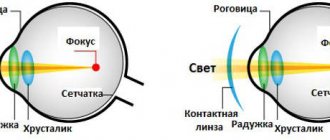
Which eye prosthesis is better - glass or plastic?
Now we will try to figure out which ocular prosthesis made of which material (glass or plastic) is preferable to use. glass eye prostheses have become most widespread (since the 1930s) in Russia.
.
This was due to economic efficiency (low production costs and speed of production), availability of raw materials, and low labor costs for the production of prostheses. At the same time, manufacturing eye prostheses from plastic
is more expensive and complex. It is enough to give an example: a glass prosthesis can be made in 20 minutes, while a plastic prosthesis will take 3 working days.
Why do you need an ocular prosthesis?
Indications for implantation of an ocular analogue are:
- absence of the organ of vision as a result of mechanical damage, thermal or chemical injury;
- underdevelopment or complete absence of the eyeball. Occurs in 3-6 cases per 100,000 newborns. In this case, prosthetics must be performed as early as possible, before the formation of skull deformation;
- artificial removal of the eyeball using enucleation or evisceration for malignant or benign neoplasms;
- impaired development of the eyeballs (microphthalmos). The pathology is often genetic in nature and can lead to asymmetry of vision, which will negatively affect a healthy organ.
An artificial eye resembles a normal eye in appearance, but is not capable of restoring vision.
In some cases, the implant may be partial and replace a specific element of the organ, for example, the lens or iris.
The purposes of ocular prostheses are:
- protection of the orbit from injury, deformation, and infections;
- maintaining the eyelids in a normal position, preventing loss of tone and sagging;
- maintaining facial expressions;
- prevention of growth retardation of orbital bones in children, as well as skull deformation;
- preservation of reflex connections of the visual system.
No matter how high-quality an artificial analogue is, it cannot replace a real eye: a living organ is capable of changing the shade of the iris, the diameter of the pupil, and is also more mobile. However, a well-made product, subject to proper use, will help solve problems not only of an aesthetic nature, but also of a psychological nature.
Eye prosthetics is the only way to return a person to a full life after losing an organ of vision.
Suggested method
We have made an attempt to use an ocular prosthesis to transmit through it data about the surrounding environment to patients with the absence of both eyes or absolute blindness. The technique is based on the impact of weak electrical impulses coming from the prosthesis on the mucous membrane of the orbital cavity and control of the device by recording the movement of the ocular prosthesis.
The theoretical basis for this possibility is several well-known facts.
- Firstly, even with complete removal of both eyes, some part of the visual analyzer is preserved.
The most well-known signs of this are the presence of dreams with visual images and the activity of the oculomotor muscles, which can be manifested by the movement of completely blind eyes or ocular prostheses, and by movement in the “right” direction. This phenomenon is well known and used by both us ocular prosthetists and disability experts. An old technique for exposing feigning blindness was to ask to look at the voice - the blind person turns his eyes towards the voice, and the pretender looks straight.
- Second. The mucous membrane covering the stump of the removed eye and the orbital cavity has a certain innervation and can perceive the effects of weak electrical impulses.
We studied the sensitivity of the conjunctiva to electrical impulses. On a healthy eye it is 80-100 mA. in persons wearing an ocular prosthesis, there is a large difference in the results and it ranges from 100 to 300 microns and possibly more since we did not study sensitivity at large current values.
- Third. The role of eye movements in the process of vision has long been well studied, and although exactly how the connection is made between the nuclei of the three pairs of oculomotor nerves and other parts of the brain that carry out the act of vision is unknown, the very existence of such a connection is undeniable.
It should be noted that the nuclei of the oculomotor nerves are located in the superior colliculus, where the first neurons of the visual pathway end and from where visual information is transmitted to the cerebral cortex. It was shown a long time ago that if an absolutely healthy eye with normal vision is artificially immobilized, it will go blind, and vision on it will not be restored until the possibility of its movement is resumed. The nature of eye movements when viewing objects has been studied and can be used to create devices to help the blind.
