Rating: 5 / 5
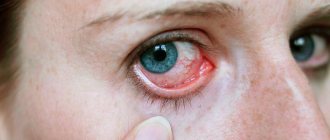
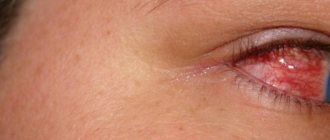
Washing the eyes with potassium permanganate helps destroy pathogenic microflora. The product is a strong antiseptic. Disinfects the mucous membrane, stops inflammation, accelerates recovery. A weak solution of potassium permanganate is used as a medicine. Soak a cotton pad and cleanse the visual organ of secretions. The main indication is inflammation of the eye membrane or conjunctivitis. The disease develops in people with weak immunity, as well as when exposed to unfavorable external factors - dust, dirt.
Therapeutic effect
Potassium permanganate is widely used in gynecology, urology, gastroenterology, dermatology, surgery, and other branches of medicine. The popularity of potassium permanganate is caused by a wide range of beneficial properties:
- disinfectant;
- antiseptic;
- antimicrobial;
- regenerating;
- drying;
- antitoxic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antifungal.
In various concentrations, potassium permanganate is used to treat skin, mucous membranes, douching, and enemas. However, when using potassium permanganate, you need to be careful and use precise dosage. When applied to the mucous membranes and skin in high concentrations, a burn and swelling appears.
In ophthalmology, rinsing with potassium permanganate is practiced for infections of bacterial and viral etymology . Dries the skin in inflamed areas, promotes its tightening, stops inflammation, and destroys pathogenic microflora.
First aid
Methods for treating burn wounds are determined by the concentration of the potassium permanganate solution and the location of the damage.
Before the ambulance arrives, you must:
- remove clothing from damaged skin areas;
- rinse the wound with soda or running water;
- treat the burn with an antiseptic, burn ointment;
- apply a sterile bandage.
When it enters the blood, potassium permanganate destroys the parenchyma of the liver and kidneys. To neutralize its effect, take a 1% solution of ascorbic acid. This prevents hepatic-renal failure in the victim.
Skin injury
If crystals or a solution of potassium permanganate get on the skin, you must immediately wash the wound. Prolonged contact with soft tissues risks penetration of the chemical into the deep layers of the dermis.
First aid for skin injuries:
- Cleansing the wound. Damaged areas are freed from clothing. Potassium permanganate crystals are removed with napkins soaked in a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution.
- Washing. For 10-15 minutes, the skin wound is washed with running water at relatively low pressure. Injured tissues are blotted with sterile gauze and bandage.
- Neutralization of the chemical reagent. In case of a burn, you need to treat the skin with alkalis. To do this, dissolve 2 tsp in 1 liter of water. baking soda. Gauze is generously soaked in the liquid and applied to the burned skin.
- Disinfection. For shallow wounds, disinfectants and wound healing drugs are used - Dexpanthenol, Sulfargin, Radevit.
Does rinsing with potassium permanganate always help?
The universal drug acts very quickly. Improvement is observed during the first days of therapy. If this does not happen, you need to start complex therapy. Experts distinguish several types of conjunctivitis. Each of them has similar symptoms, but there are differences.
- Viral. The most common type of disease. It is transmitted by airborne droplets, as well as through the belongings of a sick person. Weak immunity provokes the development of the virus. Quite often, symptoms appear after a cold or acute respiratory viral infection. And also in infants and children of primary school age. An adult can become infected with general exhaustion of the body. Symptoms of viral conjunctivitis: redness, swelling, itching, burning, lacrimation, slight discharge of purulent mucus.
- Allergic. The body's response to external irritants - allergens. The most common case is pollen allergy in spring and summer. Main symptoms: swelling, redness, severe itching, burning, profuse lacrimation. There is no purulent discharge. If mucus appears, this indicates a secondary infection.
- Bacterial. Develops against the background of low immunity and proliferation of pathogenic microflora. The presence of bacteria provokes irritation, swelling, redness, lacrimation, and copious discharge of purulent mucus. There is an unpleasant odor.
Potassium permanganate will help cope with viral and bacterial infections. In case of allergies, use is inappropriate. The exception is situations when bacteria begin to multiply against the background of an allergic reaction. Treatment in this case begins after consultation with specialists.
