Instructions for use of Prednisolone
Regardless of the dosage form of the drug, it is necessary, if possible, to undergo therapy with the lowest dosages and with a minimum course duration. This is due to both the likelihood of side effects and the possible withdrawal syndrome that may occur after using the medicine for 5 days.
The instructions for use of tablets recommend taking the medicine mainly in the morning, since it is at this time of day that the drug has the most pronounced therapeutic effect. The tablets should be taken with warm water without chewing.
The dosage in different cases may look like this:
- During the first days of therapy for acute and severe pathologies, the patient is advised to take 10-15 tablets daily (the final concentration of the substance is from 50 to 75 mg), with a gradual reduction in the dose.
- Chronic diseases require a lower dosage - from 4 to 6 tablets per day (20-30 mg).
- Normalization of the condition implies the smallest daily dose of 2-3 tablets (10-15 mg), after which it is advisable for the patient to switch to lighter drugs.
According to the instructions for use, ointment should be applied to the painful area of the skin (the amount depends on the area of the affected area) daily 1-3 times a day.
The lubricated area should not be covered with a compress or bandage, as this can allow a large amount of the substance to enter the body, which can lead to negative reactions. The duration of the course should not exceed 14 days.
Eye drops are used 3 times a day and discontinued as soon as possible (at the first improvements). At one time, one drop of the product is instilled into the conjunctival sac: to do this, you need to pull the eyelid down with your finger. Acute conditions can increase the number of instillations up to 5-7 times with an interval of two hours.
Injections with Prednisolone solution should be carried out in a medical facility with the help of qualified specialists. The instructions for the use of Prednisolone in ampoules state that in acute conditions it is necessary to administer the drug in a jet (by piercing a vein). After the patient feels better, he is transferred to a drip.
Just like with tablets, injection procedures are carried out in the morning. The dosage can range from 30 to 1200 mg, depending on the pathology. For joint injections, the dose ranges from 10 to 50 mg, with the amount of drug affected by the size of the affected bone or joint.
Contraindications to the use of Prednisolone drops
In ophthalmological practice, contraindications for use are:
- Viral diseases - dendritic keratitis, herpes rashes on the eyelids, chickenpox and measles, in which symptoms include eye lesions.
- Fungal and bacterial lesions of the organ of vision.
- Recurrent corneal erosion (epitheliopathy).
- Increased ophthalmotonus.
Contraindications include an allergic reaction to the active ingredient of the drops or additional ingredients of the composition.
Side effects
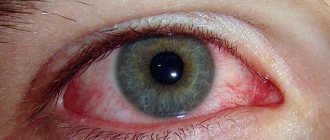
Immediately after administration of the drug, a slight burning sensation, redness, and lacrimation may occur. Such symptoms do not require discontinuation of the drug.
When used for more than 10 days, intraocular pressure may increase. Longer use can provoke the development of posterior capsular cataracts, atrophy of epithelial tissue and conjunctiva at the cellular level.
When used for more than 10 days, intraocular pressure may increase.
special instructions
The drug should not be used on its own. For a bacterial or viral infection, the medicine hides the clinical picture and makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. Combination with antibiotics is allowed.
Persons using contact lenses are advised to remove them 15-20 minutes before using eye drops and put them back on no earlier than after the same period of time. With long-term use - longer than 10-14 days - it is necessary to regularly measure intraocular pressure so as not to miss an increase.
After instillation, short-term blurred vision is possible. Therefore, persons whose professional activities require accelerated reactions should not administer the product immediately before production processes.
Persons using contact lenses are advised to remove them 15-20 minutes before using eye drops.
During pregnancy and lactation
In special situations, Prednisolone is prescribed only when the benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus or infant. Glucocorticosteroids penetrate the placental barrier and are excreted in breast milk. When prescribing a medicine, you need to inform your doctor about your condition and consult a gynecologist. If the disease cannot be eliminated without the use of hormonal drops, breastfeeding will have to be abandoned.
Use in childhood
The only contraindication for treatment is individual intolerance to the drug. When prescribing, it is necessary to consult with a pediatrician, especially when the child has a history of: diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system, renal and hepatic pathology, tuberculosis, infectious processes regardless of stage, for example, chickenpox, measles or rubella. Glucocorticosteroids should not be used during exacerbation of herpes.
