The mucous membrane of the human mouth is inhabited by many microorganisms, including pathogenic bacteria and viruses, and the anatomical structure of the face contributes to the development of all kinds of infectious diseases of the oral cavity.
One of the signs of such ailments is the appearance of small blisters, which can cause pain and inconvenience while eating, or simply create aesthetic discomfort. What do transparent bubbles in the mouth mean, how dangerous are they, and how to quickly get rid of the problem?
If a transparent bubble appears in your mouth, what could it be?
Localization of transparent blisters on the oral mucosa is a common phenomenon that can occur among both adults and children.
This kind of formation can be provoked by an acute infection or be one of the signs of internal diseases.
If the formation of blisters is accompanied by pain, inflammation and other acute symptoms, it is caused by a viral or bacterial infection.
The absence of such signs, as a rule, indicates that they are a manifestation of general pathologies (diabetes mellitus, autoimmune disorders, immunodeficiency states).
Herpangina
Herpangina is an infectious disease that differs from ordinary tonsillitis in the mechanism of development, but has similar clinical symptoms.
The causative agent of the disease is the Coxsackie virus, which has many types and varieties.
The temperature rises sharply, weakness, headache, dyspeptic disorders (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting) appear; enlarged lymph nodes are observed, as well as the appearance of inflamed areas with blisters in the throat and oral mucosa.
Herpetic sore throat is diagnosed using blood tests and throat swabs; as a rule, it does not require special treatment - symptomatic therapy, antipyretics and antiseptics are prescribed. On the 6-7th day from the moment of infection, the blisters burst leaving small wounds, after which recovery occurs.
Most often, herpetic sore throat is diagnosed in children aged 3-10 years, but it also occurs in adults, and after recovery the person develops a strong immunity.
Pemphigus vulgaris
A genetic disease of an autoimmune nature, which manifests itself as transparent watery blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose. They have a very thin shell and easily open under any influence, and in their place bright red spots remain, causing serious discomfort.
The patient cannot talk or eat, and sometimes fever, weakness and general malaise are added to the list of symptoms. If left untreated, the blisters burst and the lesions merge with each other, which significantly worsens a person’s quality of life.
Herpes
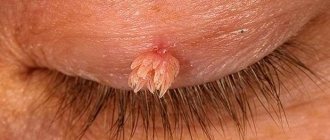
Herpes simplex is one of the most common causes of small blisters appearing on the mucous membranes, which can hurt and itch.
Their favorite place to localize is the lips, but the disease can affect the mucous membrane of the mouth and nose, sometimes accompanied by fever, lack of appetite, and deterioration in general well-being.
At first, herpetic blisters look like small blisters filled with a clear liquid, which gradually becomes cloudy, the membrane is damaged, and in their place ulcers and erosions covered with crusts appear.
The herpes virus is present in the body in 95-98% of people and it is impossible to completely get rid of it - to prevent relapses of the disease, you need to strengthen your immune system, avoid hypothermia and viral infections.
Aphthous stomatitis
The disease can develop due to the entry of microorganisms from the external environment, decreased immunity, lack of vitamins, poor oral hygiene, mechanical damage to tissues, etc.
Characteristic symptoms are the formation of bubbles with transparent contents, which degenerate into ulcers covered with a gray coating; pain and discomfort while eating; slight swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth.
Aphthous stomatitis is dangerous because, in the absence of therapy, it transforms into a chronic form and manifests itself when exposed to any external or internal negative factors.
Other reasons
Other pathologies that contribute to the development of this phenomenon include:
- shingles;
- dermatitis herpetiformis;
- erythema;
- mechanical injuries;
- diabetes;
- scarlet fever;
- allergy;
- Epidermolysis bullosa is a genetic pathology that affects newborns;
- vesical vascular syndrome, which is a consequence of hypertension;
- sexually transmitted diseases (syphilis, HIV, etc.).
The above diseases are not all the reasons why transparent blisters may appear in the mouth.
Causes of bubbles
Scratching the elements of the rash makes it difficult for crusts to form and heal. The ingress of staphylococci and streptococci leads to the appearance of ulcers.
Vesicles and pustules are symptoms of many diseases and conditions. Typically, watery blisters on the body contain transparent exudate, appear on changed or unchanged skin, and are accompanied by itching. In diseases of viral etiology, redness first appears, and vesicles appear after 24–72 hours.
Blisters due to an allergic reaction to foods, plants, or drugs can regress within a few hours without treatment. The appearance of blisters and blisters is sometimes associated with pressure, friction from clothing, or the impact of other mechanical irritants on thin, sensitive skin.
Based on the nature of the rash, experienced doctors can determine the disease:
- groups of vesicles on inflamed skin - herpetic infection,
- blisters on the lips and wings of the nose, severe itching - herpes simplex;
- numerous single-chamber, quickly drying blisters on the child’s body - chicken pox;
- vesicles with a black dot in the center - molluscum contagiosum (viral infection);
- bright pink or transparent itchy watery blisters on the hands and feet - dyshidrosis;
- multi-chamber vesicles - smallpox (defeated disease);
- redness, swelling of the skin, blisters and blisters - allergic dermatoses; severe itching, watery rash on the skin of the arms and abdomen - scabies.
