The surface of the eye is always covered with a tear film. It consists of fatty, aqueous and mucous layers. During the day, they are washed away by tears during blinking, and at night they accumulate, harden and turn into crusts. Mucus in the corners of the eyes is common. But a change in its color or consistency may indicate the development of the disease.
Mucus in the eyes in the morning is a consequence of the functioning of the lacrimal glands, due to which the surface of the eyeball is moistened and cleansed of impurities. But in some cases, this phenomenon is a sign of an eye disease. Please pay attention to:
- localization of mucus and crusts;
- frequency of discharge;
- color and consistency;
- the amount of secretion released;
- presence of other symptoms: irritation, itching, etc.
Let's look at some diseases in which mucus accumulates in the corners of the eyes.
Yellow, white or green discharge
They should be colorless. If the mucus has a white, greenish or yellowish tint, you should consult an ophthalmologist. Most likely, an infection is developing. Often this symptom is accompanied by conjunctivitis. When the conjunctiva is infected with bacteria, pus is released. With viral inflammation, signs of ARVI or influenza are observed: increased body temperature, malaise, etc. Ophthalmological symptoms appear only 7-10 days after the onset of the disease.
Severe tearing
This symptom is characteristic of an allergic reaction. But any eye allergy is characterized by severe itching. Its absence with profuse lacrimation may indicate xerophthalmia. This disease is also called dry eye syndrome. It occurs due to insufficient production of tear fluid. Tearfulness occurs as a protective reaction of the body. There may also be mucus discharge.
Thick and sticky mucus
When the lacrimal sac is inflamed, that is, with dacryocystitis, the outflow of tears is disrupted. The nasolacrimal ducts become blocked. This leads to swelling, which is localized in the corner of the eye. Along with the secretion of mucus, there may be symptoms such as lacrimation, the formation of a purulent crust, and pain.
White plaque in the corners of the eyes diabetes mellitus
There are different reasons for the appearance of white discharge in the corners of the eyes. Some of them are not dangerous to health, but some conditions require mandatory consultation with a doctor. Inflammation can be infectious or non-infectious in nature. The cause is often conjunctivitis, eye fatigue, stye, sinusitis, or simply a weakened immune system. If white plaque in the corners of the eyes is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, then this is a clear sign of some disease. Timely diagnosis and treatment will help prevent the development of complications.
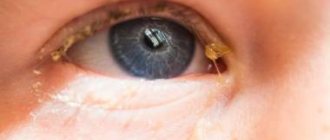
The consistency and color of discharge from the eyes varies. A more common situation is when a person wakes up in the morning with his eyelids and eyelashes glued together. This occurs due to the discharge drying out overnight. In general, eye discharge is a thick or thin substance, sometimes mixed with mucus or pus. In some cases, discharge is an indicator of some kind of infection that has entered the tear ducts. As a result, the normal secretion of large sebaceous glands is disrupted, as indicated by profuse lacrimation. The discharge may have a different color:
In the latter case, it often has a mucus-like structure, which indicates a bacterial infection. Not too thick discharge indicates an allergy. They are abundant in orbital cellulite syndrome. The condition is often accompanied by a number of other symptoms, such as:
- sore eyes;
- lacrimation;
- blurred vision;
- burning and itching of the eyelids;
- photosensitivity;
- cough, fever, nasal congestion.
Common causes of discharge are allergies, mechanical damage, irritation and diseases, both eye and other infections. The effects of chemicals and ultraviolet radiation, uncomfortable or dirty lenses, fatigue due to long work at the computer - all this leads to problems with the organs of vision. More specific causes of eye discharge are:
- Blepharitis. Causes discharge of a foamy structure, green or yellowish with the formation of scales and crusts.
- Bacterial infection. An example is conjunctivitis, in which the discharge has a thick, viscous structure, yellow-gray, brownish or greenish color.
- Cold. It develops due to the action of viruses and is accompanied by lacrimation, redness of the eyes, and tear discharge.
- Dacryocystitis. This is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac, provoked by congestion in the area of the visual organs. A clear sign is the substance leaking out of the eyes when pressed. The discharge is yellow.
- Recurrent stye. This is an inflammation of the eyelid, accompanied by swelling, redness and purulent discharge.
- Chalazion. It is an inflammation of the eyelid around the meibomian gland and eyelid cartilage. The cause is blockage of the gland's exit channel and accumulation of secretory fluid.