Signs and danger
A burn from a strong solution of potassium permanganate occurs due to incorrect concentration or mistaken ingestion of crystals, which can happen to a small child due to his natural curiosity and the attractive color of the dry substance. Burns of the skin, eyes, mucous membranes, and digestive tract are types of injuries that have their own signs and, in the absence of emergency first aid, will bring serious health consequences.
| Type of chemical burn | Symptoms |
| Leather | With 1st degree burns, the site of injury appears swollen, reddened, and pain is present. A second-degree burn is expressed by the appearance of blisters at the site of injury with light contents, swelling, redness, and pain. Stage 3 is characterized by damage to the deep layers of the skin, blisters with dark contents appear. 4th degree is expressed by necrosis of tissues, subcutaneous tissue, muscles; damaged tissues are black from charring. It will take a long time to undergo treatment. |
| Eyes |
|
| Mucous membranes of the genital organs |
|
| Digestive organs |
|
The danger of chemical burns is fraught with serious health problems later. With severe skin lesions, scar tissue may form, which will entail the need for surgical intervention. When the eyes are injured, their function suffers, vision deteriorates, dryness appears on the mucous membrane of the eyes, or vice versa, tear production increases. A burn to the mucous membranes of the genital organs will provoke vaginitis, erosion, endometriosis, and, during pregnancy, fetal rejection. In case of a burn of the digestive organs and severe intoxication of the body, narrowing of the esophagus, stomach ulcer, kidney failure, and hepatitis are likely, which can significantly complicate the life of the victim.
How to dilute potassium permanganate for eye washing
It’s worth clearing right away that the word “rinsing” means carefully wetting the eyelashes and wiping the eyelid. Do not pour it into the eyes, do not drop it with a pipette. Moisten a cotton pad or a piece of gauze and wipe the skin.
- To carry out the procedure, a weak solution of potassium permanganate is used. The finished product should be pale pink. To wash the eyes, throat, and nose, use a solution with a concentration of 0.01-0.1%. To prepare it, you need to throw 2-3 grains of potassium permanganate into a glass of warm boiled water. Stir with a spoon until completely dissolved.
- You can navigate by color. If the rinsing solution turns out bright, add water. The presence of a pale pink tint indicates the desired concentration of the drug.
Only warm boiled water is suitable for preparing the product. In case of inflammation of the eye membrane, the use of chlorinated water is not allowed. Bleach increases inflammation. Do not use hot medication. Heat promotes the growth of bacteria. Store the diluted drug in a cool, dark place. Allowed to be refrigerated. Use during the day, the rest is poured out. Before treating the eye, the product is slightly warmed.
Precautionary measures
Too saturated manganese liquid can damage the organ of vision, so it is important to consider the amount of substance for making the medicine. In order not to increase the concentration of the mixture, it is recommended to prepare the composition in a container made of transparent material (glass or plastic). Permanganate crystals are thrown into warm water and stirred thoroughly. After stirring, allow the composition to brew until the crystals are completely dissolved in water. It is recommended to dilute this composition to the desired consistency in another transparent container. To do this, it is worth diluting part of the finished mixture with water, then the ingress of undissolved crystals is excluded. Additionally, you can strain the liquid. Potassium permanganate powder should be stored in a closed container, away from moisture and sunlight.
Treatment
The product is used in parallel with chamomile decoction. Initially, crusts and dried mucus are removed, then treated with potassium permanganate. 2-3 procedures are done per day. Improvement occurs almost immediately. If after 3 days the condition does not return to normal, you should consult a specialist.
Standard scheme:
| Age | Amount of medication per day | Number of procedures | Maximum duration of treatment without consulting a doctor |
| Children | 1 glass | 3 | 3 |
| Adults | 1 glass | Up to 5 | 5 |
Long-term use of the drug causes irritation of the mucous membrane.
Contraindications, side effects
When used externally, potassium permanganate has no contraindications other than individual intolerance. It appears extremely rarely. It is expressed by an increase in unpleasant symptoms. Side effects develop with long-term treatment or high concentrations of the drug.
- Dry mucous membranes;
- Burn;
- Increased lacrimation, itching, burning;
- Swelling of tissues.
