What kind of vision does a newborn baby have?
In a baby up to one year old, vision, like the eyeball itself, is just developing. During the first check, maternity hospital doctors make sure that the pupil reacts to light. It is impossible to understand in more detail what kind of vision a newborn child has. The eyes of a newborn are not able to perceive the picture fully. The baby does not see objects, their shapes and sizes. All he can notice are dark and light spots.
At one month, the baby's eyes begin to focus on objects.
At two or three, he is already following moving objects.
With each month, vision improves, the baby distinguishes between people and recognizes relatives. The structure of a child's eyeballs changes over time. In the first days of life they have a slightly shortened shape, but then lengthen. In newborns, light rays are focused not on the retina, as in adults, but behind it. Because of this, all infants are farsighted - the closer the object, the worse they see it.
Losing course
What is strabismus? This is the name given to the deviation of one of the eyes from the joint point of fixation. In addition to a very psychologically unpleasant cosmetic defect, strabismus is the cause of serious disorders. First of all, we are talking about a disorder of binocular vision - the ability to merge images obtained on the retinas of two eyes into a single visual image. In addition, the child's visual acuity decreases.
Strabismus occurs in 2-3% of children and usually occurs between the ages of 1 and 3 years. Often, worried mothers at a doctor's appointment say that the deviation of the eye occurred because the child was scared, fell and hurt his head, or after an illness with a high fever. However, it is worth understanding that all this does not relate to the real causes of the disease - most children fall and get sick, but they do not develop strabismus. Most likely, the circumstances described above simply serve as a trigger for the appearance of deviations.
Vision in children aged 1 year: normal and abnormal
By the first birthday, farsightedness weakens significantly, but does not go away completely. Your baby may be able to walk or crawl confidently, but if he still bumps into things, there is no need to worry, this is normal vision for children his age.
Normal vision in 1-year-old children allows them to distinguish the shapes and colors of objects, but they do not recognize sizes well. You should suspect a visual impairment if the baby does not recognize relatives when they are silent. Perhaps he distinguishes them from strangers only by their voice, which indicates poor eyesight.
By the age of two, the child recognizes the distance from himself to surrounding objects, which allows him to move more or less freely. The baby can notice and copy the facial expressions and gestures of his parents. However, visual acuity usually does not exceed 0.3-0.5 (the norm for an adult is 1.0).
Where and when?
Remember that treatment for strabismus may take several years. For preschoolers, it is carried out in specialized kindergartens, where the children’s stay is organized according to the principle “while playing, we are treated.” In addition, children can receive help in inter-district vision care offices. There are also a number of eye resorts. As for operations, they are performed in eye clinics. After entering school, the child can continue treatment in the vision care office. However, maximum efforts to get rid of strabismus should still be concentrated on preschool age.
Normal vision for a 3 year old child
Physiological farsightedness in three-year-olds either disappears completely or appears slightly. The final formation of the eye is completed at three to five years. They acquire normal parameters in proportion to the size of the head and the whole body.
Normal vision for a 3-year-old child is the ability to distinguish all surrounding objects and evaluate sizes. At this age, it is extremely important to understand whether his vision is developed. The fact is that at three years old a kindergartener already evaluates and describes objects, events, and impressions. If he does not see the world around him, he has nothing to describe. This also negatively affects the further development of speech, thinking, and logic.
Diagnosis is carried out using the Orlova table. Instead of letters, there are simple pictures in it. The verification algorithm is as follows:
- print the table on a printer;
- hang on the wall at children's eye level;
- place the child in front of her at a distance of 5 meters;
- ask him to tell him what images he sees and on what line.
As a rule, tables are shown online in the required scale. Once you download them, you do not need to set the sizes. The norm is to recognize pictures on lines 7-8. It’s okay if the young patient cannot see the last line yet; the normal vision for three-year-old children allows this.
Careful inspection
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the anterior part of the eye, the refracting light of the environment and the fundus of the eye. In addition, the doctor examines visual acuity, refractive power (myopia, farsightedness or astigmatism), binocular vision, eye mobility, and the angle of strabismus. After this, the ophthalmologist develops a whole strategy of action, the ultimate goal of which is to restore binocular vision. Typically, treatment includes several stages: pleoptics, orthoptics, pre- and postoperative exercises, surgery according to indications and diploptics. Let's talk about this in more detail.