- Fourth. It has been established and officially recognized that a person can do without outside help if his visual acuity is more than 3 percent and his field of vision is more than 10 degrees in diameter. These two figures can be considered an intermediate goal for the electronic devices being developed.
Considering the above, we can offer a device to help the blind that is operational now and has great potential for improvement. The described device consists of two blocks and a laptop computer.
Types of prostheses
Artificial eyes can have different purposes: some products are used for temporary use, others for long-term use, and others are used in the postoperative period.
Implants are made from different materials: glass and plastic:
- Glass products are lighter and more fragile, have a smooth surface, are well wetted by tear fluid, but require careful wearing. Their shelf life is 1 year.
- The plastic analogues are more durable, the wearing period of which is 2 years. Such dentures are not affected by the environment, but they weigh more and are less smooth.
Plastic products are more in demand among patients.
All products are made by hand. They can be made to order or purchased ready-made. Mass-produced implants are manufactured in factories to certain standards. Such prostheses are available right and left, have different sizes (small, large, medium), shape, iris color and pupil diameter.
During prosthetics, the specialist selects an implant that is most suitable for a particular patient, taking into account the characteristics of the eye, the color of the iris, sclera, etc.
When individually manufactured, the product takes into account the characteristics of the patient’s conjunctival area, the relief and color of the iris and sclera.
In addition to artificial eyes, which are used in the complete absence of an organ, there are special endoprostheses made of biological or synthetic material. If part of the eye, such as the cornea, is affected, thin-walled products or scleral lenses are used - large contact lenses placed on the sclera.
Preliminary results
Our internal tests proved the ability to distinguish through the prosthesis the direction of hand movement on the face (from right to left or from top to bottom) and, unfortunately, we had to stop there, since for further research it is necessary to conduct a full cycle of other tests proving the safety of the device. Currently, the documentation for it has been transferred to our Ministry of Health for approval of the testing procedure.
Despite the pause in testing, I have no doubt about the performance and effectiveness of this device due to its feasibility, since it is relatively cheap and does not require surgical operations for its use. In addition, it is easily perceived by users as just a type of ocular prosthesis, which they are already accustomed to and have been using for a long time, if desired. they can just as easily refuse it. Preliminary calculations show that with a good state of innervation of the mucous membrane of the orbital cavity and a field of view of 10 degrees, it is theoretically possible to achieve a device resolution of up to 1/20-30 arc minutes, which corresponds to a visual acuity of about two to three percent. An important advantage of the device is the ability to assemble it from commercially produced parts in an ordinary ocular prosthetics laboratory.
It seems that the problem of helping completely blind people will in the near future be solved not in neurosurgical clinics, but mainly by our colleagues in eye prosthetics centers.
Zavadsky Stanislav Lazarevich, director of the Contact Lenses Plus unitary enterprise. 220040, Belarus, Minsk, st. Nekrasova, 19 tel. +375 17 202 00 80
How is the operation performed?
Prosthetics are performed in stationary conditions. First, under general anesthesia, the surgeon removes the damaged organ. The mucous surface is separated from the eyeball, after which the nerves and muscle fibers holding the organ are cut. The eyeball is then removed. The empty area must be filled with a thin plate. At this stage, it is advisable to use stepped prosthetics.
The implant is inserted approximately 7-12 days after surgery. After one or two months, when the swelling of the conjunctival sac subsides, the plate is replaced with a temporary plastic prosthesis, which is replaced with a new one after a year.
The patient is first selected an analogue that corresponds to the size of the eye socket and best matches the color of the iris and the diameter of the pupil of the other eye.
The artificial analogue is held in the eye socket using the eyelids. When the healthy eye moves, it is also able to move. Moreover, its mobility depends on the tone of the extraocular muscles.