- Otitis, sinusitis, sinusitis. Due to these otolaryngological diseases, damage to the wall of the orbit, to which inflammation spreads, is possible.
- Diabetes. High sugar levels negatively affect the eyes. With diabetes, there is a high risk of developing blepharitis, conjunctivitis, barley, and glaucoma. These diseases are accompanied by white discharge.
- Meibomite. This is an inflammation of the meibomian glands, which are responsible for the secretion of tear secretion.
- Demodecosis. This is a disease caused by parasitism of a pathogenic mite - the acne gland. Accompanied by sticky thick mucous discharge.
- Allergies, dry eye syndrome. Accompanied by clear liquid discharge. This is a reaction to irritants: animal hair, pollen, eye fatigue syndrome.
If the discharge contains pus, then in most patients this indicates the development of some kind of infection due to damage to the body by bacteria. Such discharge is white, yellowish or even greenish in color. They are not clear and watery, as with normal allergies or eye fatigue. The discharge has a thick, sticky texture, which causes the eyes to stick together. The causes of this symptom are:
- Excessive dryness of the ocular mucosa. Accompanied by brownish or yellow discharge.
- Bacterial or viral infection. Against this background, high fever, cough, headache, and body aches are observed.
- Conjunctivitis. Accompanied by dilated blood vessels, a feeling of pain and burning in the eyes, and their fatigue. Symptoms worsen in the evening.
- Inflammation of the lacrimal sac. It is provoked by viruses, parasites, bacteria or injuries to the eyeball. With this pathology, the eyelids and conjunctiva become red and swollen.
- Trachoma. Often develops when affected by chlamydial infection. The disease causes fusion of the inner surface of the eyelid and the eyeball, scarring of the conjunctiva in the transitional folds.
- Blepharitis. Accompanied by inflammation of the ciliary edge of the eyelids, redness, increased lacrimation, burning, itching, and swelling.
White discharge in the corners of the eyes appears even more often in newborns than in adults. During the first couple of weeks, infants experience white or yellowish crusts. They do not cause discomfort and are easy to separate. This is a normal phenomenon, because the child’s body adapts to the environment. In the womb, the baby is protected from everything: ultraviolet rays, infections, bacteria. Once born, a child immediately faces all negative factors.
As a result, the newborn’s protective functions are activated, but a certain time passes before they function normally, during which white matter is observed in the corners of the eyes. If the symptom persists for a long time, then the reasons are:
- dacryocystitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- blepharitis;
- trachoma;
- keratitis;
- allergy;
- cold;
- dry eyes.
If this unpleasant symptom persists for a long time or appears periodically, then this is a clear sign of infection, and not simple allergies or fatigue. You cannot diagnose yourself. Only a specialist can do this. Self-medication, especially if diagnosed incorrectly, can only worsen the situation. In general, therapy includes the following activities:
- Use of antibiotics. Prescribed in case of eye damage from a bacterial infection. Drugs in this group are prescribed in the form of tablets, eye ointments or drops. Doctors recommend drugs such as Albucid, Ciprofloxacin, Tetracycline and Ophthalmoferon.
- Massage the eyelids and rinse the tear ducts. They are additional procedures. To wash out purulent exudate, use a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Regular tea leaves will also work.
- Taking antihistamines. Prescribed to relieve inflammation due to allergies. These include Lecrolin and Opatanol.
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs of steroidal and non-steroidal nature. They help quickly eliminate inflammation, but have many side effects. Examples are Ibuprofen and Dexamethasone.
- Instillation of drops. In this case, special means are used to relieve tension and fatigue. These include Visin, Levomycetin, Maxitrol, Normax.
- Installations with a solution of dicaine 0.5% or trimecaine 3-5%. Prescribed for meibomitis.
- Surgical intervention. Indicated if there is a foreign object in the eye. Surgery is often performed when eyelashes grow into the eyelid.
The basis is still medications in the form of tablets, ointments or drops. First of all, ophthalmologists advise removing the exudate itself from the eyelids. To do this, use a weak solution of the antiseptic Furacilin or potassium permanganate. A cotton swab is moistened in it, which is then used to wipe the eyes from the outer corner to the inner. If the discharge is very thick, it is necessary to perform a light massage of the eyelids. Among the medications used to eliminate the problem are:
- Visine. These are vasoconstrictor and decongestant drops based on tetrizoline. The substance is a sympathomimetic that stimulates alpha-adrenergic receptors. The effect of the drops lasts for 4-8 hours. They reduce redness and swelling of the conjunctiva. The advantage of the drug is that it is practically not absorbed into the systemic circulation. Visin is used for hyperemia of the conjunctiva when exposed to bright light, smoke, dust, chlorinated water and for swelling and redness due to seasonal allergies. These drops are contraindicated for angle-closure glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, age under 2 years, arterial hypertension, corneal dystrophy, pheochromocytoma. It is necessary to instill 1-2 drops 2-3 times a day. After the procedure, local reactions are possible: blurred vision, redness, burning and pain in the eyes, dilation of the pupil.
