Barley on the eye occurs, as a rule, due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the hair follicles of the eyelashes and lacrimal glands. Usually the abscess goes away quickly; within a few days it matures and bursts in or out. Restoration of the skin in this case does not take much time, but a complete cure usually takes about two weeks.
But sometimes the stye does not go away as quickly as we would like, so patients worry about their health and are afraid of the complications of the stye. Usually, if a stye on the eye does not go away, this indicates a decrease in immunity. This is possible in the cold season due to constant colds, vitamin deficiency, and stress. If ulcers do not go away for a long time, you need to know what to do if the styes do not go away. This will protect patients from complications of the disease.
FAQ
- What are the symptoms of stye?
The first signs of a stye include pain, redness, swelling and tenderness. After these symptoms appear, a small pimple appears in the affected area. This is usually accompanied by puffy eyes. Sometimes it's just the affected area itself that swells; in other cases, the entire eyelid swells.
- Does stye affect vision?
Barley does not affect a person’s ability to see, visual acuity or the health of the eyeball.
- What causes a stye?
Barley is caused by staphylococcal bacteria. This bacteria is found in the nose and is easily transferred to the eyes when a person first rubs the nose and then the eyes.
- Is stye contagious?
Styes are contagious, but... Basically, all people have a bacterium that causes styes. All people, regardless of age, can get stye, even in the absence of external contamination.
Nevertheless. If you do develop stye, you should be careful so that the infection does not infect other people. Try to maintain personal hygiene, use separate bed linen, towels and other personal hygiene items.
- How to treat stye?
In most cases, styes heal on their own within a few days. You can stimulate this process by applying hot compresses (10 to 15 minutes), three or four times a day, for several days.
This will greatly relieve the pain caused by stye. In most cases, the stye will rupture, dry out, and heal without further intervention.
- Is it possible to pierce a stye?
Never puncture a stye. It is strongly not recommended to pierce a stye, because it is not a pimple. Do not touch the stye until it bursts on its own.
A stye that forms inside the eyelid (the so-called internal stye) does not rupture and does not heal on its own. Since this type of stye can be more serious, it is best to see a doctor to clean the affected area.
If you get stye very often, your doctor may prescribe a special antibiotic ointment that will prevent further stye. Your doctor may also recommend wiping your eyes with moisturizing wipes to reduce the risk of developing styes and blepharitis.
- What other eye problems can accompany styes?
With barley, tearing of the eyes often occurs, photosensitivity increases, and there is a feeling as if a foreign object has entered the eye.
What to do if stye on the eye does not go away for a long time? –
Stye is one of the most common ophthalmological diseases. If the immune system malfunctions, it is very difficult to get rid of the disease. As a rule, the pathology disappears without a trace seven days after the start of therapy. But what to do if the stye on the eye does not go away for a long time? It is important to identify the cause that provoked the development of the pathology and first of all eliminate it.
Stages of the disease
The inflammatory disease goes through several stages before the patient recovers:
- The first stage is redness of the eyelid and slight swelling. A person experiences virtually no pain or discomfort, but the affected area begins to itch very much;
- After a day or two, a head forms, containing purulent exudate. Pain occurs when pressing on the upper or lower eyelid. Characteristic signs are increased redness and hyperthermia;
- The last stage is the breakthrough of the abscess. The patient experiences relief almost immediately.
Thus, the illness lasts from three to five days. However, in some cases the pathology is prolonged or accompanied by regular relapses.
Cause of occurrence
The main factor provoking the development of an unpleasant disease is a staphylococcal infection. Harmful microorganisms penetrate the visual apparatus if personal hygiene rules are not observed. As a result, Staphylococcus aureus enters the sebaceous gland or hair follicle. Another common cause of the abnormality is a malfunction of the immune system.
Most often, barley appears after the following diseases:
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- Increased blood sugar levels;
- Failure in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- Prolonged stress;
- Vitamin deficiency and lack of nutrients;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Infection with worms.
| Remember that barley is not a contagious pathology. It is not transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person. |
Symptoms
At the initial stage, the disease manifests itself as redness and swelling of the eyelid. The patient may experience pain, discomfort, and burning. Symptoms of the pathology also include:
- An increase in the size of the lymph nodes;
- Redness of the mucous membrane of the eye;
- Migraine;
- Temperature increase.