Device for assisting the blind
One of the blocks houses a video camera, reader, antenna, and battery. All elements can be mounted on spectacle frames or sunglasses. Communication with the computer and the power supply for the computer is carried out through standard cables. Data from the video camera is transferred to a computer, where it is processed and transmitted to the reader, which communicates with the second unit using an antenna. Communication between the units is carried out in two directions using the NFC wireless communication protocol. An example of the application of such communication in other areas is the use of contactless payment cards.
The second block is placed inside the ocular prosthesis. Modern microelectronics element base makes it possible to place a microchip, an accelerometer (this is a part that allows you to register the projection of acceleration and thus record the movement of the eye prosthesis), an NFC antenna and a power source, which will provide the ability to transmit information by exposing the conjunctiva to electrical impulses of such strength that perceived by the patient.
The chip we use has 8 active leads, some of which are used for electrodes extending to the back surface of the prosthesis.
Contraindications for prosthetics
There are a number of contraindications for eye prosthetics:
- the presence of severe inflammation of the iris;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- presence of a foreign object;
- suspicion of neoplasms;
- uveitis in the relapse stage;
- fusion of the conjunctiva of the eyelid with the conjunctiva of the eyeball;
- thinning of the cornea, leading to the eyeball losing its shape.
Prosthetic eye will provide electronic vision
The development of electronic vision methods and devices for orienting the blind has been going on for several decades. Belarusian eye prosthetists are trying to create a cheap eye prosthesis that will allow those who have lost their organ of vision to see at least a little.
An attempt has been made to use an ocular prosthesis to transmit data about the surrounding environment through it to patients with the absence of both eyes or complete blindness. The technique is based on the impact of weak electrical impulses coming from the prosthesis on the mucous membrane of the orbital cavity and control of the device by recording the movement of the ocular prosthesis.
The theoretical basis for this possibility is several well-known facts.
- Even with complete removal of both eyes, some part of the visual analyzer remains.
- The mucous membrane covering the stump of the removed eye and the orbital cavity has a certain innervation and can perceive the effects of weak electrical impulses.
- The role of eye movements in the process of vision has long been well studied, and although exactly how the connection is made between the nuclei of the three pairs of oculomotor nerves and other parts of the brain that carry out the act of vision is unknown, the very existence of such a connection is undeniable.
- It has been established and officially recognized that a person can do without outside help if his visual acuity is more than 3 percent and his field of vision is more than 10 degrees in diameter. These two figures can be considered an intermediate goal for the electronic devices being developed.
Taking into account the above, a device is proposed to help the blind, which is operational now and has great potential for improvement. The described device consists of two blocks and a laptop computer.
Device for assisting the blind
One of the blocks houses a video camera, reader, antenna, and battery. All elements can be mounted on spectacle frames or sunglasses. Communication with the computer and the power supply for the computer is carried out through standard cables. Data from the video camera is transferred to a computer, where it is processed and transmitted to the reader, which communicates with the second unit using an antenna. Communication between the units is carried out in two directions using the NFC wireless communication protocol. An example of the application of such communication in other areas is the use of contactless payment cards.
The second block is placed inside the ocular prosthesis. Modern microelectronics element base makes it possible to place a microchip, an accelerometer (this is a part that allows you to register the projection of acceleration and thus record the movement of the eye prosthesis), an NFC antenna and a power source, which will provide the ability to transmit information by exposing the conjunctiva to electrical impulses of such strength that perceived by the patient.
The chip used has 8 active leads, some of which are used for electrodes extending onto the back surface of the prosthesis.
How the device works
The device is only at the initial stage of development. Now it is limited only to the analysis of the brightness of the background and individual fields of the environment.
The video camera has a field of view of 80 - 120 degrees, of which at any given time only a 10-degree area is active and it is in constant motion.
When an object appears that differs significantly in brightness from the background in one direction or another (darker or lighter than the background), a short-term electrical impulse is applied through the electrodes to a certain part of the mucous membrane located under the prosthesis. This impulse is quite clearly felt by the user as a weak prick and allows the user to determine from which direction the light or shadow appeared. If the user moves the visual axis of the video camera towards this object, then a repeated impulse will be transmitted in the center of the prosthesis.
