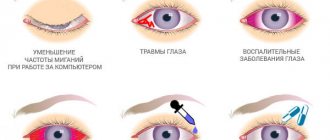
How to remove redness: treatment methods
Treatment is prescribed depending on the degree of injury to the eyeball; it will be individual for each patient. Therapy for hemorrhage in the optic organ is aimed at preserving:
- eyes and restoration of the basic functions of damaged tissues;
- vision or its complete restoration.
Different types of hemorrhages have their own treatment methods.
Hyphema: drops for redness
This is an accumulation of a blood clot in the anterior chamber of the eyeball. With hyphema, a person sees poorly, fog or a veil appears before his eyes, and visual acuity is greatly reduced.
Any treatment for hemorrhage is prescribed by a specialist based on an examination. Depending on the clinical picture, the following drugs may be prescribed:
- Eye drops that will relieve pain and inflammation: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, etc.
- Hormonal containing glucocorticosteroids.
- Aminocaproic acid or other agents to stop bleeding.
- Special medications that strengthen blood vessels and help stagnant blood dissolve.
- Drugs that help normalize eye pressure.
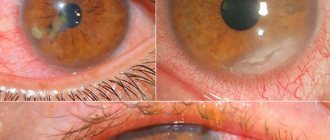
Photo 1. Hyphema of the eye. There is extensive hemorrhage in the anterior chamber, as well as damage to the ocular vessels.
Vessels burst - this is hemophthalmos. How to treat red eye
Hemophthalmos is a disease in which blood, resulting from rupture of blood vessels, accumulates in and around the vitreous body.
If the hemorrhage is total or subtotal, then the patient must be urgently hospitalized, since in such situations, surgical intervention will most likely be required, after which complex therapy will be prescribed. With a mild form of hemophthalmos, the patient should remain in bed, wear an eye patch and eat properly. The same medications are used for any form of the disease:
- Vikasol or other hemostatic agent;
- drops to remove blood clots;
- vitamin complexes;
- hormonal drugs;
- calcium gluconate injections.
In addition to medications, electrophoresis is prescribed. During this procedure, the drug is injected directly into the eye area using electrical waves. Often, for hemophthalmia, aloe injections are prescribed for rapid cell regeneration and improvement of the patient's condition.
Photo 2. Hemophthalmos in the eye. The eye vessels are seriously damaged, the whites are completely swollen with blood.
Retinal hemorrhage
In most cases, blood enters the retina of the eye due to injury. There are several degrees of eyeball contusion:
- Mild - slight swelling of the cornea or retina without tissue damage.
- Moderate - swelling with damage to the tissue of the eyeball, and vision is greatly impaired.
- Severe - observed when the retina and blood vessels are ruptured, and the lens may be damaged. The consequence is complete loss of vision.
Hemorrhage does not always require special treatment. If blood stains do not damage the structure of the eyeball, they will simply resolve over time. If the symptoms are dangerous, the specialist may prescribe drug therapy or surgery.
Medicines prescribed for the treatment of hemorrhage:
- Injections of special vascular drugs to improve the condition of the walls of blood vessels.
- Corticosteroids. Used for severe swelling of the retina of the eyeball.
If drug treatment does not help, laser surgery is performed, during which the damaged vessels are removed and blood circulation is restored.
Photo 3. Fundus of the eye with retinal hemorrhage. Moderate swelling, in this case laser correction is required.
It is worth noting that laser therapy is the most effective method of treating retinal hemorrhage.
Medicines for damage to the orbital cavity
Currently, there are many medications that are used in the treatment of hemorrhage:
- herbal based;
- products with heparin;
- based on vitamin B;
- warming agents.
All medications are sold in pharmacies.
In case of hemorrhage, you can use badyagu; it has a decongestant, analgesic effect and improves blood circulation.
Blood poured into the retina
Behind the vitreous body of the eye there is a retina. It is responsible for the perception of light. Behind it is the choroid, in which there are blood vessels.
The manifestation of bleeding into the retina boils down to the fact that visual acuity, sometimes a certain field of vision, sharply decreases. Usually no pain or discomfort is felt.
Retinal hemorrhages are classified into three degrees:
- with a mild degree, slight swelling of the cornea or retina is noticeable, the tissue is not damaged;
- in moderate cases, swelling occurs with damage to the tissue of the eyeball;
- in severe cases, the retina and its vessels are torn; the lens is often damaged; severe degrees can lead to complete loss of vision.
In case of frequent relapses, it is necessary to undergo treatment in a specialized hospital. A surgical method of intervention is often used - laser coagulation.
How to treat
If a hemorrhage occurs in the eye, the patient needs to provide first aid. First of all, apply a cold compress (several pieces of ice wrapped in a sterile bandage) to the affected eye. After about 2 hours, the compress should be removed. This procedure will reduce swelling and stop bleeding by constricting blood vessels under the influence of cold. Also, for hemorrhage, the use of “Ascorutin”, “Calcium chloride” and “Vikasol” is indicated.
