It is no secret that the eyes are the most important human sense organ. Any violations lead to irritation and discomfort. Especially after 60 years.
For the normal functioning of the visual organs, regular hydration is necessary. Because its absence often leads to decreased vision. It is important that normal eye pressure at 60 years of age is not impaired.
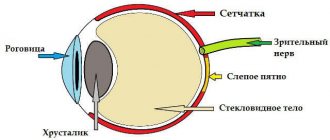
Eye pressure (OP) in medicine is called ophthalmontus. This is nutrition of the eye and maintaining the shape of the eye shell. The eye is formed by the outflow and inflow of fluids inside the eye. If their number does not correspond to the norm, then the pressure will be increased.
High and low blood pressure
The average rate of ophthalmontus is from ten to twenty millimeters of mercury. If it’s three or four marks higher, that’s also acceptable. This indicator indicates that the metabolism and microcirculation of the eye are normal and that the retina is functioning normally.
Reduced eye pressure in women after 60 occurs, but much less frequently. If treatment and prevention are not started in time at the first symptoms, glaucoma may appear. It is more difficult to get rid of and can lead to partial or complete blindness.
Correction of eye pressure is based on the use of medications. But! A positive effect will be observed only after the eye gets used to the product. Everything is individual, and even a very good product may not be right for you. Don’t worry, your doctor will definitely choose the right drug for you.
Who needs a fundus examination and in what cases?
Experts recommend undergoing a fundus examination 1-2 times a year.
And for those who have problems with visual impairment, even more often. The fact is that thanks to fundus diagnostics, it is possible to identify not only eye pathologies, but also to identify various diseases at different stages. Such timely diagnosis will allow us to identify diabetes and hypertension at the earliest stages, and begin to treat them before they cause serious harm. In case of vision problems, a fundus examination will help assess the condition of the retina and its individual structures. Thanks to this, you can monitor the dynamics of treatment and, if necessary, adjust it.
There are many categories of people who are recommended to undergo this examination:
- People with hypertension, cataracts, atherosclerosis, high renal pressure;
- Patients with category 2 diabetes, since with this disease retinal detachment often occurs, which in the absence of timely qualified assistance can lead to very unpleasant consequences;
- People with hemeralopia and color vision impairment;
- Pregnant and premature babies;
- People with high intracranial pressure;
- Persons who have suffered eye injuries, even if no problems have been identified so far.
Hypotension
It is also low pressure inside the eye. Causes:
- If your blood pressure has dropped. Studies have shown that blood pressure is closely related to blood pressure.
- Unsuccessful surgery.
- Inflammation of the eyeball. For example, iritis is inflammation of the iris.
- Injury or something getting into the eye. May contribute to eyeball atrophy.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Kidney problems and others.
Speaking of symptoms, with dehydration and an infectious nature - this is dryness in the eye, loss of pupil luster, in rare cases the main apple sinks. But it is still difficult to determine incorrect ophthalmontus, because these symptoms manifest themselves mildly and imperceptibly. The only true symptom is a feeling of blurred vision.
Maintaining eye pressure of sixty is a really important point. Check your vision regularly, and if you notice the slightest symptoms, contact a specialist.
Methods for measuring intraocular pressure
An experienced ophthalmologist can give a rough estimate of intraocular pressure without instruments by palpating the patient's eyeball through the eyelids.
Several techniques are used to accurately measure intraocular pressure. Non-contact tonometry is widely used. This method is based on assessing the flattening of the cornea by air flow. Non-contact tonometry is mainly used for screening, and not for managing patients with glaucoma, as it does not provide a completely accurate result.
The scatter in intraocular pressure values may be a consequence of measuring it using different methods.
During one study, four measurements are taken. This number of measurements is sufficient to obtain an average value that can be used for diagnostic purposes. When determining intraocular pressure using this method, using a Goldmann tonometer or ICare, the normal value for people under 40 years of age is 9–21 mmHg. Art.
The advantages of the ICare contact method include the portability of the tonometer and the ability to use it to measure intraocular pressure in children of different ages without the need for anesthesia. In addition, the ICare tonometer is convenient for self-monitoring eye pressure at home. The main disadvantage of the device is its high price.
To measure intraocular pressure, the Maklakov tonometry method is actively used. What is considered normal pressure with this method? Since its difference is the displacement of a larger volume of fluid from the chambers of the eye, the normal range in the age group up to 40 years is 12–25 mm Hg. Art. Tonometry according to Maklakov is considered a fairly accurate and reliable technique with minimal dependence on the researcher.
The scatter in intraocular pressure values may be a consequence of measuring it using different methods. It should be remembered that it is impossible to compare the results of measuring intraocular pressure obtained by studying different methods, since different standards are used for them. If it is necessary to monitor the pressure inside the eye over time (especially for patients with glaucoma), it is recommended to always measure it using one method.
Portable tonometer ICare provides fairly high accuracy of measurements at home
Ophthalmohypertension
Doctors call this increased blood pressure and divide it into three types:
- Stable. The norm is permanently exceeded.
- Labile. Standard pressure alternates with increased pressure.
- Transitional. A single case of increased blood pressure, after which everything returns to normal. Prevention is definitely needed here so that the problem does not return.
In most cases, increased eye pressure is associated with hypertension. But don’t forget about visual fatigue: long-term work at a computer or sitting in front of a TV with a bad screen can also cause ocular hypertension. At the same time, glaucoma can develop if measures are not taken.