Prednisolone injection solution
Intravenously (drip or stream), intramuscularly.
The intravenous drug Prednisolone Bufus is usually administered first as a stream, then as a drip.
The dose of the drug and the duration of treatment are determined by the doctor individually depending on the indications and severity of the disease.
In case of acute adrenal insufficiency, the drug is administered in an initial single dose of 90-120 mg to 180 mg, the daily dose is 300-390 mg.
For severe allergic reactions, Prednisolone Bufus is administered in a daily dose of 90-120 mg to 180 mg for 3-16 days.
For bronchial asthma, the drug Prednisolone Bufus is administered depending on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of complex treatment from 60-90 mg to 660 mg per course of treatment from 3 to 16 days; in severe cases, the dose can be increased to 1380 mg per course of treatment or more, with a gradual reduction in the dose.
For status asthmaticus, Prednisolone Bufus is administered at a dose of 510-1200 mg per day, followed by a reduction to 300 mg per day and switching to maintenance doses.
For thyrotoxic crisis, the recommended initial dose of Prednisolone Bufus is 90-120 mg; daily dose – 300 mg. If necessary, the daily dose can be increased to 900 mg. The duration of administration depends on the therapeutic effect, usually up to 6 days.
In case of shock that is resistant to standard therapy, the drug Prednisolone Bufus is usually administered as a bolus at the beginning of therapy, after which it is switched to drip administration. If blood pressure does not increase within 10-20 minutes, repeat the injection of the drug. After recovery from the shock state, drip administration is continued until blood pressure stabilizes. The initial single dose is 60-150 mg in severe cases - up to 390 mg. The drug is re-administered after 3-4 hours. The daily dose can be 300-1200 mg, followed by a dose reduction.
In case of acute hepatic-renal failure (in acute poisoning, in the postoperative and postpartum periods, etc.), the drug Prednisolone Bufus is administered at 30-90 mg per day; if indicated, the daily dose can be increased to 300-1500 mg per day or higher.
For rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, the drug Prednisolone Bufus is administered in addition to systemic administration of the drug at a dose of 60-120 mg per day for no more than 7-10 days.
For acute hepatitis, Prednisolone Bufus is administered at a dose of 60-120 mg per day for 7-10 days.
For poisoning with cauterizing liquids with burns of the digestive tract and upper respiratory tract, Prednisolone Bufus is prescribed at a dose of 60-390 mg per day for 3-18 days.
Single dose for children: children from 2 to 12 months are administered at the rate of 2-3 mg/kg body weight; from 1 to 14 years – 1-2 mg/kg intravenously or deep intramuscularly. The intravenous solution should be administered slowly (about 3 minutes). If necessary, you can repeat the administration of the drug after 20-30 minutes.
If intravenous administration is not possible, Prednisolone Bufus is administered intramuscularly in the same doses. After relief of the acute condition, prednisolone tablets are prescribed orally, followed by a gradual reduction in the dose.
With long-term use of the drug, the daily dose should be reduced gradually. Long-term therapy should not be stopped suddenly!
Drug interactions
If eye drops with corticosteroids are recommended to be used in conjunction with other medications, you must inform your doctor.
Effect of joint use:
- The effect of anticoagulants and hormonal contraceptives is enhanced.
- The therapeutic effect of blood pressure-lowering drugs and the antibiotic Rifampicin is reduced.
- It is possible to increase intraocular pressure when taking antipsychotics, antidepressants, antihistamines and anticholinergics.
- There is a risk of developing cataracts while taking Azathioprine and Carbutamide.
Glucocorticosteroids penetrate the placental barrier and are excreted in breast milk.
When used simultaneously with diuretics, disturbances in water-electrolyte balance and the development of dehydration were noted.
Reviews
Irina, 36 years old, Kirov: “I use drops every year for allergies to poplar fluff. There were no side effects."
Sergei Ivanovich, 76 years old, Tver: “We were prescribed Prednisolone for the eyes after cataract surgery. There was a slight burning sensation, but the rehabilitation went without complications.”
Alina, 22 years old, Kostroma: “I had to drip after an allergy to cosmetics. The redness of the eye disappeared after 2 days.”
Robert, 34 years old, Kazan: “After the first application, a strong burning sensation occurred and lacrimation began, which lasted 10 minutes. I had to buy an analogue.”