"Vikasol"
Using eye drops
In rare cases, such as severe bleeding in the retina of the eye, a vitrectomy (a surgical procedure in which the doctor removes parts of the vitreous humor) is performed. Surgical intervention, as a rule, is required only in case of complications of the pathology caused by untimely treatment. After such procedures, the patient must follow all the doctor’s recommendations for a quick recovery.
Microinvasive vitrectomy surgery of the eye
Causes
Development factors vary. Depends on the specific type of hemorrhage. If we talk about the most common provoking factors:
- Diabetes. A real disaster for the eyes. The reason is the intensive supply of blood to the organs of vision. Namely, the vessels become the target of endocrine disorders in the first place. With careful treatment and control of the deviation, there is every chance of avoiding dangerous ophthalmological complications.
- Atherosclerosis. Due to excess cholesterol or smoking, drinking alcohol, or drug addiction. The essence is always the same - a decrease in the lumen of the vessel, an increase in pressure in it and an increase in the likelihood of rupture. This reason provokes any of the named types of pathological process. After therapy, the risks disappear.
- Retinal vascular thrombosis. The result of a blood clot breaking away from the primary site, injury, or taking certain medications. The prevalence is low. Among all patients of an ophthalmologist, up to 4% of the total number of patients are admitted with a similar problem. In essence, this is a blockage with disruption of local blood flow, destruction of the vessel and copious release of blood. Almost 60% end in blindness in the affected eye, even with treatment. Because they start it at the wrong time.
- Hypertension. There is also a symptomatic, persistent increase in blood pressure. Sooner or later it leads to angiopathy: chronic disruption of vascular function, and this is a factor in the development of hemorrhage in the retina and vitreous body. High-quality correction of the underlying condition using angioprotectors reduces the risk of bleeding to a minimum.
- Eye tumors. Especially the retina.
- Increase in intracranial pressure. As a result of excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), tissue compression by hematoma or neoplasm. It also causes disruption of the supply of the optic nerve, which is also a risk factor for blindness.
- Anemia. Blood pathologies.
- Congenital disorders of the structure of retinal vessels.
- Eye injuries are a separate category. Contusion, other forms. Often such conditions lead not only to hemorrhage, but also to retinal detachment. The cause-and-effect relationship is clearly monitored, so diagnosis is not difficult.
- Physical activity with a sudden change in body position. Subjective reason, which is based on a pressure surge.
- Autoimmune diseases. As a complication.
- Inflammatory processes in organ structures (uveitis, neuritis and others).
The causes of hemorrhage in the eye are injuries or acute/chronic diseases; less often, the provoking factor cannot be detected.
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
Hyposphagma is the spontaneous accumulation of blood in the space between the outer and white membranes of the eye. The source of the deviation is the disruption of small vessels in the conjunctiva, from which blood leaks into the subspace.
The hypothesized root causes of the formation of the disease are presented:
- Direct injury to the eyeball area - mechanical friction, impact, ingress of foreign particles, chemical substances, sudden deviations in barometric pressure;
- An increase in the level of both arterial and venous pressure - an attack of a hypertensive crisis, excessive physical activity, sudden bending, a state of suffocation, a cough reflex, sneezing, efforts during childbirth, tension during constipation, vomiting, crying in a baby;
- Difficulties with blood clotting - pathology of the hemostatic system of a congenital and acquired nature, the use of medications with an anticoagulant and antiplatelet spectrum of action;
- Pathologies provoked by bacterial agents - infectious jaundice, enteroviral conjunctivitis;
- Particular fragility of the bloodstream - with atherosclerotic pathology, diabetes mellitus, insufficient amounts of vitamin K2 and ascorbic acid, system-wide connective tissue lesions - vasculitis, lupus erythematosus;
- Postoperative period – after surgical interventions on the eyes.
Traditional methods of treatment
To enhance the effect of drug therapy, many resort to traditional medicine. With their help, you can not only alleviate the general condition of the patient, but also completely eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Treatment with folk remedies
Let's look at the most common recipes:
Brew black tea in bags and, after waiting until it cools, apply to the affected eye for 10-15 minutes. Regular implementation of this procedure helps relieve the inflammatory process;
Tea bag compress
- mix 1 tbsp. l. ash, 200 ml of boiled water and a few drops of table vinegar. Make eye compresses from the prepared product;
- to alleviate the symptoms of a pathological condition with hemorrhage in the eye, radish peel or cheese is often used as a lotion;
- Decoctions made from various medicinal plants can also help relieve symptoms of bleeding in the eye. The most commonly used are chamomile, thyme or aloe. From the prepared decoctions you need to make eye lotions every day.
Chamomile decoction
It is worth noting that in case of severe damage to the organs of vision, the use of traditional medicine is powerless. In such cases, conservative treatment with the use of potent drugs or surgery is required. Unfortunately, it is impossible to get rid of such pathologies on your own.
