Visual impairment is a deterioration in the clarity of vision for a specific reason. Such disorders may be associated with refractive errors and accommodation, or with any eye diseases that lead to deterioration in visual acuity.
According to statistical studies, about 4 billion people out of more than 6 billion people on Earth suffer from visual impairment. At the same time, only 1.3 billion people use vision correction devices. It is necessary to note the high importance of clear vision for humans, since through the visual analyzer we perceive up to 95% of all information about the world that surrounds us. That is why vision loss causes maladjustment in society, depression, loss of ability to work and other negative consequences.
Regarding ability to work, it is worth noting that visual impairments can serve as a contraindication to engage in a number of professions. People with poor eyesight cannot engage in martial arts, strength sports, serve in elite troops such as paratroopers or special forces, or fly airplanes.
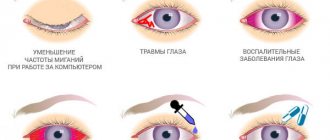
Of course, vision problems leave their mark on human psychology. Also, people who have severe visual impairments are exposed to various types of dangers due to poor vision clarity. This includes falls, street collisions, and traffic accidents.
Types of visual impairment:
- Refractive error is the loss of the eye’s ability to clearly distinguish objects that are located at a certain distance from it.
- Accommodation disturbance is a deterioration in the clarity of vision when a person examines objects at different distances from him (for example, presbyopia).
- Impaired peripheral vision is the loss of the ability to clearly see objects that are to the side of the eyes, objects in motion.
- Adaptation disorder is a disorder of visual perception due to the fact that the eyes adapt less well when the lighting changes rapidly. Thus, people with this type of visual impairment take a long time to get used to the dark, or cannot get used to it at all.
- Hemeralopia is the inability to navigate well at dusk or when a person is in a dark room (nyctalopsia - night blindness).
Help for people with visual impairments
Most often, glasses or contact lenses are used to correct vision impairment. In some cases, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Surgical vision correction
It is most often recommended for vision defects that cannot be corrected with glasses and lenses, severe visual impairment, as well as functional and organic pathologies, without eliminating which it is impossible to restore vision. Such ailments include cataracts, glaucoma, scars after eye injury and other conditions.
But in any case, a specific correction method is prescribed only after studying all the individual characteristics of the situation.
Auxiliary correction methods
We must not forget that the treatment of all diseases, including ophthalmological ones, requires complex solutions. Any doctor’s actions will be ineffective if the patient himself does not pay attention to his own health.
To improve vision characteristics, stabilize it and prevent further decrease in visual acuity, you must follow several simple rules:
- Create a daily menu that includes foods containing vitamins A, E, B, C, zinc, selenium and lecithin, which regulate and maintain normal all functions of the optical system. If for any reason diet correction is not possible, take specialized vitamin complexes for vision, which your doctor will recommend to you.
- Make it a habit to regularly take walks in the fresh air and ventilate the rooms in which you work and sleep. Human eyes receive the bulk of oxygen directly from the air, so its quality and “freshness” are an important factor in preserving and maintaining eye health.
- Take care of your visual hygiene: choose the right lighting for your workplace, when working at a PC, take an hourly break for a 5-minute eye exercise, and to perform delicate and visually tiring work, use an electronic magnifying glass, which will make the process comfortable and prevent eye fatigue.
So, at your service are the achievements of modern medicine, the latest technological solutions and a set of simple rules - together, all this will return clarity and bright colors to the world around you.
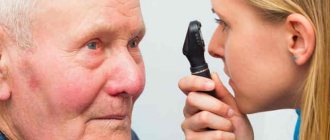
Diagnostic research methods
Diagnosis of vision defects begins with an examination of the eye and clarification of the patient’s complaints. Determining a patient's diagnosis is possible using methods such as:
Fluorescein angiography can be useful in eye examination.
- eye examination;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- autorefractometry;
- amnioscopy;
- side lighting method;
- biomicroscopy;
- echoophthalmography;
- transmitted light examination method;
- fluorescein angiography of the retina.
If you experience fatigue, pain in the eyes or worsening vision, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist, since timely diagnosis of vision defects helps to avoid the development of serious diseases and prevent blindness.
Interesting facts about myopia and farsightedness
More than half of Russian residents have some kind of visual impairment. 30% of people are nearsighted, 33% are farsighted. If you are among this number and want to know a little more about your disease, read our article. We have collected educational information about eyes and vision, myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism.
Myopia and farsightedness are the most common vision defects in the world. For example, in Russia, on average, 25-30% of people are nearsighted, and 33% are farsighted, of which 6% are children under 15 years of age.
In this article
The deterioration of vision of the nation and the world as a whole is greatly influenced by the modern rhythm of life: the development of digital technologies and highly intelligent gadgets that spoil vision. However, the same progress of modern times successfully relieves patients from myopia and farsightedness: laser correction and surgical methods for solving eye problems, optical contact lenses with excellent properties of moisture and oxygen permeability, which are able to correct vision without requiring replacement for up to a week of constant wear, have become available to almost everyone . Ophthalmology has made great progress, but some facts about myopia, farsightedness and other ailments still remain unknown to many. Let's talk about them in more detail.
