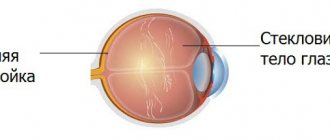
The vitreous body is an intraocular liquid tissue that consists almost entirely of water and fills the space between the lens and the retina (i.e., more than half of the total volume of the eyeball). Despite the absolute, up to 99%, predominance of water in the composition, the vitreous body is closer in consistency to gels. This is explained by the fact that the vitreous substance contains a truly amazing “supplement” - hyaluronic acid, known to many as a component of anti-aging cosmetics or as a plastic implant. Hyaluronic acid, a high molecular weight polymer, is a natural lubricant, i.e. moisturizing “lubricant”, and provides the vitreous body with the necessary elasticity, firmness, and reliable adherence to the intraocular surfaces. In addition, the vitreous body contains a certain amount of salts, ascorbic acid and protein compounds, and its shape is given by special fibrous inclusions - fibrils.
Given its location, the vitreous body should normally be, of course, homogeneous and absolutely transparent, otherwise the visual system would be partially or completely deprived of the optical conditions of functioning. However, this is exactly what happens in a number of diseases and pathological conditions: the vitreous body detaches from the retina and/or lens, loses volume, becomes cloudy, and loses homogeneity - which inevitably affects the most important characteristics of vision and can lead to very serious consequences.
In the context of the more general problem of vitreous detachment, a particular pathological phenomenon is considered, consisting of local, focal opacity (or reduced transparency), which is caused by the formation of various kinds of clots, compactions or rarefaction, biochemical precipitation and other heterogeneities. This phenomenon is called “destruction of the vitreous.”
Causes
Destructive changes in the vitreous body are caused by a gradual transformation of the physico-chemical properties of its constituent colloidal gel. This is due to local inflammation caused by keratitis, blepharitis, endophthalmitis, etc. In addition, the composition of colloids is directly related to the health of the liver, kidneys, and endocrine system. Their dysfunction leads to disruption of the physiological balance of fluid, glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans with stromal components. Deterioration of metabolism, disturbances in the functioning of the vessels of the retina or brain, cause weakening of blood flow, which provokes neurocirculatory spasm of the eye muscles, triggering the development of destructive processes in the vitreous body.
The rheological characteristics of the colloidal gel of the vitreous body of elderly people tend to deteriorate in the central sections and thicken in the periphery. The force of gravity peels off the crystals and collagen masses deposited in the retinal area over the years, which accumulate in the central region of the vitreous body.
Myopic refraction, in which the round shape of the eyeball is transformed into an ellipsoidal one, can also become a kind of trigger for this pathology. After all, the changes it causes lead to deformation of almost all intraocular structures.
In addition, this pathology can occur due to trauma to the eye or orbit. The reason is the loss of integrity of the gel-like component, damage to the primary collagen structure, and the development of hemophthalmos due to vascular damage.
The risk group for DTD includes persons with diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation, Parkinsonism, and asthenopia. The least common cause of pathology is damage to the structure of the vitreous body in cataract therapy.
What diseases affect the structure
The vitreous body may have congenital abnormalities, but this is extremely rare. As a rule, the structure is affected by acquired pathologies that are the result of some other ophthalmological diseases.
Developmental anomalies
Developmental anomalies are quite rare in ophthalmological practice.
One of them is primary persistent hyperplastic vitreous.
During development inside the womb, the baby develops blood vessels that pass through the vitreous body. By the time of birth, the artery and its branches regress and disappear, but in some cases membranes remain, directed from the site of exit of the optic nerve deep into the vitreous body.
Classification and pathogenesis
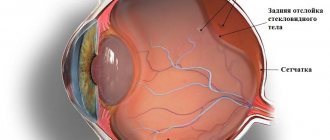
DST can be either partial or complete. As a rule, the process of destruction first affects the central parts of the organ. First, cavities are formed in which liquid and individual collagen masses are found. Subsequently, an increasing number of fibrillar proteins are susceptible to coagulation. They go beyond the structure, the gelatinous substance of the vitreous body liquefies. Films and cords of various origins are formed inside, sometimes fixed on the fundus, which leads to wrinkling and the formation of adhesions. The decreasing volume and deformation of the vitreous body causes tension in the vitreoretinal connections, which subsequently provoke retinal detachment.
CT destructions differ in form: filamentous, granular, crystalline. The cause of the filamentous form of DST is progressive myopia or atherosclerosis. Granular lesions of the vitreous body arise due to inflammation in the inner layer of the retina. In rare cases, damage to the colloidal gel is caused by deposits of tyrosine and cholesterol crystals.
Folk remedies in the fight against destruction
Massaging the eyeballs helps normalize blood circulation during destruction. In addition, the following folk remedies are effective in treating vitreous disease:
- Drops based on honey diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 2.
- Drops of honey and aloe, where the juice of this plant replaces water.
- Propolis infused with water, which is dropped into the eyes.
Please note that the use of these components may cause an allergic reaction. In addition, you should not self-medicate. These recipes can only be used on the advice of a doctor and used as an addition to the main treatment.
Symptoms and diagnosis of DST
When the vitreous body is destroyed, patients may notice the appearance of light phenomena, a “veil,” in their field of vision. Hemophthalmos often develops after vascular rupture, which causes a decrease in visual acuity. One of the specific symptoms is “floaters”, clearly visible when looking at a uniform background (sky, white wall). An attempt to focus on them leads to the movement of the “front sights” or their disappearance. As a rule, symptoms develop gradually. Therefore, the sudden appearance of a mass of black dots before the eyes may indicate a complication of DST with retinal or vitreous detachment.
