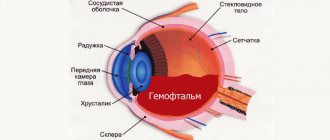
The human visual system consists of muscles, cornea, retina, and transparent body.
The lens is a biconvex lens that has an elastic shell. The beam passes through it and is focused on the retina.
The lens changes to provide better clarity of vision.
When the muscles are relaxed, the biconvex lens of the eye becomes flat in shape. When you need to look up close, the lens looks like a ball. When this process is disrupted, refractive errors occur, expressed in myopia, hypermetropia or astigmatism.
Farsightedness in children: causes? How does a child see the world with vision plus 4 and 5?
In order for an ophthalmologist to understand how to correct or completely eliminate myopia or farsightedness, he needs to know the nature of the anomaly and the causes of its occurrence. Thus, the most common causes of myopia include:
- Inherited predisposition - if at least one parent has a predisposition to this eye pathology, the risk of its occurrence in the child is very high;
- Frequent and prolonged work with objects at a distance close to the visual organs - the problem most affects people whose activities involve using a computer, drawings, sewing, etc. Also, school-age children may suffer from deviations from the visual norm, since the load on the vision occurs during the formation of the visual system;
- A weakened body - here a variety of health problems can contribute to the development of myopia. For example, mechanical injuries during childbirth, low immunity, infectious pathologies, fatigue, diabetes, problems with the cardiovascular system.
- Shape of the eyeball;
- Unfavorable working conditions (for example, poor lighting).
Ophthalmologists include the following key causes of farsightedness:
- Reduced size of the anteroposterior axis of the eyeball - deformation of the axis leads to improper refraction of light rays in the visual system;
- Age-related changes in the body - babies are already born with farsightedness, only in the process of formation of the visual system does the ability to see clearly stabilize. By the age of 25, slight deviations in vision from the norm may occur; the eye muscles and lens (natural biconvex lens) tense up and compensate for deficiencies in image perception. However, after 40-45 years, farsightedness becomes pronounced, which is associated with a change in the curvature of the lens and loss of its elasticity.
It is important to understand that the occurrence of myopia and farsightedness is possible at absolutely any age, since the human body is susceptible to the influence of its environment.
Several simple reasons lead to the occurrence of the disease:
- Hereditary genetics. Both parents suffer from myopia - the child will be born with a defect.
- Overstrain of the visual organs. Prolonged daily visual stress at close distances, insufficient poor lighting of the workplace, and incorrectly chosen posture during exercise contribute to the development of pathology. The defect is considered an occupational disease of jewelers, dentists, computer scientists, and schoolchildren.
- Late implementation of the visual correction process. Lack of correction contributes to the progression of the disease and worsening severity. Treatment started at the first signs can restore vision.
The reasons for the decrease in sharpness are: spasm of the ciliary muscle, changes in the curvature of the cornea, inadequate changes in the curvature of the lens, injuries - injury to the brain and the eye itself. No one is immune from them; most often it is an accident.
Other causes can be easily eliminated with timely treatment.
This feature is explained by the following data confirming the correct development of the visual organs. The list shows deviations in diopters that do not go beyond normal values for the corresponding age:
- 3±0.5 – immediately after birth;
- 1.15±0.15 – from one year to 2 years;
- 0.5±0.2 – three years.
In a newborn baby, the size of the eyeball along the optical axis is 17±1 mm. The shorter distance allows focusing behind the retina, which creates a blurry image of distant objects. Vision plus 3 in a child is not a pathology! By 5-6 years, the eye increases to 24±1 mm, which corresponds to the normal indicators of an adult.
Significant deviations in any direction indicate possible problems. An experienced ophthalmologist can give a qualified recommendation after diagnosis.
Experts recommend organizing an appropriate examination no later than 5-7 months of age!
According to available statistics, up to 40-60% of problems of this type are explained by hereditary factors. For genetic and some other congenital abnormalities, treatment of astigmatism in a child begins at one year of age.