The symptoms are as follows:
- At dusk, vision becomes blurry.
- My eyes began to see noticeably worse.
- Visual coverage has decreased.
- Unreasonable eye fatigue or unusual fatigue on a normal day.
- Redness.
- Pain in the suprafrontal arches and temples.
- Reading, watching TV or sitting at a PC feels uncomfortable.
- The so-called “midges” that appear in good lighting.
Symptoms of IOP
Parents should contact a pediatric ophthalmologist if their child complains of frequent headaches and discomfort in the eyes.
Signs of the disease include noticeable red capillaries in the eyes.
If the normal pressure is violated, the eyes react painfully to light. These are common symptoms of high IOP. If the pressure is increased, then red capillaries are noticeable in the eyes, nausea and tearfulness appear. Headaches and dry eyes are also signs of hypotension. If there are violations, the child’s memory and attention deteriorate, and loss of consciousness is possible. Children become lethargic, sleepy and apathetic.
Daily tonometry
The early stage of glaucoma is successfully determined by a medical procedure such as tonometry. This is a regular daily measurement of blood pressure in the morning, afternoon and late afternoon. Repeat the procedure for a week. Tonometry is carried out in different ways: a Goldman tonometer, a Maklakov tonometer, as well as a variety of non-contact devices that measure eye pressure. The norm, we remind you, is from ten to twenty-three mmHg.
Based on comparison and analysis of parting indicators, doctors can make a correct diagnosis. At 65 years old, when treating an eye, the doctor’s verdict should be especially clear.
Causes of increased eye pressure in children
The main reason is the significant load on the visual analyzer. For a child, this is a mental and emotional load. IOP increases as a result of two main reasons:
- formation of excessive amounts of fluid;
- disruption of the outflow of fluid through the drainage system of the eye due to its changes.
In children, the cause of increased IOP is congenital glaucoma, which develops as a result of intrauterine influence of unfavorable factors. For example:
- infections suffered by the mother;
- endocrine disorders;
- severe toxicosis;
- hypoxia;
- influence of radioactive waves.
Symptoms
The clinical picture is not much different from the symptoms in an adult. Signs of ocular hypertension:
- impaired visual perception at dusk;
- severe fatigue;
- redness of the mucous membrane during prolonged reading and writing;
- headache;
- flashing of midges before the eyes;
- sensation of swelling of the eyeball;
- deterioration of peripheral vision;
- increased photosensitivity;
- blurred contours of the objects in question.
Drop review
This is the simplest and most economical way to normalize ophthalmontus. The eye is nourished and excess is removed from the eyeball. During treatment, the doctor may change the drops, because the organs of vision are the most sensitive, and it is better to avoid getting used to the drug.
A group of prostaglandins - drops that are aimed at removing excess fluid inside the eye. The effect appears after 1.5-2 hours. Minor side effects may occur: changes in the color of the iris, redness of the eye and increased eyelash growth. For example, travatan.
Beta blockers reduce the amount of fluid that is produced in the eyeball. They act quickly, thirty to forty minutes after use. From this category, choose Betoptik, because this drug has less pronounced side effects.
Cholinomimetics promote fluid outflow. They lead to contraction of the eye muscles and narrowing of the pupil. Side effects: a decrease in the visual field and slight pain in the temporal area. Examples of drugs in this group: carbocholine and pilokartin.
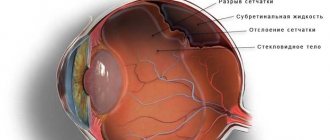
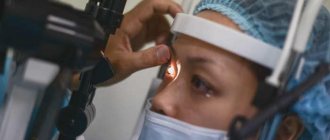
How is a fundus examination performed?
The examination is called ophthalmoscopy, and it is carried out in several main stages:
- The patient must remove contact lenses if he wears them. It is important that the patient warns the specialist about increased intraocular pressure.
- The patient is administered safe medications that dilate the pupils. This is necessary so that the doctor can assess the condition of the retina and its structures as accurately as possible.
- A specialist uses equipment (mirror ophthalmoscope) to direct a thin beam of light to illuminate the fundus of the eye.
- To better examine the condition of the inner surface of the eyeball, a specialist may use additional devices.
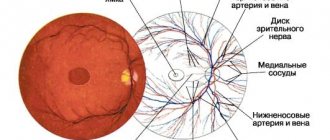
- The doctor carefully examines the condition of the optic nerve head, blood vessels, and retina. A good ophthalmologist is able to identify even the slightest deviations from the norm. The doctor assesses the general condition of the fundus, including its color.
- If any abnormalities are detected, the ophthalmologist prescribes an additional, more detailed examination.
Today, in addition to ophthalmoscopy, other procedures and devices are used that make it possible to objectively assess both the physical and functional condition of the fundus of the eye. This allows you to notice the slightest pathological changes in the retina. With the help of modern equipment, it is possible to show the patient the changes that occur with the inner surface of the eyeball.
Prevention
Do eye exercises every day (there are many examples on the Internet). Include sports activities, no matter how small. When you relax, do not choose a TV or computer as your companion. Take vitamin complexes periodically. When choosing drinks, forget about alcohol and coffee. Or at least reduce their use to a minimum.
Now you know what GD is normal at 60-65 years old in women. It is very important not to overstrain your eyes, eat a balanced diet and undergo a medical examination regularly (every 1-2 years).