If additional warning signs appear, consult your doctor immediately.
| As the disease progresses, an abscess appears at the site of the edema. It may resolve or break through. Such a manifestation signals that inflammatory processes in the visual apparatus continue to develop. |
Stye or chalazion?
If the inflammation does not cause pain, but persists for a long time, perhaps another disease is hidden under the mask of barley - chalazion.
Only an ophthalmologist can make an accurate diagnosis. Most often, the anomaly develops against the background of barley, as a complication.
For this reason, the patient does not even suspect that he is developing another pathology; he is sure that the abscess simply cannot break through for a long time.
At the first stage, physical therapy and medications are sufficient to eliminate the chalazion. But if the disease is advanced, then such measures will not bring the expected result. In this case, a drug is injected into the tumor to cause its resorption.
Sometimes doctors recommend surgery. This is required if the size of the chalazion exceeds six millimeters. The procedure lasts a maximum of ten minutes and does not pose any danger to human health.
Treatment
To speed up the recovery process, it is necessary to select an effective therapeutic program. If possible, the fight against the disease begins immediately after the first symptoms appear. Styes are often confused with abnormalities such as chalazion or demodex. If the pathology is incorrectly identified, the treatment will not work.
For this reason, it is recommended to contact an experienced ophthalmologist, who, after a visual examination, will make an accurate diagnosis and formulate a course of treatment. The first measure to combat the anomaly is the use of antibacterial drugs. If they do not produce results, another tactic is selected.
Most often, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- "Tobrex". The drops contain tobramycin. Effectively fights not only barley, but also chalazion. Can be used in children from one year of age;
- "Floxal". They have an antimicrobial effect and are suitable for newborn babies;
- "Hydrocortisone ointment." It is not recommended to use without consulting a doctor, since the ingredients include a powerful corticosteroid hormone;
- "Levomycetin", etc.
| Drops are used four times a day. Three drops into the affected eye; for a healthy eye, one drop is enough as a preventive measure. |
Physiotherapy is recommended to speed up the recovery process; ophthalmologists usually send patients to UHF. Traditional medicine recipes will be an additional assistant in the fight against barley. Most often used:
- Rinse with Furacilin solution;
- Using compresses with infusions of chamomile, sage, string, etc.;
- Applying a fabric bag filled with heated salt to the affected eyelid.
A chicken egg effectively copes with the disease. Boil it, wrap it in cloth and apply it to the affected eye. Hold until the egg has cooled. Such heating can be performed only when barley is starting. If it is ripe, the procedure is prohibited!
Reasons for the protracted course of the disease
The main factors provoking the long-term course of the pathology are:
- Malfunction of the immune system. This may be a temporary manifestation after an infectious disease. Accompanied by constant relapses of inflammation. In this case, you need to start taking immunomodulators, select a vitamin complex and adjust your lifestyle;
- The formation of a growth on the eyelid that presses on the eyeball and resembles a stye in appearance. This anomaly is called a chalazion; at the initial stage, you can get rid of it using conservative methods; in the future, only surgery will help;
- Delayed therapy. Ophthalmologists recommend starting to combat the anomaly when the primary signs appear;
- Piercing and extrusion of the head. In some cases, patients cannot wait to get rid of the “uninvited guest”, and they decide to take extreme measures without waiting for the abscess to mature. However, by doing this you will not only prolong the course of the disease, but can also worsen your health;
- Prolonged stay in unfavorable conditions (high humidity, draft);
- Inflammatory processes in the visual apparatus. In this case, you should not postpone your visit to the hospital for a long time, as the risk of complications increases.
| If the stye does not break through and the unpleasant symptoms last for more than a week, this is a good reason to visit the ophthalmologist’s office. |
In what cases is it necessary to consult a doctor?
Most often, when barley appears, they do not consider it necessary to seek medical help, since the disease is not classified as a dangerous inflammation. Usually this is true, but there are exceptions to every rule. In some situations, you cannot do without the help of a doctor.
You should contact the clinic if the following symptoms appear:
- Severe swelling of the eye, resulting in deviations in visual acuity;
- Barley appears regularly;
- The illness lasts more than five days.