Treatment
Most patients are treated on an outpatient basis, hospitalized only:
- seriously ill patients;
- patients with complications;
- little children;
- people with sickle cell anemia.
The nature of therapy is determined by the cause of hyphema formation, its degree and the presence of complications. As a rule, they initially try to cope with the problem with conservative measures, and if they are ineffective or complications develop, they resort to surgical intervention. But even with a slight hemorrhage in the eye, it is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist in order to protect yourself from the development of undesirable consequences and to speed up the onset of recovery as much as possible.
Attention! You cannot decide on your own to cover the injured eye with a bandage or apply any compress, as this may cause the condition to worsen.
General recommendations
All patients should:
- try to adhere to bed rest;
- sleep with the head of the head raised;
- avoid physical activity;
- do not take painkillers, since almost all of them affect blood clotting;
- on the recommendation of a specialist, cover the injured eye with a soft bandage for two weeks.
To speed up recovery, it is recommended to sleep on a high pillow or otherwise raise the head of the bed so that an angle of 45-60 degrees is formed between the head and the surface of the bed
Drug therapy
If the patient is taking anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents, that is, medications that thin the blood, they are discontinued during the treatment of hyphema. To eliminate traces of hemorrhage, the following is prescribed:
- drops with corticosteroids (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone) - to eliminate the inflammatory process and pain;
- hemostatic agents (Gemaza, Purolaza, aminocaproic acid);
- vascular strengthening drugs (Actovegin, Emoxipin);
- absorbable medications (Mannitol, Glycerol);
- mild pain relievers (Tylenol);
- atropine and drops with β-blockers (Thymol, Acetazolamide) - to normalize intraocular pressure.
If severe pain appears in the affected eye, especially in combination with attacks of nausea and vomiting, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this may be signs of increased intraocular pressure, which requires an immediate response and adjustments to the prescription.
Drops with corticosteroids - the basis of conservative treatment of hyphema - gallery
Sofradex
Pharmadex
Maxitrol
Maxidex
Surgery
Surgery is a last resort. Its implementation is indicated when:
- staining the cornea with blood;
- formation of clots;
- complete filling of the anterior chamber with blood;
- no improvement within 5–10 days of drug treatment;
- increased intraocular pressure and the ineffectiveness of medications to lower it.
Hyphema
Bleeding in the anterior chamber of the eye involves the gap between the cornea and iris. In normal condition, this area is filled with a transparent liquid, without foreign impurities.
The main source of hemorrhage is damage to the integrity of the blood vessel. Experts identify three possible causes of the disease.
Traumatization is one of the frequently recorded primary sources of hyphema formation. Prerequisites are further subdivided:
- Penetrating type - under the influence of sharp or blunt objects. Damage provokes a direct connection between the internal structures of the eyeball and the surrounding space;
- Non-penetrating – the internal structures of the eyeball are destroyed, which causes bleeding in the anterior chamber of the eye. Traumatization is the result of the influence of blunt objects, and there is no violation of the integrity of the outer shells;
- In the operating room - any type of surgical interventions on the organs of vision are considered injuries that can provoke the formation of hyphema.
Neovascularization is an eye disease accompanied by the formation of defective blood lines inside the organ. Fresh capillaries are characterized by structural defects and increased fragility, which leads to frequent hemorrhages with minimal or no external influences. The main prerequisites for the abnormal condition are presented:
- Diabetic angiopathy – as a consequence of diabetes mellitus;
- Overlapping of the lumens of the venous pathways in the retina;
- Retinal detachment;
- Neoplasms located inside the organs of vision;
- Inflammatory reactions occurring in the internal structures of the eyes.
Certain diseases of the body can also provoke hemorrhage in the scleral area. The problem may be caused by:
- Stable poisoning of alcoholic or drug origin;
- Problems with normal blood clotting;
- Malignant processes;
- System-wide lesions of connective tissues.
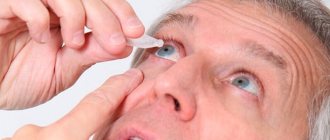
How to instill drops and carry out treatment: general recommendations
Important! For this ophthalmological disorder, it is necessary to follow the basic rules for instilling eye drops. These instructions are quite easy to remember and follow:
- Before the procedure, you should always wash your hands thoroughly , and it is advisable to use bactericidal soap.
- used must only have a current expiration date . Expired drops may not cause any harm, although they will not have any effect, but may have a negative effect.
- A new and newly opened bottle must be immediately inspected for possible damage to the tip . It should not have nicks or burrs. Although touching the tip directly to the eye during instillation is strictly not recommended, this can happen accidentally and such defective dropper bottles can cause injury.
- Contrary to popular belief, it is not necessary to instill the product while lying down . Moreover, there is simply nowhere to lie down at work or school. You can perform the procedure while sitting, but you must tilt your head as far back as possible.