Other causes of farsightedness (hypermetropia):
- poor nutrition, alcohol consumption, infectious diseases and other negative effects on the fetus during pregnancy;
- insufficient production of melanin or complete blocking of this function (albinism);
- pathological damage to the retina with a pronounced deterioration in photosensitivity;
- abnormal development of bone tissue;
- violation of the geometric parameters of the lens;
- injuries received by the child after birth;
- a tumor that changes the shape of the eyeball.
The level indicated in the title of this section is critical. Such a deviation is acceptable only in the first year after birth. However, if there is no subsequent normalization, appropriate measures should be taken. If a child has vision plus 4 or more, he will not be able to clearly distinguish objects near him. This negative situation provokes the following problems:
- rapid fatigue
- headache, allergic reactions;
- impaired perseverance;
- poor appetite.
Experts focus on the characteristics of mental development. With plus 4 vision, it is very difficult for a child to coordinate the motor skills of his fingers. Handling small objects becomes more difficult. It is impossible to correctly repeat the actions of adults, which slows down the development of new skills.
As compensation, the speech apparatus is actively developing. However, harmonious development is blocked by the lack of joint actions with objects. Exploration of the world around us slows down. Associative connections are not formed quickly enough.
We should not forget that in preschool age development is focused on independent activity. A child's plus 5 vision impedes movement and makes it difficult to play together and communicate with peers. At this stage, a limited supply of knowledge and mastered skills has a negative impact. Decreased social activity slows down mental development.
Separately, we can consider the process of mental operations with images. This technique allows you to perform a variety of actions with parts and objects without directly performing physical actions. However, plus 6 vision in a child does not allow one to obtain objective information about small details. Accordingly, the quality of perception of the surrounding world deteriorates.
Specialists consider the following mental characteristics that form the personality structure:
- processes – thinking, speech;
- states - emotions;
- states - character, abilities.
Vision plus 7 in a child has a strong negative impact on the positions noted in the list. With severe farsightedness, children begin to realize their differences in preschool age. Teenagers perceive this deviation as a significant physical defect. This factor is the cause of various stressful and conflict situations.
Vision plus 8 in a child is a dangerous level, indicating the presence of significant physiological abnormalities. With such a violation, objects are poorly visible not only near, but also at a distance. Contact lenses (glasses) will have to be worn constantly. A range of 6-8 diopters of farsightedness is a legal basis for exemption from military service for health reasons.
Symptoms of farsightedness in children.
Most often, children do not understand and cannot express that they see poorly. The symptoms of farsightedness are such that they do not lead parents to think about vision problems. Thus, farsightedness in children under one year of age is not expressed at all by external signs. In older children, it can result in restlessness and refusal to draw, sculpt, or do other nearby activities. Farsightedness in a 6-8 year old child can cause poor sleep, fatigue, inability to concentrate on tasks, etc. With farsightedness over 5.0 diopters, sometimes there is pain and pain in the eyes. Only regular vision diagnostics helps to distinguish physiological and pathological hyperopia (farsightedness).
Treatment of farsightedness in children at the ophthalmological clinic of Svetlana Bogacheva. Because pathological farsightedness depends on the innate structure of the eyes, the task of treatment is to choose the right glasses (correction), to cure amblyopia is to teach the eyes to look and see with glasses. Changing the structure (shape of the eye) is unlikely. Visual impairments caused by farsightedness have to be treated: strabismus, amblyopia, asthenopia, etc. The pediatric ophthalmologist prescribes a set of measures: glasses, adhesives (occlusions), hardware treatment, special gymnastics for the eyes. Glasses are prescribed for constant wear, and courses of hardware treatment are carried out 3-4 times a year.
A farsighted child without glasses experiences discomfort in all areas of life and may not be successful in school. With farsightedness of II and III degrees, a child wearing glasses can read, write, and play sports without any restrictions. It is even useful for him to use gadgets (to train his vision), unlike other children. Hypermetropia in children is a feature of the optical structure of the eye, and wearing glasses does not hinder the development of good vision in children.
