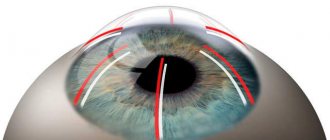
The term “biomicroscopy” should not be confused with the alarming word “biopsy”. In general, there is no need to worry in this case: biomicroscopy is one of the routine and widespread studies in ophthalmology, and it is not associated with the collection of any smears, tissue fragments, etc. This is a non-contact procedure that allows, without any intervention, to examine intraocular structures and environments at the microscopic level in their natural state and functioning.
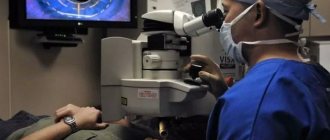
The instrument with which biomicroscopy is performed combines in its design the microscope itself and a special mode of illumination of the field under study. This device is called a “slit lamp”. Its main functionality includes:
- detailed visual examination of the eyelids and conjunctiva (mucous membrane of the eye);
- examination of the cornea, assessment of its thickness and structure, detection of possible pathological changes, clarification of their nature and location;
- examination of the anterior ocular chamber (the space between the cornea and iris) with an assessment of its depth and the condition of the intraocular fluid filling the chamber;
- detailed visual analysis of the iris;
- study of the shape, size, transparency of the lens and adjacent tissues, early diagnosis of cataract changes;
- visual examination of the vitreous substance in its anterior part, identifying areas of reduced transparency, traces of hemorrhage, signs of pigmentation, etc.
The name “slit lamp” was not given to the device by chance: the built-in light source is designed in such a way that the light flux is directed in the form of a scanning plane and allows you to examine the ocular media layer by layer. In fact, this relatively simple, in modern times, device is an optical tomograph for intravital “slice” visualization of the internal space of an organ, and the cost of a slit lamp, of course, cannot be compared with the prices of modern high-tech equipment.
Indications for examination
Biomicroscopy is prescribed for diagnosis:
- pathologies of the conjunctiva of various etiologies, incl. provoked by allergic reactions, inflammatory phenomena;
- eyelid injuries;
- inflammation, tumors of the eyelids;
- abnormal conditions of the sclera: keratitis, corneal dystrophy, etc.;
- inflammation and other pathologies of the iris;
- glaucoma;
- cataracts;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the cornea;
- endocrine diseases, due to which complications appear on the organs of vision.
This type of examination is used to monitor the effectiveness of therapy for eye diseases and preparation for surgical interventions.
Biomicroscopy can evaluate:
- health of the eyelids and conjunctival membrane;
- the condition of the cornea, its structure and thickness;
- the amount of fluid circulating in the anterior chamber of the eye;
- depth of the anterior chamber;
- transparency of the iris and lens;
- Parameters of the vitreous body - transparency, the presence of cloudy areas, blood.
The advantage of the examination is its ability to detect various eye pathologies in the early stages. The doctor can also accurately determine the degree of moisture in the eye and the amount of water in the anterior chamber, which is important for the early diagnosis of ophthalmological pathologies. During the examination, the doctor gets a clear picture of the eye.
There are practically no contraindications for the procedure. In exceptional cases, the study in question is not carried out if the patient has acute mental pathologies or aggression. Eye diagnostics are not carried out in patients who are intoxicated under the influence of drugs or alcohol. Restrictions are associated with the patient’s inability to sit motionless for a long time.
How to prepare for diagnosis
- If you wear contact lenses, you should stop using them until diagnosis and switch to wearing glasses.
- Contact lenses change the shape of the cornea, and it takes some time for it to recover.
- Stop wearing soft contact lenses 7 days before diagnosis, hard contact lenses – 3 weeks.
- During the examination, the pupils are dilated with medication (the effect of the drops lasts on average up to 20 hours). During this period, it is better to refrain from driving (due to insufficient clarity of vision and photophobia); discomfort may occur when reading.
What is the methodology based on?
This examination is performed using a slit lamp. It includes a light source, a stereoscopic microscope and a lens. The device also has a slit diaphragm, which creates the lighting slits necessary for examining the eye.
The body of a special microscope has a device that allows you to magnify the image several tens of times. Above the microscope there is a negative lens of 60 diopters, which allows you to examine the fundus of the eye. Diagnostics of the organ of vision is carried out in complete darkness. This is the only way to create the necessary contrast between the bright lamp and the darkened areas of the eye.
