Pritulo O.A., Ngema M.V., Prokhorov D.V., Smolienko V.N., Vintserskaya G.A., Ravlyuk D.A. State Institution “Crimean State Medical University named after. S.I. Georgievsky"
Demodectic mange is a chronic parasitic disease of the skin of humans and animals, widespread in all climatic zones of the globe. Its causative agents are demodicid mites, representatives of the group of Arachnids, the family Demodecidae, most adapted to the parasitic lifestyle [3,6,8,11,13,15].
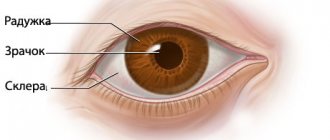
It has now been proven that the causative agents of human demodicosis are mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis, belonging to the phylum Arthropoda, the class Arachnida, and the genus Acarina. They are representatives of an independent family Demodecidae from the order Trombicliformes [1,2].
Pets also suffer from demodicosis. Infection of cats and dogs by Demodex cati (a parasite of cats) and Demodex canis (a parasite of dogs) mites causes a disease known as glandular red mites, which can be accompanied by severe inflammation of the hair follicles and sebaceous glands, hair loss, peeling, thickening of the skin, the formation of pustules, sometimes boils, generalization of the pathological process and even end in death.
According to the concept of the life pattern of species, mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis belong to permanent monoxenic skin parasites; in addition, mites are community-hospital, that is, they parasitize together on the same host [5]. In accordance with the high level of topical and trophic specificity, the causative agents of demodicosis predominantly affect the skin in the area of nasolabial folds, chin and eyelids [7,9,14].
Demodex folliculorum is most often found in the area of the nose and outer ear in 38% of cases, in the forehead in 30%, and in the perioral area in 29% [10]. As for Demodex brevis, its primary localization is the skin of the upper half of the chest and neck.
Depending on the predominance of certain symptoms, several clinical forms of demodicosis . Some researchers distinguish erythematous-squamous (or seborrheic), papular, papulovesicular, pustular, rosacea-like, combined and asymptomatic forms.
Others note low-symptomatic, erythematous-squamous, acneiform, rosaceomorphic, sycosiform, small-nodular forms, while others note erythematous, pustular, papular, and combined forms. Depending on the prevalence of the A.A. process. Antonev et al [1]. The following forms of demodicosis are distinguished: limited (with localization of rashes mainly in the folds and near the corners of the eyes), diffuse, in which the entire skin of the face is affected; common when the inflammatory process extends beyond the face.
According to the course of the disease, acute, subacute and chronic recurrent demodicosis are distinguished. According to the clinical picture, the following forms of skin demodicosis have been identified: low-symptomatic erythematous-squamous, papular, pustular, combined and cystic [4].
In addition, there are several types of arrangement of efflorescences during demodicosis :
- central type , in which the rashes are localized mainly in the T-zone (the central part of the forehead, the glabella, the back and wings of the nose, the nasolabial zone, the central part of the chin) - the zone of greatest density of the sebaceous glands;
- medial type - the rashes are located mainly in the area of the frontal tubercles, the central part of the cheeks and the area of the chin protuberance;
- asymmetrical type - rashes are found only on one side of the face; lateral type - rashes are located on the sides of the face;
- total type - rashes are distributed evenly over the entire surface of the face.
The clinical picture of human demodicosis may resemble the clinical picture of rosacea, acne vulgaris, photodermatosis, and seboroid. Often, on a congestive-hyperemic, slightly swollen, flaky background with symptoms of oily seborrhea, follicular rashes of the small-papular and small-pustular type are located. Also, some researchers note that the clinical picture of demodicosis resembles rosacea, identifying demodicosis with rosacea.
Properties
For demodicosis and acne, for face and body.
Stop Demodex® liquid soap is the first step in the fight against demodicosis. It affects the subcutaneous tick, blocking at the cellular level the inflammatory reaction provoked by the bacteria Propionopacterium acnes, and also prevents re-infection and the development of demodicosis.
It is used as a daily hygiene product to prevent activity or recurrence, and in the treatment of demodicosis and acne with the Stop Demodex® complex. Using Stop Demodex® soap in the treatment of demodicosis, gentle exfoliation of the upper layer of the epidermis occurs due to the action of surfactants of increased softness.
When using Stop Demodex® soap, acne completely disappears over time, and the condition of the skin improves significantly. Gives the skin a feeling of cleanliness, comfort and freshness.
Properties:
- has a neutral pH level;
- gently cleanses the skin;
- strong anti-inflammatory and restorative effect;
- blocks the development of bacteria;
- regulates the production of sebum, prevents changes in its composition;
- significantly reduces pores;
- relieves irritation;
- increases the protective properties of the epidermis;
- refreshes complexion;
- gives the skin softness and elasticity;
- antiseptic and disinfectant;
- antiparasitic effect;
- analgesic and healing properties;
- restores the natural level of moisture;
- antifungal effect;
- relieves itching.
