Causes of edema with headache
Frequent headaches, which are accompanied by swelling of the face, limbs or the whole body, most often indicate the presence of unpleasant pathologies in the body. These include cerebral edema, surges in intracranial pressure and osteochondrosis.
In addition, the cause of swelling and headaches can be a cyclic disorder of the nervous system, which manifests itself in the form of periodic cluster headaches.
Brain swelling
Cerebral edema is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the brain or spinal cord. Edema leads to an increase in organ volume and increased pressure in the cranial cavity. Most often, swelling occurs against the background of the following pathologies:
- head injury;
- severe hypothermia;
- hypoxia of brain tissue;
- hydrocephalus;
- microembolism of cerebral vessels;
- carotid artery occlusion;
- alcoholism;
- oncology.
The disease is accompanied by a headache of moderate or high intensity, a feeling as if the skull is bursting from the inside, nausea, vomiting at the peak of the pain syndrome, clouding of consciousness, and swelling.
Treatment of headaches due to cerebral edema is possible only after consulting a doctor. Do not neglect contacting a specialist, otherwise swelling can lead to displacement or deformation of brain structures, depression of breathing, vision and blood circulation.
First aid is to call an ambulance. Before the ambulance arrives, you can wrap your head with a towel soaked in cold water. Depending on the cause of the disease, the patient must be hospitalized in a neurological or neurosurgical department.
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial hypertension occurs when cerebrospinal fluid stagnates in various parts of the brain.
The reasons for increased pressure may be:
- skull injury;
- meningitis;
- disruption of fluid exchange in the body;
- hypoxia of brain tissue;
- stroke;
- migraine attack;
- encephalitis;
- brain tumor.
Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure are as follows:
- bursting headache, most often occurring in the morning;
- pain when tilting and turning the head;
- broken state, loss of strength;
- swelling of the optic nerve;
- visual and hearing impairment;
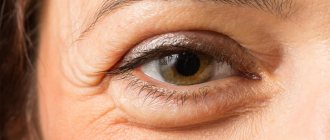
- swelling of the face, eyelids, bags under the eyes;
- nausea or vomiting;
- increased sweating;
- clouding of consciousness.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting and depending on the cause of increased intracranial pressure. Do not ignore the symptoms of intracranial hypertension and consult a doctor. Taking painkillers will not help eliminate the disease.
Pressure on the brain can cause a decrease in mental abilities, disruption of the central nervous system and, as a result, all organ systems. As first aid for intracranial hypertension, diuretics are indicated to help reduce the amount of fluid in the tissues.
If there is no threat to the patient’s life, then therapy to regulate blood pressure and sedatives are prescribed.
Beam (cluster) headache
Cluster headache occurs against the background of a cyclic nervous disorder. Most often, men who have reached puberty are susceptible to such pain. The etiology of this disease is not fully understood.
It is believed that cluster pain occurs due to regular shifts in the internal biological clock due to frequent flights, time zone changes, sleep disturbances, and genetic predisposition. In most cases they occur during sleep.
Main symptoms of cluster headache:
- severe headache localized in the area of the right or left eye;
- swelling of the eyelid, sometimes of the cheeks on the side where the pain occurred;
- redness of the eye;
- visual impairment;
- congestion in the ear;
- the appearance of perspiration on the forehead;
- facial redness.
The pain can be so severe that a person may lose consciousness. For this reason, the first aid for such pain is to immediately take painkillers.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine occurs due to degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc. The disease leads to spasm of the vertebral artery. The causes of osteochondrosis are:
- flat feet;
- poor posture;
- low physical activity;
- intervertebral disc injuries;
- shifting the daily load on the spine (for example, carrying a heavy bag on only one shoulder);
- obesity;
- lack of nutrients.
Against the background of cervical osteochondrosis, a throbbing, burning headache often occurs, which may be accompanied by swelling of the arms and shoulder girdle. In addition, symptoms such as:
- pain in the neck and shoulders that gets worse with movement;
- muscle spasm;
- numbness of the limbs;
- feeling of aching in the shoulders and neck;
- dizziness;
- visual disturbances: colored spots before the eyes.
The main measures for the treatment of osteochondrosis include relieving pain, eliminating dysfunction of the spinal roots and preventing further deformation of the spine.
First aid for headaches due to osteochondrosis is to take painkillers and massage the collar area.
In addition, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures: physical therapy, manual therapy, spinal traction using special equipment, therapeutic massage and physiotherapy.
Cardiovascular diseases
In cardiovascular diseases, blood pressure increases due to increased cardiac output or increased total peripheral vascular resistance. Features of arterial hypertension in cardiovascular diseases:
- The headache is paroxysmal, the pain occurs when the pressure increases, and its intensity decreases when it decreases;
- With heart failure, swelling of the legs periodically occurs, most often in the evenings; in the morning the swelling goes away. The face with cardiac edema usually does not swell;
- Blood pressure is increased due to systolic (upper) pressure;
- Pain in the heart, feeling of constriction, palpitations;
- The swelling does not hurt, it is elastic to the touch, a hole remains at the place of finger pressure, which disappears within a few seconds;
- Minor subcutaneous hemorrhages may occur;
- There is no change in the amount or composition of urine;
- A severe complication of cardiovascular disease is pulmonary edema, which is accompanied by shortness of breath, palpitations, chest pain and fear of death. In case of pulmonary edema, you should immediately call an ambulance, give the patient a comfortable sitting position (orthopnea with legs down), while tourniquets can (and even should) be applied to the leg area to reduce the flow of blood into the upper torso.