By focusing the light, the doctor is able to see all surfaces of the organ of vision and its structures. When an inflammatory process or clouding is detected, the ophthalmologist sees the depth and localization of the changed area.
If light is focused onto the lens of the eye, the lens, the ophthalmologist sees a biconvex body. It may contain pathological stripes and opacities, which indicate the development of the initial stage of cataracts.
An ophthalmologist also has the opportunity to study the retina, the optic nerve head. Diagnostics of the vitreous allows one to detect characteristic symptoms of inflammatory processes in the eyeball. Biomicroscopy allows you to characterize the condition of the iris and conjunctiva.
Advantages of biomicroscopy:
- non-contact examination;
- accuracy of the results obtained;
- the ability to examine the eye at different depths;
- efficiency;
- possibility of conducting research on an outpatient basis:
- low cost;
- almost complete absence of restrictions;
- can be performed for any eye pathology.
Slit lamp: design features
This is a device designed to perform eye biomicroscopy. Sometimes ophthalmic equipment is connected to a digital camera. Adapters are used for this purpose. Doctors receive high quality images. Documentation and storage of information obtained during the examination of the patient is carried out using software.
The device is installed on a special table or on the ophthalmologist’s workstation. The slit lamp is attached to the surface with screws. Modern manufacturers develop devices that are characterized by precise functioning of mechanical elements. The use of high-quality optical systems is an important advantage. Doctors perform a thorough examination of the visible parts of the eye. They analyze the data obtained and make a diagnosis.
Ophthalmic equipment has a thoughtful design. Controlling the lighting and setting the necessary settings is done with one hand. Using a special handle, the lamp moves in the desired direction and is fixed in a certain position. For convenience, some models have “extended focus”. This is an ideal option for doctors who wear glasses.
The slit lamp is a useful ophthalmic instrument designed for detailed examination of the structure of the eyes. To ensure the best visualization, the device is equipped with a variety of filters: red, cobalt blue, neutral, heat-absorbing. With the help of some, the vascular system is better studied, while others - the cornea.
The slit lamp contains the following elements:
- binocular microscope is a device for obtaining magnified images of small objects. It allows a specialist to examine the structure of three-dimensional structures of the organ of vision.
- lighting system – LED or halogen lamps are used
- adjustable face supports – ensures patient comfort
- additional components: barrier filter, beam splitter, inclined prism head
To solve a wide range of problems, slit lamps are combined with other devices. For example, this could be an applanation tonometer designed to measure intraocular pressure. It is equipped with a digital display, thanks to which the doctor receives readings even in poorly lit rooms. It is possible to use a gonioscope. This is a device for determining the form of glaucoma. Additional accessories include patient head rests, fixation marks, eyepieces of different magnifications, and light-emitting elements.
To ensure efficient work of specialists, clinics are equipped with high-quality equipment. In ophthalmology offices, a slit lamp from well-known brands is installed. The production of devices for eye examination is carried out by Inami (Japan), Keeler (UK), Quantel Medical (France).
- Devices from leading brands have many advantages:
- high-quality optics – high resolution and good light transmission are ensured. Real colors are not distorted, detail is not compromised
- Stylish design design – ophthalmological devices fit harmoniously into the surrounding space
- reliability – high-quality materials and components are used
- Wide range of slit adjustment is an important feature that increases the capabilities of doctors
- long service life - devices are used for many years
Using a slit lamp, the condition of the eye structures is assessed. Thanks to the use of a powerful directed beam of light and a binocular microscope, disorders and pathological processes are detected. The doctor changes the width, length and intensity of the light beam. The beam can narrow to a small point. This ensures a high-quality examination of the organ of vision.
Types of biomicroscopy
There are different types of eye biomicroscopy depending on the combination of lighting options:
- with direct focused light - in order to study the transparency of the optical medium of the organ of vision and identify areas of turbidity in it;
- with reflected light - to detect edema and the presence of foreign bodies;
- with indirect focused light - for detailed detection of changes;
- indirect diaphonoscopic examination is used to detect the exact location of pathological disorders in the structures of the eyeball.