Materials and research methods
At the Department of Skin and Venereal Diseases of the Crimean State Medical University. S.I. Georgievsky. We used a series of drugs “Stop Demodex”, produced in Ukraine, as an additional external therapy, which consists of a mild cleansing soap for the facial skin, shampoo, therapeutic and prophylactic balm and eyelid gel. The active components of the drugs are metronidazole and birch tar, which have pronounced acaricidal properties against Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis mites, as well as bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effects. Extracts of white willow bark and witch hazel, which are included in the preparations, help reduce sebum secretion by blocking the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. Super critical - CO2 - chamomile extract contains a high concentration of matrixin and azulene - powerful antihistamine components that almost instantly relieve redness. Vitamin A stimulates tissue regeneration and promotes rapid regression of rashes without scarring. In addition, according to a number of researchers [12], with demodicosis, immunological changes and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract are observed, which makes it advisable to prescribe Stop Demodex drops based on plant extracts. Thus, Echinacea purpurea extract is used as a powerful immunostimulant and anti-inflammatory agent. It is used as an adjuvant in the complex treatment of various skin diseases (demodex and acne). Calendula officinalis has an anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effect. Calendula preparations accelerate tissue regeneration processes and promote faster epitheliation. Common yarrow has a general strengthening, antispasmodic effect. They help with gastrointestinal diseases, especially peptic ulcers, and improve metabolism.
45 patients with demodicosis were examined . The diagnosis was confirmed by laboratory (microscopic examination). The largest number of our clinical observations were women (67%), men – 33% of patients. The distribution of the studied patients with demodicosis by age and gender is presented in Table 1 .
The distribution of all examined patients into subgroups depending on the form of the disease and the prevailing nature of the eruptive elements in the lesions of the skin was carried out according to the classification:
- The erythematous form of the disease was observed in 13 patients.
- The papular form of the disease was observed in 17 patients.
- The pustular form of the disease was observed in 8 patients.
- The combined form of the disease was observed in 7 patients.
Against the background of persistent red or bluish-red congestive erythema with an abundance of thin and wide telangiectasia, characteristic papular and pustular elements were located. More often, a grouping of papular elements into bluish-red or bluish-colored plaques was observed, on the surface of which small (1–2 mm in diameter) and large (up to 5–6 mm in diameter) pustular elements, as well as purulent and bloody-purulent crusts were detected .
We also examined all patients for the presence of specific eye damage, we took into account the data of the disease history, clinical picture and laboratory tests, the secretion of the sebaceous gland of the hair follicle of the cilia was taken from all patients, and if a mite was detected, the patients were sent for a consultation with an ophthalmologist.
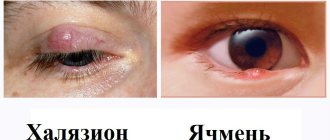
Depending on the form of eye damage in patients with demodicosis, asymptomatic carriage, erased form, blepharoconjunctivitis and episcleritis were distinguished (Table 2).
Asymptomatic carriage was observed in 8 (17%) patients, in which the diagnosis was verified by the detection of acne glands on the roots of the eyelashes and in the secretions of the sebaceous glands. Such patients did not complain, however, from the anamnesis it was possible to find out that previously they periodically noted redness of the edges of the eyelids, itching and the sensation of a foreign body in the eye.
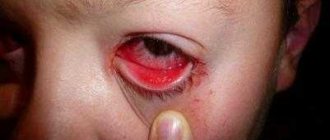
An erased form of demodicosis of the eyes was observed in 4 (9%) patients, in this case there was: severe itching of the eyelids, especially in the morning after sleep, pain in the eyes, loss of eyelashes. Biomicroscopy revealed enlarged and dark bulbs of individual eyelashes, translucent and cylindrical muffs at their roots, and sometimes small multiple papillomas, which is typical for chronic blepharitis. Demodectic blepharitis was diagnosed in 3 (7%) patients and manifested itself with more pronounced changes than erased forms of the disease. First, focal lesions appeared, localized around the eyelashes, then they spread and captured the entire edge of the eyelid. Conjunctival hyperemia was accompanied by moderate mucous discharge, accumulating on the edges of the eyelids in the form of yellowish crusts.
The duration of the disease with demodicosis ranged from 4 to 15 years. Previously, all patients were treated using general and local therapy. Stop Demodex drugs were prescribed as additional therapy.
The treatment was prescribed according to the following scheme
It was recommended to wash with Stop Demodex mild cleansing soap twice a day. A small amount of soap was applied to the skin of the face, foamed, left for 20–30 s and washed off with water.
Treatment and prophylactic balm “Stop Demodex”: applied to cleansed skin of problem areas 2 times a day for 45 days.
