Mechanism of action of antibiotics
Medicines from this group are widely used in medicine. But their use has a number of features that must be taken into account in order for the therapy to be effective and the risk of side effects to be minimized.
These are special drugs that act on pathogenic microorganisms. The main purpose of antibiotics is the complete destruction of pathogenic bacteria. This group of drugs has two mechanisms of action:
- Bactericidal involves damaging the cell membrane of harmful microorganisms, which leads to their death.
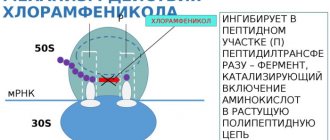
- Bacteriostatic is based on the effect on protein synthesis, stopping the proliferation of harmful microorganisms. Drugs with this effect are used not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of infectious diseases.
High-quality antibiotics should block pathogenic bacteria without harming healthy cells. This is possible due to the special property of drugs in this group - selective toxicity. The exception is especially strong antibiotics that have side effects.
Contraindications
It is necessary that antimicrobial ointments be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the patient’s condition and concomitant diagnoses. This is due to the presence of contraindications for their use. Self-treatment can lead to an increase in recovery time and serious complications. The instructions for each medicine stipulate prohibitions for use. General restrictions include:
- sensitivity to the components of the product;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- pregnancy period;
- childhood;
- breast-feeding;
- renal dysfunction;
- large affected area.
Antibacterial ointments are drugs that are available without prescription. The medicine can be ordered from catalogues, purchased from online pharmacies or purchased at your place of residence. The cost of ointments in rubles depends on the composition and amount of the drug in the tube. In Moscow pharmacies it is:
Antibiotic-based ointments have been used in medicine for many years. They are easy to buy at any pharmacy, and often they are not taken as seriously as drugs in tablets. The MedAboutMe portal looked into whether such medications can be used without a doctor’s prescription, and in what cases they are really necessary.
Principles of treatment
To get only positive results from antibiotic treatment, you need to adhere to certain principles:
- Rationality means that the pathogen must be correctly identified. Therefore, only the attending physician should prescribe antibiotics based on analysis and medical examination.
- “Umbrella” - this principle is used if it is not possible to determine the type of pathogenic bacteria. The patient is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics, which are effective for most diseases. Therefore, the doctor prescribes combination therapy to prevent antibiotic resistance.
- Individualization – when selecting medications, the doctor takes into account all the client’s characteristics. The specialist must also decide how to administer the medications in order for the therapy to be effective.
The doctor should select antibiotic therapy, taking into account all these principles, in order to minimize the risk of side effects.
Review of popular antibiotic ointments
The prescription of topical antimicrobial drugs is made by a doctor, taking into account an individual approach to each patient. In this case, the nature of the disease, the size of the affected area, and the location of the infection are taken into account. Popular pharmacological agents with antibiotics:
- Tetracycline ointment – actively counteracts aerobic gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms;
- Levomekol – contains the immunostimulating substance methyluracil;
- Dioxidin - treats complex, deep, long-lasting purulent cavities, wounds, ulcers.
- Baneocin is a combination drug that includes bacitracin, neomycin sulfate, antibiotics that destroy bacteria;
- Fulevil - treats bedsores, rectal fissures, burns, severe wounds;
- Lincomycin ointment - draws pus from wounds, counteracts infectious pathologies of tissues and skin;
- Gentamicin sulfate – suppresses most pathogenic microorganisms;
- Bactroban has a bacteriostatic effect, and with an increased dosage it has a bactericidal effect.
The list of popular remedies includes antibiotic ointments for purulent wounds:
- Fusiderm – has an antiexudative, antipyretic, antiallergic effect;
- Nitacid - absorbs purulent-necrotic masses, relieves inflammation, cleanses, dries the wound, reduces the risk of re-infection;
- Heliomycin - effective for infected eczema, dermatological pathologies, rhinitis with purulent discharge, has a vasoconstrictor effect;
- Erythromycin ointment - promotes the healing of burns, pustules on the skin and soft tissues.
Baneocin
Antibiotic ointment for wound healing has a strong antimicrobial effect. Baneocin contains two active substances - neomycin sulfate, bacitracin, which can penetrate the skin and destroy the infection. The drug is not recommended for use on fresh wounds and is prohibited for kidney pathologies. The drug Baneocin:
- has an anti-inflammatory effect;
- accelerates the process of cleansing the wound from pus;
- promotes tissue regeneration.