Despite the fact that the drug is considered safe, before starting treatment you need to confirm the diagnosis and consult a doctor.
Reviews
Marina: “I remember when I was a child, manganese was used very often. My sister and I were given it for intestinal poisoning, my mother used it on her lips for herpes. As an adult, I was prescribed a douching solution for gynecological diseases. Then the product disappeared from the pharmacy. They declared its danger to the body. Now again not so widely, but used in medicine. I had stye or conjunctivitis in one eye in childhood. Lubricated with potassium permanganate. It's been a week. Nobody went to the doctor with such problems back then.”
Alina: “My son’s eyes started to water a lot. The eyelid is a little red. We were then visiting our parents. We arrived for a few days. My sister is a paramedic by training. I immediately applied the solution and treated the eyelid. By evening it got better. We treated for another day, everything went away.”
Inna: “There are a lot of eye diseases with similar symptoms. I would not treat myself without knowing the diagnosis. Once after an illness I woke up in the morning, I couldn’t open my eyes, everything was stuck together. I made a solution of manganese and washed it. I went to the doctor that same day. Antibiotics were prescribed. If I had simply rinsed with potassium permanganate, the treatment would have taken a very long time.”
How to wash eyes for conjunctivitis in children and adults: pharmaceutical preparations and folk recipes
Conjunctivitis is a common disease because it has many causes. One of the generally accepted procedures for conjunctivitis, to which there is practically no alternative, is eye rinsing. Both pharmaceutical and traditional remedies are effective. But if you use them incorrectly or choose them “at random,” then instead of curing you can worsen the disease.
Cool
Send
Types and symptoms of the disease
To protect the eyeball from external mechanical, chemical and biological irritants, the mucous membrane, called the conjunctiva, is used.
In addition to the eye itself, the conjunctiva also lines the inner surfaces of the eyelids. Part of this film forms the so-called vaults: upper and lower.
The arches are arranged like blind pockets and provide the eye with freedom of movement to control the pupil.
Reference! Comfortable conditions for the eyes are achieved due to the fact that the conjunctiva actively secretes mucin, which is the main component of mucous fluids in the body. This is a type of protein with a gel-like consistency. Mucin and tear fluid form a durable film that covers the eyes to moisturize and protect.
As the name suggests, conjunctivitis is a type of disease of the conjunctiva, or rather a whole group of diseases in which its inflammation occurs. Despite the variety of types of conjunctivitis and a wide etiological list, there is a common part of the symptomatic picture.
Patients experience characteristic irritation and burning in the eyes, as well as sensations similar to those that occur when small foreign bodies enter the eyes. Redness and swelling are accompanied by abundant purulent and pathological tear-mucous secretions, which thicken, blind the eyelids and harden on the eyelashes and in the corners of the eyes.
Based on the form and duration of the disease, acute and chronic conjunctivitis are distinguished:
- Acute conjunctivitis is most often bacterial in nature and lasts from several days to two to three weeks. It appears unexpectedly, accompanied by cutting and other painful sensations, first in one and then in both eyes. The inflammatory process may be accompanied by pinpoint hemorrhages. Characterized by high fever, general weakness, and headaches.
- In the chronic form, gradual development of the disease and its long course are observed. Often chronic conjunctivitis is a consequence of insufficiently high-quality and consistent treatment of acute, incorrect or delayed diagnosis, weakened immunity. The insidiousness of a chronic disease lies in the deceitfulness of the individual sensations of the patient, who can attribute them to ordinary eye fatigue and high overall workload. The advanced chronic form is fraught with deterioration of vision and even blindness, and other harmful consequences.
Inflammation of the conjunctiva is caused by infectious and non-infectious factors. Their list is very large: adenoviruses, herpes viruses, cocci, bacilli, chlamydia, parasitic fungi, allergens, toxins, chemical and mechanical (dust, sand, shavings, etc.)
d.) irritants, poorly selected or low-quality cosmetics, contact lenses. The cause of conjunctivitis can also be certain pathologies, such as congenital or acquired trichiasis: the abnormal direction of eyelash growth towards the eyeball.
Pregnancy is a special case of a condition in the body when the response of the immune system may be delayed, and the system itself may be weakened. This is called reactivity reduction. At the same time, the body experiences a deficiency of vitamins and a number of macro- and microelements.