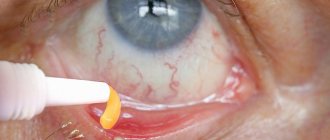
Before applying the eyelid gel, it was recommended to treat their edges with tincture of calendula or eucalyptus using a cotton pad that was soaked in the solution. The procedure was repeated after 15 minutes. In case of simultaneous damage to the ear canal, ears, eyebrows, it is also recommended to treat these areas before applying the gel.
Stop Demodex eyelid gel was applied to the eyelids as close as possible to the eyelash growth area for 30 minutes. Must be applied twice daily for 45 days. Excess gel is removed using a cotton swab.
In case of damage to the scalp, it was recommended to wash the hair with Stop Demodex shampoo 2 times a week for at least 6 weeks. Apply to damp hair for 2-3 minutes. Rinse with water.
As a general tonic, after completing the course of treatment, it was recommended to take “Stop Demodex” drops based on plant extracts as a dietary supplement to the diet for 30 days, 30 drops 2 times a day with meals.
Results and discussions
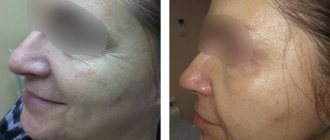
Thus, complex therapy using the “Stop Demodex” series of drugs has significantly improved the results of treatment of patients with demodicosis, especially with the papulopustular clinical form. From the start of treatment on days 6-7, there was a decrease in the inflammatory reaction of fresh elements. On day 15, the itching of the skin disappeared and the number of rashes decreased. Complete regression of the rash was observed after 4 weeks of treatment. After the end of treatment on the 10th day, the absence of mites on the skin and in the area where the ducts of the sebaceous glands are excreted, in the area of eyebrows and eyelashes was laboratory confirmed.
Recommendations for use
Recommended for use as a cleanser for the face and body for demodicosis and acne.
It is recommended to use regularly, using together with the Stop Demodex® complex.
Remember! The subcutaneous parasitic mite has its own life cycle of at least 45 days. For effective treatment it is necessary to complete a full comprehensive course of treatment. When treating demodicosis and acne, it is important to maintain hygiene, the order of procedures and a certain diet. It is also advisable to consult a dermatologist.
conclusions
Taking into account the presence of clinical and laboratory changes in various clinical forms of demodicosis, a scientifically based treatment complex with a series of drugs “Stop Demodex” has been introduced into practice. Its effectiveness can be seen both in complex treatment and in the prevention of demodicosis. There is an elimination of the very cause of the disease - the uncontrolled reproduction of the Demodex mite, as well as a strong anti-inflammatory and restorative effect - rapid elimination of the symptoms of the disease. As a result of the use of drugs in this series, after just a few days there is a significant cleansing of the skin from foci of inflammation and, subsequently, a complete regression of this dermatosis.
Literature
- Akbulatova L.H. Human demodicosis./L.Kh. Akbulatova // Bulletin of Dermatology. – 1964. – No. 3 – pp. 32 – 42.
- Akbulatova L.H. The pathogenic role of the Demodex mite and clinical forms of demodicosis in humans. /L.H. Akbulatova // Bulletin of Dermatology. – 1966. – No. 12. – P. 57–61.
- Valne M.S. Populations of iron mites in perioral dermatitis and rosacea./M.S. Valne, A.B. Lange .//All-Russian Congress of Dermatologists and Venereologists: (VI; 1989; Moscow) VI All-Union Congress of Dermatologists and Venereologists: Abstracts. report – M., 1989. – Part 2. – P. 135 – 138. 04. Kogan B.G. Morphological, biological and functional characteristics of human demodicosis mites – mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis at the current stage. /B.G. Kogan, V.I. Stepanenko//Dermatovenerology.Cosmetology. Sexopathology. – 2001. – No. 23(4) – P.70 – 75.
- Kogan B.G. Specificity of Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis mites – causative agents of human demodicosis / B.G. Kogan, V.T. Gorgol //Ukr. Journal of dermatology, venereology and cosmetology. – 2001. – No. 1. – P.37 – 41.
- Kulaga V.V., Romanenko I.M. Treatment of skin diseases. – Lugansk, 1996. – 414 p.
- Maychuk Yu.N. Parasitic eye diseases./Yu.N. Maychuk – M.: Medicine, 1988. – 288 p.
- Malakhova M.Ya. Methods for recording endogenous intoxication: A manual for doctors./M.Ya Malakhova – St. Petersburg, 1995. – 125 p.
- Malygina E.L. "Ivomek" in the external treatment of demodicosis. // Problems of achievement of biomedical sciences and practical healthcare. Proceedings of KSMU named after S.I. Georgievsky / E.L. Malygina - Simferopol: Publishing center of KSMU, 2001. - 137 T., Part 1. - P. 78 -79.
