Lagophthalmos is an ophthalmological pathology in which a person cannot completely close his eyelids. In common parlance it is also called “rabbit eye”. In addition to the fact that the palpebral fissure always remains open, dryness and lacrimation appear. Against the background of all the changes, vision decreases, the risk of conjunctivitis, keratitis and other eye diseases increases. Treatment of lagophthalmos is the only way to avoid severe consequences. Sometimes medications and occlusive dressings are enough, but more often you still cannot do without surgery.
Characteristics of the disease
Lagophthalmos is a common ophthalmological pathology not only in adults, but also in children. It occurs with equal frequency in men and women. A person cannot close his eyelids completely. Even at night he sleeps with his eyes slightly open. As a result, the mucous membrane dries out, and there is a high probability of inflammatory diseases.
Most often lagophthalmos is paralytic. In 60% of cases it occurs as a result of facial nerve paralysis. But there are other reasons. When choosing a treatment method, it is important to understand what triggered the appearance of hare's eye. Based on this, the most effective therapy is selected.
What is lagophthalmos?
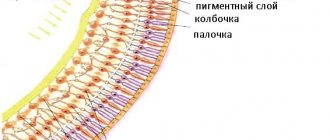
Translated from Greek - the eye of a hare. The root cause of lagophthalmos is paralysis of some facial muscles. Statistics say that impaired eyelid closure after paresis or paralysis develops in 30 patients out of every thousand. 60% of patients who sought help claim that the root cause is neuritis of the facial nerve. Determining the severity, form and type of treatment. This is done by eye clinics that have the equipment necessary to combat the disease. Men and women are equally susceptible to the disease and the pathogenesis is not affected by seasonality, climatic conditions or geographic location. Lagophthalmos affects people of all ages. Due to the high probability of a person becoming disabled, the problem has a social status. The photograph shows how the oculomotor nerves and muscles function.
The process of impaired eyelid closure develops due to an anomaly in the anatomical structure, exposure to external factors, or a disorder of innervation. The etiological factors of lagophthalmos include:
- Paresis and paralysis of the facial nerves. The most common causes are severe illness, injury or poorly performed surgery. The innervation of the orbicularis oculi muscle, which is responsible for the mobility of the eyelid, is disrupted.
- Problems with the trigeminal nerve. The reasons are the same. If the normal functioning of the V pair is disrupted, motor functions are disrupted, affecting pain, temperature and tactile sensitivity.
- Anomalies in development. Patients who have undergone symblepharon suffer from lagophthalmos. In which palpebral and orbital conjunctivitis are fused. This prevents the eye from closing normally. Therapeutic treatment cannot eliminate it. Surgical assistance will be required.
- Development of exophthalmos. The eyeball moves forward. This will not allow the eyelids to close even with normally developed facial muscles.
- Cicatricial eversion. Ectropion is caused by severe sagging of the lower eyelids. This prevents the eye from closing tightly, leaving a gap.
- Retraction of the upper eyelids. Lagophthalmos develops due to upward displacement of the skin folds of the eyelids. This exposes the sclera.
An experienced ophthalmologist determines the extent of damage and the type of disease. The quality of the chosen treatment will ensure a quick recovery. With normal functioning of the nerve endings and muscle tissue, the orbicularis muscle contracts easily, ensuring that the eyelids close tightly. Lagophthalmos is rarely a consequence of body pathology. Patients who have suffered a serious illness, injury or complex facial surgery suffer much more often from lagophthalmos. With lagophthalmos, the amplitude of blinking decreases critically. This negatively affects the distribution of tear fluid. Such changes lead to dryness of the conjunctiva, a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the eye. The lower lacrimal opening is everted due to displacement of the lower eyelid and decreased turgor. Effective treatment is possible with early identification of the causes. Special complexes of therapeutic effects are used.
Causes of lagophthalmos
There are several main factors that lead to impaired eyelid closure. These include structural anomalies, for example, congenital shortness of the eyelids, mechanical damage, for example, the entry of a foreign body, as well as a violation of innervation. In fact, lagophthalmos can be paralytic, traumatic and congenital.
