In case of an eye injury, if it is accompanied by severe damage, pain, bleeding, or inability to walk, call an ambulance.
The single telephone number for round-the-clock ambulance and emergency services in Moscow is
103.
more about calling ambulances here >>
If your condition is not very severe, you can move around on your own - immediately go to the emergency department of a specialized eye hospital in your area.
Where to go in Moscow for an eye injury
Adults will receive emergency eye care in Moscow around the clock and free of charge, including on weekends, at the following addresses:
First City Hospital named after N.I. Pirogov (City Clinical Hospital No. 1)
- Address: Oktyabrskaya (ring) or Shabolovskaya metro station, Leninsky Prospekt, building 10, building 7 (area No. 2), 1st floor, 23 reception department
- Phones: information desk, reception department - (495)531-69-67
- Website: gkb1.ru
State Clinical Hospital named after S.P. Botkin, Moscow City Ophthalmological Center
- Address: Moscow, 2nd Botkinsky pr-d, 5, building 19 (checkpoint No. 4 from Polikarpova street)
- Telephones: emergency ophthalmology, contact center of the Botkin Hospital, emergency department (for hospitalization issues) - (495)699-10-75
- Website: botkinmoscow.ru
How to get to the Botkin Hospital:
- metro station "Dynamo", trolleybus No. 82, stop at the main entrance (checkpoint No. 1) or bus No. 207, stop at checkpoint No. 1 or No. 3 (for ambulances, pedestrians are allowed entry).
- Begovaya metro station, bus No. 847, stops at checkpoint No. 2 (Polikarpova St.) or checkpoint No. 3 (Boris Petrovsky St.).
Social buses No. C23 run from Begovaya metro station and CSKA metro station to the Ophthalmological Center of the Botkin Hospital (checkpoint No. 4). Buses run daily from 7-00 to 20-00 at intervals of 20 minutes.
Helmholtz National Medical Research Center for Eye Diseases
- Address: Krasnye Vorota metro station, Sadovaya-Chernogryazskaya street, building 14/19, entrance to the institute from Furmanny Lane, emergency ophthalmological care department
- Telephones: information, emergency ophthalmology
- Website: helmholtzeyeinstitute.ru
City Clinical Hospital named after F.I. Inozemtseva
- Address: st. Fortunatovskaya, building 1. Directions: Partizanskaya metro station - the last car from the center. Then take bus No. T22 to the stop “Izmailovo station” (one stop) or walk 15 minutes.
- Phones: contact center, reception department
- Website: inozemtcev.ru
City Clinical Hospital No. 15 named after O.M. Filatova
- Address: metro station Vykhino, Novogireevo or Novokosino, Veshnyakovskaya street, building 23
- Telephones: 24-hour hotline GKB-15, emergency department, hospital information center - (495)375-71-01
- Website: https://gkb15.moscow/
If a child has an eye injury, contact the emergency department of the largest Moscow children's hospital 24 hours a day and free of charge:
Morozov Children's Clinical Hospital
- Address: metro station Dobryninskaya, Serpukhovskaya or Oktyabrskaya, 4th Dobryninsky lane, building 1/9. Entrance to the territory is from 1st Dobryninsky Lane. The reception department is located in building 1A.
- Phones: information, ophthalmology department
- Website: https://morozdgkb.rf/
You can come to the above institutions on your own or, in serious condition, by ambulance.
You can call in advance, but even if you don’t get through, come to the hospital without calling: with acute ophthalmopathology you will be admitted at any time, including at night and on weekends.
Mechanical eye injuries
Mechanical damage to the visual organs includes injuries along with blunt trauma to the eyeballs. As well as the adnexal apparatus and bone bed. Mechanical injury to the eye may be accompanied by hemorrhage into the soft tissue and structure of the eye. Subcutaneous emphysema is also possible, along with prolapse of the intraocular membrane, inflammation, decreased vision, and the like. Diagnosis of mechanical eye damage is based on information collected during examination of the victim by specialists such as an ophthalmic surgeon, neurosurgeon, otolaryngologist, and maxillofacial doctor.