Vulnerability to allergens and a variety of irritants increases. In such a situation, local and global prerequisites for conjunctivitis appear. Most often - viral etiology.
For a more complete understanding and obtaining a systematic picture, it is advisable to show the classification of types of conjunctivitis on two more grounds.
According to general cause-and-effect factors:
- endogenous – develop as a complication against the background of another disease;
- exogenous - arise as a result of external influences and pathogens entering the body.
According to the nature of the exudate (discharge) and the degree of damage to the conjunctiva (against the background of swelling, redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes and eyelids):
- catarrhal - increased lacrimation, mucus, possible appearance of pus from the conjunctival sac;
- purulent - copious discharge of pus, “acidity” of the eye sockets, likely sticking of the eyelids;
- fibrinous - the formation of films of fibrin that cover areas of the conjunctiva where necrotic processes occur;
- follicular – structural (morphological) changes in the tissues of the eyeball, loosening of the conjunctiva.
Early diagnosis and full implementation of the cycle of treatment procedures prescribed by the ophthalmologist not only prevents the development of severe forms and types of conjunctivitis, but also allows you to avoid inevitable consequences for vision due to damage to the cornea.
Basic rules for washing eyes in adults
To successfully use rinses for inflammation of the conjunctiva, the following conditions must be strictly observed:
- accurate differential diagnosis of pathology by an ophthalmologist;
- taking into account the general condition of the body, the characteristics of possible concomitant diseases;
- use only those products that are prescribed or approved by treating specialists;
- taking into account individual contraindications and drug compatibility;
- compliance with the recommended dosages and frequency of the procedure;
- proper preparation for the procedure (including compliance with hygiene standards) and its correct implementation.
IMPORTANT. It is not allowed to reuse tampons and cotton pads, contaminated items, as well as containers simultaneously used for other purposes (drinking, eating, household situations).
Four methods are used to treat the eyes:
- wiping the bent eyelids with a cotton pad or swab dipped in a solution;
- gently watering the eye with a solution from a funnel-shaped cup (in a thin stream);
- washing the conjunctival sacs from a syringe (rubber bulb) or generously instilling the composition using a pipette;
- the use of a special plastic bath of an anatomical shape, which allows you to literally “bath” the eyes one by one.
The general rule when using cotton pads and swabs is to wipe the eyelids from the inner corner of the eye to the outer edge.
It should be understood that not all described methods are applicable for every patient and specific drug. It is best to seek the recommendations and instructions of your doctor.
Treatment solutions
Both special and general-purpose pharmacological preparations, as well as time-tested folk recipes that were used before the development of medicine to the modern level, are used as rinsing agents. It is advisable to talk about the main and most popular means separately, since each of the solutions has its own characteristics.
Furacilin
This antimicrobial drug is effective in treating almost any type of infectious conjunctivitis. The active component is nitrofural: a local antiseptic that prevents the growth of microbial flora and kills the cells of pathological microorganisms.
To prepare a solution of furatsilin yourself, just take two tablets of the substance and dissolve it in a glass of warm, prepared water (boiled or settled drinking water). After 10 minutes, the solution is filtered through several layers of gauze. The finished product is stored for no more than 2 days.
Saline solution
This is one of the most affordable and versatile pharmaceutical drugs, which is used in many cases. Here are just a few examples of its use:
- in case of extensive blood loss - for temporary replacement of blood plasma;
- as a detoxification solution for a dropper or its base;
- in case of dehydration - to restore the water-salt balance in the body;
- as a basis for inhalation formulations for colds;
- for removing mucus from the nose and nasopharynx by rinsing;
- for therapeutic-prophylactic or sanitary-hygienic washing of the eyeballs and the inside of the eyelids.
Saline solution is an isotonic solution with properties similar to blood plasma. It is prepared from distilled water with the addition of sodium chloride (substance concentration is 0.9%). If necessary, it is easy to prepare a close analogue of saline solution yourself using table salt.
For making your own saline solution – 100 ml. distilled water should take 900 mg. regular salt without any additives. It can only be used as a means for inhalation, rinsing and washing, since, unlike pharmaceutical solutions, it is highly likely not to be sterile.
The antiseptic properties of saline solution allow it to be used externally in the area of inflammation - for the effective and gentle removal of pus, impurities and the elimination of pathogenic microflora.