- Normax. The active ingredient of this drug, norfloxacin, is an antibiotic. The medicine is available in the form of drops and tablets. They are indicated for external and internal otitis, conjunctivitis, trachoma, keratitis, corneal ulcer, blepharitis. The dosage is determined by the disease. Contraindications include sensitivity to fluoroquinolones, pregnancy, and breastfeeding. Side effects include allergies, itching, and rash.
- Maxitrol. Contains neomycin and polymyxin, has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. Indications for use are blepharitis, keratitis, iridocyclitis, keratoconjunctivitis. It is necessary to instill 1-2 drops every 4-6 hours. Maxitrol should not be used for shingles, tuberculous or fungal eye infections, chicken pox, or the condition of the cornea after removal of a foreign body. After instillation, itching and swelling of the eyelids are possible.
- Levomycetin. Based on chloramphenicol, available in the form of drops and alcohol solution. Their action is antibacterial, so they are used for bacterial infections, including blepharitis, keratitis, scleritis, and conjunctivitis. One drop should be instilled into each conjunctival sac 3-4 times a day. Side effects and contraindications are numerous, so it is better to study them in detailed instructions.
A number of folk remedies can be used against the background of drug treatment. Their recipes involve instilling medicinal decoctions into the eyes. They are also consumed orally or used for compresses. The following recipes are effective:
- Take 3 large spoons of chamomile or calendula flowers. Steam them with 200 ml of boiling water. After cooling, strain. Soak cotton pads in the broth and apply them to the eyelids for 15 minutes. Repeat up to 5 times a day.
- Add a couple of drops of fresh St. John's wort juice to the calendula decoction prepared according to the previous recipe. Next, pour the liquid into a container, where you then immerse your face for a few seconds. You can simply wipe your eyes with the same product.
- Mix plantain leaves, sage, hop cones, string and birch buds in proportions 3:3:2:3:2. Next, brew the herb collection with 0.5 liters of boiling water and let it stand for about an hour. Take the decoction orally, 100 ml 3 times throughout the day.
- Take a couple of elderberries and brew them like regular tea. Use the cooled rinse or lotion. It eliminates itching and inflammation well.
source
Surely many have noticed a white coating that appears in the corners of the eyes in the morning. Most people do not attach any importance to it and simply wash their face, but in fact it is a symptom indicating a disorder in the body. The reasons for its appearance are very diverse, so only a specialist can make a diagnosis.
Timely detection of the disease and proper treatment guarantee a quick recovery and the elimination of complications.
The most common causes of plaque, itching and similar phenomena in the corners of the eyes: purulent infection, conjunctivitis, inflammation, eye fatigue syndrome, blepharitis, chalazions, recurrent styes, otitis media, sinusitis, sinusitis, meibomitis, demodicosis, weakened immunity.
First of all, the doctor conducts an external examination, which allows you to identify pustules and other pathological formations on the outside and inside of the eye. The patient must take a microflora test.
The doctor should also rule out the presence of chlamydial conjunctivitis, because it can also cause itching and plaque. For these purposes, a scraping is made and sent to the laboratory. To exclude the development of demodicosis, an examination of the eyelash and its bulb is carried out.
The main directions of therapy are preventing the inflammatory process and suppressing infection. The doctor may prescribe antibiotics and combine them with anti-inflammatory drugs.
If the plaque is caused by excessive stress and fatigue, special drops are used, for example, Visin, Normax, Maxitrol, Levomycetin.
In some cases, massage of the eyelids and rinsing of the tear ducts are necessary.
If white plaque appears due to meibomite, install a solution of dicaine (0.5%) or trimecaine (3-5%) into the conjunctival sac.
Such remedies cannot be used as primary therapy, but complement it well. For example, it is useful to drink a course of decoctions of plantain, St. John's wort, nettle, chamomile and elderflower.