Reasons for its appearance:
- paresis or paralysis of the facial nerve;
- orbital tumors;
- trigeminal nerve damage;
- congenital developmental anomalies, for example, coloboma, symblepharon;
- dysfunction of the eyelids due to injuries, blepharoplasty, scar changes;
- enophthalmos and exophthalmos;
- eversion of the eyelid (ectropion);
- mechanical injury;
- Graves' disease.
As a rule, the appearance of pathology is associated with injuries to the face or base of the skull, unsuccessful surgical or plastic surgeries, and structural anomalies. The pathology brings significant discomfort to the patient. Although physiological lagophthalmos also occurs, which does not bother a person at all. It appears for unknown reasons; all of the above pathologies in no way affect its development.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Most often, L. is caused by paralysis of the facial nerve, which innervates the orbicularis oculi muscle, with the help of the cut the eyelids close. L. is observed, as a rule, with peripheral damage to the facial nerve due to otitis media, fractures of the base of the skull and other diseases. With central damage to the facial nerve, the orbicularis muscle is usually not involved in the process. Spastic L. occurs much less frequently, caused by spasm of the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid, the edges are innervated by the oculomotor nerve, or spasm of the circular fibers of the ciliary muscle (Müller muscle), which takes part in raising the upper eyelid.
The causes of L. can also be congenital shortening of the eyelids, cicatricial eversion after burns, wounds, pronounced exophthalmos in orbital tumors and in severe forms of Graves' disease.
Clinical manifestations
The main signs of the pathology are the inability to completely close the eyelids, dryness or lacrimation. In the early stages, the conjunctiva is predominantly affected. Due to incomplete closure of the eyelids, it dries out and becomes inflamed. First of all, this is manifested by redness of the mucous membrane. In addition, there is a feeling of cutting, burning, sand in the eyes.
As the disease progresses, other symptoms of lagophthalmos appear:
- photophobia;
- clouding of the cornea - leukoma;
- deterioration of visual acuity, “fogginess”;
- painful sensations.
Over time, due to pathological changes, the sensitivity of the cornea decreases, so the symptoms of lagophthalmos weaken. However, this does not mean that your health is improving. Without treatment, the disease progresses and external manifestations worsen.
In later stages, the upper eyelid does not droop and therefore is not involved in blinking. In addition, ptosis of the lower eyelid and its lag from the eyeball occur.
When the orbicularis muscle is paralyzed, the eyelid is everted. Ultimately, the lacrimal punctum becomes displaced, causing the eyes to constantly water.
In addition to physical discomfort, patients with lagophthalmos also experience psychological discomfort. Due to the severity of external changes, some people have to wear sunglasses to hide visible defects.
Symptoms of lagophthalmos
At the first stage of development, the pathology is accompanied by incomplete closure of the palpebral fissure.
In this case, the person’s conjunctiva dries out. The following symptoms of lagophthalmos also occur:
- burning;
- severe tearing;
- conjunctival hyperemia.
As the disease progresses, the upper eyelid does not droop. As a result, the person cannot blink. Redness of the orbital conjunctiva is more pronounced in the morning, since the palpebral fissure remains open at night.
Patients complain of the appearance of a veil before their eyes. Excessive lacrimation in this pathology is complemented by photophobia. If there is loss of the corneal reflex, corneal irritation does not lead to eye closure.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the origin. When paralysis of the orbicularis muscle occurs, ectropion appears. If the lacrimal punctum is displaced, excessive tearing occurs. Signs of blepharitis appear quite early, and sluggish conjunctivitis develops.
If lagophthalmos of the eye is associated with pathology of the trigeminal nerve, the production of tear fluid is disrupted. Damage to the seventh pair of cranial nerves provokes dryness and a feeling of the presence of a foreign object. The prolonged presence of paralysis causes the development of atrophic changes, which manifest themselves as a decrease in eyelid turgor. They can move downwards or evert out.