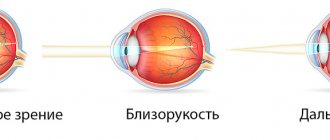
What happens to vision with myopia and farsightedness
Myopia or, as experts call it, myopia is characterized by a shift in the focus of the image not on the retina, but in front of it. It is for this reason that a person poorly recognizes objects located at distances far from him, but sees well close
In this article
located objects. In patients suffering from this anomaly, the length of the eyeball is often increased, or the cornea has greater refractive power. In the first case, such myopia is called axial, and in the second - refractive. As a rule, myopia occurs between the ages of 6 and 20, when vision is subject to heavy load in the form of reading and writing during the learning process, as well as when using a computer, gadgets, and watching TV.
Farsightedness, or hypermetropia, is a visual deviation characterized by focusing the image behind the retina. The patient has a reduced eyeball, so he sees close objects poorly, but can clearly distinguish objects in the distance.
In the presence of farsightedness, the refractive power of the eyes is rather weak; in order to focus the image on the retina, the visual muscles are forced to undergo strong tension, changing the curvature of the lens. In addition, farsightedness can be characterized, among other things, by a strong deterioration in distance vision if the disease progresses.
Complete ophthalmological examination for myopia 3-6 diopters - features
In this article
People who have never encountered eye pathology often wonder what it is, farsightedness, how it manifests itself and how a person sees when he encounters this disease. Experts give the following definition of farsightedness - it is a vision defect that is characterized by blurriness and blurred images close up, and, conversely, an excellent picture at a distance. Why is this happening? There are several reasons for this phenomenon: either the ocular axis is shortened, or the cornea has a weak refractive power.
Experts talk about three degrees of the disease depending on the number of diopters: first (up to 3), second (up to 5), third (above 5). Let's describe each in more detail. With a weak degree, there are only headaches and severe fatigue; with a moderate degree, there are difficulties when viewing or interacting with nearby objects; with a high degree of farsightedness, a fuzzy picture is observed at both distances. To determine the degree of farsightedness, you should be examined by a specialist.
As mentioned above, with farsightedness, focusing occurs not on the retina (as with healthy vision), but behind it. If a person has such a vision defect, then his eyes do not cope well with diverging rays from close objects.
For both mild and moderate and high myopia, routine examinations by an ophthalmologist are mandatory. Myopia can progress and it is very important to get timely advice and follow the instructions of a specialist.
Main stages of the examination:
- external examination - the condition of the eyelids, the symmetry of the position of the eyes, the position of the eyeball, sclera, cornea, and the width of the palpebral fissure are checked;
- vision test according to the table without eye drops and with eye drops;
- examination of the cornea, iris with a convex lens and a binocular loupe;
- studies of refraction of the eye, fundus;
- testing of visual functions, visual acuity and field of vision;
- ocular tonometry - such an examination is very important for the timely diagnosis of glaucoma.
A complete ophthalmological examination allows the doctor to see the full picture, as the condition of the retina, fundus of the eye is checked, intraocular pressure is measured, etc.
How farsightedness occurs
The main reasons are considered:
- Shortening of the eyeball, short anterior-posterior axis of the eyeball.
- Age-related changes in the structures of the eye - loss of elasticity of the lens, decrease in the contractility of the ciliary muscle.
- Insufficient curvature of the cornea, either alone or in combination with insufficient refractive power of the lens.
- Increased lens density.
- Deviation of ocular optical parameters.
- Age. After 25 years, many begin to experience malfunctions in the functioning of the visual organs; after 40, the problem becomes urgent.
- The lack of a thorough examination and adequate treatment will lead to a more complicated clinical picture.
Important! Deterioration in visual acuity can occur at any age. In addition to the listed factors, the development of myopia and hypermetropia is influenced by the environment - dry air, dust getting into the eyes.
Farsightedness in children: causes? How does a child see the world with vision plus 4 and 5?
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms and improve the physiological state of the visual organs, various physiotherapeutic technologies are used:
- massage;
- microcurrent stimulation;
- exposure to electromagnetic fields, ultrasonic vibrations, and visible radiation.