- Before instillation, the eyelid of the eye being treated must be pulled back with the thumb and forefinger of your free hand . Then you need to bring the bottle of medicine at a distance of 1-1.5 centimeters from the eyeball and lightly press on the body of the container.
- It is necessary to maintain a time interval of 20-30 minutes between instillation of different medications .
Retinal tear
Among a number of ophthalmological diseases, a special place is occupied by such a pathology as a rupture of the retina, which is characterized by a violation of the integrity of the eye tissues with subsequent detachment. Fluid penetrates into the location of the retinal break, which forms between the choroid and the retina itself from the area with subretinal fluid. As a result, vision decreases, and the retina itself can detach from the membrane.
Types of retinal tears
- Valvular ruptures - these disorders develop as a result of the penetration of a minimal amount of fluid into the posterior vitreous detachment, where changes occur in the vitreous membrane and the retina itself.
- Perforated tears - develop with peripheral retinal dystrophy.
- Detachments of the retina from the dentate line - develop after eye injury.
- Macular holes - a pathology formed when the vitreous body fuses with the retina and is considered one of the most severe.
Causes of retinal tears
A tear in the retina of the eye can occur for several reasons, but most often the reason lies in the person’s history of a disease such as myopathy (myopia), when the vitreous body has an elongated shape, which leads to stretching of the retina and its rupture. In addition, the cause of visual pathology is often age, when the vitreous body decreases in size, which entails excessive stretching of the retina. Predisposing factors to the development of a retinal tear are the following disorders:
- excessive physical activity;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system;
- hypertensive crisis;
- head and eye injuries;
- physiological aging of the body;
- concomitant eye diseases.
Symptoms of a retinal tear
The clinical picture of a retinal tear may be absent, and the first symptoms are observed only when retinal or vitreous detachment begins to occur. Then the following symptoms are noted:
- the appearance of “flies” before the eyes;
- the appearance of “blind fields” before the eyes;
- decreased visual acuity;
- light flashes before the eyes.
Treatment of retinal tears
A retinal tear is very dangerous as it can lead to retinal detachment and complete loss of vision. Therefore, the key to successful treatment is a timely visit to an ophthalmologist who can diagnose the disease and provide quality treatment.
Treatment is carried out using modern methods that allow treatment and restoration of vision in a short time. If the retinal detachment is minor, then the doctor prescribes laser coagulation or cryosurgery.
Laser coagulation seals holes in the retina. After the procedure, scars are formed that block the penetration of fluid under the retina. Cryosurgery (freezing). After cryosurgery, as well as after laser surgery, scars form that do not allow fluid to penetrate under the retina. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
The prognosis after treatment is favorable only if surgery was performed on time. After treatment for a retinal tear, the patient needs to be under the supervision of an ophthalmologist for a long time, and it is also necessary to avoid provoking factors. It should be noted that retinal rupture is possible and observation by a specialist is extremely necessary.
Vitreous hemorrhage
The vitreous body is a transparent substance with a gel-like structure. Placed behind the lens. Its main function is to support the shape of the eye and transmit light to the retina from the pupil. Bleeding in this structure is a relatively rare phenomenon, because this structure does not have blood vessels, so bleeding occurs when the blood vessels located in the retinal area burst.
The following reasons can provoke the appearance of hemorrhage in this case:
- Eye injury.
- Hemorrhage.
- Vitreous detachment.
- The appearance of pathological vessels in the retinal area (if a person has diabetic retinopathy).
- Damage to retinal vessels due to hypertension, atherosclerosis and other diseases.
- Neoplasms in the eyeball area (if this area swells and adjacent tissues are damaged).
- Carrying out various ophthalmological procedures and operations (including laser).
Preretinal hemorrhage in the retina and vitreous body leads to blurred vision, dots, “spots”, etc. are formed. When you look, the world around you becomes reddish, objects seem a little reddened. The disease usually affects one eye (left, right), is unilateral and rarely spreads to the adjacent eye.
If the case is advanced, then patients experience a gradual deterioration in vision, which is constantly progressing.
The disease is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist, who examines the eye using a slit lamp and prescribes an ultrasound examination. The patient must undergo a general blood test (to exclude the infectious nature of the disease). In difficult cases, people are sent for a computed tomography scan.
Therapeutic tactics for this disease will depend entirely on the reasons that caused the hemorrhage:
- At the first stage, the main source of the bruise is accurately determined.
- After which the bleeding stops.
- Next, procedures are carried out aimed at restoring the structure of the retina so that the person does not lose his vision.
- At the last stage, everything necessary is done to restore normal visual acuity.
It is impossible to cure this type of disease at home, because specialized treatment is required, including laser coagulation. After this, you need to wait for complete resorption of the blood (10-20 days). At this time, you need to avoid any physical activity so as not to provoke new bleeding.