Carrying out biomicroscopy
When performing eye biomicroscopy, the patient should sit opposite the ophthalmologist and place his chin on a fixed stand in the ophthalmological lamp. This device creates a narrow beam of light that hits the eye directly.
If it is necessary to examine the vitreous body, a small amount of solution is instilled into the eye to increase the diameter of the pupil. In most cases, Tropicamide is used for this.
When examining the integrity of the cornea, a dye is injected into the eye. It interacts with the tissues of the eye and is then washed off. If there are affected areas of the eye, then particles of the coloring substance remain on them.
During an eye examination, the doctor turns off the light in a dark room. After this, he sits opposite the patient on the side of the ophthalmic lamp. During the procedure, the brightness of the light directed into the eyes is adjusted so that all affected areas can be covered.
The patient must remain motionless during the diagnostic process. As much as possible, he should refrain from blinking or do so less frequently. If it is impossible to maintain a certain position of the eyes, anesthetic drops are instilled into them.
The duration of biomicroscopy of the anterior segment of the eye takes no more than 10 minutes. After this, the person does not need restorative measures. Any side effects from drugs that are instilled into the eyes have a short-term effect.
For children under three years of age, the eye biomicroscopy procedure is performed only in a supine position. Drugs are instilled into the eyes to reduce the sensitivity of the cornea.
Decoding the results
After completing the diagnostic measures, depending on the readings of the diagnostic device, the doctor assesses the condition of the eye, and if pathology is present, he draws up a general picture of the examination.
In glaucoma, the central zone of the cornea is slightly clouded due to the presence of proteins (proteins) on its surface. An expansion of the scleral openings and a pronounced increase in the choroid are detected.
With cataracts, clouding of the peripheral areas is detected. The size of the optical section of the eye is significantly reduced. So-called watery cracks appear. If the doctor is dealing with advanced cataracts, then the beam is completely reflected from the affected lens, since the latter does not completely transmit light.
If there are foreign particles in the eyes, the blood vessels in the eye dilate significantly. Foreign bodies are detected in the eyes as yellowish dots. The procedure helps determine the depth of the foreign body.
With keratitis, proliferation of blood vessels occurs. There are small blisters on the outer layer of the cornea. If purulent inflammation occurs, then there is a defect in the central part of the stratum corneum. In advanced cases, an ulcer appears at the site of the defect.
If an ulcer appears in the thickness of the iris, this indicates the development of the congenital disease coloboma. When tumors occur, adjacent structures in the eyes become displaced. Proliferation of the choroid is detected.
What the doctor sees (signs)
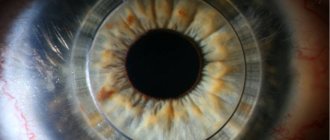
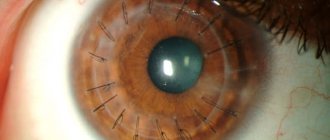
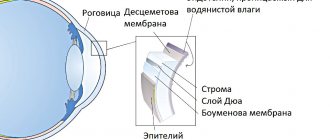
The main signs of the disease are a change in the profile of the cornea (its protrusion), Vogt's striae (stripes under Descemet's membrane - visible nerve endings) and Fleischner's ring (an accumulation of the dark yellow pigment hemosiderin in the form of a ring at the base of the cone, in the deep layers of the epithelium).
Fig. 2 Visual signs of keratoconus: Vogt’s striae and Fleischner’s ring
The disadvantage of such diagnostics is that visible changes appear only at stages 3-4, and in the initial stages they go unnoticed and the patient not only does not receive the necessary treatment, but can also undergo laser vision correction.
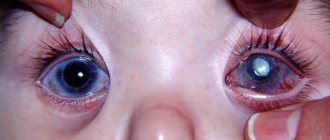
In the terminal stages, you can see opacities of the cornea at the apex of the cone, a cone-shaped change in the shape of the cornea (even with the naked eye!) and swelling of the cornea in acute keratoconus (hydropsus) - Fig. 3.
Fig. 3 Appearance of the cornea with keratoconus
Useful video
More useful information about ophthalmoscopy can be found in these videos:
Biomicroscopy is an examination that allows you to detect various eye pathologies. It is painless, highly informative and has no side effects.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2029
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.