To increase the effectiveness of treating low vision in children, specialized equipment with complex characteristics is used. The modern ZEVSONIK device, for example, provides local exposure to a magnetic field and acoustic waves. Regular implementation of procedures trains muscles, reduces swelling, and improves blood circulation. After several cycles, intraocular pressure normalizes.
Glasses and lenses
For quick correction, specialized optical products are used. With a small level of farsightedness, glasses are used only for working with a tablet and computer. It is recommended to choose lightweight models with thin glasses and comfortable frames.
Contact lenses are preferred for long-term use. The use of such products does not limit freedom of movement in active games and prevents ridicule from peers. Additional benefits:
- maintaining real image proportions;
- correct assessment of the distance to objects;
- wide angle of view;
- safety;
- good compatibility with scuba diver's mask and headgear.
Laser correction
The feasibility of surgical intervention is limited to the age of 10-12 years, which is due to the natural increase in the size of the eye. Laser correction is recommended for farsightedness levels of more than 6 diopters. However, a qualified decision can only be made after a professional diagnosis. If there is no special need, the procedure is performed after reaching adulthood.
Physics will help you understand the process of pathology occurrence. A ray of light, passing through the pupil, overcomes several media: the cornea; posterior/anterior chamber of the visual organ; lens; vitreous body. And only then is it perceived by the retina.
The ability to clearly receive an image is due to the ability of the lens to change curvature. This is possible as a result of tension and relaxation of the eye muscles. If there are no deviations, the image is focused on the retina. If there are deviations, the location where the rays are collected changes.
Myopia progresses gradually. The degree of increase in diopters per year is from one and above. School-age children are susceptible to illness due to daily heavy visual stress, improper positioning at the desk, and poor lighting. There is insufficient nutrition of the eye tissues, clouding of the vitreous bodies.
One question that worries all people with myopia: can myopia turn into farsightedness? Definitely not. But hypermetropia can be added to myopia, then this is astigmatism or presbyopia.
Vision problems occur frequently in children. Until the age of 11, hypermetropia is considered an acceptable phenomenon, then it returns to normal. But when this does not happen, the child faces serious consequences. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to children’s vision.
The first signs of the disease can be detected at three months of age. They are identified during an initial examination by an ophthalmologist, who: examines the dilation of the pupils, reaction to movement, and checks the deformation of the eyeball.
The disease has a bad effect on the general condition of the baby. Headache, irritability, poor health, and loss of strength may occur. All problems are positively resolved by a visit to an ophthalmologist, a competent examination, and timely adequate treatment.
How is vision tested for myopia?
Vision is checked using tables, as well as using special equipment with preliminary eye drops of mydriatics. Children with a small margin of farsightedness need constant vision monitoring; they are prescribed a set of preventive measures to prevent the onset of myopia. Hardware therapy, eye gymnastics, massages, physical activity in the fresh air - all this contributes to the overall health of the body and prevents the progression of myopia.
At school age, myopia progresses in many children, since excessive visual stress and spending a long time with smartphones and tablets do not contribute to normal vision. Depending on the characteristics of the refractive error, there are several degrees of myopia.
Curvature of the natural lens in the optical system of the eyes
In order to understand what happens to a person’s vision in the process of viewing objects, it is necessary to know what processes occur in the optical system of the eyes. It consists of many interconnected elements, each of which is responsible for the refraction of light rays and their focusing.
Thus, the optical system consists of the cornea, anterior chamber, vitreous body, lens, retina and other components. When beams of light rays hit the cornea, they pass through it and then enter the anterior and posterior chambers, which are filled with fluid. After this, they reach the lens and vitreous body and are captured by the photoreceptors of the retina. On the retina, literally opposite the natural biconvex lens, there is a yellow spot where the image is focused.
It is due to the fact that the curvature of the lens changes that the picture is clear. However, the image is projected onto the grid. Deviation of at least one of the above-described elements of the visual system contributes to the development of myopia or farsightedness. It is not uncommon for a patient to experience both of these diseases at the same time.