Tip 4 So that the child understands what will be required of him at the time of testing - a vision test, show him the table in advance and ask him to name what is depicted on it.
- Pleoptics is the name given to the treatment of amblyopia - decreased visual acuity. It begins with prescribing glasses for the child, usually for constant wear. They are needed so that clear images are formed on the retina of the diseased eye and it can work more actively. In addition, sometimes glasses restore symmetrical position of the eyes and help them start working together.
- In addition, pleoptics includes direct occlusion (covering the better-seeing eye), various types of glare (“lazy eye” looks at bright light), classes on special equipment with various visual loads, and medical and pedagogical exercises. We are talking about activities with mosaics, beads, modeling and weaving rugs from paper (the size of the parts of the games is selected according to the degree of vision impairment). In addition, recently new directions in the treatment of amblyopia have appeared: laser, reflexology, electrical stimulation, computer treatment, biofeedback methods, and so on.
- If, after the measures taken, vision has improved and the eyes have begun to fixate correctly, the doctor moves on to the next stage - orthoptics, that is, the development of the ability to combine two images into a single visual image under certain conditions. If the problem cannot be solved with the help of orthoptics, surgery is prescribed. Its goal is to achieve correct eye position. The optimal period for surgical intervention is 4-5 years.
- The final stage of treatment is diploptics - the development of binocular vision in natural conditions: the patient “works” with one object common to both eyes, as happens in real life. Diploptics is prescribed if the position of the eye has become symmetrical or close to it.
Attention! If you notice one or more of the following signs: wandering eyes, involuntary eye movements (scientifically called nystagmus), photophobia, swelling or clouding of the cornea, a white-gray rather than black area of the pupil, consult a doctor immediately!
Vision of children from three to seven years old
At this age, the eyes are exposed to stress: the child watches books and cartoons, draws, learns to read and write. Classes should be interrupted for gymnastics, walks, and socializing. Any rest for the eyes is beneficial.
The normal vision level for seven-year-old children is 1.0, the same as for an adult, but first-graders have a high risk of developing myopia due to stress during education. Therefore, schoolchildren’s vision should be checked at least twice a year. If negative symptoms are detected - four times a year.
Normal vision in school-age children
According to statistics, myopia is most often diagnosed between 7 and 10 years of age. Then the likelihood of myopia gradually decreases, but in the presence of the following factors it remains throughout life:
- constant stress on vision when reading, working at a computer and watching TV;
- hereditary predisposition;
- poor nutrition.
If one of the parents or grandparents has been diagnosed with myopia, the child is very likely to develop it. In such a situation, it is necessary to regularly check his vision at home and with an ophthalmologist. A schoolchild's diet should include healthy foods rich in vitamins, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
It is important that the diet is balanced and varied. If a child does not like certain foods and does not eat them, you should find out what beneficial substances they contain and give them in the form of dietary supplements. It is best to consult an ophthalmologist and pediatrician.
Read about vitamins for children with myopia in the article at the link.
Characteristics of children with visual impairments
Children with low vision perceive most information through hearing and touch. Their idea of the world around them differs from that of children with normal vision. Completely blind children can easily recognize different birds or different types of cars by sound, which is rarely possible for sighted children who have not been specifically taught this.
They are also better than other people at recognizing odors. Visually impaired and blind children may incorrectly perceive the speech of others and may not understand some words. The fact is that they do not compare words with real objects, actions and events, because they have not seen them.
As a result, sometimes they do not understand what is being said to them. Teaching such children requires special qualifications of the teacher. Some children have noticeable delays in height and weight, chest volume and, as a result, lungs.
In the absence of physical activity, stooping, weakening of muscles, and weakness appear. There is virtually no facial expressions or gestures. This is an approximate characteristic of children with visual impairments, but a different picture is also possible.
The real reasons
What can lead to strabismus?
- Noticeable decrease in vision in one eye. It can be associated with certain diseases or injuries, due to which the worse-seeing eye cannot work actively and deviates in one direction or another.
- The difference in the refractive power of the two eyes when images of different sizes are formed on the fundus. In some circumstances, the ability to merge visual images into a single whole is lost, and the eye, which finds itself in worse conditions, begins to squint.