Complications
Lagophthalmos is accompanied by drying out of the cornea, which causes complications. Against this background, chronic and even catarrhal conjunctivitis, xerophthalmia, and neurotrophic keratitis develop. As a result, more serious problems arise.
The nutrition of the cornea is disrupted, its sensitivity decreases, and it begins to become cloudy. Ulcers do not heal well, so inflammation often occurs, infiltrates and a cataract (leukoma) form. As a result, visual acuity decreases. If treatment for lagophthalmos is not started at this stage, corneal perforation occurs. Then endophthalmitis develops - purulent inflammation that affects the inner membranes of the eyeball and the vitreous body. As a result, there is a risk of enucleation. This is an operation to remove the eyeball.
All these dangerous consequences can be avoided if the pathology is detected in a timely manner and treated.
Diagnostics
To confirm or refute lagophthalmos, the ophthalmologist performs an external examination. The doctor asks the patient to close his eyes. Thanks to this, he can determine the severity of the pathology.
To exclude other eye diseases, as well as to identify possible complications, the doctor conducts an ophthalmological examination. Applies the following techniques:
- Biomicroscopy. Involves examining the structures of the eye using a slit lamp. Allows you to identify damage to the cornea and conjunctiva, symptoms of inflammatory or infectious diseases.
- Visometry. Used to measure visual acuity.
- Ultrasound. It is a universal diagnostic method in ophthalmology for identifying a wide range of eye diseases. Allows you to understand what causes the appearance of symptoms of lagophthalmos. Ultrasound is predominantly performed in B-mode, which is advanced. Thanks to it, you can get a clear image of the lens, retina, eye muscles and other structures of the eye.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT). This is the most informative diagnostic method. Thanks to it, it is possible to identify the most minor pathological changes, since it is possible to obtain an image with the maximum degree of detail.
To determine the type of lagophthalmos, the doctor examines the patient's medical history. It is important for him to know whether the onset of the pathology was preceded by injuries, paresis or inflammatory processes.
The doctor may also prescribe additional examinations, such as a CT scan or MRI of the brain. Since the causes of the pathology are varied, endocrinologists, neurologists, neuropathologists, and otolaryngologists can participate in the study.
Treatment
Treatment of lagophthalmos is related to its cause and is always aimed at eliminating it. Different causes of this disease require fundamentally different methods of therapeutic intervention.
If the cause of the disease is associated with neuritis of the nerve, then treatment for lagophthalmos that occurs should be handled by a neurologist with parallel consultation with an ophthalmologist. When treating this pathology, measures are used to disinfect the conjunctiva, moisturize it and prevent complications. For this they usually use:
- the use of instillation of solutions of furatsilin, sulfacyl sodium or “artificial tears”;
- securing the eyelid with a plaster to prevent tearing;
- applying a protective bandage;
- use of antibacterial ointments;
- protective wearing of lenses.
For dystrophic processes of the cornea, the following are used:
- application of vitamin ointments (0.5% thiamine), sterile fish oil;
- putting Vaseline or sea buckthorn oil (sterile) into the eye;
- subcutaneous injections of B vitamins (B1, B6) 1 ml daily.
Very often, surgical treatment of hare's eye syndrome is prescribed. This is necessary when:
- congenital underdevelopment of the eyelids;
- cicatricial ectropion or severe sagging eyelids.
For such complex pathologies, partial blepharorrhaphy (suturing the palpebral fissure to reduce it) is usually offered.
Surgical treatment is one of the most effective treatment measures for lagophthalmos.
The surgical procedure for lagophthalmos looks like this:
- An incision is made above the edge of the eyelid by 8 mm (to relax tense muscles), extending to the outer and inner canthuses.
- A flap of the patient's skin (graft) is first prepared, taken from certain areas of the body (scalp, behind the ear, back of the head or shoulder).
- The prepared area of skin is used to close the resulting eyelid defect. The graft is fixed with interrupted sutures and a special bandage is applied for 5-7 days.