Ophthalmologists warn that when the lens undergoes degenerative changes, which can be caused by genetic predisposition, age-related transformations, exposure to external factors and other reasons, it becomes harder and loses its elasticity.
With myopia, the curvature of the lens turns out to be extremely large in order to interact with photons that have traveled a long distance, their inertial force is weakened. While the attractive force of a natural lens with a large curvature is designed for a large inertial force of photons. This is why light rays are refracted at a larger angle than is required to hit the macula of the eye. As a result, the ability to clearly see objects in the distance decreases.
With hypermetropia, the opposite process occurs in the visual system. Thus, a weakened accommodative muscle leads to a hardening of the lens with farsightedness. In normal vision, the muscle responsible for accommodation must contract in order for the zonules of Zinn to relax and change the curvature of the lens.
If the patient is farsighted, this does not happen because the natural lens remains essentially at rest. Therefore, photons entering the visual system at close range with a large force of inertia are refracted at a smaller angle than necessary. When a person reaches the age of 60-65 years, he develops age-related farsightedness (presbyopia) and myopia at the same time, which is explained by the complete loss of elasticity lens and deterioration in the functioning of the optical system.
Diagnosis of diseases
A timely visit to a specialist will help determine the occurrence of visual pathologies. Postponing it can result in irreversible consequences. The worst thing is blindness. It is important to clearly distinguish the symptoms of each disease. Only an ophthalmologist can determine the defect and prescribe treatment.
Characteristic signs of insight are: fatigue; headache during prolonged work; objects nearby appear blurry; frequent conjunctivitis or stye. Regularly recurring symptoms listed above require immediate medical consultation using modern computer technology.
Lack of insight has its own symptoms. The main signs are: increased visual fatigue; squinting; distant objects are seen unclearly, contours are poorly visible.
Everyone can independently determine deviations. Only a specialist can carry out a complete diagnosis. Possible examinations: checking sharpness using tables, diagnosing the fundus, measuring the length of the eyeball, checking refraction. Timely examination and effective treatment give a person a chance.
Regardless of whether you have myopia or hypermetropia, you should undergo checks with an ophthalmologist twice a year to monitor the progression of the disease. Timely diagnosis will make it possible to detect dangerous diseases - cataracts, glaucoma, which are frequent companions of disorders.
Severity of myopia and hypermetropia
Every person, regardless of whether he has vision problems, should undergo routine examinations by a specialist at least once a year. And in the presence of severe myopia or farsightedness, much more often. Regular examination of the quality of vision will help to timely identify the progression of anomalies and select methods for their correction, as well as detect dangerous diseases of the visual system, for example, cataracts or glaucoma, which are often concomitant.
Presbyopia, or when the arms are not long enough
Farsightedness, which is associated with age-related changes in the accommodative apparatus of the lens, is called presbyopia. Another name for it is “short arm disease”; This humorous definition is due to the fact that the presbyope needs to move the text a significant distance from the eyes in order to read it.
As the accommodative capabilities of the lens weaken, this becomes insufficient, and the person notices that reading the small print on the medicine package, in a book, or on the phone has become a problem.
Presbyopia can be combined with myopia or farsightedness. The ophthalmologist must take this into account when selecting glasses or contact lenses.
How do diseases differ?
With myopia, a person sees objects in close proximity well. Distance vision is blurry, the whole picture is as if in a fog. If a person develops hypermetropia, then objects located far away are clearly seen. Another difference is the origin of the disease.
Myopia is caused by genetic abnormalities and is fully manifested in 12-year-old adolescents. Farsightedness is a result of age-related changes. Not everyone knows how to identify a disease or understand whether it exists at all.
To do this, you can conduct a simple experiment: try reading a book at different distances from your eyes. If the text is equally visible when moving away or zooming in, then there is no need to worry. If you can make out the words when the book is close - myopia. If it is visible only in the distance, it is farsightedness.