Traditional healers recommend instilling 2 drops of olive or peach oil at night. No less useful will be compresses based on a decoction of calendula, birch leaves/buds, and plantain.
Discomfort and unpleasant phenomena do not always indicate the presence of pathology. Both plaque and bruising, redness, and itching can occur due to external irritants. Poor-quality allergenic cosmetics, certain eye drops, prolonged wearing of contact lenses, foreign bodies, overexertion and ordinary fatigue are the main external causes.
In these cases, as a rule, no treatment is required; it is enough to take the following measures:
- eliminate the source of irritation;
- good rest;
- change the brand of cosmetics, etc.
But if there is deterioration in vision or a person has allergies, you need to consult a specialist to conduct a diagnosis, identify the exact cause and prescribe adequate treatment.
It is worth noting such a phenomenon as a crack in the corner of one eye or both. The wound may occur due to allergies due to frequent rubbing of the skin, or due to conjunctivitis.
At first glance, the crack does not pose a danger, but this is far from true, because a secondary infection can penetrate through the damage. So you need to quickly seek help from a doctor to prevent complications.
Itching, as already mentioned, can also be a symptom of conjunctivitis, but it is also characteristic of allergies. Usually it is accompanied by a runny nose, sneezing, and tearfulness. Demodectic mange should not be ruled out, although it usually occurs in people with weakened immune systems.
Those who work at a computer for a long time suffer from “dry eye syndrome,” so the appearance of irritation, itching and cracks in the corners indicate that you need to do special exercises and regularly be distracted by other activities. People who wear contact lenses and glasses should also remember that their eyes need to rest periodically.
Such defects may indicate overwork, stress, or serious health problems. First, it is recommended to rest well, get enough sleep, you can take sedatives, if necessary, and take a walk.
When the work and rest schedule is normalized, but unpleasant phenomena do not go away, you need to contact a specialist. In this case, only he will be able to make a diagnosis, find out the cause and prescribe appropriate measures.
It is worth noting that drooping corners, plaque and other phenomena may be associated with age-related changes. However, hormonal imbalances and vitamin deficiencies cannot be discounted. These two conditions provoke pigmentation of the skin and the appearance of bruises.
Appearance can also deteriorate due to sudden weight loss. Problems with the heart and kidneys, exhaustion of the body after a protracted illness can also be provoking factors.
When your eye hurts, there is a bruise in the corner or other unpleasant conditions, you need to consult a doctor to rule out chronic pathologies and active inflammatory processes.
This cosmetic defect is especially common among newborns and the elderly. If in the former it is associated with a change in environment, then in the older it is usually caused by hormonal imbalances.
If a wen appears, and bags or bruises are added to it, you need to consult a therapist. The doctor, based on the patient’s medical history and complaints, will recommend treatment or refer you to specialized specialists, for example, an endocrinologist or gynecologist.
First you need to find out what reasons provoked this phenomenon. It is worth noting that this also applies to other cosmetic defects, including plaque in the corner of the eyes. If the wen is the result of a hormonal imbalance, efforts must be made to eliminate the latter, otherwise, even after removing the defect, it may appear again.
If your eye hurts or becomes red, cracks or wen appear in the corners, or itching or burning bothers you, you should consult a doctor. Some of these conditions may be caused by ordinary fatigue, then there is no need to worry.
However, the corners of the eyes can become inflamed as a result of more serious impacts. Therefore, it is better to undergo an examination and refute the presence of the disease rather than allow its development.
source
White plaque in the corners of the eyes can be a natural physiological process, like in a baby, or a consequence of fatigue and stress. No less often, various kinds of discharge, especially purulent-mucous discharge of an unnatural color that accumulates, indicate eye infections or exposure to adverse external factors. Treatment is carried out in accordance with the diagnosis established by the attending ophthalmologist.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Even “neglected” vision can be cured at home, without surgery or hospitals. Just read what Yuri Astakhov says and read the recommendation.
White discharge in a person on the eyelids and in the corners of the eyes, a mucous mass that collects immediately after sleep, is considered by many to be a phenomenon not worthy of attention. Sometimes this is true. The reasons for adults are simple: the person was overtired, did not sleep well, was in the hot sun for a long time, a foreign body or irritating chemical got in, sat too long at the computer, put on lenses that were not washed. It is enough to bring the body back to normal or eliminate irritating factors, and the white plaque goes away and the edges of the eyes become clear. The same accumulations can be observed in a child of any age.