Types of defects
Farsightedness
Pathology develops when the visual apparatus weakens. Mild farsightedness in young patients is not felt until the period of age-related changes in accommodation. With high and moderate severity of the disease, optical correction is necessary.
Lead to the development of a defect:
- visual fatigue;
- age-related changes;
- sclerosis of the lens.
Amblyopia is an underdevelopment of the visual system, which results in reduced picture quality. All age categories of patients are susceptible to anomalies. The development of the defect is provoked by factors that interfere with normal vision. Amblyopia is treated at an early age up to 5 years, since treatment in a later period is not effective. Therapy includes:
- individual vision correction;
- training the affected organ;
- elimination of strabismus.
Myopia
Myopia is a common disease in which the refraction of the eye is impaired, and the image is formed not on the retina, but in front of it. In ophthalmology, two types of impairment are distinguished: axial (the length of the eye increases) and refractive (the refractive power increases).
In patients diagnosed with myopia, the distance from the retina to the corneal surface is increased. Light that enters the system is focused directly in front of the retina and then scattered. A patient diagnosed with myopia sees not a clear image, but a blurry picture. To look at an object, you need to bring it closer to your eyes. To see objects in the distance, you can squint, as this position of the eye creates a smaller opening for light to pass through.
Degrees of myopia:
- up to 3 DD – weak;
- from 3 to 6 DD – average;
- from 6 DD – strong.
The development of myopia may be associated with genetic predisposition, unbalanced, poor nutrition, when the diet contains too few microelements such as chromium, copper, zinc, etc. Also at risk are patients who constantly work at the computer, loading the visual apparatus while being in low light conditions.
To prevent the development of myopia, follow these simple recommendations:
- observe lighting conditions, use high-quality table lamps;
- regularly visit an ophthalmologist and carefully follow all his instructions;
- do gymnastics;
- choose the right correction methods;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- adjust your daily diet, enrich it with vitamins and minerals.
People who work a lot behind a screen are susceptible to the disease. Gymnastics is important in preventing the development of a pathological process. Perform a set of exercises every 30 minutes of intense work.
If it was not possible to prevent the development of the disease, you need to correctly approach the issue of vision correction. For myopia, one of the methods described below is most often used.
- Implantation of phakic lenses.
Fast, efficient, reliable. The result is instant. The list of contraindications and adverse reactions is minimal. - Spectacle correction.
If you choose this technique, prepare to view the world through a “small TV” (glasses). - Use of contact lenses.
The method is not suitable for everyone. Lenses cause discomfort with dry eyes and can provoke the development of allergies and irritations. - Laser correction
. It has a large number of contraindications and a long rehabilitation period. The results do not last a lifetime.
Myopia is a serious problem of our age. You need to be able to solve it correctly and in a timely manner, because ignoring it can lead to complete loss of vision or the development of concomitant pathologies.
Interesting facts about farsightedness
- All children are born farsighted; this is a common phenomenon. Vision improves during development, and a child will be able to focus on one object with both eyes by the age of 7.
- In old age, farsightedness develops again, as the body ages and so does the visual system. In particular, the properties of the lens, retina and cornea are weakened.
- Farsightedness is the official reason not to serve in the army, but the diopter indicator must be more than 8 units, which is already a high degree.
- In 6% of children under 15 years of age, farsightedness is present; it is not treated with medication or hardware, but is corrected with the help of special exercises.
- Mild hypermetropia can be treated well with visual exercises. For this purpose, many lessons and even applications have now been created on computers and smartphones.
- Farsightedness does not only occur in humans. For example, the same visual defect is present in owls, who cannot clearly see objects close up, but see perfectly well into the distance.
Farsightedness
Farsightedness (hypermetropia) is the same as nearsightedness - a refractive error. With it, the image in the resting state of accommodation is focused incorrectly, behind the retina. Farsightedness is common among children under 3 years of age and is considered physiological. Among older children, up to 12 years old, it is also common. In addition, this vision defect is often observed in adults 18 and older. Hypermetropia is accompanied by headaches, burning eyes and increased fatigue of the visual area. This disease also develops in old age. Farsightedness can be successfully treated comprehensively, especially if it is weak or moderate. A high degree is amenable to surgical treatment.
About vision pathologies
Pathologies of the visual organs are divided into congenital and acquired during life. Congenital defects of the visual apparatus develop against the background of:
- vision problems as a result of somatic disorders in the fetus;
- genetic abnormalities;
- the appearance of retinopathy due to premature birth;
- infectious microflora in the mother during pregnancy;
- difficult birth or injury during the process;
- taking antibiotics during pregnancy;
- drinking alcohol, drugs or smoking during pregnancy.
Acquired defects of the visual apparatus arise due to the influence of external provoking factors:
- reading literature at a distance of less than 40-45 cm;
- watching TV for a long time;
- muscle strain as a result of mental activity;
- minimal lighting in the room;
- prolonged work at the computer;
- bad habits;
- incorrect position during intensive work of the visual organs;
- visual injuries;
- emotional stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- age-related changes in the retina.