Methods of treatment and vision correction for plus 3 and 2
Any disease of the visual organs is a violation of the shape of the eyeball. Using medication treatment, you can achieve a short-term effect. However, as soon as you stop taking the drugs, the positive effect ends and visual clarity decreases.
Taking vitamins and special courses of eye gymnastics help cope with minor symptoms of the disease. General strengthening activities - swimming, contrast showers, massage of the collar area, also help fight pathologies. They cannot completely cure the disease.
The most effective method that can restore normal refraction is correction. It is carried out in three ways - spectacles, contact, surgical. Wearing glasses and contact lenses is prescribed at the initial stage, surgical correction is done in case of a sharp exacerbation of the disease.
Important! Timely treatment helps stop the disease process, in some cases even restore severity.
With relatively small deviations from the norm, external manifestations are weakly expressed. Vision plus 1 in children is not accompanied by significant difficulties (painful reactions). The following behavioral characteristics of a child may indicate a higher level of farsightedness:
- often closes his eyes, relieving tension and fatigue;
- performs manipulations with small objects at a great distance;
- complains of pain, dizziness, pain.
In some cases, hypermetropia provokes conjunctivitis, excessive lacrimation, and allergies.
It is not recommended to make independent decisions without consulting an ophthalmologist. It is necessary to remember that it is relatively simpler to eliminate physiological problems identified at an early stage. The critical age is 12-13 years. After this, the effectiveness of therapeutic and preventive techniques is significantly reduced.
If a child has plus 2 vision, a positive result can be obtained using special eye exercises. Also used:
- change in diet;
- hardening;
- reducing the load on the visual organs (limiting reading and computer games);
- hardware physiotherapeutic procedures.
Gymnastics
Preventive eye exercises are used to solve the following problems:
- improvement of blood circulation in the cervical spine (visual organs);
- strengthening muscle groups;
- relieving cramps and fatigue.
In practice, various gymnastics are used to improve vision:
- universal;
- for children with myopia and farsightedness;
- developed by ophthalmologists taking into account the characteristics of a particular patient.
With a small child, tasks are performed by adults to eliminate erroneous actions. The simple exercise below is performed near a window. In a standing position, the gaze is consistently transferred to the palm of an outstretched hand, a frame, a tree or another distant object on the street. The cycle is repeated at a slow pace 10-15 times.
The following complex can be used by children and adults (number of gymnastics):
- sit on a chair with a straight back, turn your head left and right simultaneously with your gaze (10-12);
- with an outstretched arm, they raise their thumb up, consistently focusing their gaze on it and a distant object in the room (8-15);
- standing, with hands behind the head, bend the spine back, lifting onto the toes, returning to the starting position (5-10);
- make a rotational movement with outstretched arms (right/left alternately), without taking your eyes off your palms (2-3 minutes);
- massage the back of the head and neck in a circular motion (1-2 minutes).
Nutritious food
For the normal functioning and development of the visual organs, optimizing the daily diet is useful. It is recommended to consume foods with a high content of vitamins A and B (1, 2, 6 and 12) and microelements. The standards established by nutritionists should not be exceeded in order to eliminate the negative effects of the active substances on the human body. Vitamin C provides a general strengthening effect.
Examples of food products:
- carrots, sorrel, apricots – A;
- bread (rye), potatoes, yeast – B1;
- cheese, nuts, apples – B2;
- cabbage, kefir – B6;
- spinach, tomatoes, lemons – C.
The most common and fairly effective ways to correct both myopia and farsightedness is wearing glasses or contact lenses. The former are a more familiar means for most; besides, the modern optical market is replete with a large number of aesthetically beautiful and fashionable frames.
As soon as you receive a prescription for glasses, having undergone a comprehensive vision diagnostics, you can begin choosing them. However, it is important to remember that frames should not only be beautiful, but also comfortable to use. That is, their size should not be too large or too small, they should not put pressure on the bridge of the nose, the areas behind the ears and temples. During the consultation, the specialist will give you a number of important recommendations or help you choose glasses on the spot.