Additionally, radiography of the orbit is performed in combination with biomicroscopy, ophthalmoscopy, ultrasound echography and biometry, tests with fluorescein, and more. The method of treatment for mechanical eye damage depends directly on the nature and extent of the injury received, as well as on the complications that arise.
What to take with you
When contacting a medical institution, take the following documents:
Adults:
- Passport
- Temporary registration (for foreign citizens)
- Compulsory medical insurance policy or VHI policy
Children:
- Parent's passport
- Child's birth certificate
- Compulsory medical insurance policy or VHI policy
If there is a possibility that you may be hospitalized, take things for hospitalization: a robe, tracksuit, slippers, toothpaste, brush, etc.
How to restore vision
Perhaps the unpleasant and most insidious side of this problem is that people’s vision suddenly deteriorates. In this regard, it is worth considering methods for restoring vision at home. In order to stimulate blood circulation, and at the same time preserve or restore vision after an eye injury, the following methods will be useful:
- Self-massage of the eyes.
- Using preparations with blueberries and fresh berries.
- Recovery thanks to the use of natural honey.
- Taking regular rest from external irritants.
- Drinking freshly squeezed vegetable juices.
- Following the recommendations of yogis.
Conditions for providing emergency and emergency assistance
Emergency assistance to eliminate a threat to life is provided free of charge to all residents of Moscow, the Moscow region, citizens of the Russian Federation, foreign citizens and stateless persons.
Emergency ophthalmological care is provided to foreign citizens and stateless persons if they have a passport and a valid compulsory medical insurance or voluntary medical insurance policy. If there is no policy, for a fee based on an agreement on the provision of paid medical services.
Emergency assistance is provided immediately, the waiting period for emergency assistance is no more than two hours from the moment of contacting a medical institution.
Open type of injuries: what are such lesions?
Open eye injuries are of the following nature:
- Lacerations of the eyeball in the form of a penetrating wound caused by a blunt object. The eyeball may fill with incompressible fluid, causing injury to temporarily increase intraocular pressure. Eye ruptures can occur directly in the area of impact, in an area where the sclera is very weak, usually around the limbus of the cornea, in the area of the attachment of the extraocular muscle, near the optic nerve. And also in the area of the wound, for example, after a previous operation.
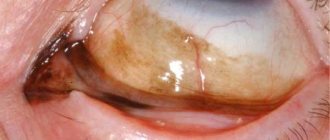
- Perforating injuries in the form of a penetrating wound to the eyeball caused by a sharp object, knife, damage from glass or a piece of wood. In this case, the entrance wound is usually visible, which can be closed or completely hidden by a hematoma or conjunctiva. Through such a wound, fluid leaks out of the eyeball or the structure of the visual organ falls out. In the case of corneal wounds, an irregular pupil is often observed, and partial prolapse of the iris occurs in the wound. There is blood in the area of the anterior chamber. In case of injury to the sclera, as a rule, hemorrhage begins under the conjunctiva of the eye and a dark strip of the membrane becomes visible. In both cases, loss of the lens from the eyeball or vitreous can be observed.
- Penetrating injuries occur mainly in the orbit where the foreign body is located.
