My eyes lovingly contemplated the flowers in the dew, the transparent sky, renewing the world, renewing my heart. And again the jubilant power of the day. I.V. Goethe The human eye is an organ created to perceive light. This is the most valuable and amazing gift of nature. Our eyes reflect everything we feel: joy, suffering, indifference, love and hatred.
Eyes are not only the mirror of the soul, but also a mirror of overall health.
The eye is a very sensitive and easily vulnerable organ.
Too bright light causes pain to the eyes, polluted air, smoke, dust cause watery eyes, and sometimes even inflammation of the eyes.
Eyes...Are you aware of the role your eyes play in your daily life? And do you know what and how to do to keep your eyes healthy?
Among the impressions perceived by our sensory organs from the external environment, visual ones are especially important, since 90% of the information that enters our brain passes through the eyes. And only 10% falls on all other senses.
Most people abuse their eyes, do not give them any rest, overstrain them, irresponsibly forgetting that the work of the eyes during wakefulness does not stop for a second and that everything they perceive is transmitted to the brain for comprehension.
To help your eyes, you need to take care of nutrition, blood circulation, muscle tone and an even mood.
You can sleep and rest a hundred times, but if a person has “bags” under his eyes, he will still look tired and sick. It would seem that the problem is not serious: after all, nothing hurts, does not itch or itch. However, living with it is, at a minimum, unpleasant, and at a maximum, it can signal significant health problems. The organ of vision is the most important tool for understanding the outside world. Basic information about the surrounding reality enters the brain through the analyzer. I.M. Sechenov and I.P. Pavlov attributed cognitive power to the visual analyzer. Its functions underlie all human creative labor activity. All sense organs, including the visual analyzer, function as devices for perceiving signals. The eye sends information to the brain, which is encoded into neural activity through a chain of electrophysiological impulses. Signals entering the cerebral cortex are analyzed and synthesized into a visual image. The eye is a distant analyzer of the highest order.
The doctrine of eye diseases was created from year to year, from century to century. Each era had its own traditions of treating eye diseases.
All ancient medicine is replete with folk remedies. The beginnings of the ancient science of eye diseases were in Egypt 4400 years BC.
42 books were recovered from the tombs of the pharaohs, 6 of which dealt with eye diseases. Bottles made of steorite, alabaster, and ivory with remains of eye medicines were also found in the tombs of the pharaohs. (S. M. Magilnitsky). Medical papyri contain information about a number of eye diseases of that time: strabismus, cataracts, hemorrhages, lacrimation, suppuration. The Bible of the ancient Jews contains information about exophthalmos, red eyes, lacrimal fistulas, corneal spots, cataracts, and trachoma.
What it is?
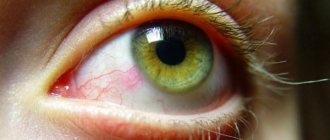
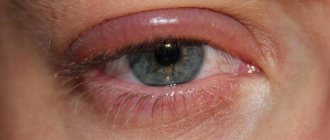
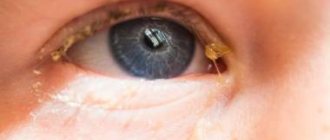
Periorbital edema is a symptom characterized by swelling of the upper, lower, or upper and lower eyelids due to the accumulation of fluid in the fatty tissue of the eyelids. The symptom can be permanent or temporary, sometimes appearing at regular intervals. The frequency of occurrence depends on the predisposing factor - physiological characteristics or severe disease of the internal organs.
REFERENCE! Most often, swelling is observed in the area of the lower eyelids, and popularly this problem is called bags under the eyes.
Periorbital edema occurs most often in the morning, and gradually disappears during the day, when the fluid flows into the lower part of the body. With complex chronic lesions, this does not happen: fat accumulating between the orbit of the eye and the eyeball stretches the thin membrane, and it protrudes outward. In this case, neither folk recipes nor cosmetics will help, and the problem can only be solved through surgery.
It is possible to get rid of edema on your own only if a person knows for certain its cause and it has nothing to do with serious illnesses, although such a conclusion cannot be made without consulting a doctor. Periorbital edema can indicate not only an excess of salty and spicy foods in the diet, for example, but also malignant processes in the brain, so treatment should always begin with a visit to the hospital and identifying the cause.