If the blisters are not scratched or the tires are not peeled off, then after a few days the natural regression of the rash elements begins. When contact with the allergen continues, the area of inflammation covers new areas of the skin, and the number of vesicles increases. It is necessary to monitor which foods, medications, physical or other factors aggravate symptoms.
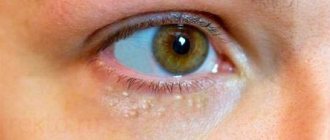
Localization of bubbles with clear liquid in the oral cavity
Primary diagnosis of the formation of blisters largely depends on their location - each disease has a typical clinical picture, that is, it affects a certain part of the oral cavity.
On the mucous membrane of the cheeks
Most often, the inner sides of the cheeks are affected by pemphigus vulgaris, which is congenital, as well as by stomatitis and mechanical injuries (accidental biting of the mucous membrane).
Bubbles under the tongue
In the sky
The appearance of blisters on the hard palate is characteristic of stomatitis, dermatitis herpetiformis, and epidermolysis bullosa.
On the gum
Bubbles on the gums can appear due to any diseases of the oral cavity, including infectious lesions, autoimmune disorders, allergic reactions, burns. In addition, this symptom is characteristic of advanced pulpitis, caries and periodontal disease.
On the tongue and lips
Typically, blisters on the lips and tongue appear during an exacerbation of the herpes virus, as well as mechanical injuries or burns of the mucous membrane of the tongue.
The location of the bubbles in the oral cavity may indicate a certain pathology, but is not the final diagnostic criterion, since the disease can become atypical, and the bubbles are localized in a variety of places.
Blisters on the skin
Bubbles are the primary morphological elements of an exudative nature, cavitary, contain fluid and slightly rise above the skin level.
In the vesicles there is a cavity filled with serous, less often serous-hemorrhagic contents, a tire and a bottom. The blisters can be located under the stratum corneum, in the middle of the epidermis, and between the epidermis and dermis. They can be single-chamber and sometimes multi-chamber. In this case, it seems that the patient has a bladder, but it does not have partitions. The bubble size ranges from the size of a pinhead to the size of a lentil. The contents of the vesicle may be transparent, serous, or less often bloody. It often becomes cloudy and purulent, which occurs when the vesicle turns into an abscess. The liquid separated from the bubble dries into a crust or its tire bursts, an erosive surface is formed and weeping occurs.
Blisters can be located on unchanged skin, but more often have an inflammatory erythematous base. On the oral mucosa and on the contacting surfaces of the skin, the bubbles quickly open, revealing erosive surfaces. In places with thicker tires, for example, on the palms with dyshidrosis, they last longer. The blisters pass without a trace or leave behind temporary pigmentation , as, for example, with Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis.
When vesicles form, spongiosis (eczema, dermatitis), ballooning degeneration (simple vesicular and herpes zoster, chicken pox), intracellular vacuolization (dyshidrosis) are observed histologically.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of lesions of the oral cavity by blisters is based on an external examination of the mucous membranes and examination of smears taken from the oral cavity.
Sometimes blood tests are needed to determine:
- inflammatory processes;
- autoimmune disorders;
- the presence of syphilis pathogens;
- immunodeficiency and other diseases.
A therapist, dentist or dermatologist makes a diagnosis for this symptom; sometimes a consultation with an immunologist, endocrinologist and other specialized specialists may be necessary.
Treatment for watery blisters in the mouth
Treatment of blisters in the oral cavity depends on the cause and causative agent of the disease, and is usually carried out by local means (ointments, rinses, lotions, etc.). When the pathological process is advanced, it is necessary to take medications orally, and in the most severe cases, intramuscular administration of antibiotics and other drugs.
Conservative therapy
In about half of the cases, the cause of blistering on the oral mucosa is the herpes virus.
Treatment of infection involves the use of special antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Zovirax) in the form of ointments, taking immunostimulating agents, and sometimes requiring the introduction of a herpetic vaccine.
Bacterial diseases require treatment with antimicrobial agents, topical or in the form of tablets and capsules.
To combat aphthous stomatitis, antiseptic solutions, ointments containing lidocaine, antihistamines, vitamins and immunostimulants are used. Therapy for pemphigus vulgaris involves constant use of corticosteroid drugs, but it is very difficult to completely get rid of the disease - sometimes this requires special blood purification procedures.
It is strictly not recommended to use medications on your own to treat blisters in the mouth, as they can lead to a worsening of the condition and the disease becoming chronic.
Traditional methods
In the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the mouth, traditional recipes are used in combination with conservative therapy after consultation with a doctor:
- Herbal decoctions. The most effective means for treating blisters in the mouth are rinsing with decoctions of chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, sage, and oak bark. They relieve inflammation and pain, promote healing of ulcers and tissue regeneration.
- Garlic. Garlic has antiseptic properties and effectively destroys pathogenic microorganisms. Take 3-4 cloves of garlic, grind and mix with a tablespoon of sour milk. Treat the mucous membrane three times a day.
- Aloe. Wash the fleshy aloe leaf, chop it, squeeze out the juice and lubricate the affected areas several times a day. You can simply chew pieces of the plant in your mouth, spitting out the pulp.
Before using traditional methods of treatment, you should always make sure that there are no contraindications or allergic reactions to the components of the products.
Transparent blisters on the oral mucosa can be a symptom of a serious illness, so you should not delay a visit to the doctor or self-medicate. An experienced specialist will quickly determine the cause of the problem and prescribe the correct treatment.