Usually the inflammation subsides after four days; in the presence of a strong abscess, the recovery process can drag on for a week. If after seven days the barley does not go away, we can talk about a relapse, which signals a malfunction of the immune system.
| In this case, it is important not only to undergo a course of therapy, but also to pay attention to preventive measures. If barley persists for two months, the problem cannot be eliminated without the help of a doctor. |
If the course of the disease is favorable, the abscess breaks out on the third or fourth day. Do not open it yourself under any circumstances, you may get an infection!
Conclusion
Barley is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist or dermatologist. Frequent relapses require examination by specialized specialists. If the disease is regular, make every effort to strengthen your immune system. Barley requires complex treatment under the supervision of an ophthalmologist. If treatment is ignored, it can persist for a long time.
From the video you will learn why this pathology occurs and how to treat it correctly.
What to do if stye on the eye does not go away for a long time? Link to main publication
Source: https://zdorovoeoko.ru/bolezni/chto-delat-esli-yachmen-na-glazu-dolgo-ne-prohodit/
Diagnosis of barley
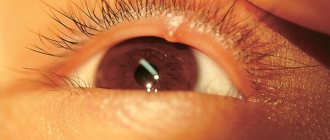
First, a small red bump appears on the eyelid, which may be slightly itchy and/or even very itchy. Over time, a small white suppuration will begin to form in the center of the redness.
Also, as a rule, with barley, the eyelid swells, in some cases it swells so much that it completely closes the eye. The swelling often lasts for several days, then the stye “explodes” and dries out on its own. Sometimes the inflammation spreads to areas of the face surrounding the eyes, in which case it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Styes can also cause tearing of the eyes with increased sensitivity to light, which is associated with swelling of the eyelid. There may also be noticeable discomfort when blinking.
Although styes are quite common and almost anyone can get them, there are a number of factors that will increase your risk of getting one:
- People with chronic diseases such as diabetes, seborrhea and blepharitis are more at risk of developing styes, as well as people with chronic degenerative diseases.
- People with high blood lipid levels are at increased risk because their oil glands are more likely to become blocked, causing styes to develop on the eyelid.
- Very often, barley develops in people exposed to constant stress, as it significantly reduces the body's natural immune defense.
- A high incidence of barley is observed in people aged 30 to 50 years.
Differential diagnosis of barley is also important. In this aspect, it is important to know the difference between a stye and a chalazion. A chalazion is similar to a stye in shape and also in that it is associated with a blockage of the sebaceous duct on the eyelid. A chalazion or meibomian cyst is a harmless slowdown in the flow of secretions, which is accompanied by chronic inflammation of the cartilage of the eyelid. A swelling appears under the skin of the eyelid, which sometimes breaks through, or a nodule the size of a millet grain to a bean seed appears in this place.
In appearance, a chalazion is usually larger than a stye, but grows more slowly and painlessly. As a rule, it is harder to the touch than barley, resembling a bone under the skin.
A chalazion (chalazion) usually goes away on its own after a month or two as the gland returns to normal function. Otherwise, if the size of the “bone” reaches 5 mm or it puts significant pressure on the eyeball, the chalazion must be removed surgically. The operation is absolutely simple and is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis - the bone is excised and all the pathological contents located in the eyelid are scraped out, then antibiotic ointment is applied to the excision site and the eye is tightly sealed with a plaster or a tight monocular bandage for several hours. After surgery, excision of the gland is not visible, because it is done from the mucous membrane, so there is no cosmetic defect left after removal of the chalazion. As a rule, the operation takes place without complications.
What to do if the stye does not go away for several months?
Barley on the eye occurs, as a rule, due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the hair follicles of the eyelashes and lacrimal glands. Usually the abscess goes away quickly; within a few days it matures and bursts in or out. Restoration of the skin in this case does not take much time, but a complete cure usually takes about two weeks.
But sometimes the stye does not go away as quickly as we would like, so patients worry about their health and are afraid of the complications of the stye. Usually, if a stye on the eye does not go away, this indicates a decrease in immunity.
This is possible in the cold season due to constant colds, vitamin deficiency, and stress. If ulcers do not go away for a long time, you need to know what to do if the styes do not go away.
This will protect patients from complications of the disease.
Causes of prolonged illness
Exacerbated chronic diseases can provoke a sharp decrease in the body's defenses. In this case, barley can last 3 weeks or even longer.