According to the instructions, the antibacterial agent is characterized by:
- The therapeutic effect is counteracting gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms, relieving inflammation, accelerating healing.
- Indications for use: pustular skin lesions, trophic ulcers, wounds, injuries, otitis externa, mastopathy.
- Dosage - the drug is applied in a thin layer to the affected surface, a bandage is applied, which is changed up to three times a day depending on the condition of the wound, for burns - once a day.
A local antimicrobial agent has:
- Advantages - can be used for cosmetic purposes - treatment of acne, acne - applied pointwise.
- Side effects - allergic reactions - occur rarely.
- Contraindications – large area of damage, sensitivity to antibiotics in the composition, impaired excretory function caused by renal, heart failure, lactation, pregnancy. The medicine is prohibited for the treatment of eye infections.
Tetracycline
This drug is recommended for use for the treatment of minor burns, minor damage to the skin - abrasions, scratches, cuts. Tetracycline ointment is widely used in ophthalmology for the treatment of eye infections. Medicine:
- has a bacteriostatic effect on microorganisms;
- active against most pathogens;
- accelerates cell regeneration;
- not recommended for diseases caused by group A streptococci;
- if there is no effect of treatment within two weeks, you need to see a doctor to change the drug.
The instructions for Tetracycline ointment stipulate:
- Therapeutic effect - the proliferation of bacteria is suppressed, inflammation is relieved, and the spread of infection is stopped.
- Composition – active substance – tetracycline hydrochloride.
- Indications for use: furunculosis, trophic ulcers, acne, pathologies of the organs of vision.
- Dosage - the duration of the course is determined by the doctor; the composition is applied to the skin in a thin layer; when treating the eyes, a small strip is placed under the lower eyelid.
Rules for taking antibiotics
Antibiotics are prescribed with caution because they can negatively affect healthy cells in the body. Therefore, there are a number of rules that must be followed:
- Antibiotics can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
- They should not be taken for viral infections, because there is a risk of complicating the course of the disease.
- It is best to take medications at the same time of day. It is not recommended to stop taking them on your own, even if you feel better. There is a risk that the disease will appear again.
- You cannot change the dosage of medications on your own. If it is reduced, the therapy may not be as effective. And if you increase it, there may be an overdose.
- Take the tablets with water only. Other drinks reduce their effectiveness.
- Distribute the time of taking medications so that there is an equal interval between them.
- During antibiotic therapy, it is not recommended to exercise.
- Drinking alcohol is prohibited.
By following these simple rules, you can take antibiotics with minimal risk of side effects. And the treatment will be more effective.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
These are the most frequently prescribed medications from this group. They are also called new generation antibiotics and are prescribed in the following cases:
- the pathogenic microorganism and type of infection have not been determined;
- the disease progresses too quickly;
- several pathogenic processes occur simultaneously;
- the causative agent of the disease is resistant to drugs in this category;
- after surgery to prevent infection;
- common disease.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics should be prescribed by a doctor. Below is a brief description of the most popular medications.
"Amoxicillin"
This medicine is available in tablet form. The minimum period for taking Amoxicillin is 3 days, the maximum is 10 days, but this is in the case of preventing complications after therapy.
This antibiotic should be given with caution to patients with diseases of the liver, kidneys, stomach and intestines. Taking Amoxicillin is prohibited for people suffering from:
- hypersensitivity to the components of this antibiotic;
- jaundice, the cause of which is a violation of the outflow of bile;
- disturbances in liver function;
- viral infections of the spleen, lymphoid tissue;
- blood diseases.
Based on medical history, the attending physician determines the dosage for adults and children.
"Ceftazidime"
The medicine is available in powder form, from which a solution containing ceftzidime is prepared. It is used intravenously and intramuscularly. It is prohibited to use a dropper with Ceftazidime for people with hypersensitivity to the components of the medicine. Only freshly prepared solution can be used.
"Levofloxacin"
Produced in the form of tablets or solution. Taking this antibiotic is prohibited:
- with damage to ligaments and tendons;
- for epilepsy;
- pregnant women and women during lactation;
- children;
- hypersensitivity and allergy to the medication.