American doctors have found that even a one-time examination by an ophthalmologist and following his recommendations in old age reduces the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease by 64%.
Persistent formation, when mucus regularly accumulates around the edges and collects in the corner of the eye, indicates pathology, even serious ophthalmological diseases. The reasons can be different - both external factors and internal diseases. These include:
- Blepharitis. Foam collects in the eyes, yellow discharge accumulates, and crusts and scales form.
- Conjunctivitis. The separated substance has the appearance of a viscous mass of greenish or grayish color.
- Dacryocystitis. Inflammation of the lacrimal sac; when pressed, purulent yellow mucus flows out.
- Barley. Inflammation on the outer edge of the eyelid.
- Chalazion. Inflammation of the meibomian gland. The cause is blockage of the tear duct.
- Demodecosis. Caused by glandular acne, a type of pathogenic mite.
- Trachoma. The result of chlamydia infection.
Return to contents
Hard lumps, a spot of mucus on the outer edges of the eyelids and in the corners of the eyes in a newborn are natural phenomena that are observed in the first 2 weeks of life. This is how the child adapts to new conditions in the outside world, including immune defense. A simple hygiene procedure performed daily can easily remove discharge. If the eyes do not clear, then you should visit a pediatric ophthalmologist to rule out possible bacteriological diseases of the baby’s eyes or allergies.
Therapy is carried out after examination and an accurate diagnosis. The doctor prescribes medications, most often these are ointments, tablets, gels, and sprays. Among the popular products are “Vizin”, “Normax”, “Maxitrol”, “Levomycetin”, and many others. Almost all pharmaceutical medications have contraindications; the doctor will definitely take them into account and give recommendations on how to properly carry out the treatment.
Against the background of drug therapy, but not as the only and main type, it is recommended to use folk remedies from medicinal herbs. Self-medication is unacceptable, you should also remember about allergies. Decoctions, infusions, lotions, ointments, rinsing mixtures are easy to prepare at home. The raw materials are:
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort;
- sage;
- hop cones;
- plantain;
- series;
- birch buds;
- elderberry flowers and berries.
Women cry 47 times a year, and men - 7. From a physiological point of view, this is a very useful process that protects against eye infections.
Preventing eye diseases comes down to simple rules that you should always remember. Possible unsanitary conditions in a bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, or polluted open water bodies increase the risk of contracting any infectious disease, including ophthalmological ones. An allergy to ultraviolet radiation requires wearing dark glasses. Prolonged work at a summer cottage in a bent position provokes increased intracranial pressure. Excessive sitting at the computer is a sure path to vision loss. It is a good idea to regularly wash your eyes with disinfectant solutions. Do not sleep with makeup on your eyes, do special exercise therapy for your eyes, especially for computer scientists. These simple recommendations will help maintain eye health into old age.
source
- Types of fungal eye disease
- Symptoms of the disease
- Treatment of fungal eye disease
- Treatment of eye fungus with folk remedies
How to treat eye fungus, the symptoms of this disease - such questions interest many patients. Fungal eye diseases or ophthalmomycosis were very rare 100 years ago. Nowadays, fungal eye diseases are becoming more common. This may be due to the development of technology that helps identify the most complex diseases. However, there are a number of other reasons why the fungus affects the organs of vision.
Among them are the use of antibiotics, reduced immunity, eye injuries and injuries, diabetes mellitus, the use of lenses, and violation of hygiene rules. Drug addicts and people with AIDS are at risk. The following categories of people are most often exposed to this disease: residents of rural areas, livestock breeders, workers of elevators, granaries, weaving factories, that is, people whose profession is associated with the risk of eye injury and dust and foreign bodies entering them during work.
Ophthalmomycosis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva that occurs due to the entry of a fungal microorganism into the eye area.
Currently, about 50 species of fungi are considered pathogenic for the eyes.
Depending on the type of fungus, ophthalmomycosis is divided into:
- Actinomycosis. This is a common disease. Its causative agents are actinomycetes - bacteria present in large numbers on the mucous membranes and in the intestinal tract of humans and in the bodies of many animals. Fungal spores are found in the air and in some plants.
- Candidomycosis. This is a yeast-like fungus; its spores are found in large quantities in the environment and in the human body.
- Sporotrichosis. The cause of this disease is a dimorphic fungus. Its causative agents are present in plants and soil. You can become infected through contact with a sick person or animals.
- Aspergillosis. The causative agent is a mold fungus; its spores are found on the conjunctiva and skin.