Ptosis
Drooping of the upper eyelid - ptosis (ptosis) can be congenital or acquired. The latter occurs due to injury to the eyelid and paralysis of the oculomotor nerve. Based on the degree of drooping of the eyelid, partial and complete ptosis are distinguished. With congenital ptosis, patients raise their eyelids, straining the frontalis muscle, as a result of which the skin of the forehead gathers in folds; The patient's head is slightly tilted back. Sometimes patients, especially children, lift their eyelids with their fingers.
Treatment , which can be conservative in cases of acquired ptosis, should be aimed at eliminating the cause of the underlying disease; To clarify this, the patient must be shown to a neurologist. In case of irreversibility of the process, as well as in congenital ptosis, surgery is indicated, the purpose of which is to strengthen the function of the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid.
Chalazion
This disease is a benign compaction in the thickness of the cartilage of the eyelid. It occurs against the background of an inflammatory process. Due to blockage of the excretory ducts of the meibomian glands, fatty secretions accumulate in the eyelids. Infection triggers inflammation. Chalazion often develops against the background of styes, blepharitis or conjunctivitis. The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- itching on the eyelid;
- lacrimation;
- swelling and hyperemia;
- blurred vision due to diplopia.
If the chalazion becomes complicated, headaches, nausea, and dizziness appear. The patient's body temperature rises. These signs are also observed in preseptal cellulite.
Allergic swelling of the eyelids
Quincke's edema is characterized by a sudden appearance and equally rapid disappearance. Edema is one-sided, very significant, not accompanied by any subjective sensations, and develops more often in the upper eyelid. The basis is an allergic reaction.
Products - like: eggs, milk, chocolate, citrus fruits, flowers and other irritants.
Treatment is to eliminate the underlying cause. Desensitizing drugs are prescribed orally and parenterally.
Drug allergic edema
Causes
There are many reasons for the occurrence of periorbital edema: from drinking a large amount of liquid the day before to problems with the functioning of internal organs. In some cases, it is impossible to get rid of a symptom due to individual characteristics, but this is rather an exception to the rule. Much more often, the problem can be solved only with the help of medical or cosmetic techniques.
REFERENCE! A slight swelling of the lower eyelids is typical for people of the Asian race: this is their feature and does not need to be eliminated.
In other cases, swelling should be dealt with and the cause of its occurrence should be determined.
- One of the most harmless reasons is excessive drinking.
- If the day before a person drank more liquid than usual (for example, on a too hot day), you should not be surprised at the appearance of significant swelling in the morning. This situation does not require medical intervention, provided that there is no swelling the next morning.
- Eating foods that promote fluid accumulation in tissues. An excess of salty, spicy, and smoked foods in the diet leads to disruption of the water-salt balance and stagnation of water, which makes you more thirsty. A vicious circle is formed, as a result of which swelling of the face, including the eyes, appears in the morning. Among the products there may also be those that have a diuretic effect (watermelon, plum and others).
- Fatigue or lack of sleep. The cause of swelling can be severe fatigue, overwork or poor short sleep. This is also a one-time symptom that can appear, for example, during a sleepless night before an exam.
- Crying before bed. Many parents calm their crying children by worrying about the appearance of swelling and redness of the eyes in the morning. Indeed, if you spend the evening crying hysterically, dark circles under your eyes and swelling will appear in the morning.
- Diet, fasting or poor nutrition. If the diet contains a lot of salt, complex carbohydrates, the amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates is not balanced, a person eats only 2-3 times a day and does not drink enough water, periorbital edema may appear with a certain frequency.
- Smoking or alcohol abuse. Cigarettes and alcoholic drinks contain toxins that lead to stress, fatigue, hormonal changes, and these, in turn, provoke fluid retention in the body.
- Allergic reaction. With allergies, “leaks” occur in the capillary system, blood begins to accumulate under the dermis, and cellular metabolism in a certain area of the skin (for example, under or above the eyes) is disrupted. Liquid may accumulate in this area.
- Infectious mononucleosis is one of the common viral diseases, which is characterized by damage to the tonsils, severe increase in temperature, fever, enlargement of the lymph nodes, spleen and liver. The causative agent is the Epstein-Barr virus, and more often it affects fragile children's bodies. The disease is dangerous, and the effectiveness of treatment depends on timely consultation with a doctor. During the incubation period, a characteristic symptom is redness and swelling of the eyes, as well as pain and itching of the eyelid area.
- Some skin diseases. With certain skin lesions, it becomes very sensitive and susceptible. Thus, periorbital edema can accompany lichen, dermatitis and other diseases of the dermis.