The duration of treatment with Levofloxacin is from a week to two weeks. If an intravenous solution is prescribed, then treatment is until the symptoms disappear and 3 more after to prevent a relapse.
"Clarithromycin"
The drug is produced in the form of tablets. The duration of treatment for adults should not exceed more than 14 days. Children can take it for no more than 10 days. Taking Clarithromycin is prohibited for people suffering from:
- acute and chronic liver diseases;
- diseases of a nephrological nature;
- hypersensitivity to the components of this antibiotic;
- diseases for the treatment of which wormwood tincture is used.
It should also not be taken by people who are allergic to these components.
"Amikacin"
This antibiotic is available in the form of an injection solution. It is prohibited to prescribe:
- pregnant women;
- people suffering from chronic kidney and liver diseases;
- patients with high sensitivity to the components of the drug;
- people with acoustic neuritis.
The maximum period of treatment with Amicacion when administered intramuscularly is 10 days, when administered intravenously - no more than 7 days. The dosage of the drug is determined by the doctor depending on the age and weight of the patient.
Antimicrobial drugs and their characteristics
Sofradex - Sofradex.
INN (international nonproprietary name) - Dexamethasone + Framycetin + Gramicidin.
Release forms. Ointment, eye (ear) drops. Translucent ointment of yellowish-white color, sterile; transparent colorless sterile drops.
Compound. Framycein sulfate BP (soframycin), gramicidin and dexamethasone.
Pharmachologic effect. This effective drug has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Indications. Blepharitis; otitis externa.
Contraindications. Viral or fungal infection, purulent inflammation of the eyes, glaucoma, herpetic keratitis. For otitis externa, do not use in case of perforation of the eardrum due to the risk of ototoxicity.
Application and doses. Drops - adults (including the elderly) and children, 2 or 3 drops; introduce gradually one drop 3-4 times a day. Ointment - 1-2 times a day.
Supirocin-B - Supirocin-B.
Combined drug.
INN (international nonproprietary name) - Betamethasone + Mupirocin.
Release form. Ointment for external use in tubes of 15 g.
Compound. Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% and mupirocin 2%, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. Betamethasone is a topical glucocorticosteroid, classified as strong (group 2) with anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, anti-edematous, antipruritic effects. Mupirocin is an antibiotic of natural origin, depending on the concentration, bactericidal or bacteriostatic: Gr + cocci and Gr - rods.
Indications. Non-allergic and allergic contact dermatitis, as well as seborrheic, atopic, exfoliative dermatitis, dermatitis herpetiformis, eczema, neurodermatitis. Also, this broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug is used for urticaria and psoriasis, complicated by secondary bacterial infections.
Contraindications. Bacterial, viral, fungal skin lesions, trophic leg ulcers associated with varicose veins, rosacea and acne vulgaris, skin cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, melanoma, nevus, atheroma, hemangioma, xanthoma, post-vaccination skin reactions, as well as pregnancy, lactation, children's age up to 12 years.
Side effect. Non-allergic and allergic contact dermatitis, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, hypopigmentation, skin atrophy, acne-like rashes, perioral dermatitis, secondary infection, maceration, prickly heat.
Application and doses. Apply a thin layer to the affected areas 2-3 times a day for 5-14 days. Only for treating affected areas no more than 10 cm long and up to 100 square centimeters in area. If there is no improvement within 3-5 days, the patient should be re-examined.
Special notes. Avoid contact with eyes, mucous membranes, and open wound surfaces. Due to its potent characteristics, it is preferable to use this antimicrobial agent only in the acute period of the disease, and for a short time, on minor surfaces of the skin.
Treatment of children
Experts have long debated whether antibiotics can be prescribed to children. This is due to an underdeveloped liver enzymatic system and kidney filtration mechanisms. Therefore, children under 12 years of age are prescribed a reduced dosage, and from 12 years of age - as for adults.
Parents should remember that antibiotics are prescribed only to treat bacterial, not viral diseases. The most common side defect in children after taking antibiotics is disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
Most antibiotics for adults should not be prescribed to children. But there are medications that pediatricians often prescribe for treatment.
"Oxacillin"
This penicillin-based antibiotic is available in powder or tablet form. The powder is used to prepare a solution for injection. It may be prescribed to newborns and premature infants. Taking Oxacillin is prohibited if you have hypersensitivity to penicillin and its derivatives.