The patient's condition is changeable - the state of health can change dramatically during the day under the influence of emotional or physical stress, drinking coffee, alcohol, or smoking.
For the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmic drugs, and diuretics are prescribed.
Swelling and headache during pregnancy
Swelling of the limbs is one of the common symptoms during pregnancy. The main signs of swelling:
- rapid weight gain - more than 1 kilogram per week;
- change in the shape of the face, enlargement of the lips and nose;
- swelling of the eyelids, bags under the eyes;
- the foot does not fit into worn-out shoes;
- numbness and tingling of the limbs;
- It’s hard to bend your hand into a fist, it’s hard to move your toes.
If swelling is accompanied by a headache, you should immediately consult a doctor. This condition indicates gestosis, which is especially dangerous in the last trimester of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the list of drugs that can be used to relieve pain is very limited. Of the approved drugs, you can take Ibuprofen or Nurofen (only in the first and second trimester), Papaverine and Paracetamol.
Limiting daily fluid intake and taking diuretic medications will help relieve swelling: Canephron, Phytolysin, Eufillin. You can also take infusions and decoctions of cranberries, lingonberry leaves, lovage, bearberry leaves and birch.
Before taking any medications, you should consult a supervising obstetrician-gynecologist.
Prevention measures
To reduce the likelihood of headaches and puffy eyes, certain preventive measures should be followed. Experts recommend:
- Introduce a sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits into your diet, as they contain vitamins and minerals that support the immune system.
- Follow a daily routine, sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Stop drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Rule out head injuries.
- Treat kidney and cardiovascular diseases in a timely manner.
- Exercise.
- Visit your doctor regularly for preventive examinations.
- Avoid hypothermia and overheating in the sun.
Attention! Preventive measures will help not only avoid headaches and swelling of the eyes as a result of physiological causes, but also reduce the risk of developing dangerous conditions accompanied by these symptoms.
Swelling of the eyes, face and headache may indicate the development of serious diseases that require urgent treatment. But most often they appear against a background of lack of sleep and fatigue. It is important for patients to know that they should consult a doctor in cases where other symptoms occur along with headache and swelling of the eyes. This is due to the fact that certain conditions characterized by these signs can become a threat to life and health.
source
Other reasons
Headache and facial swelling can also occur due to physiological reasons. They do not pose a danger to the life and health of the patient. Unpleasant symptoms occur due to natural causes.
The main signs of physiological swelling and pain are:
- Swelling for a short time. They appear in the morning and subside fairly quickly.
- The headache is moderate, localized on one or both sides, but does not spread.
- Not accompanied by symptoms such as shortness of breath, tachycardia, pain in the chest, lumbar region, or increased temperature.
The causes of physiological swelling and headaches are often associated with bad habits or climate. Unpleasant symptoms may occur in the following cases:
- Drinking large amounts of liquid.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Overheating in the sun during the hot season.
- Eating large quantities of fatty, salty or spicy foods.
- Lack of sleep.
- Drinking alcohol.
Headaches and facial swelling are also common during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester.
Unpleasant symptoms caused by certain physiological conditions can be easily eliminated without medical help. It is enough for a person to rest, get enough sleep, go into the shade, and reduce the consumption of junk food and liquid.
Why does the upper eyelid swell and cause a headache?
Headache and swelling of the eyelids occur simultaneously quite rarely. Usually these two signs are not related. Sometimes their appearance indicates the development of severe pathologies of internal organs. In what cases should you definitely see a doctor? Let's consider the causes of swelling of the upper eyelids in the presence of a headache.
Blepharitis: swollen eyelid and headache - what to do?
Blepharitis is inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. Often the disease takes a chronic form and often recurs. There are many causes and types of blepharitis, but in most cases inflammation of infectious etiology is detected. The most common types of this
Each of them has its own symptoms. We can briefly list the following signs of all blepharitis:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- itching and burning;
- increased sensitivity of the eyes to light and wind;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- pain in the eyeball area;
- blurred vision;
- discharge of purulent masses;
- sticking and loss of eyelashes;
- the appearance of scales;
- rash on the upper eyelids and skin around the eyeballs;
- accumulations of foamy discharge in the corners of the eyes.
With blepharitis, the upper eyelid usually becomes inflamed. In this case, inflammation can be bilateral or unilateral. Symptoms can be obvious or mild. It depends on the form in which the pathology occurs - acute or chronic. With blepharitis, headaches are not common. This symptom may appear in two cases:
- the patient puts a lot of strain on his eyes by reading or working at the computer during the treatment period;
- the disease has become more complicated, and the inflammatory process has spread to the conjunctiva or cornea.
Blepharitis is treated with eye drops and ointments. The type of drug is determined by the etiology of the disease.