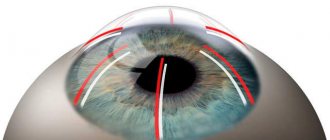
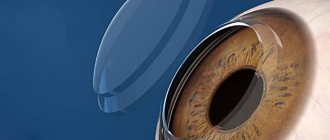
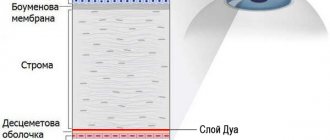
Keratoplasty is a surgical intervention on the cornea, consisting of its complete or partial replacement. The indication for surgery is the need to change the shape, correct the corneal surface or restore function (transparency). Most often, corneal defects are acquired, resulting from injuries or previous ophthalmological diseases. This treatment technique involves replacing parts of the cornea with a donor or artificial implant. The transplanted area can be transplanted to the anterior surface, posterior fornix, or into the thickness of the cornea.
A direct indication for this type of ophthalmic surgery is keratoconus in an advanced stage. The effectiveness of keratoplasty has also been confirmed in the following clinical situations:
- the presence of dystrophic or burn corneal cataract;
- corneal dystrophy of any etiology (congenital or acquired);
- the presence of scars on the surface of the cornea (as a result of injuries, inflammatory diseases or after surgical treatment);
- Defects of the cornea of a traumatic nature, leading to the destruction of its parts or loss of function.
Artificial biocompatible materials are recognized as the most affordable, safe and physiological transplants today. In our medical center, patients undergoing keratoplasty are offered the latest achievement - “Corneal graft”. This unique material is developed taking into account the principles of safety, biocompatibility and resistance to environmental factors in which it will take root and function. Unlike materials of previous generations, the Corneal Transplant biomaterial is not subject to turbidity. Thorough numerous studies confirm its bacteriological and virological resistance. In addition, studies of the endothelial cell layer make it possible to predict the survival rate and further viability of implanted petals. The introduction of grafts of this class has significantly increased the success of surgical treatment for keratoconus, and also made surgical treatment predictable for a number of other corneal pathologies.
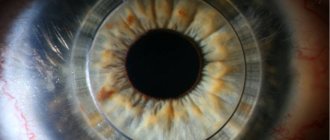
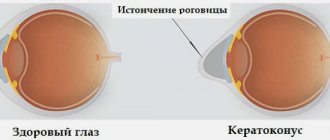
What is keratoconus
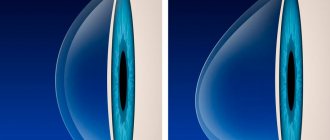
When the disease occurs, pathological changes occur in the tissues of the cornea; under their influence, it becomes thinner, ceases to maintain its normal spherical shape and moves forward in the form of a cone.
The first signs of the disease are recorded in adolescents under 16 years of age; in rare cases, the disease first appears after 25 years of age. There was no dependence on race or gender; among elderly patients of the ophthalmologist, practically no pathology was detected.
Corneal deformation in keratoconus is associated with many biochemical changes. The disease is characterized by a decrease in the production of collagen and total protein, enzyme deficiency is recorded, and antioxidant activity decreases. Under the influence of all these changes, the cornea loses elasticity and is easily stretched, as a result of which it takes on a cone-shaped shape.
The disease is dangerous due to decreased vision and the development of astigmatism. And although retinal dystrophy never leads to complete loss of vision, it can worsen it so much that a person will have to give up his usual activities.
Objectives of keratoplasty
The main goal of surgical treatment for keratoconus is to improve visual acuity by restoring the shape of the cornea. The operation allows you to stop or significantly slow down the progression of the pathology. Keratoplasty is also indicated in the following clinical situations requiring correction of the shape of the cornea:
- severe burns of the cornea (surgical treatment is most effective in case of fresh burns);
- tumors of the cornea, sclera, limbus;
- corneal ulcers;
- keratitis;
- deep dystrophic changes in the cornea;
- pterygium;
- perforations and fistulas of the cornea;
- epithelial cysts of the anterior chamber of the eye.
Keratoplasty is also performed to improve the appearance and reconstruction of the cornea. Surgical treatment is equally effective both for congenital defects and for eliminating the consequences of injuries and diseases that have caused deformation of the cornea.
Causes
A certain role among the causes of the disease is given to hereditary fermentopathy, which begins to progress under the influence of hormonal changes that occur in adolescence. The disease is often detected in members of the same family, identical twins.
The disease often occurs with diseases such as:
- Down syndrome.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Hay fever.
- Eczema.
- Addison's disease.
- Keratoconjunctivitis.
Read on for a color perception test. Find out if you are a color person?
In the news (link) treatment at home for Iridocyclitis.
Reviews about hypromellose! https://moezrenie.com/lechenie/kapli-dlya-glaz/gipromelloza-protektor-epiteliya-rogovitsy.html
Ultraviolet irradiation, dusty air, and radiation doses contribute to thinning of the cornea. The progression of the disease is facilitated by microtraumas and mechanical friction of the eyes.