If the blood accumulated in the vitreous body covers other structures of the eye, continues to flood and interferes with therapy, then surgical intervention is indicated to remove the vitreous body, which will stop the bleeding (the structure is completely removed). After the operation, a special silicone substance is injected into the area of the eyeball to keep the retina in its usual place. Operations of this type are performed in special ophthalmology clinics. Despite their complexity, they are relatively safe and cannot harm human health (regardless of his age).
Bleeding in the eye - causes and treatment
Why does it happen that, seemingly for no apparent reason, the white of the eyeball suddenly turns red? Sometimes it is a very small spot, and sometimes the blood stain can completely cover the entire sclera. The main reason is the fragility of the smallest vessels - capillaries, which penetrate all the tissues of the eye. The reason for the fragility of blood vessels in the eye is much deeper and is one of the symptoms of serious diseases.
Reasons why blood vessels in the eye may burst:
- Arterial hypertension. Violation of the integrity of blood vessels is facilitated by a sharp jump in pressure during a hypertensive crisis. The vessels cannot withstand the sudden pressure and burst. And it’s good that the vessel ruptured under the conjunctiva, and not somewhere in another organ. You understand that a burst blood vessel in this case can cause a hemorrhagic stroke, myocardial infarction, dissection of the aortic wall, which sometimes threatens life.
- Diabetes. One of its manifestations is diabetic angiopathy. Increased blood sugar leads to the destruction of blood vessels. The disease manifests itself not only in hemorrhages in the eye, but also in a noticeable deterioration of vision, up to complete blindness. Vessels can be damaged for no apparent reason, even from slight physical activity.
- Infectious diseases accompanied by fever or profuse vomiting (foodborne diseases, rotavirus infection, dysentery, etc.).
- Eye diseases - conjunctivitis, keratitis, in which, in combination with profuse lacrimation, hemorrhages in the eye are observed.
- Eye injuries - a sharp mechanical impact on the eyeball leads to rupture of blood vessels. This can also include injuries associated with eye surgery.
- Blood diseases caused by poor clotting.
- Lack of vitamins C, A, and routine leads to a decrease in the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels and their rupture.
- Tumors located near the eye contribute to compression and deformation of the vessel, resulting in the vessel bursting.
- Alcoholism - drinking alcohol in large quantities leads first to a sharp dilation and then a rapid narrowing of blood vessels. The vessels cannot withstand it - they burst.
Other causes may include long-term use of certain medications, which can cause bleeding as a side effect.
And also a change in intracranial pressure, which occurs in people with increased meteosensitivity, during caisson disease, when they quickly float to the surface from great depths or descend from the mountains. And that is not all. Vessels can burst from visual strain when working at a computer for a long time, reading text with small print, or during painstaking manual work. This can happen in people with increased physical activity, for example, when lifting weights, in women during childbirth during pushing, or with a strong cough. Even visiting a hot bath or sauna can lead to rupture of capillaries.
Causes of hemorrhages
Like any other organ, the eye is supplied with nutrients through blood vessels. Blood can leave them if the walls cannot withstand the influence of the environment: damage can cause a strong blow, high blood pressure. Thin and fragile capillaries can burst when sneezing, loud screaming, laughing, overexertion - including as a result of constipation. Other events that can cause hemorrhage include:
- reduced blood clotting: hereditary, with vitamin K deficiency, from taking Aspirin, Warfarin and other medications;
- eye surgeries;
- damage to capillaries as a result of infections;
- diabetes;
- retinal atherosclerosis;
- the appearance of blood clots in the vessels of the eyes;
- injuries leading to suffocation;
- diseases that cause severe vomiting;
- smoking, alcohol: bad habits make capillaries even more fragile, they collapse more easily.
In a newborn, red spots on the eyes occur due to errors during childbirth or its severe course: the baby may receive accidental injuries from equipment, suffer from the effects of auxiliary drugs or breathing problems in the woman in labor. It is very easy to damage a child’s fragile blood vessels, but, fortunately, hemorrhages are rarely dangerous. In the first year of life, hemorrhage also occurs due to improper motion sickness, which turns into shaking. To avoid complications, it is better to show your baby to a doctor immediately.
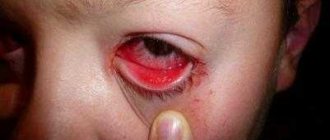
What is hemorrhage in the eye?
Damage to the small blood vessels in the eye causes the eye to become red or bleed. Depending on the location of the damaged vessel, the following are distinguished:
● subconjunctival hemorrhage. The vessels of the mucous membrane of the eye are damaged. As a rule, they are spontaneous and develop without an obvious reason.
● Hyphema. Hyphema is a collection of blood in the anterior chamber of the eye (between the cornea and iris). Typically the result of blunt trauma to the eye. Accompanied by severe pain and blurred vision. Such hemorrhage in the eye requires emergency care.
● Hemophthalmos. Vitreous hemorrhage inside the eye. In other words, internal hemorrhage in the eye. With hemophthalmia, a pronounced fog appears before the eye. In the case of complete hemophthalmos, vision loss occurs. Hemophthalmos is a severe eye lesion. Without treatment, permanent vision loss is possible.