Dangerous ophthalmopathologies
As soon as possible, you need to contact an ophthalmologist in a specialized medical institution for the following conditions and symptoms:
- Penetrating injury to the eyeball
- Thermal or chemical burn to the eye
- Ultraviolet radiation burn
- Contusion resulting from a blow from a fist or large object
- Corneal ulcer with perforation
- Foreign body entry
- Superficial damage with scratches on the cornea or conjunctiva
- Hematomas of the eyelids
- Acute inflammation
- Acute optic nerve disease
- Uveitis – inflammation of the choroid
- Acute attack of glaucoma
- The occurrence of sharp or dull pain
- Sudden blurred vision, fog before the eyes, partial loss of visual fields, double vision
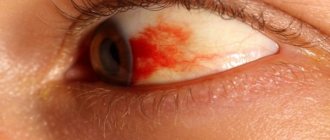
- Severe redness, hemorrhage in the conjunctiva, eyelid skin, bleeding
- Excessive lacrimation
- Photophobia
The severity of the lesion does not always correlate with the intensity of pain and other traumatic manifestations.
It is difficult for a non-specialist to determine the degree of risk. Therefore, even with, at first glance, not a very serious injury, it is important to urgently go to an eye traumatology department.
What to do if the cornea is damaged
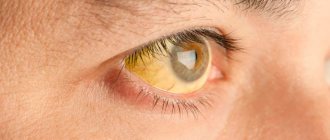
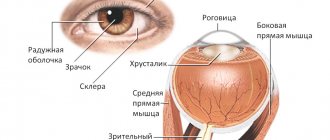
The cornea in humans separates the anterior eye chamber from the external environment and is distinguished by the appearance of a hemisphere with a diameter of 10 millimeters. It consists, as a rule, of collagen fibers, which are absolutely transparent. The inside of this part of the eye is covered with multilayered epithelium. Its central sector is approximately twice as thin as the peripheral one. Symptoms of damage to the cornea of the eye are as follows:
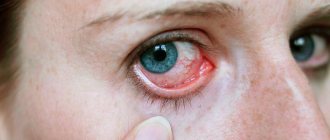
- When the cornea is damaged, lacrimation is observed along with photophobia, blepharospasm (reflex closure of the eyelids), and redness near the transition to the sclera.
- Directly based on the depth of the lesions, erosions differ from corneal ulcers, as well as penetrating wounds and foreign bodies.
First aid for eye injury
After an injury, to avoid aggravation of the condition and complications:
- don't rub your eyelids
- do not instill drops without a doctor’s prescription
- in case of contact with chemicals, rinse your eyes with cool, clean water for at least 10 minutes (remove your lenses first if you are wearing them)
- For all other injuries, except for exposure to chemicals, it is better not to remove the lenses and not to rinse them with water.
- Do not try to remove on your own a large foreign body stuck in the eyeball - a piece of glass, metal shavings, scale, etc.
- cover the injury with a sterile gauze bandage
- As soon as possible, go to the eye trauma center of a specialized hospital, where the need and timing of surgical intervention in a hospital setting will be determined
Timely treatment will restore the integrity of the eyeball, avoid possible serious complications, ease the course of the postoperative period, and in many cases preserve vision.
“Prevention of eye injuries in children”
“Prevention of eye injuries in children”
Damage to the organ of vision in children is one of the main causes of decreased vision, loss of vision and death of the eye. Eye trauma remains the most common cause of blindness in childhood worldwide. The high incidence of eye injuries is largely due to the characteristics of childhood. Children are characterized by exceptionally high mobility, they show interest in everything new to them - various kinds of technical devices, explosive substances, but do not have the necessary experience and caution.
Eye injuries in schoolboy boys are observed 3-5 times more often than in girls. The most “traumatic” age for boys is between 10 and 13 years old. For girls, the most “traumatic” age is 6–9 years.
There are seasonal variations in the incidence of childhood eye injury. The greatest number of visual injuries in children occurs in the summer. During the holidays, there is an increase in gaming activity, which in turn leads to an increase in injuries to the eye and other parts of the body.
Recently, there are real prerequisites for an increase in the frequency of childhood injuries, which is associated, first of all, with the deterioration of social and living conditions in Ukraine. As is known, an increase in prices for vouchers to various health camps, sanatoriums and holiday homes leads to a significant reduction in the opportunities for organized recreation for schoolchildren. In addition, increased employment of parents increases the number of children walking unsupervised in the yard and on the street, which in turn contributes to the manifestation of injury-prone initiatives and, as a consequence, an increase in children's eye injuries.