"Cefixime"
The drug is produced in tablet form and is widely used in pediatrics. But its use is prohibited in such cases as:
- individual intolerance to the drug and its components;
- chronic kidney diseases;
- underweight (up to 25 kg).
It can be prescribed to infants, but it only needs to be crushed into powder. The dosage and duration of treatment is determined by the pediatrician.
"Aztreonam"
This antibiotic is available in powder form for intramuscular or intravenous administration. It is prescribed to children with serious illnesses. The dosage and duration of therapy is determined by the pediatrician.
Treatment with Aztrenom is prohibited if:
- liver and kidney diseases;
- hypersensitivity to the drug or all antibiotics;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The need to take Aztrenoma is determined by the pediatrician, as well as the dosage.
External antimicrobial agents: indications and contraindications
Triderm - Triderm.
INN (international nonproprietary name) - Betamethasone + Gentamicin + Clotrimazole. Combined drug.
Release forms. Ointment and cream 15 g each.
Compound. Betamethasone dipropionate, clotrimazole, gentamicin. For external use.
Pharmachologic effect. Betamethasone dipropionate is a fluorinated external glucocorticoid, classified as moderately strong (group 3) with anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antiexudative and antipruritic effects. Clotrimazole has an antifungal effect against dermatophytes and yeast-like fungi. Gentamicin is an antibiotic of the aminoglycoside group, has a bactericidal effect on Gr+ and Gr- bacteria.
Indications. Dermatoses complicated by secondary infection; mycoses of the hands and feet, smooth skin, inguinal mycosis.
Contraindications. Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, lactation.
Side effect. Exudation, erythema, pigmentation disorder, burning sensation, itching. Betamethasone-induced folliculitis, hypertrichosis, acne, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, skin maceration, development of secondary resistant flora, skin atrophy, stretch marks, prickly heat, burning, itching, dryness. Caused by clotrimazole - erythema, peeling, swelling, maceration of the skin, urticaria, paresthesia, itching. Caused by gentamicin - hyperemia, itching.
Application and doses. Apply a thin layer to the affected and surrounding skin in the morning and at night for 3-4 weeks. Use with caution during pregnancy; lactation is incompatible with the use of the drug.
Special notes. When applying this broad-spectrum antimicrobial ointment to large surfaces, as well as when using occlusive dressings, suppression of the production of corticosteroid hormones is possible. Avoid application to damaged skin and open wounds. If resistant bacterial or fungal microflora appears, you should stop using the drug and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Fucidin G - Fucidin N.
INN (international nonproprietary name) - Hydrocortisone + Fusidic acid. Combined drug.
Release form. Cream for external use in tubes of 15 g. Homogeneous white cream. Keep out of the reach of children.
Compound. Active ingredients: fusidic acid hemihydrate (an antibiotic of a polycyclic structure) and hydrocortisone acetate. Pharmachologic effect. Combines the antibacterial effect of fusidic acid - against staphylococci, streptococci, as well as the causative agent of lichen versicolor, etc. and the anti-inflammatory effect of hydrocortisone.
Indications. Complicated by bacterial infection, non-allergic and allergic contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis, lichen planus, discoid lupus erythematosus.
Contraindications. Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, as well as skin tuberculosis, manifestations of syphilis on the skin, chicken pox, viral and fungal skin infections, post-vaccination skin reactions, trophic ulcers, rosacea, acne vulgaris, open wounds.
Side effect. Itching, burning, tingling, erythema, dry skin, as well as irritation and rash. Rarely, when using this antimicrobial drug, acne-like rashes, hyperpigmentation, folliculitis, stretch marks, skin atrophy, hypertrichosis, and allergic contact dermatitis are possible.
Application and doses. Apply a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day for 2 weeks. During pregnancy and lactation, do not use for a long time and in large quantities; when breastfeeding, do not apply to the mammary glands.
Special notes. Use cautiously on the face, in skin folds and in children. Avoid contact with eyes.
Local antibiotics
The peculiarity of this group of drugs is that they are applied to the site of infection. Therefore they are widely used for:
- treatment of skin and soft tissue diseases;
- therapy of diseases of the mucous organs of the respiratory and hearing organs, oral cavity and genital organs.
They are produced in the form:
- ointments;
- powder;
- solution.