● Retinal hemorrhage. Retinal hemorrhage develops as a result of bleeding from the vessels of the retina. The retinal tissue is very sensitive and thin. Therefore, even small hemorrhages can lead to significant vision loss and the development of retinopathy.
Subconjunctival hemorrhage. Usually, apart from severe local redness of the eyes, there are no other symptoms. Very rarely, in case of damage to a large vessel, pain may occur. With extensive hemorrhage, a feeling of pressure in the eye may occur.
The area of hemorrhage in the eye itself is bright red in color and has clear boundaries. In case of extensive hemorrhages in the eye, the blood spreads to the entire tunica albuginea.
There are the following reasons for the appearance of this symptom:
- Eye injuries.
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye caused by viruses.
- Sudden and rapid increase in blood pressure.
- Severe cough, vomiting.
- Taking blood thinning medications (aspirin, salicylates, anticoagulants).
- Vitamin K deficiency.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- General diseases: Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension, systemic vasculitis.
- After eye surgery.
Contact your doctor immediately:
- hemorrhage occurred simultaneously in 2 eyes at once
- sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes
- strong fog before the eye
- hemorrhage is accompanied by pain and decreased vision
- hemorrhage in the eye occurred as a result of an eye injury
- you are taking blood thinning medications
Subconjunctival hemorrhage in most cases does not require treatment and goes away on its own.
If you experience pain and discomfort, your doctor may prescribe decongestant and anti-inflammatory drops. For concomitant eye infections, antibacterial or antiviral drugs are prescribed. As a rule, subconjunctival hemorrhage resolves within 2 weeks, without complications.
In other cases of hemorrhages in the eye, immediate treatment is required in an eye hospital.
If bleeding occurs in the eye, you should not:
- rubbing your eyes, this increases bleeding
- instill eye drops without a doctor's prescription
- put on contact lenses
- You should not stop taking medications on your own; if you are taking blood thinning medications, tell your physician if bleeding occurs.
Only subconjunctival hemorrhage can go away on its own without consequences for your vision and health.
In other cases, if left untreated, complete and irreversible loss of vision is possible. The appearance of such a symptom indicates a serious problem with the eyes or the whole body.
There are no specific measures to prevent the development of hemorrhage in the eye. If you experience frequent hemorrhages, be sure to get examined by a therapist to find out the cause.
Treatment of the underlying disease, such as diabetes or hypertension, can prevent complications such as bleeding in the eye from developing.
What drops to drip
Hemorrhages in the eye area often require the use of special drugs that eliminate the pathological process and restore the normal state of the visual organs. Frequently prescribed medications include drops:
- Vixipin.
- Albucid.
- Taufon.
- Potassium iodide.
- Emoxipin.
- Diclofenac.
- Hyphenation.
Medicines in drip form are indicated for patients whose hemorrhage does not resolve within 6–7 days and is accompanied by other negative symptoms (pain, development of an infectious process).
Vixipin
This domestic drug is recommended for patients in whom hemorrhage occurred in the anterior chamber of the eye or in the sclera. The product containing methylethylpyridinol hydrochloride as the main component is prescribed no earlier than 18 years of age.
The medicine helps reduce capillary permeability, strengthen vascular walls, stabilize the cell membrane, and normalize blood viscosity. The hyaluronic acid present in the solution ensures complete hydration of the cornea, eliminates discomfort, and improves the tolerability of the drug.
Instillations are carried out 2-3 times a day, introducing 1-2 drops of medication into the affected eye. The duration of the course depends on the severity of symptoms, type of diagnosis and can take from 3 to 30 days. You can buy Vixipin for 198–215 rubles.
Albucid
The active ingredient of this product is sulfacetamide. The main action of Albucid is antimicrobial, bacteriostatic, anti-inflammatory. The medicine is considered safe and can be used even during the neonatal period.
The drug helps fight hemorrhages in the eye area caused by various factors. Adult patients are prescribed a 30% solution, and a 20% solution is prescribed for children. The medication must be instilled 3–5 times during the day, 2–3 drops each. The frequency of use is reduced as symptoms weaken. The average price of the drug in the Russian Federation is 55–62 rubles.
Taufon
The main ingredient of Taufon is the metabolic compound taurine. The medicine, produced in Russia, is intended for the treatment of persons over 18 years of age. The product accelerates the healing of damage in the eye area, improves the functioning of cell membranes, promotes better metabolic and energy processes, and better conductivity of nerve fibers.
The medication is administered intraconjunctivally, 1 drop four times a day. For hemorrhages in the organs of vision, a course with this remedy can last about a month. You can buy the drug for 112–130 rubles.
Potassium iodide
The domestic eye drop product contains potassium iodide as a base. Instillations with potassium iodide are resorted to in the development of various ophthalmological pathologies, including hemorrhages in the eyeball area.