- Hypothyroidism and other lesions of the endocrine system. Hormonal imbalances (including during pregnancy) almost always affect the condition of the skin: it becomes more sluggish, thinner, and dark bags appear under the eyes.
- Periorbital cellulitis. This is a pathology in which not fluid, but fat accumulates in the eyelid area. The reason for this is malfunction of the excretory system and improper nutrition. A characteristic feature of edema caused by cellulite is the bluish appearance of the swollen skin.
- Chagas disease, or trypasonosis. This is an acute disease of an infectious nature, the source of which is some tropical protozoa. Chagas disease affects only one eye and causes headache and itching.
- Frequent stress, nervous strain, and neuroses can manifest themselves in the form of permanent dark circles under the eyes and puffiness, as well as restless sleep.
- Trichinosis is a helminthic infection caused by helminths that live in meat and dairy products from infected livestock. With trichinosis, severe swelling of the entire face appears.
- Pathologies of the lacrimal glands. When the lacrimal glands do not function properly, swelling occurs, accompanied by discomfort and pain.
- Heart pathologies, in particular heart murmurs, can manifest themselves in the form of unilateral periorbital edema.
- Pyelonephritis and other kidney diseases directly affect the body's excretory abilities. Usually, constant swelling forces a person to go for an ultrasound of the kidneys, and this is correct: swelling is the first sign of problems in the kidneys.
Abcess of the century
Caused by pyogenic microbes, most often after infected lesions. The causes may be local purulent inflammation: barley, boil, ulcerative blepharitis. Inflammation can move from border areas and occur metastatically with septic foci in other organs. The abscess develops acutely with increasing diffuse infiltration of the subcutaneous tissue of the eyelid. The eyelid is swollen, the skin is tense, hyperemic, hot to the touch. Palpation is sharply painful. The abscess may open spontaneously, after which the symptoms subside. Treatment at the beginning of the disease is dry heat, preferably UHF currents. Instill a 30% solution of sulfacyl sodium at least 5-6 times a day. It is necessary to prescribe antibiotics intramuscularly.
Cellulitis (phlegmon) of the orbit: stages of pathology
This diffuse pathological process is acute and develops rapidly, but gradually. One of the stages is preseptal (periorbital) cellulite. First, the eyelids and skin around the eye socket become inflamed. Since the infection has entered the orbit, exophthalmos is observed already at the first stage of its development. The mobility of the eyeball is preserved. Visual functions are not affected.
The second stage is caused by the transition of inflammation to the tissues of the posterior part of the orbit. Ophthalmoplegia occurs. Swelling and redness of the affected areas of the eyelids and skin become more pronounced.
The third stage is subperiosteal abscess. Purulent masses accumulate between the periorbital wall and the periosteum. The eye begins to shift towards tissues that are not yet affected by the inflammatory process. Swelling increases. The palpebral fissure closes almost completely. Vision deteriorates.
The last stage is abscess and phlegmon of the eyeball. Pus fills the cavity formed in the tissues of the orbit. All symptoms of the disease intensify, which ultimately leads to complete blindness.
Ptosis is unilateral; bilateral.
Moderate ptosis with retraction of the eyeball into the orbit (enophthalmos) and constriction of the pupil (miosis) is observed with paralysis of the branch of the sympathetic nerve, which innervates part of the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid (Müller's muscle). This symptom is often one of the manifestations of a disease of the nervous system.
Inflammation of the lacrimal gland - dacryoadenitis - is rare. In its acute form, the disease manifests itself in most cases as a bilateral process with redness and soreness of the eyelid skin at the outer corner, swelling and drooping of the eyelid, more on the outside. When the eyelid is pulled back and the patient looks inside, toward the nose, an enlarged, inflamed gland is visible protruding from under the outer edge of the orbit. Acute dacryoadenitis develops as a complication of infectious diseases: influenza, typhoid fever, pneumonia, tonsillitis, paratyphoid fever.
Treatment: UHF therapy, dry heat or in the form of warming compresses. Ingestion of sulfonamides or intramuscular injections of penicillin. When the gland is suppurated, sometimes an additional incision is made on the skin side, followed by suction dressings. Chronic inflammation of the lacrimal glands is also possible due to Mikulicz's disease (simultaneous disease of the salivary and lacrimal glands), tuberculosis, leukemia).
How does swelling manifest itself?
Expert opinion
Kim Oksana Alexandrovna
Head of the ophthalmology clinic. Ophthalmologist with more than 10 years of experience.