Why can’t a person get rid of barley for so long? There are the following reasons for this:
- Incorrect treatment of an abscess. This can happen if people do not seek professional help, do not know how to properly apply a compress or warm up, and treat the disease with inappropriate means that doctors prescribed once to them or their friends and relatives.
But you need to understand that in each specific case the disease develops specifically, and if earlier, for example, Erythromycin ointment helped, now it may not cope with the pathological process. If therapy is inadequate, you should not expect positive results, because such treatment will be ineffective.
It is in this case that recovery is delayed. Usually, the symptoms of such barley do not disappear, although patients should feel much better immediately after the abscess breaks out.
And in some cases, the abscess does not break out at all, sometimes increasing or decreasing in size. This is the first sign that the disease is entering a chronic stage.
- Weak immunity. If the abscess does not go away for a long time, then this is confirmation that the body’s defenses are not enough to fight the disease. Such stye usually lasts several weeks longer than usual and brings minor discomfort, which does not allow us to talk about a complete recovery.
Usually, barley with weak immunity is recurrent - it seems that the abscess has passed, the swelling has disappeared, and the redness has already become equal to the color of healthy skin, when swelling, pain and purulent contents appear again.
Such styes may not break through, but regress until almost complete recovery, then appearing again. Very often, such abscesses can plague young children - with weak immunity, stye on the eye does not go away for 2 months or more.
- Hidden diseases. Also, ulcers may not go away for a long time due to another serious disease of the body. Most often, this situation with barley is observed in diabetes mellitus and HIV infection. Usually this diagnosis can be made quite quickly when first interviewing the patient or reviewing his medical record. In the future, the doctor determines the treatment strategy for barley, taking into account the underlying pathology.
Chalazion development
Separately, it is worth highlighting the reason why barley does not go away on the eye - a complication of the pathological process. Most often, a chalazion appears against the background of barley. This is a growth about one and a half centimeters in diameter, around which healthy tissue is located. Chalazion is a chronic pathological process that provokes difficulty in the outflow of tears and secretions from the glands.
Quite often, pathological microorganisms “move” from one place to another, and a new inflammatory process begins. Since the localization most often does not change dramatically, patients think that the stye will not go away, but in fact a new disease develops.
If it is a chalazion, then most often patients do not feel any discomfort other than aesthetic. A lump the size of a pea or hailstone can become a significant cosmetic defect.
If the chalazion is large, the lump can even put pressure on the eyeball, causing even greater complications, including worsening vision.
Therefore, in severe cases, the formation is most often removed so that the disease passes without complications.
Typically treatment is carried out as follows:
- At the initial stage of the development of the disease, conservative treatment methods can be used - ointments (Vishnevsky, Hydrocortisone, Levomekol, etc.), physiotherapeutic procedures (UHF, ultraviolet irradiation).
- If the seal does not go away and becomes harder, then in this case doctors administer an injection solution (Kenalog), which promotes the resorption of the internal contents of the chalazion. Typically, this method can get rid of a seal less than five millimeters in diameter.
- If the chalazion is larger, then doctors resort to surgical intervention. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis, the patient is sent home the same day, and there are no scars left after the incision. Anesthesia is performed locally. The procedure does not pose a threat to vision, so it can be performed without fear.
When treating barley, it is important to understand that the disease requires a qualified approach, since we are talking about vision. If the stye does not go away for a long time, it means that the means used were ineffective.
The pathological process must be eliminated correctly and in a timely manner. Therefore, if barley does not go away for several months or appears again and again, then in this case you cannot do without professional help.
Loading…
Source: https://doloypsoriaz.ru/yachmen/lechenie-05/pochemu-ne-proxodit.html
Drug treatment of barley
Apply a hot compress. Doctors recommend applying a compress for 10-15 minutes, 4-6 times a day. This will increase blood flow to the affected area and speed up the rupture and drying of the stye.
To make a compress, soak a clean towel in warm water, wring it out, then apply the compress to your closed eye and leave for 10-15 minutes until it cools, reheating the towel if necessary.
An alternative method is to wrap a towel around a hot water bottle and place it over your closed eye. This method helps keep the towel warm for a longer time.