- Ponomarev B.A. The main problems of ectoparasitic infection /B.A. Ponomarev., V.P. Kulagin, G.D. Selissky.// Vestn. dermatol. – 2000. – No. 1. – P. 39 – 40.
- Potekaev N.N. Rosacea: Etiology, clinic, therapy. / N.N Potekaev - M.: Biom, 2000. - 142 p.
- Endogenous intoxication syndrome in patients with demodicosis / D.A. Slevareva, O.A. Pritulo // Problems, achievements and prospects for the development of biomedical sciences and practical healthcare: Proceedings of KSMU named after. S.I. Georgievsky. – Simferopol: Publishing Center of KSMU, 2007. – T. 143, Part V. – P. 325-327.
- Desch CE Morphology and functional anatomy of Demodex folliculorum (Simon) of man / CE Desch, WB Nutting //Acarology. - 1977. - V.19, No. 3. - P. 422.
- Erbagci Z. High incidence of demodicidosis in eyelid basal cell carcinomas. / Z. Erbagci, I. Erbagci, S. Erkilic. //Int. J. Dermatol. – 2003. – V.42. – P. 567 – 571.
- Katz AM Rosacea: epidemiology and pathogenesis/A. M.Katz.//J. Cutan. Med. Surg. – 1998. – V. 2. – P.5-10.
Composition of the balm
The main active ingredients are metrinidazole and birch tar, as well as extracts of white willow bark and hemamelis, which effectively fight acne. Thanks to these components, the skin looks healthy and inflammation is significantly reduced.
The calendula extract and panthenol included in the composition have a powerful antiseptic effect. Vitamin A (retinol) and E promotes rapid tissue healing without the appearance of scars.
Apply the balm 2 times a day. Apply directly to the affected area. Does not need to be washed off with water.
Storage conditions
The gel is stored at a temperature not exceeding 25 C.
The price of the original Stop Demodex gel is quite reasonable.
- During therapy, you must adhere to the following rules:
- use disposable napkins instead of a cloth towel;
- Regularly treat personal cosmetics with alcohol or liquid antiseptic;
- replace pillows with natural down or feathers with synthetic padding;
- refuse caring creams and decorative cosmetics;
- Check your pets for demodicosis.
Reviews confirm the high effectiveness of this drug. During treatment, you should strictly follow all the instructions of your doctor. After completing therapy, you will need to take tests to the laboratory to make sure that demodicosis is completely defeated.
Mechanism of action and composition
The active components of the balm penetrate into the deep layers of the dermis and cleanse them. The product does not dry the skin, quickly restores lipid metabolism, softens the epidermis, cleanses pores, restores the formation of subcutaneous sebum, prevents the appearance of marks, scars and scars, and also deprives the tick of its nutritional environment.
The main active ingredients are:
- calendula ether is an excellent antiseptic;
- calendula extract – a fighter against bacteria and some pathogens (staphylococcus, streptococcus), quickly heals wounds, eliminates inflammation, relieves pain, reduces pores;
- mannan is a good skin moisturizer;
- urea – retains moisture and serves as a conductor for active components.
The lotion is applied to a cotton pad, which is used to wipe the face, eyebrows, ears and eyelids.
Gel Finish Control
Created specifically to eliminate defects after acne and demodicosis - scars, spots, scars, hyperpigmentation. The mechanism of action is based on the restoration of the missing amount of oxygen, ascorbic acid and collagen.
The duration of gel treatment is 1, 1.5 months. During this time, keratinization, pigmentation is restored, and the skin texture is evened out.
The composition of the drug includes:
- vitamin C, PP, K1;
- collagen – regenerates tissue;
- hyaluronic acid;
- hydrolysis of the placenta and vitamin E - improve cellular respiration, reduce skin pigmentation, facilitate the elimination of acne, and resist subsequent clogging of the follicles.
Apply the gel to scars, scars, spots and areas with hyperpigmentation 2-3 times a day in a thin layer.
Important! If swelling appears on your face after use, wash it off with baking soda diluted with water. In summer, you need to use a cream with UV protection.
Symptoms and signs of glandular acne lesions
The disease can manifest itself with poor immunity, prolonged and severe stress, and metabolic disorders.
Also, an exacerbation of the disease is observed in the autumn, since the excessive dose of ultraviolet radiation received over the summer worsens the condition of the skin.
Manifestation of symptoms of demodicosis
- Swelling, eye fatigue.
- Burning, itching, redness. The skin of the eyelids becomes thin and peels, so in the area where eyelashes grow, you can detect hyperemia and the presence of small white scales.
- The appearance of small pustules. The acne worm parasitizes in the ducts of the sebaceous glands, as well as in the mouths of hair follicles, and the formation of blackheads with purulent contents inside is observed.
- Eyelash loss. The parasite affects the hair follicles, which adversely affects the growth of eyelashes.