Constant control by adults over behavior in kindergarten, school, at home and especially on the street, landscaping courtyards, equipping them with special playgrounds, organizing leisure and summer recreation for children, storing sharp and cutting objects, explosives, toxic and flammable liquids in places inaccessible to children, teaching children how to use sharp household items are the most important measures to prevent eye injuries in children. Parents, educators and teachers must remember that it is possible to avoid injuries in general and eye injuries in particular in children only by educating and instilling in them strong skills of safe behavior.
In the structure of children's eye pathology, injuries occupy almost 10%.
Most often, eye injuries occur due to various small bodies getting into them: fragments of metal, stone, coal, grains of sand and specks, husks of seeds, ears of corn, etc.
Eye damage in children (from piercing and cutting objects: a fork, scissors, a stone or a nail from a slingshot, crossbows or explosives) often occurs during games and pranks due to parental negligence.
Types of eye injuries
There are several types of eye injuries:
- industrial;
- agricultural;
- household;
- combat.
A special place is occupied by household eye injuries in children and adolescents.
Depending on the source of injury, there are:
-mechanical injuries;
- eye burns;
- radiation damage to the eyes.
Mechanical eye injuries
can be superficial and penetrating. They arise as a result of exposure of the eye to cutting and piercing objects, and may be accompanied by the penetration of foreign bodies into the conjunctiva, cornea, sclera and into the cavity of the eyeball. In addition, there are blunt injuries to the eye, the causes of which can be: a blow to the eye with a stick, a bounced twig when chopping wood, a fist, etc.
Most common sign of blunt trauma (60% of cases)
– damage to the cornea, accompanied by severe photophobia, lacrimation, and pain. Hemorrhages in various parts of the eye are possible. The most serious consequences of blunt trauma: clouding of the lens (cataract), retinal detachment, rupture of the optic nerve. Blunt injuries are also possible in which the anterior part of the eyes is not changed, and when testing vision, almost complete blindness is noted. Therefore, not a single case of even minor blunt trauma to the eye and head area should proceed without a thorough examination by an ophthalmologist.
To mechanical damage of a penetrating nature
This also includes eye injuries accompanied by damage to its internal structures. The danger of a penetrating wound is due to the fact that it is almost always infected and causes an infectious process.
Eye burns
According to the nature of the pathology, they are divided into:
— thermal burns
– getting boiling water, hot oil, hot metal, etc. into the eye.
- chemical burns
- exposure to chemical compounds - acids and alkalis - on the eye.
Radiation and light damage to the eyes
– influence of ultraviolet and infrared radiation.
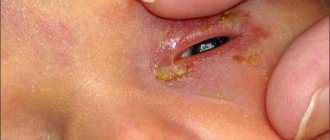
Signs of damage (injury) to the eye:
Pain
– is one of the main signs of eye injury.
Photophobia, lacrimation
– observed with superficial damage to the cornea.
Hemorrhages
- Possible due to damage to the blood vessels of the eye.
Relative softness of the eyeball
, which occurs as a result of the leakage of intraocular fluid and vitreous humor, is a sign of penetrating injury to the eye.
Very severe complication
A penetrating injury to the eye is panophthalmitis (purulent inflammation of the eye), leading to damage to the second (undamaged) eye.
damage to the second (undamaged) eye
Treatment of eye injuries
Treatment of victims
should be performed by an ophthalmologist depending on the nature and severity of the injury.
First aid
for a mild eye injury, it involves instilling anti-inflammatory eye drops into the eye, applying a sterile bandage to the eye and urgently referring the victim to a specialist.
For severe injuries
, for example, with damage to the inner membranes of the eye, hospitalization is necessary.
For thermal burns
You can use anti-inflammatory drops and ointments. Then the victim must be shown to a specialist doctor.