Thanks to instillation, the following results can be obtained:
- increase lipoprotein concentration;
- reduce blood viscosity;
- expand the lumens of the vascular walls.
It is recommended to use this remedy for the treatment of children no earlier than 2 years of age.
A 3% solution is intended for injection into the eye area. The solution should be instilled into the conjunctival sac, 2 drops, 3-4 times a day. The average duration of therapy is 10–15 days. Eye drops cost about 150 rubles.
Emoxipin
The medicine produced in the Russian Federation includes methylethylpyridinol. The medication is prescribed to patients with intraocular hemorrhages, thrombosis in the central vein of the retina, and glaucoma. The drug promotes effective protection of the organs of vision after laser coagulation and sunburn.
To undergo treatment with this drug, the patient must reach the age of majority (18 years).
The solution should be used once a day, in a volume of 0.2–0.5 ml in the area of the affected eye. The duration of treatment may take from 10 to 30 days. The drug has a moderate cost - about 144 rubles.
Diclofenac
This product is produced by pharmaceutical companies in different countries - Russia, Germany, India, Slovenia. The main ingredient of the instillation solution is sodium diclofenac (1 mg per 1 ml). The medicine belongs to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
The drug is widely used by ophthalmologists for various eye disorders, including hemorrhages. To perform instillations, a 0.1% solution is used. The dosage and frequency of administration are determined by the doctor individually. Typically, patients are prescribed 1-2 drops of medication into the problematic organ of vision, up to 5 injections during the day.
Diclofenac eye drops are used to a limited extent for the treatment of children under 12 years of age and the elderly. The price of the product is affordable - 45–55 rubles. per bottle with 10 ml of solution.
Hyphenleuse
This domestic drug, which helps with hemorrhages in the eye area, can be bought for 40–47 rubles. The medicine contains hypromellose and auxiliary components. The main property of Defislez is the protection of the corneal epithelium.
Instillations with this medication can be carried out no earlier than 8 years. The frequency of instillation of the solution reaches 4–8 times a day. A single dose for bleeding in the eye area is 2 drops. Treatment is carried out over 2–3 weeks.
Types of hemorrhages
The causes and treatment of hemorrhages in the eye are closely related, and the types of pathology also play an important role. When choosing therapy, the severity of the disease, areas of localization, etc. are taken into account.
Depending on the severity, the following types are distinguished:
- The first is accompanied by mild hemorrhage, there is no damage to the eye, visual function is preserved, there is no need for complex therapy;
- The second is accompanied by mild damage to the tissues of the visual apparatus; medications are used in treatment;
- The third is characterized by significant damage up to the destruction of eye tissue; surgical intervention is used as part of therapy.
Varieties by location:
- Hyphema - accompanied by hemorrhage in the anterior chamber, a uniform smudge with smooth borders appears on the eyeball, vision deteriorates when the entire pupil is filled with blood;
- Hemophthalmos is an outpouring of blood into the vitreous body, a leak forms in the back of the lens; with complete outflow, vision deteriorates quickly, with partial outflow - slightly. The pathology is accompanied by the appearance of flashes of light and dark spots;
- Effusion into the retina - in the early stages of the development of the disease, the pathology does not manifest itself in any way, there is no leakage. In this case, there is a decrease in the sharpness of the picture when looking at objects;
- Hemorrhage into the orbit - the pathology is accompanied by injury to the orbit and decreased visual function.
Diagnostics
With severe hyphema, when the spilled blood fills the entire volume of the anterior chamber of the eye, its diagnosis is not difficult, since it is easily visualized. If intraocular hemorrhage is suspected, it is necessary to identify the cause of the incident. If a recent injury or eye surgery is mentioned, this may be the likely cause of the pathological condition.
If there were no external factors, it is necessary to exclude other causes of hyphema: systemic diseases, taking substances and drugs that thin the blood. To do this, the patient is prescribed a laboratory blood test for coagulation - a coagulogram.
Treatment of the retina with folk remedies
The main cause of retinal damage is deterioration of blood supply due to sclerotization or destruction of the vessels that are responsible for the blood supply to the retina. Photosensitive cells die, and as a result, the perception of color, light, and shape of objects is impaired, and the range of vision and visual acuity decreases.
The blood supply to the retina may suffer from atherosclerosis, increased intraocular pressure, and systemic and hormonal disorders (for example, diabetes mellitus).
Traditional medicine uses the following natural ingredients to treat the retina:
- honey,
- lemon,
- Pine cones,
- rue,
- mallow,
- sweet clover,
- lemon balm,
- primrose,
- mordovnik seeds,
- pine buds.
Products that contain vitamin C are traditionally beneficial for the eyes:
- blueberry,
- cowberry,
- blueberry,
- grape,
- cranberry,
- raspberries,
- citrus.
Provitamin A, which is contained in carrots, has the best effect on visual acuity. Traditional medicine offers to cure the retina of the eyes in the following ways.