Often the disease occurs in a mild form, without pronounced symptoms. To establish a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to determine the type of fungus and confirm that it was this pathogen that caused the disease. If there are any other eye diseases, some ophthalmomycosis remains unrecognized. Therefore, the treatment process can be complex and lengthy.
The incubation period from the introduction of the fungus to the appearance of the first signs of the disease is from one day to three weeks. Main symptoms of the disease:
- redness and inflammation of the eyes;
- pain and burning in the eyes;
- purulent discharge;
- formation of a film on the eye;
- corneal damage;
- conjunctival ulcers;
- feeling of a foreign object in the eye;
- White flakes are visible in the eyeball.
Fungal disease also appears on the eyelids.
From the eyelids, the infection often spreads to the conjunctiva and eyeball, and reverse spread is possible. In the eye area, the infection most often comes from the soil, can be transmitted from one person to another, or comes from foci of the disease located in the mouth, nose, or conjunctiva. When a fungal infection of the eyelids occurs, the following symptoms are observed:
- eyelids become red, swollen and swollen;
- White discharge accumulates in the corners of the eyes, sticking the eyelids together;
- severe itching and burning;
- scales form at the base of the eyelashes, which can lead to eyelash loss;
- Ulcers, ulcers, and blisters form on the skin of the eyelids.
Eye fungus, the symptoms of which are described above, requires mandatory treatment from a specialist who will determine the type of disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The most commonly prescribed are fungicidal and antimycotic agents. Antibiotics may be prescribed, and in addition to the main treatment, antihistamines, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. The treatment process takes about a month. At the same time, the doses of medications are gradually reduced. Strengthening the immune system plays an important role in the treatment process. You should eat more dairy products, reduce your sugar intake, and garlic is good for you.
During treatment, great attention must be paid to hygiene. You should not touch your eyes unless absolutely necessary. If you still need to touch, it is better to use sterile wipes. Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules can lead to re-infection or various complications.
To successfully treat a fungal eyelid disease, it is necessary to determine the specific type of fungus and the severity of the lesion. Currently, there are effective medications, and methods of physiotherapy have been developed. But treatment can be lengthy and require patience and persistence. Careful eyelid hygiene plays a major role. It is necessary to wipe the eyelids twice a day with a damp swab soaked in saline or a solution of alcohol and ether. After this, the eyelids are carefully lubricated with the ointment prescribed by the doctor. Most often it contains corticosteroids and antibiotics.
It is possible to treat ulcers on the eyelids with a solution of brilliant green. The main rule is not to self-medicate. All medications should only be prescribed by a doctor. Proper nutrition is important. It is necessary to follow a dairy-vegetable diet, avoid fried, salty, and spicy foods. During treatment of fungal eye diseases, it is better not to use cosmetics or wear contact lenses. Eight hours of sleep is necessary, as the eyes must be fully rested.
You can watch TV no more than 2 hours a day and from a distance of at least 4 meters. When going outside in the summer, it is better to wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from dust and ultraviolet radiation. If conservative treatment does not help, surgical treatment is performed - opening abscesses, curettage of foci of infection.
Before using any folk remedy to treat your eyes, you should consult your doctor. Traditional medicine must complement traditional medicine, only then can the greatest effect be achieved. It has long been known that tea is an excellent anti-inflammatory agent. Only it should not be freshly brewed, but dormant. It is used to make eye lotions; it relieves pain, burning, and inflammation.
Fresh cucumbers help with eyelid diseases. Peel the cucumber, cut it finely and pour boiling water over it. Add half a teaspoon of soda. Then they let it brew and filter. A cotton swab is moistened with this solution and applied to the eyelids.
Decoctions of herbs such as yarrow and calamus are used to wash the eyes. A decoction of linden blossom is considered a good remedy. A sterile cotton swab should be moistened with an infusion of herbs and rinsed the sore eye from the outer edge to the inner. Prevention of fungal eye diseases is of great importance. One of the main factors of protection against infection is a strong immune system, so you should strengthen it in all possible ways - hardening, exercise, proper nutrition.
Personal hygiene plays a special role. Fungal spores are found in the soil, on plants, and in the bodies of animals. Therefore, you need to wash your hands with soap more often, wash vegetables and fruits before eating. Particular attention should be paid to the cleanliness of contact lenses. Before touching the lenses, wash your hands thoroughly and dry them with a clean towel. You cannot swim, shower or bath in the lenses.