Causes of keratoconus
To date, the reliable causes of ocular keratoconus are unknown to medical scientists. There are several theories based on research data. However, none of them fully explains the reasons for the triggering of pathological changes. Most likely, in reality there is a combination of several causal factors.
The following factors play a role in the occurrence of ocular keratoconus:
- Genetic predisposition. Sometimes this disease is indeed inherited, and cases of conical corneal deformation are much more common in certain families. According to the latest information, the probability that the pathology will be inherited is 1:10. However, most patients with keratoconus do not have a family history of keratoconus. There are frequent cases of keratoconus in patients with congenital genetic diseases - Down syndrome, Eulers-Danlos syndrome, Leber congenital amaurosis.
- Some researchers believe that poorly fitted and even minimally traumatic contact lenses for the cornea can cause conical deformation of the cornea. This theory does not yet have a sufficient evidence base and is debatable.
- Allergic factor. The number of people with various atopic changes is higher among patients with keratoconus than in the general population. Itching, redness and irritation in the eye area cause additional trauma to the cornea. This theory also does not have a full-fledged evidence base.
- Oxidative stress. Some studies indicate abnormally high levels of superoxide radicals in the cornea affected by keratoconus, as well as the involvement of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of the disease. Like any other part of the body, the cornea produces potentially harmful metabolic products. Normally, there is a defense system that neutralizes these free radicals so that they do not damage the collagen fibers. The cornea with keratoconus cannot independently eliminate free radicals, which leads to further structural damage.
- Another hypothesis indicates the involvement of the endocrine system in the pathological process, in particular, during hormonal changes during puberty.
Symptoms
Due to the fact that in the early stages, keratoconus is similar in symptoms to other eye diseases, the diagnosis is rarely made immediately. A doctor may suspect a disease even when it is impossible to achieve clear vision when using corrective glasses and lenses.
The disease is characterized by a number of specific signs, so a thorough history taking of the patient is a prerequisite for examination.
At the beginning of the pathological process, the patient complains of:
- Blurred image - when looking at an object, it appears to have many contours. Testing this sign is not difficult - the patient is given a black sheet of paper with a white dot on it. With keratoconus, a person will see several randomly located points instead of one.
- Doubling of objects, distortion of the shape of letters when reading.
- Light scattering around light sources.
- In the later stages, photophobia and constant eye fatigue occur.
Signs of vision deterioration are first determined in one eye, then recorded in the other. In the early stages, all signs of pathology are recorded only during twilight and night hours, then the patient begins to see poorly during the day. In the later stages, the elongated, cone-shaped shape of the cornea is noticeable to both others and the patient himself.
In most patients, the disease progresses slowly, with changes observed over 10 years or more. In half of the patients, dystrophic changes stop at an early stage, and the disease enters the stage of long-term remission.
Sometimes the progression of dystrophic changes and stretching of the cornea leads to its complete thinning and rupture. The complication is characterized by corneal edema and severe pain. The acute stage can last up to three weeks, then scars form on the cornea, and vision partially improves.
How is keratoplasty performed in our ophthalmology center?
The Moscow Ophthalmological Center offers treatment of keratoconus and other corneal diseases using keratoplasty (penetrating and anterior layer-by-layer). The operation is performed by ophthalmological surgeons with professorial titles.
At the first stage of surgical treatment, a micro-instrument and a femtosecond laser are used, with the help of which the doctor creates a corneal flap. The damaged area is separated from the cornea, and then a “corneal graft” of the desired shape and size is placed in its place. The implant is secured with a special suture material on the peripheral part of the cornea. At the end of all surgical procedures, a sterile bandage or a special protective lens is applied to the eye.
Keratoplasty in our clinic is performed on an outpatient basis on a one-day basis. The patient does not need to stay in the clinic, since in most cases the operation is performed under local anesthesia. If desired or medically indicated, general anesthesia may be used. The doctor performs a follow-up examination after the operation. The decision to go home is made together with the patient. If the patient feels unsure, he can stay overnight or several days in the hospital under the supervision of qualified staff.
Keratoplasty is an operation with a long recovery period. Only after 6-12 months are the stitches removed. For a whole year, you must follow the instructions of the ophthalmic surgeon and attend regular appointments. The structural features of the cornea require compliance with a number of restrictions after surgery and monitoring the dynamics of recovery. During this period, heavy physical activity should be avoided. The surgeon gives additional recommendations after the operation on an individual basis. In the same way, gradually, based on the results of dynamic observation at the next appointment, the ophthalmologist removes certain restrictions, including those related to visual load.
Stages
It is customary to classify the disease into several stages; ophthalmologists often use the Amsler classification.
- Identified astigmatism can be corrected using cylindrical lenses. Visual acuity is 1,0-0,5.
- Astigmatism is more pronounced, but can also be corrected. Vision within 0,4 – 0,1.
- The cornea becomes thinner and noticeably stretches. Vision is within 0.12-0.02 , correction is possible only with the use of hard lenses.