Periorbital edema is swelling of the area around the eyes. Most often it appears in the morning: immediately after waking up, a person notices that his eyelids look swollen. Swelling can spread only to the lower eyelids, only to the upper eyelids, to the lower and upper eyelids at the same time, occur in one or both eyes, and also affect the mucous region - the place where eyelashes grow. Based on the location of the swelling, the doctor can guess what the cause is.
Other manifestations of periorbital edema are:
- redness of the eyes;
- tearfulness;
- blueness of the skin around the eyes;
- itching and discomfort at rest.
In some conditions (such as injury), touching the swollen area causes pain.
Possible complications
Aesthetic problems and discomfort that arise with the development of perioral dermatitis can provoke various psychological problems, cause depression or neuroses. This is a chronic disease, so relapses may be accompanied by more severe symptoms (discomfort and skin rashes).
Complications of perioral dermatitis
Incorrect or untimely treatment can cause acne scars or pigment spots to appear on the skin. In addition, the affected areas of the skin become drier, pale and tight.
Ways to relieve swelling
Methods for relieving edema can be divided into two large groups: cosmetic and medical. In the first case, we are talking about some procedures that cosmetologists do (massage, injections, external use of creams) to restore the elasticity, firmness and firmness of the skin.
In the second case, a comprehensive examination is required, which will help to identify the root cause of swelling, make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
REFERENCE! Sometimes the reason lies in disruption of sleep and rest patterns, neuroses, excessive eye strain and improperly organized daily routine. In this case, you can cope with the problem yourself or with the help of a psychologist.
Injection technologies for restoring skin turgor
Skin turgor is a medical term for firmness, tone and elasticity of the skin. The problem of its restoration is dealt with by cosmetologists who offer various cosmetic procedures that help restore the freshness and youth of the skin: lymphatic drainage, electrical stimulation, vacuum massage.
Preseptal cellulitis: treatment methods
Preseptal cellulitis and orbital cellulitis (cellulitis) of the orbit are treated with antibiotics. The choice of drug is influenced by the etiology of the disease, the nature of the inflammation, the presence or absence of signs of complications and other factors.
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis. This is determined by the causes and severity of the pathology. Preseptal periorbital cellulitis caused by an upper respiratory tract infection is treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics. If the disease develops in a mild or moderate form, the patient remains at home. Antibiotics are taken in tablet form. In case of severe illness, the person is hospitalized. The course of antibiotics can be extended. Medicines are administered intravenously.
For local periorbital cellulitis, that is, caused by dacryocystitis and other ocular inflammatory diseases, it is necessary to treat the underlying pathology. For eyelid injuries that provoke purulent cellulitis, parenteral antibiotics are prescribed. In addition, tetanus prevention is carried out.
Animal and insect bites can cause organic material to become lodged under the skin. This leads to the need to prescribe drugs that are effective against anaerobic organisms that can grow in the absence of oxygen.
In rare cases, beta-hemolytic streptococcus can cause necrotizing fasciitis, a type of necrotizing soft tissue injury. This type of cellulite of the eyelid develops very quickly. Severe swelling is observed. Its edges become blurred and the skin turns purple. This indicates necrosis and the so-called toxic streptococcal shock syndrome. The patient must be urgently hospitalized. Resuscitation measures are being carried out. Serious doses of strong antibiotics are administered intravenously. If antibiotic therapy does not help, surgical treatment is performed.
Differences in treatment between adults and children
The only difference in treatment between adults and children is that some harmless causes that are typical for adults are not applicable to children. For example, alcohol abuse, age-related changes, and the growth of fatty tissue are not found in children.
Often, the causes of puffy eyes in children lie in illness, poor diet, or disruption of sleep and rest patterns. In any case, parents should not rely on folk methods or their own experience and should immediately take the child to the doctor.
Also, cosmetic methods for eliminating swelling are not applicable to children, since they are performed only on people over 18 years of age.
Orbital phlegmon
Phlegmon of the orbit is orbital cellulitis, which is a purulent diffuse inflammation. The disease requires urgent treatment. It occurs acutely with pronounced symptoms, and not only ophthalmological ones. Orbital cellulitis can be a complication of periorbital cellulitis, as well as a stage of a complex diffuse pathological process that affects the eye tissue behind the orbital septum.
Orbital phlegmon cannot be called a common disease. However, it poses a serious danger not only to the patient’s vision, but also to his life. Purulent inflammation can spread through the veins to other organs. In severe cases, it affects the blood vessels of the brain, causing thrombosis. Sometimes orbital cellulitis of the orbit causes meningitis. Approximately 20% of patients with this disease die. In this case, as a rule, children under 5 years old suffer from orbital phlegmon. In adults, pathology is detected very rarely.