The diagnosis is confirmed after a comprehensive examination, which includes: ophthalmoscopy, B-scan with ultrasound of the eye, biomicroscopy, OCT, tonometry, visometry.
With the help of ophthalmoscopy, empty optical cavities are identified in patients with DST, often defined as vertical slits. Specific changes practically do not affect the limiting membrane, but fibrous fragments with a gray or white tint are revealed behind it. With complete destruction, a single cavity is formed in the vitreous body, including fragments of fibrils. Sometimes destruction of the limiting membrane occurs, which is characterized by the absence of a retrolental space. When opacities are located at the edge of the retina, a complete absence of specific changes is possible.
Studies in lateral light, during biomicroscopy, help to detect an altered consistency of the vitreous substance and the presence of multiple opacities in the form of flakes. With DST of a filamentous form, the collagen fibers become loop-shaped. In the case of granular destruction, clusters of small gray or brown particles are visualized. The later stages of the disease are characterized by the appearance of conglomerates from the accumulation of grains, which are clearly visualized by biomicroscopy.
The most informative research method for DST is eye ultrasound. The B-scan procedure is prescribed in case of hemorrhage into the vitreous body. It makes it possible to identify the source of hemorrhage, as well as internal crystalline structures that reflect echo-negative signals. When the vitreous fluid liquefies, the mobility of crystals, collagen fibers and granular conglomerates is revealed.
OCT of the eyes is necessary when there is insufficient information from other diagnostic techniques. Its implementation during DST reveals a decrease in the size of the vitreous body, heterogeneity of the structure, turbidity and changes in its shape. However, in case of massive hemophthalmia, this procedure is not recommended.
Using visometry, the degree of deterioration in the quality of vision is assessed - its acuity is checked. Tonometry determines the level of IOP; with the destruction of CT, it is slightly increased.
Treatment of DST
To date, there are no specific treatments for vitreous destruction. Therapeutic tactics are based on the degree of damage, or more precisely on the degree of deterioration in the quality of vision. If the destruction is partial and does not significantly impair vision function, drug treatment will be recommended, as well as correction of the patient’s lifestyle. He is instructed to streamline his work and rest schedule, and with prolonged eye strain (computer, reading, TV) to perform special eye gymnastics.
Drug treatment involves the local use of potassium iodide, which helps to resolve the obstructions floating in front of the eyes, as well as antioxidants (methylethylpyridinol), which promote better microcirculation.
The drugs Vinpocetine or Cinnarizine, which activate cerebral circulation, are prescribed internally. It is also necessary to take angioprotectors and microcirculation stimulants.
With severe degrees of DST, surgical treatment of the pathology may be required. Today, there is a method that allows the patient to be relieved of large disturbances in the field of view by precisely crushing them with a laser beam. The method is called vitreolysis and is performed using special YAG laser systems. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia with a pre-dilated pupil (Tropicamide is usually used). Vitreolysis does not affect the state of visual function and does not cause vision impairment. If collagen accumulations inside the vitreous are excessively mobile, the process of surgical intervention may be difficult.
In case of total DST with serious deterioration of vision due to interference, surgical vitrectomy is prescribed. It is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. The operation is performed using microsurgical instruments and is aimed at removing the vitreous.
Its first stage is the separation of the colloidal gel into small sections, then they are subjected to aspiration. To normalize intraocular pressure, at the next stage of the intervention, a balanced salt solution, silicone oil or gas is injected into the cavity.
Prognosis and prevention
A preventive measure for the destruction of the vitreous body is to undergo regular ophthalmological examinations, which is especially important for people in the older age group. Examinations must include mandatory ophthalmoscopy, visometry, and tonometry. It is also necessary to reduce visual stress by performing eye exercises when working with a computer or printed texts. It is recommended to review your diet in favor of fortified foods and avoid foods containing a high percentage of animal fat.
Myopic people need to have their visual acuity examined in a timely manner and have it adequately corrected. For patients with diabetes, it is better to undergo ophthalmological examinations twice a year for timely detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
If DST was identified and treated in a timely manner, the prognosis for vision is favorable. In the later stages of the disease, only surgical treatment—vitrectomy—can improve a person’s visual acuity and improve their quality of life.
The specialists of our clinic will help you undergo diagnostics to identify the destruction of the vitreous body and receive all the necessary assistance in full. The latest diagnostic equipment, modern operating rooms and the vast experience of our employees guarantee patients timely detection and successful treatment of any eye diseases.
Forecast
The prognosis for the development of the disease is favorable in most cases. Opacities stabilize relatively quickly after the onset and development of the disease. The occurrence of remissions during destructive processes is extremely rare, and floating opacities in terminal form remain in the cavity of the eyeball.
Destruction of the vitreous body of the eye, manifested in a mild form, does not have a noticeable effect on a person’s ability to work and does not cause serious complications. The development of severe forms of the disease can significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life. The constant movement of floating elements obstructs the viewing of various objects and interferes with the performance of work duties.
Due to constant visual strain in the process of viewing the environment, there is a need to clear the field of vision from existing blurring using eye and head movements. This behavior leads to constant overload of the eyes and cervical spine. As a result, a person may develop serious psychological problems and develop persistent stress or depressive conditions, which manifest themselves in the form of constant anxiety and sociopathy. However, this is not the only danger of destruction of the vitreous body of the eye. In advanced cases, there is a high probability of developing blindness.