Contact lenses are an ideal vision correction tool for people with an active lifestyle. They absolutely do not hinder movement, provide a greater viewing angle than glasses, do not fog up and are not visible on the face. Today there are a huge number of lenses that differ in material of manufacture, possible period of use, wearing mode and other parameters. Only an ophthalmologist can select them for the patient.
Myopia and farsightedness at the same time
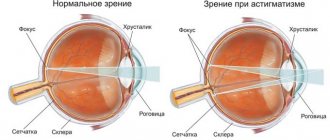
Sometimes people begin to see poorly distant and close objects. The fact is that different areas of the eye are able to capture light waves differently. It turns out that the beam is not focused at one point. This pathology is called astigmatism. It has properties that are inherent in both visual impairments.
Several factors can influence the development of the defect: the presence of congenital pathology, damage received from physical trauma, poor hygiene of the visual organs, and previous operations.
There is no clear answer whether farsightedness can turn into nearsightedness or vice versa. It is certain that pathologies can be combined. The disease manifests itself as rapid eye fatigue, blurred vision, and headache. People with mild forms do not experience any unpleasant sensations. They learn about astigmatism only after examination.
Causes of myopia and its degree
Mild refractive errors, up to 3 diopters, are classified as first degree myopia. Myopia of up to three diopters can be practically invisible if people’s activities are not related to information processing, working with small details, etc.
The danger of such a pathology is that if the disease is ignored, it continues to progress. Without taking any actions aimed at restoring normal blood circulation to the organs of vision, vitaminization, a person risks the health of his eyes. Myopia with diopters of 3 or more units, up to 6 diopters, is classified as moderate.
The second, average degree of myopia, significantly reduces the quality of life of patients, since they cannot see normally without glasses or contact lenses. This form of myopia also leads to certain restrictions, including professional activities. At this stage, diseases accompanying the main diagnosis appear. With myopia of more than 3 diopters, changes in the fundus of the eye, retinal dystrophy, etc. are often recorded.
The third degree of myopia is characterized by significant changes in the shape of the eye. Myopia of 6 or more diopters negatively affects the condition of the retina, often accompanied by astigmatism. Young men with such vision may have limited suitability for military service. If myopia is 6 or more than 12 diopters, category “D” is assigned (unfit).
Laser surgery
Myopia and farsightedness can not only be corrected, but these eye diseases can be eliminated forever with the help of laser surgery. The peculiarity of this surgical intervention is that it is very quick, painless, and the rehabilitation period is quite easily tolerated by the patient, imposing minor restrictions on him.
Myopia and farsightedness are eliminated under local anesthesia in an average of 20 minutes. The doctor's laser manipulations take no more than 1 minute. At the end of the process, the patient does not require hospitalization; after a few hours he can go home.
How to cure hypermetropia
Optical correction
The prescription for contact lenses will be different from the prescription for glasses, primarily because they must be placed directly on the eye, and not in front of it. Measuring the corneal curvature is crucial.
Like glasses, contact lenses can be bifocal or trifocal. Can change eye color if necessary. There are different types of contact lenses:
- Soft lenses: Made from a thin, flexible material that covers most of the vision, including the pupil and iris. Most SCLs are designed to be worn every day and removed before bed.
- Rigid gas permeable lenses: These are smaller than SCLs and only cover the pupil and a little of the iris. Thinner, but tough, which means they keep their shape. The permeable material allows oxygen to reach the cornea.
- Monolenses: The practice of wearing one contact lens corrected for distance vision in one eye and one corrected for intermediate or near vision in the other.
Glasses can correct almost any type of refractive error. It is recommended to use bifocals. The upper part allows you to look into the distance, the lower part allows you to look close. This is the most convenient way to correct farsightedness.
Laser correction
Laser surgery, originally developed for nearsightedness (myopia), now treats farsightedness. Patients can choose between different types of laser eye surgery to correct their vision:
- Photo-refractive keratectomy involves removing the outer layer of the cornea and then using a laser to remove a small amount of tissue underneath the surface of the cornea to reshape it. Surgery is performed under the corneal epithelium. Using special devices, the protective layer covering the cornea is removed or cleaned.