Barley
Barley (hordeolum) is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle or sebaceous gland at the root of the eyelashes.
Barley - appears as a swelling, painful, when the barley is opened, pus is released. Squeezing is strictly prohibited due to possible blood poisoning and inflammation of the meninges.
Ingestion of brewer's yeast is also recommended. The disease begins with limited hyperemia and painful swelling of the skin at the edge of the eyelid. Soon an abscess appears, upon opening of which pus and particles of necrotic tissue are released. Styes often recur and often accompany blepharitis. Dry heat or UHF therapy is applied locally. Due to the danger of the process spreading through the venous system, ointments should not be rubbed in or barley squeezed out. In the intervals between relapses of styes, the same local treatment as for simple blepharitis is useful.
Preventing bags under the eyes
The main rule for maintaining healthy eyes is healthy, full sleep - at least 8 hours a day. In this case, it is advisable to go to bed no later than 23:00, ensuring comfort in the room: completely close the curtains and ventilate the room before going to bed.
REFERENCE! You should not go to bed with remnants of eye makeup: in the evening, you must rinse off the makeup well and apply a special product (cream or mask).
It is not advisable to drink a lot of water or eat a lot before going to bed. Also, you shouldn’t spend too much time on your smartphone with the lights off while lying in bed: this increases eye strain, causes the nervous system to become excited and contributes to dry eyes.
Other preventative measures include:
- Normalization of the diet (inclusion of fruits and vegetables in the menu).
- Regular breaks while working on a computer, laptop, or tablet.
- Alternating passive and active activities: if the work is sedentary, you need to do exercises or take a 5-minute walk every 50 minutes, and vice versa.
- For eye health and sufficient oxygen supply to cells, you need to walk in the fresh air for at least an hour a day.
- See a doctor promptly if redness, tearing, swelling and discomfort in the eyes occur.
Useful video
Problems of the periorbital zone, dark circles under the eyes, puffiness, sagging:
Recommendations
- Plast Reconstruct Surg
. 1995 January; 95 (1): 37–42. “Fat pads of the suborbicularis oculi: anatomical and clinical study. C» Aiache AE, Ramirez OH. - How do you like; Paul Lazare, MD
- Plast Reconstruct Surg
. 1995 January; 95 (1): 37–42. "Fat pads of the suborbicularis oculi: an anatomical and clinical study". Ayache AE, Ramirez Ohio. - Merck Manual
, 18th edition, Merck Research Laboratories, 2006. - Medical Parasitology by Markell and Voege
, John and Petrie, Ninth Edition - Carroll G.G. "Multiple cranial neuropathies." Semin Neurol
. 2009;29(1):53-65. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/588522_9 - Gr, Decker; LU, Berber; Wee, Sulika (May 1991). "Periorbital edema and eyelid edema: the initial manifestation of acute infectious mononucleosis." Kutis
. PMID 2070653. Received 2020-06-03. - Beauty Doctor Hotline; Fredrik Haberman, DD
- https://www.google.com/patents/US5643587?dq=live+yeast+cell+derivative&hl=en&sa=X&ei=sAPGUNbYH4vIswaMtICQBQ&ved=0CEkQ6AEwBg Composition and method of lightening the skin under the eyes USPTO patent number: 5643587
- Nourish your skin from the inside out
Diagnostics
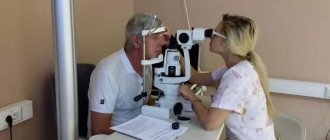
Before selecting a therapeutic course, the doctor conducts a detailed examination to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the cause of the spread of the anomaly. Mandatory procedures include:
- Tonometry. Measuring intraocular pressure;
- General blood analysis;
- Scraping from the mucous membrane for bacteriological examination;
- Ophthalmoscopy. Examination of the fundus to assess the condition of the structures of the visual apparatus;
- Ultrasonography;
- Radiography;
- Biomicroscopy. It is carried out to analyze the anterior and posterior sections of the eyeball.
Special attention should be paid to differential diagnosis, which will help exclude diseases such as epidermal tuberculosis, benign or malignant tumors, etc.
| Chemosis is diagnosed in patients of different age groups, but most often the disease affects adults. Children have a hard time with this pathology; usually their inflammation is accompanied by an infection. |