Some people use hot tea bags as a compress. They are quite small and great at storing heat, but are no more effective than any damp cloth. Apply the compress exclusively to the closed eye.
over-the-counter pharmaceuticals We are talking about creams, ointments and wipes that help clear the eye of the infection that causes stye. Try to find products that contain polymyxin B sulfate, which is an effective antibacterial agent.
You can also use non-prescription medications to reduce pain. Conventional non-steroidal pain relievers such as ibuprofen and others can relieve the pain and inflammation caused by stye. However, always follow the instructions on the medication package.
Although it can sometimes be extremely difficult to resist the urge to pierce a stye to speed up its healing, never do it. Needling a stye can make the infection worse and may also cause it to spread to the upper/lower eyelid of the affected eye or even the other eye. Much more effective is to simply apply a hot compress.
If swelling appears. If pronounced swelling has already appeared on the eye, then all thermal procedures are contraindicated. In such cases, in order for the barley to ripen and burst, doctors advise cauterizing the site of infection with alcohol, calendula tincture or brilliant green, but when carrying out these procedures you should be extremely careful not to get the medicine on the cornea of the eye, this can cause a burn.
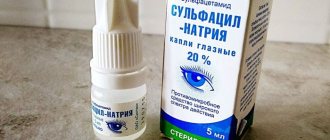
Being an infectious disease, barley is very effectively treated with antibiotics. You can use albucid (sodium sulfacyl), as well as a 0.25% solution of chloramphenicol, 1% solution of erythromycin or penicillin. If there is a risk of developing an allergic reaction, it is necessary to use drugs from a different group, for example, gentamicin. Also, if the higher price does not bother you, you can use the latest generation of drugs - Ciprolet or Tobrex (suitable for pregnant women and newborns). It is also worth noting that before starting to use antibiotics, you should consult your doctor to determine the most suitable drug, its dosage and timing of use. At night, it is recommended to use 1% tetracycline or erythromycin ointment; they are carefully placed behind the lower eyelid.
If the patient does not have an increase in body temperature, the doctor may prescribe UHF therapy (exposure to the body of a high-frequency electromagnetic field), this procedure helps to quickly cope with the disease.
Treating stye at home
Avoid makeup while you are sick. During stye, you should not use eye makeup, in particular mascara, eyeliner and shadows. This will help avoid eye irritation and reduce the chances of re-infection or worsening the disease.
Since signs of infection may appear long after the infection itself, it is best to get rid of (throw away) any makeup that was used during the suspected period of illness.
Do not wear contact lenses. During stye, you should refrain from wearing contact lenses. The fact is that contact lenses can cause additional irritation to the eyes, which will increase the pain. Instead of contact lenses, try wearing glasses for a while until the stye goes away.
Keep your hands clean. Wash your hands with unscented soap and hot water before and after touching your eyes. Touching your eyes with unwashed hands increases the risk of transmitting infection and making the disease worse.
Give your eyes a rest. It is important that your eyes get enough rest while treating styes. Try to get enough sleep at night, avoid overexertion, which puts additional stress on your eyes. If during work you have to significantly strain your eyes (working at a computer, working with small parts, welding, etc.), try to periodically close them and give them a rest.
When to seek medical help?
Be sure to consult a doctor if the stye does not dry out within 2-3 days. You should also consult a doctor if you notice signs of blurred vision or other problems.
In most cases of stye with complications, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics, for example, ointment or eye drops, which will help get rid of the infection. In particular, the doctor prescribes antibiotics when the infection becomes acute, or in cases of frequent relapses of barley.
If after a long time the stye does not show signs of healing, the doctor may resort to cutting it to remove the infection from the eye. Often, this procedure is performed in a doctor's office under local anesthesia and does not require hospitalization. If the stye affects an infant or newborn child, cutting can be done under general anesthesia with a short hospitalization period to avoid complications or re-infection of the eye.
What to do if a stye on the eye does not go away for 2 weeks or a month?
Stye is an inflammatory disease of the upper or lower eyelid, which is accompanied by itching, redness, swelling and other external signs.
In most cases, the inflammation persists for several days and goes away on its own. In some cases, the inflammatory process can continue for weeks or even months.
What are the reasons for a long breakthrough and how to speed up recovery - in this article.
If barley does not go away for several months: causes of complications
The appearance of stye means that an infection or virus has entered the hair follicle of the eyelash. The pathogen provokes swelling, redness, and soreness in the eye.