A possible example is that a blind person is in a room that has a bright window and an open door to a dark corridor. When a light window or a dark door enters the active part of the device’s field of view, a person will feel an impulse and turn the device’s “look” to it.
Preliminary results
During internal tests, the ability to distinguish through the prosthesis the direction of movement of the hand on the face (from right to left or from top to bottom) was proven, and the developers had to stop there, since for further research it is necessary to conduct a full cycle of other tests proving the safety of the device. Currently, the documentation for it has been transferred to the Ministry of Health of Belarus for approval of the testing procedure.
The demand for the device is obvious.
- It is expected that it will be efficient, effective, and relatively cheap, which is important - it will not require surgical operations for its use.
- In addition, it is easily perceived by users as just a type of ocular prosthesis, which they are already accustomed to and have been using for a long time, if desired. they can just as easily refuse it.
Preliminary calculations show that with a good state of innervation of the mucous membrane of the orbital cavity and a field of view of 10 degrees, it is theoretically possible to achieve a device resolution of up to 1/20 -30 arc minutes, which corresponds to a visual acuity of about 2-3%. An important advantage of the device is the ability to assemble it from commercially produced parts in an ordinary ocular prosthetics laboratory.
Material provided:
Caring for your prosthesis
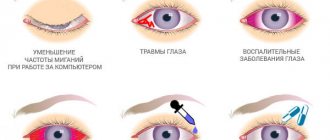
The frequency of implant treatment is determined individually. If there is clear discharge from the eyes, it is recommended to rinse the artificial eye once a week. However, if the ophthalmologist recommended taking the product out at night, hygiene must be observed every day.
If white, yellow or green discharge appears, an infection can be suspected. In this case, in addition to hygiene procedures, drug treatment will be required.
When wearing an implant, the patient must adhere to the following rules:
- if the prosthesis causes discomfort and pain, you must inform your doctor about this;
- When diving, you should not allow water to enter. When bathing, eyelids should be kept closed;
- Without the recommendations of an ophthalmologist, you should not remove the artificial eye without permission. In some cases, this can lead to a shrinkage of the eye cavity;
- It is necessary to wipe the eyelid from the outer to the inner edge, from bottom to top, otherwise the lower eyelid may become flabby and not tightly hold the bottom of the implant.
The prosthesis and suction cup can be washed with plain water and baby soap, clearing them of plaque with a piece of gauze. If there is purulent discharge, Miramistin solution is applied to a cleanly washed implant. In addition, special care products are used for cleaning, for example, Biotrue (USA) or Solo care (Switzerland). The product is soaked in the solution for 15 minutes, after which it is wiped with a cotton swab. It is recommended to drop special drops into the conjunctival sac and onto the implant itself, for example, Comfort Drops.
To clean the artificial eye and the eye socket itself, it is prohibited to use potassium permanganate, Albucid, Furacilin, alcohol-containing solutions and solvents: they can lead to wear of the product.
How the device works
At the initial stage, we limit ourselves to only analyzing the brightness of the background and individual fields of the environment. The video camera has a field of view of 80 - 120 degrees, of which at any given time only a 10-degree area is active and it is in constant motion.
When an object appears that differs significantly in brightness from the background in one direction or another (darker or lighter than the background), a short-term electrical impulse is applied through the electrodes to a certain part of the mucous membrane located under the prosthesis. This impulse is quite clearly felt by the user as a weak prick and allows the user to determine from which direction the light or shadow appeared. If the user moves the visual axis of the video camera towards this object, then a repeated impulse will be transmitted in the center of the prosthesis
A possible example is that a blind person is in a room that has a bright window and an open door to a dark corridor. When a light window or a dark door enters the active part of the device’s field of view, a person will feel an impulse and turn the device’s “look” to it.