Oat decoction
To prepare it, you need to take 500 g of oats, always washed. Whole washed oats are sold at any pharmacy. Soak the oats for 4 hours, then drain the water and place the oats in another container, into which pour 3 liters of filtered water. Place the pan on the fire, after boiling, boil for another 30 minutes (cook over low heat). When it cools slightly, drain the water and drink a glass at least 4 times a day. Usually this infusion is taken for about 2 weeks, but it is better to consult a doctor to clarify the course of treatment.
Decoction of pine cones
Unripe pine cones are poured with cold water, after boiling, rue flowers and honey are added and boiled for up to half an hour. The decoction is taken without restrictions (if there are no allergic manifestations).
Medicinal collection
A medicinal mixture that includes St. John's wort, crushed violet herb (1 part each), bearberry (2 parts), and knotweed herb (3 parts) has a good effect. Take 1 tbsp. l. collection, pour water (a glass of boiling water), wait half an hour, filter. It is recommended to consume a third of a glass half an hour before meals, drink the decoction no more than 3 times a day and no more than 10 days.
Mordovnik seed tincture
Buy a ready-made tincture or prepare it yourself (pour the Echinops seeds with alcohol) - it’s your choice, and use the tincture starting with ten drops per dose and up to forty, three to four doses per day. The course is a month.
Infusion of pine needles
Many people advise starting treatment to strengthen the retina by using an infusion of pine needles. We cut off the pine needles (they should be young and fresh) and chop them with scissors. 6 tbsp will be enough, they need to be filled with water (0.5 liter will be enough) and boiled for 15 minutes, then left overnight. Divide the resulting infusion into small portions, always drink slightly warmed, several times a day (up to 5 times).
Treatment prognosis
In mild cases, it takes several days to a week for the hyphema to completely resolve. But approximately 1/5 of the patients experience more intense bleeding within 3-5 days, so it is very important to consult a doctor and follow his recommendations exactly.
In general, the prognosis regarding the restoration of previous visual acuity may be different, since this is influenced by many factors, especially the volume of blood shed and the value of intraocular pressure. If the latter remains within normal limits and there is no other damage to the structures of the eye, vision is usually completely restored after a few weeks.
How to treat?
If you find a bruise on your eye, you shouldn’t worry too much in only one case: if your eye doesn’t hurt and your vision isn’t impaired. Otherwise, you will have to consult a doctor to find out why the bleeding in the eye occurred: treatment may require quite a long and serious period.
If the eye is very red or bruised, but there is no pain or foreign body sensation, pharmaceutical drops or home remedies are usually used to quickly relieve the redness.
Pharmacy drugs
Visine, octilia, naphthyzine for the eyes, okumetil - vasoconstrictor drops that prevent blood from escaping through the walls of blood vessels. They are usually used to quickly remove even fairly intense redness.
Home Remedies
Treatment of hemorrhages in the eye takes longer and requires careful observation and accuracy. The main methods of treatment are the application of cold (ice, food from the freezer), as well as compresses from herbal decoctions, tea leaves, and juice of house plants.
Here are a few recipes that can help you get rid of bruises in your eyes:
Strong tea compress
Brew the black tea stronger, let it cool (the colder the brew, the better), moisten a cotton ball (wrap it in a bandage to prevent lint from getting into the eye) and apply it to the sore eye. Lie down for 15-20 minutes.
Chamomile compress
Brew strong chamomile tea (two tablespoons of dried flowers per glass of boiling water), let it brew and cool. Strain the infusion and soak a cotton ball wrapped in a bandage in it. Apply to the sore eye and lie there for a while.
A lotion of water with vinegar or ash
Add one or two drops of ordinary vinegar to a tablespoon of boiled water, stir and moisten a cotton swab, which should be applied to the sore eye.
The same can be done with ash: if you have it, you need to boil a little ash in water, strain the broth and apply a swab dipped in this liquid to the sore eye.
Cottage cheese lotion
If you have fresh cottage cheese in the refrigerator, you can take a teaspoon of the product and apply it to your eye, wrapping the cottage cheese in a bandage or a piece of clean natural fabric. A compress made from whey will also give a good effect.
Cabbage or cabbage juice lotion
A leaf of fresh cabbage should be crushed into a puree and the resulting pulp should be applied to the sore eye, wrapped in a piece of clean cloth. Freshly squeezed cabbage juice will give the same effect.
All compresses and lotions should be applied several times a day until the eye condition improves.
In summer, the diet of people with problems with vascular permeability should include seasonal fruits, berries and vegetables, and in winter - sauerkraut and citrus fruits.
It must be remembered that bruises in the eyes are not only a cosmetic defect, but also a cause for concern - especially if they appear regularly and for no apparent reason. Hurry to the doctor - you may have serious health problems: that's what your eyes are talking about.
It will be useful for you to know what to do if a blood vessel bursts in your eye.