Timely surgical treatment allows you to prevent a “bouquet” of serious eye problems with lagophthalmos.
The following surgical techniques are also used for this pathology:
- use of eyelid implants;
- surgical correction of the innervation of the orbicularis oculi muscle.
In the conservative treatment of lagophthalmos in the remission stage, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and sanatorium-resort treatment are used.
Treatment of lagophthalmos
It can be conservative or surgical. The main method of treatment, of course, is surgery. Medicines are used to moisturize and protect the cornea from inflammation and reduce the likelihood of complications.
In the drug treatment of lagophthalmos, the following groups of drugs are used:
- antiseptics, antibacterial drugs;
- moisturizing drops – artificial tear preparations;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
Medicines are chosen depending on the stage and type of disease. For example, in the treatment of lagophthalmos with a pronounced decrease in tear production, artificial tear preparations are extremely important. They prevent dryness, irritation and redness.
In addition to medications, blindfolds are used. They are designed to correct the position of the eyelids. However, this treatment method has a short-term effect. The pathology can only be cured through surgery.
The type of surgery, of course, is determined by the doctor depending on the cause and severity. To correct the position of the eyelids and narrow the palpebral fissure, the following interventions are used:
- Tarso- or blepharorrhaphy – operations to close the palpebral fissure;
- the use of special silicone threads that are passed through the eyelid;
- implantation of platinum or gold implants into the upper eyelid;
- canthoplasty – changing the shape or shape of the eyes by correcting the corners;
- recession (movement) of the muscle that raises the upper eyelid;
- injections of hyaluronic acid or botulinum toxin.
Classification of lagophthalmos
Depending on the degree of intensity of the symptoms of the disorder, the following classification of lagophthalmos is found:
- weak degree - this disorder is characterized by a slight widening of the palpebral fissure. In this case, the extreme part of the lower eyelid often droops. In the medial third, it is clear that the dermis is smoothed. The patient manages to close his eyes almost completely. At the same time, during sleep the palpebral fissure is slightly open;
- moderate degree - symptoms of pathology appear more clearly than with a weak degree. As the disorder develops, the folding of the skin decreases. To close your eyes, a person has to make a lot of effort. Closing the palpebral fissure involves the orbital fragment of the orbicularis muscle. When a person sleeps, his eyes remain open;
- high degree - the eyes do not close at all. In this case, increased dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea is observed. As a result, inflammation and dystrophy of the visual organ develop.
Prevention measures
There are no specific recommendations. It is necessary to avoid injuries and treat infectious diseases in a timely manner, not only ophthalmological, but also of the ENT organs. When working at a computer, you should use artificial tear drops, since the mucous membrane is not sufficiently moisturized.
The prognosis for lagophthalmos is favorable only if treatment is started on time. It is important to restore the functioning of the eyelids as quickly as possible. Moreover, this can only be done through surgery. But there is no need to be afraid of surgery. Because the consequences of untreated pathology are much worse.
Lagophthalmos can significantly reduce quality of life. Moreover, there is a high probability that pathology will deprive you of the most valuable thing - the ability to see the world. If you know for sure that you sleep with your eyes slightly open in your sleep, go to an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Express Your Reaction
Similar articles:
Myths do not help cure cataracts
Lack of knowledge often leads to misconceptions: this is how myths appear. In turn, for example...
Conjunctivitis
Every person has probably encountered conjunctivitis at least once in their life. Seemingly at first glance…
Cataract - the story of one operation
The editors of Health Expert received a letter from our reader: “At the age of 58, my mother developed an ear infection...
Computer syndrome: vision when working on a computer
Coronavirus has fully opened up a new reality for us - virtual. In it we can fully work...
Laser vision correction: arguments for and against
Some people see this world brightly and clearly, but for others everything around is unclear and blurry. Save your...
Myopia goes away without surgery - truth or myth?
“One hundred percent vision without glasses or contacts!” - such tempting promises beckon us from the covers...