The most popular antibiotics from this group are Sintomycin, Tetracycline and Levomycetin.
"Sintomycin"
This is an ointment that is used to treat purulent diseases. Its use is prohibited for psoriasis, skin rashes and the presence of fungus. Cotton swabs are soaked with “Synthomycin” or a thin layer of ointment is applied to the affected area, and a sterile bandage is placed on top.
"Tetracycline"
This ointment is prescribed for the treatment of skin diseases with complications in the form of suppuration. You cannot use Tetracycline if you have a fungus and are individually intolerant to the drug or its components. It should also not be taken by pregnant women or women during breastfeeding.
"Levomycetin"
This local antibiotic is available in the form of a solution. Used for damaged skin, otitis media and purulent lesions. There are a number of contraindications for treatment with Levomycetin:
- individual intolerance;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- violation of pigment metabolism;
- age up to one year;
- fungal diseases;
- psoriasis and eczema.
The duration of use of the ointment is until the skin is completely healed.
Anti-inflammatory antimicrobial agents and methods of their use
Lorinden S.
Combined drug.
Release forms. Cream and ointment in tubes of 15 g.
Compound. 1 g of this antimicrobial drug contains 200 mcg of flumethasone pivalate and 30 mg of iodochlorhydroxyquinoline.
Pharmachologic effect. The first component is a local fluorinated glucocorticoid, classified as moderately strong (group 3) with antiallergic, antipruritic and antiexudative effects, and the second component has antibacterial and antifungal effects.
Indications. Allergic dermatoses complicated by bacterial infection, dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, including old cases on the scalp, atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, discoid lupus erythematosus, urticaria, bacterial and fungal skin infections complicated by local allergic reactions, impetigo. In the acute phase of the disease, a cream is used, and then an antimicrobial ointment is used.
Contraindications. Viral skin lesions, skin manifestations of tuberculosis and syphilis, neoplasms and precancerous skin diseases, acne vulgaris and rosacea, perioral dermatitis, trophic leg ulcers associated with varicose veins, conditions after vaccination. For occlusive dressing - skin infections.
Application and doses. Apply to affected areas of skin 3 times a day until improvement. During pregnancy, do not use in the 1st trimester, later - only on small surfaces.
Special notes. This antimicrobial agent of modern pharmacology requires caution when administered to nursing mothers.
Oxycort - Oxycort.
INN (international nonproprietary name) - Oxytetracycline + Hydrocortisone. Complex drug.
Release forms. Ointment in a tube of 20 g, aerosol for external use in a bottle of 75 g.
Compound. The ointment contains oxytetracycline hydrochloride 3% and hydrocortisone acetate 1%; aerosol - 0.4 and 0.13%, respectively. Pharmachologic effect. A broad-spectrum antibiotic provides an antibacterial effect, and a glucocorticoid is anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and antipruritic, with a weak effect (group 4). The aerosol has a pronounced drying effect.
Indications. Dermatitis, eczema, atopic dermatitis, complicated by pyogenic infection, as well as trophic ulcers, sunburn, frostbite, strepto- and staphyloderma, erysipelas, infected diaper rash. This broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug is also used for other dermatoses complicated by secondary bacterial infection.
Contraindications. Skin manifestations of skin tuberculosis, viral and mycotic infections, pregnancy (if there are large areas of damage), individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Side effect. Rarely, when using this antimicrobial drug, an allergic rash appears, and with prolonged use, steroid acne, skin atrophy, telangiectasia, and hypertrichosis are possible.
Application and doses. Apply a thin layer to the affected areas 2 times a day. Spray the aerosol from a distance of 15-20 cm 2 times a day.
Special notes. Avoid contact of the drug with mucous membranes; Do not inhale the aerosol.
Where to buy drugs in Moscow
The Aptstore pharmacy chain offers a large selection of antibiotics for both general purpose and local use. All medications meet all quality and health safety requirements.
You can select the medications you need in the electronic catalog on the pharmacy website. In total, there are 34 branches in Moscow. Delivery can be ordered to the nearest branch. All addresses are indicated on the map on the website. When purchasing an order, the client must show a doctor’s prescription for taking antibiotics.
If the antibiotic you need is not in stock, you can pre-order it. When the goods arrive, the client will receive a notification about its arrival.