Levomycetin
The usual form of this drug for the treatment of ophthalmic diseases is drops containing 0.25% chloramphenicol. The active substance is an antibiotic, the auxiliary substance is boric acid. Works well against most cocci, bacilli and many other bacteria, including those resistant to streptomycin and penicillin. Does not affect fungal parasites.
When using this medicine, its highest concentration is achieved in the cornea, iris and vitreous body.
For infectious conjunctivitis, Levomycetin is prescribed among specialized drugs. It often outperforms more expensive equivalents.
The procedure for using the medicine is described in detail in the instructions. In addition to drops, bottles with solutions of 1% and 3% of the substance are sold.
IMPORTANT. Levomycetin is contraindicated for pregnant women, nursing mothers and babies under 4 months. Harmful for children under 2 years of age.
Potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate has antibacterial, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and antifungal effects. In the complex treatment of conjunctivitis, a solution of potassium permanganate is usually used to thoroughly clean the eye sockets immediately before instilling the drug. A fairly weak pale pink solution is used, with a strength of 0.01% to 0.1%.
If the solution is not filtered, there is a risk of crystals of the substance entering the eye, which cause severe irritation of the mucous membrane and its local staining.
Boric acid
This antiseptic can be purchased in the form of a ready-made preparation for instillation, an alcohol solution (concentration varies from 0.5% to 5%) or a dry substance: white fine-crystalline powder.
Having a rather low (by modern standards) antimicrobial effectiveness, boric acid is, nevertheless, actively used in complex therapy.
This is due to its low irritant effect on areas affected by inflammation and wounds, as well as a good anti-putrefactive effect.
To prepare a 2% solution of boric acid yourself, you need to dilute 2.4 g of powder in 120 ml. hot boiled water. Be sure to strain the solution through a layer of cotton wool. It should be noted that the prepared aqueous solution is stored sealed in the refrigerator for no more than 10 days.
Miramistin
Miramistin is a broad-spectrum cationic antiseptic with anti-inflammatory properties, which is now often used to replace Penicillin (for example, in case of danger of an allergic reaction to the latter). The advantages of this tool:
- not absorbed through mucous and epithelial membranes;
- very effective as a medicine for infections and inflammatory processes;
- helps restore local immunity;
- has a relatively small list of contraindications and side effects, as well as low allergenic properties.
Its only drawback is the cost in comparison with similar analogues.
Typically, this medicine is sold in bottles with dispensers that allow you to simply spray the product onto a cotton pad before cleansing the eye. The usual concentration of the substance for topical use is 0.01%.
Is regular water okay?
Rinsing with plain water will cleanse the organs of vision from exudate, will somewhat reduce discomfort and pain, and will help remove foreign bodies from the eye socket. But direct therapeutic or antiseptic effects cannot be achieved in this way.
You should not use untreated tap water; it should be boiled and filtered. It is better to let even bottled drinking water sit for some time in a separate container. The optimal water temperature for washing the organs of vision with conjunctivitis is room temperature.
It is best to use bottled mineral water for rinsing: alkaline and still. Its properties are close to saline, so it will speed up healing.
Strong tea
Tea is a natural antiseptic and antibiotic that has long been used to treat “festering eyes.” A few spoons of black or green dry tea leaves are poured with boiling water so that the strength of regular tea leaves is obtained. Black varieties are considered the most powerful in terms of their effect on pathogens.
The herpes virus is especially sensitive to the effects of the active components of tea leaves. As a rule, cotton pads or other clean hygroscopic materials are used to care for the eye sockets using tea leaves.
IMPORTANT. The tea leaf should not contain flavorings or foreign flavoring additives.
Herbal infusions
A considerable list of herbs has bactericidal and anti-inflammatory properties. For washing the eyes, preference is traditionally given to infusions and decoctions of chamomile, sage, yarrow or eyebright. To prepare the medicine, as a rule, take a tablespoon or dessert spoon with a heap of dry herbal mixture per glass of water (200-250 ml).
There are several cooking methods:
- brewing under a lid (long brewing - under a towel);
- infusion in a thermos;
- water bath;
- other.
Source: https://proglaza.net/lechenie/chem-promyvat-glaza-pri-konyunktivite