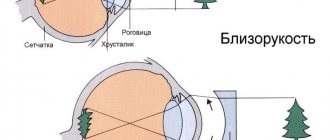
- Strabismus can occur as a result of increased (due to farsightedness) or weakened (due to myopia) accommodation - this is the name given to the eye’s adaptation to clearly seeing objects that are located at different distances from it. In the first case, convergent strabismus develops, in the second, divergent strabismus.
- Problems with the central nervous system - inflammation, trauma, tumors - can lead to strabismus.
What are they made of... The human eye is an almost perfect sphere with a diameter of about 24 mm. It consists of three membranes: outer (fibrous), middle (vascular) and inner (retina). The transparent structures of the eye include the lens, vitreous body and intraocular fluid. The fibrous membrane consists of an opaque white part - the sclera and the cornea - the front, transparent part of the outer layer of the eye. The iris, located behind the cornea, is a membrane with a hole in the center - the pupil. In bright light the pupil constricts, and in the dark it dilates to allow more light to reach the retina. Behind the iris there is an elastic, dense formation - the lens. It is transparent, has the shape of a biconvex lens and, together with the cornea, makes up the optical system of the eye. The retina lines the fundus of the eye and is part of the central nervous system. Through the cornea and lens, rays from the objects in question enter the retina and form an image on it, which is then converted into nerve impulses.
What parents need to remember
Despite all the limitations, the development of blind and visually impaired children requires regular activity: movement, sports, games and walks. Thanks to this, they develop coordination, orientation in space, and strengthen their muscles.
At the same time, overloads can also have a negative effect. An hour of walking and activity outdoors or in the gym is enough per day. It is important that every minute of his life, especially when learning something new, the child knows that there are helpers next to him. He must understand that if he moves unsuccessfully, he will be caught and stopped, and that he will not get injured. You need to choose the right toys. Let these be bright objects with different textured surfaces, different shapes and sizes.
It is good to choose toys with sound effects and music.
The psyche of a visually impaired child
Despite the presence of physical activity and the aggravation of the other five senses, the development of children with vision pathologies is slow, since the information received is still not enough. Deviations in the development of memory and attention are possible. With age, a child realizes that he is not like his peers, and often falls into a state of depression. Ridicule from peers, which, unfortunately, periodically happens in the company of children, is especially negatively perceived. At such moments, he especially needs the support of his family.
Characterized by impulsiveness, irritability, and harshness. Such children are vulnerable and perceive conflict situations painfully. The isolation of visually impaired children is explained by the fear of self-expression and new ridicule, as well as a lack of understanding of the mood of the interlocutor. Since a sick child is forced to remember information only by ear (and not by ear and visually, like healthy people), he may be forgetful and absent-minded. Knowing his own characteristics, he may consider them shortcomings and avoid society for this reason.
Visually impaired children: criteria
A child whose diagnosis does not imply improvement in vision in the near future may become disabled. The causes of visual impairment are not taken into account when registering disability. According to Federal Law 95-FZ “On Social Protection of Disabled Persons in the Russian Federation” dated February 2006, children with the following indicators become visually impaired.
- The third group - vision 0.1-0.3, visual field width 20-40 degrees, second degree of impairment.
- The second group - vision 0.05-0.1, field of vision 10-20 degrees, third degree of pathology.
- The first group is complete blindness or vision up to 0.04, field of vision up to 10 degrees, fourth degree of pathology.
Disability is assigned to people who do not have the ability to fully care for themselves, navigate in space and move around. In the future, such children often cannot obtain education and jobs that could support them. Therefore, they need a pension from the state and assistance in integrating into society.
These are rehabilitation programs for obtaining work skills from qualified teachers, communication training, psychological support, etc. In Russia, all children and adolescents under 18 years of age with the specified criteria are classified as “disabled children.” The group is assigned only upon reaching adulthood. If the normal vision of children is impaired, this cannot be ignored. The earlier a problem is diagnosed, the easier it is to fix it. Timely medical assistance and further prevention are the key to a child’s health and a full life.
Classification of farsightedness
Severity of hypermetropia in children:
- The weak stage of farsightedness is characterized by indicators up to 2 diopters inclusive - children have no symptoms due to compensation for the accommodative abilities of the visual organ. The first stage of the disease is detected during preventive examinations and can be easily corrected with the help of special eye exercises.
- Average degree of pathology (from 2.25 to 5 diopters) - the child sees poorly near, but can clearly distinguish distant objects.
- High degree of impairment (5.25 diopters and above) – vision is significantly reduced, both near and far.