- The cornea takes on a cone shape, vision is 0.02-0.01 , and practically cannot be corrected. Complete opacity of the cornea is revealed.
Treatment and diagnosis
If there is suspicion, in addition to taking an anamnesis, specific diagnostics are carried out:
- Refractometry.
- Skiascopy reveals the “scissors effect” characteristic of keratoconus - a beam of light is perceived by the patient as the movement of two scissor blades.
- Corneal topography is considered one of the most accurate diagnostic methods.
Keratoconus must be differentiated from other ophthalmological diseases that have similar symptoms. After all the examinations, the doctor decides on conservative or surgical treatment.
Correction of the identified changes is carried out by wearing semi-rigid lenses, designed in such a way that their central part has a rigid base, and the edges are made of soft material. Such lenses allow you to press the cornea, giving it a normal position.
Additional treatment is the prescription of vitamin therapy, antioxidants, immunomodulators, and eye drops. The use of magnetic therapy and phonophoresis with tocopherol is effective.
As the disease progresses, implantation of corneal rings is used to stabilize the condition of the cornea. Surgical operations for the disease also include keratoplasty - transplantation of a donor's cornea. The operation allows almost all patients to achieve 100% return of vision.
Cost of the operation
Keratoplasty using a donor cornea is performed in exceptional cases. Leading vision care centers also perform other equally effective surgical interventions.
- PRK+FTK – excimer laser procedure is performed in the initial stages. Its implementation makes it possible to stop degenerative changes and reduces the likelihood of developing indications for penetrating keratoplasty. PRK+FTC improves vision and reduces astigmatism. The cost is approximately 30,000 rubles per eye.
- Crosslinking is an operation aimed at increasing the strength of the cornea. The manipulation consists of removing the surface epithelium of the cornea, followed by instillation of riboflavin and irradiation with UV rays. After the procedure, the patient can wear regular glasses or soft lenses. The cost of the procedure is from 30,000 rubles .
- Keraring is the implantation of half rings that allow the cone-shaped stretching of the cornea to be corrected. After kerraring, visual function improves, astigmatism decreases, and lens selection becomes easier. The cost of the operation is within 35 thousand rubles without the cost of half rings.
Please note - Balarpan eye drops. Detailed description of the drug.
In the article (link) Arutimol eye drops.
Instructions for oxolinic ointment!
Where is the best place to have surgery?
Surgeries related to the eyes should be performed only in trusted clinics that have been treating keratoconus for several years. Before choosing a technique, the doctor must fully explain the pros and cons; in some cases, surgery is not advisable.
In Moscow, the disease is treated at the Eye Surgery Center, at the New Look and Excimer clinics. Before performing an operation, it is advisable to communicate with real patients, this will help to evaluate the quality of medical care.
Treatment at home
Home remedies for keratoconus are not effective. The patient can only minimize degenerative changes by wearing contact devices prescribed by the doctor. An ophthalmologist may recommend the use of biostimulants and immunomodulatory drugs.
Patients with keratoconus should refrain from scratching their eyes, as this further contributes to the thinning of the cornea.
What drops are prescribed?
For this disease, Taufon eye drops are usually prescribed. These drops prevent the development of the disease in question and improve eye nutrition. The drops stimulate energy and recovery processes, replenish the natural deficiency of taurine, and also normalize the functions of the cell membranes of the eye tissues.
In addition, Aisotin may be prescribed for this disease. These drops have a complex of natural origin. Aisotin is a general strengthening and restorative agent used to restore visual acuity.
You should take 1-2 drops 3 times a day, but for prevention purposes, you should instill 1 drop before going to bed. The drug has no contraindications, overdose, or side effects.
Prices for surgery for a diagnosis of keratoconus
Below we present the basic cost of operations; the exact cost of treatment can only be determined during a face-to-face consultation with a specialist.
- Corneal crosslinking - 34,000 rubles
- Implantation of stromal segments (with femtosecond support) - 100,000 rubles
- Phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) - 80,000 rubles
- Installation of intraocular posterior chamber phakic lenses ICL - from 180,000 to 200,000 rubles
- Penetrating or layered keratoplasty (including transplant) - from 300,000 to 600,000 rubles
The material was prepared by an ophthalmologist: Sagonenko Dmitry Alekseevich
You can ask clarifying questions and make an appointment at our clinic online or by phone in Moscow: Diagnosis and surgical treatment of keratoconus Selection of hard scleral contact lenses.
Prevention
Carrying out general strengthening actions not only helps stop the progression of the disease, but also prevents its occurrence. It is best to replace lenses designed to improve vision with regular glasses. This step will reduce the damage occurring in the eye several times.
To relieve itching, burning or increased fatigue of the eyes, you need to rinse and make compresses from herbs such as chamomile and sage. Additionally, these herbs should be taken internally as tea. Such prevention will have an immunocorrective effect on the human body. For these purposes, you can also use a decoction prepared from echinacea leaves.
Attention! Only use herbs that you are not allergic to.