- LASIK involves making a small incision through the surface of the cornea, creating a “flap” so surgeons can reach the underlying tissue. The inner part of the corneal shell is then treated with an excimer laser and given a new shape. This procedure places the focus correctly on the retina. The flap is then closed back and the cornea heals.
- Epi LASIK is a modified version of LASIK that uses a mechanical device to remove the outer layer of the cornea. The method was developed in 2003. To carry out surgical intervention, a specially designed device is used - an epikeratome. It separates the corneal epithelium along the anatomical boundary of the layers. This procedure is considered more advanced; it eliminates the risk of flap displacement.
New improvements to these procedures are constantly being developed.
These methods are approximately equally effective in improving visual perception. Infection after surgery is possible. The first signs appear after a few days. After surgery, antibacterial eye drops are immediately prescribed.
The operations are quick and painless; there will be a slight sting for several days after the procedure.
Laser surgery is performed only on uninfected healthy eyes. These surgeries are not suitable for children and teenagers because their vision is still changing.
They don't always give the desired result. Study results vary, but most people with farsightedness who have surgery say their vision improves.
Lens replacement
This operation is performed on patients with severe refractive error. Offered to those who want to get rid of glasses and contact lenses forever. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia.
Operation process:
- A thorough diagnosis is carried out. The operation cannot be performed in the presence of infections or inflammatory diseases.
- A small incision is made on the cornea.
- The natural lens of the eye is removed using a vacuum. Only the contents are removed, the capsule remains intact.
- The artificial lens is then placed in the capsular bag. It is made of special plastic that does not age. Having installed an implant, a person will forget about means of correcting visual perception for the rest of his life.
- After installation of the intraocular lens, no sutures are required. A few hours later the patient leaves the clinic.
The procedure lasts no more than 40 minutes.
Often, replacing the lens is the patient’s only option to maintain vision. It is prescribed at a young age, when the eye is fully formed. Surgery is possible for patients over 45 years of age if there are medical indications.
The operation is performed on only one organ of vision. If intervention is indicated in the second eye, you will have to visit the ophthalmologist again. The lens on the second organ of vision is replaced no earlier than after 6 months. This is necessary so that the first eye has time to heal well.
conclusions
As we have found out, eye pathologies such as myopia and farsightedness can occur in every person, not only with an inherited predisposition, but also under the influence of external factors. To avoid serious complications, it is worth undergoing regular examinations with a specialist, monitoring the stress on the visual organs and ensuring a balanced diet, since the presence of vitamins and beneficial microelements also affects the condition of the eyes.
Signs of nearsightedness (myopia) and farsightedness occur in most people in the world. It should be remembered that these diseases can progress. Therefore, it is very important to consult an ophthalmologist when the first symptoms of vision deterioration appear. Timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment will protect the eyes from further progression of these diseases. Remember that mild myopia and hypermetropia can still be cured in the early stages of the disease.
How myopia and farsightedness occur can be read briefly at the link.
Symptoms of the presence of myopia and farsightedness at the same time
A pathology such as astigmatism can lead to both myopia and farsightedness. The cornea and lens are irregularly shaped, resulting in blurry images. Typically, astigmatism is either myopic or hypermetropic. A more rare form is mixed.
In this case, patients experience symptoms of myopia and hypermetropia simultaneously. Main signs of pathology:
- inability to see clearly both near and far;
- frequent headaches;
- discomfort in the eye area;
- the appearance of fog and veils before the eyes;
- ghosting;
- formation of spots and dots before the eyes;
- high sensitivity to light.
If such symptoms appear, you should consult an ophthalmologist. With mixed astigmatism, only an experienced doctor can select glasses or lenses. These correction methods do not eliminate the disease, but make it possible to see clearly. The mixed form can only be cured through surgery.
The simultaneous presence of myopia and hypermetropia can develop in old age. This deviation is called presbyopia and it occurs due to loss of elasticity of the lens. To correct vision, special glasses are prescribed.