For chemical burns
Emergency assistance to the victim should include:
— removal of burn components;
— Immediately flush the eyes with plenty of water and for a long time
(up to 15 – 20 minutes);
— thorough eye examination
with inversion of the patient's eyelids;
— You can use a neutralizing solution
(if the chemical compound is known) - a burn with acid is neutralized with a 2% solution of sodium bicarbonate, a burn with alkalis - with a 2% solution of boric acid or a 0.1% solution of zinc sulfate;
— if present in the eye
particles of metal, lime and other foreign bodies, they are carefully removed with a damp cotton swab, then disinfectant ointments are placed behind the eyelids, after which the victim is sent to an ophthalmologist.
Prevention and protection measures
Constant control
on the part of adults to monitor behavior in kindergarten, school, at home and especially on the street - this is the most important measure for the prevention of household eye injuries in children.
Yard landscaping
, equipping them with special playgrounds.
Leisure organization
in children's free time and summer holidays.
Storage
sharp and cutting objects, explosives, toxic and flammable liquids in places inaccessible to children.
Teaching children
rules for using sharp household items (fork, knife, fountain pen, etc.).
Sanitary education work
among children, parents, educators and teachers.
Children should know that their health and well-being largely depend on themselves!
Parents, educators and teachers must always remember that it is possible to avoid injuries in general and eye injuries, in particular, in children and adolescents only by educating them and instilling in them strong skills of safe behavior.
3
Consequences
The consequences of eye injury directly depend on their degree and the timely provision of first aid to the person. If the treatment turns out to be of poor quality and the treatment is inadequate, a number of the following complications may develop:
- The occurrence of sepsis. This is a very serious condition, which is caused by the entry of infectious agents into the blood and poisoning of the entire body with all sorts of toxic products of their vital processes.
- Loss of an eye along with permanent vision loss.
- The development of a brain abscess, which is characterized by a purulent accumulation in the cranial cavity.
- The occurrence of panophthalmitis, which is accompanied by global inflammation, which is purulent in nature, causing melting of the membranes and structures of the eyeballs.
- Development of sympathetic inflammation. It is expressed in the fact that the healthy eye begins to suffer. This is a kind of reaction to the trauma of the first. Fibrous plastic iridocyclitis is the most common complication that affects uninjured eyes.
- The development of endophthalmitis is an accumulation of purulent mass in the area of the vitreous body of the eye. In this case, inflammation of the internal structure of the organ occurs.
- The appearance of disfiguring scars.
- The occurrence of deformation of the soft tissues of the face along with inversion, eversion and ptosis of the eyelids.
- The appearance of dysfunction of the lacrimal apparatus.
Eye burn: what first aid should be
Burns appear from exposure to thermal, chemical and thermochemical factors. As part of providing first aid for eye burns, the doctor also has to deal with eye damage from ultraviolet radiation.
Electroophthalmia is the reaction of the visual organ to ultraviolet radiation. It appears when participating in electric welding work without eye protection. A similar reaction can occur under the influence of solar ultraviolet radiation, which is reflected from the snow surface.
With burns, there are complaints of severe photophobia along with a feeling of sand and severe stabbing pain in the eyes is likely. Dacryagogue is objectively determined along with spastic contraction of the eyelids and conjunctival hyperemia. As part of first aid, drops are instilled with a solution of "Dicaine", "Novocaine" or "Lidocaine", cold lotions will not interfere, along with placing the victim in a dark room.
Thermal burn of the eyelids is usually combined with damage to the face. The degree of such a burn is determined according to the same rules as on other surfaces of the body. As part of the assistance, analgesics are used orally and parenterally. The burned surface is treated with an alcohol solution of brilliant green. In case of an isolated burn of the eyelids, the victim should be taken to an eye hospital. When eyelid burns are combined with other injuries to other surfaces, a person needs a special hospital.