Often barley goes away on its own even without the use of medications - activated immunity leads to the destruction of the source of inflammation, the abscess breaks through and the eyelid is restored.
To speed up this process, ointments, drops and disinfectant solutions are used.
Barley that does not go away for a long time indicates the presence of negative factors that impede healing. These include:
- low protective abilities of the immune system (the body is not able to defeat the disease without help);
- prescription of ineffective therapy or its incorrect implementation;
- chronic viral or infectious diseases occurring in the body;
- hormonal imbalance;
- infection with acne gland (parasitic mite).
Let's consider how one or another of the listed circumstances prevents barley from going away quickly.
If the protective abilities of the immune system are insufficient, inflammation cannot be stopped because a sufficient number of protective cells (for example, lymphocytes) are not produced to suppress the infection.
For this reason, long healing of barley is typical for patients who have recently suffered from infectious or viral diseases, and also have chronic abnormalities. A decrease in immune abilities also occurs due to the following reasons:
- poor (unbalanced) nutrition with frequent irregularities;
- unstable and weak sleep, overwork, constant stress;
- neglect of hygiene recommendations;
- living in polluted domestic or environmental conditions;
- long-term use of medications that inhibit microflora (including those performing protective functions).
In this case, treatment of stye on the eye should be continued, combined with measures aimed at strengthening the immune barrier.
When, after making enormous efforts, the stye does not go away for 2 weeks or a month, suspicions arise that the organs of the endocrine system are not functioning properly.
First of all, such suspicions arise when the patient has problems with the thyroid gland or suffers from diabetes.
The production of hormones and enzymes is a key component of counteracting foreign microflora, including streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus.
With stable endocrine organs and strong immunity, stye should disappear from the eye within a week, maximum two. When this does not happen, doctors first of all suspect patients of an incorrect approach to treatment.
| How a frivolous approach worsens the condition of barley | ||
| Error | Hope that everything will go away on its own | An attempt to squeeze out |
| Consequences | Due to the fact that inflammation can go away on its own, many people do not perceive styes as a dangerous disease, which, at a minimum, can cause them discomfort for a long time, and at a maximum, grow into a larger inflammation affecting the tissues. Therefore, facial hygiene and consistent use of prescribed products are extremely important. | The opening of the capsule should occur after “ripening”. This way the purulent masses come out completely, and the inflamed area is washed well. If you try to squeeze out the abscess earlier, the process will continue, and perhaps worsen in an open wound. In addition, this action can provoke the appearance of new inflammatory nodes. |
What to do when a stye on the eye does not go away
If the inflammatory process persists for a long time, you cannot act independently and try self-medication. If a week, two weeks or even a month has passed, it is unlikely that you will be able to find an effective method of getting rid of severe inflammation at home.
At this time, it is important to determine exactly what causes are preventing the disease from going away and to address them in a timely manner. Therefore you need to do the following:
- Go to an ophthalmologist. Diagnosis and treatment of stye on the eye - the profile of this specialist. Only he will determine exactly how difficult the process is, what prerequisites are most likely for complications and in what order should be acted. A visit to the doctor allows him to assess the potential risk to vision caused by a stye and distinguish it from a chalazion. Based on the results of the examination, he reports which specialist should be examined to look for factors that impede recovery.
- Go to an immunologist. As mentioned above, strong immunity is the main weapon in the anti-barley arsenal. Firstly, weak protection allows more pathogens to pass through. Secondly, poor immunity often causes vision problems. Strengthened body defenses will in any case help get rid of the disease as soon as possible.
- Visit an endocrinologist if there is an assumption that prolonged inflammation is caused by endocrine disorders. To clarify the overall picture, it is necessary to undergo laboratory tests.
It is better not to put off treating styes on the eye. Even a weak inflammatory process, without meeting resistance, can grow into a strong pathology, which will take a lot of time, effort and money. Take the necessary treatment measures from the first day the disease is detected, and if there is no effect, consult a doctor for help immediately.
Did you like the post?
Rate it - click on the stars!
articles / 5.
Source: https://www.spacehealth.ru/bolezni-glaz/veki/yachmen/chto-delat-esli-yachmen-na-glazu-ne-prohodit-2-nedeli-ili-mesyats/