Vision is an essential sense for every person. Reducing its severity entails a lot of problems, ranging from difficulties associated with carrying out work activities and ending with everyday difficulties. There are many eye diseases that can be successfully treated in various ways. In some cases, surgical intervention guarantees partial or even complete restoration of vision. Let's find out whether cataract surgery can significantly affect vision and significantly improve the clinical picture.
What is a cataract?
You may be interested in: Redness in the corners of the eyes: causes and treatment
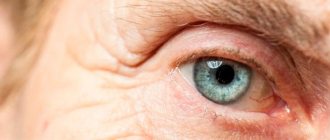
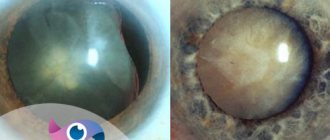
Ophthalmologists diagnose this disease in the case of clouding of the lens, which has the functions of a specific lens. It is located in the center of the eyeball and helps light enter the retina. Cloudiness interferes with visual acuity and can lead to blindness in the future.
At the initial stage of the development of the disease, the patient notices spots in the eyes, and later a kind of veil appears or, as some say, they see through the fog.
Overview of Cataract Surgery
In the initial stages, only an ophthalmologist can detect the disease during a detailed diagnosis. Surgical intervention is prescribed for rapid decline in visual acuity. Such a process causes discomfort not only in everyday life, but also in work.
A doctor must select a lens for transplantation. The lens replacement surgery is performed under local anesthesia. Before the intervention begins, anesthetic drops are injected into the conjunctival sac. The duration of the procedure is thirty minutes. A hospital stay is not required; the person operated on can go home on the same day.
If visual function is completely lost, even surgical intervention will not bring results. Therefore, you should not postpone the operation and risk your health. Lens replacement is carried out in different ways. But the essence of the intervention remains identical. An intraocular lens is installed in place of the clouded element.
Reasons for development
Most cataracts are an acquired disease. In the world, there are only 3% of patients with congenital pathology of this kind, which occurs in utero due to diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy or her chronic ailments. Prerequisites for the appearance of cataracts in a newborn may be:
- rubella;
- toxoplasmosis;
- diabetes;
- calcium deficiency;
- hypothyroidism
You may be interested in: I can’t see well up close – what should I do? What is vision called when you can't see well up close?
In children, the disease usually does not progress unless it is combined with other serious illnesses, and vision drops to 0.3 and remains so for a long period. In some cases, infants are indicated for cataract surgery, but this decision is made by the doctor together with the baby’s parents.
Acquired lens opacification develops at a fairly mature age and progresses rapidly. About 90% of pathologies are associated with aging of the entire body, and 10% occur due to external factors such as injury or radiation.
The most common causes of cataracts in adults are:
- ultraviolet or radiation radiation;
- age;
- injuries affecting the lens;
- infectious diseases;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- thyroid problems;
- ophthalmic comorbidities;
- operations on the eyeball;
- long-term treatment with corticosteroids;
- influence of toxic substances.
Causes and symptoms of cataract development
The reasons for the development of cataracts can be:
- age-related changes in the lens;
- hereditary predisposition;
- various eye injuries;
- operations ever performed on the organs of vision;
- receiving a large dose of ultraviolet radiation;
- inflammation of the optic nerve (neuritis);
- smoking;
- side effects of medications;
- diabetes;
- consequences of exposure to ionizing radiation.
Symptoms of cataracts:
- progression of myopia;
- color vision impairment;
- double vision;
- blurry image;
- discomfort with a bright sensation.
When the disease is at an early stage, you can choose glasses that will help improve your vision. But if the process of cataract formation progresses, then the question arises about the need for surgical intervention.
Development of the disease
Before deciding on surgical intervention, it is necessary to undergo an examination and find out at what stage of development the cataract of the eye is currently at. Surgery may be delayed until other treatments have been tried. The disease can progress in different ways. For some, therapeutic treatment may be enough to stop the clouding of the lens, while others will be operated on as soon as possible.
You may be interested in: How to relieve eye strain: the best methods and medications
There are four stages of cataract development:
- Initial, when the lens becomes cloudy in distant areas. The patient does not experience any discomfort, does not notice the disease, there is a slight decrease in vision, and sometimes double vision. If therapy is started at this stage, the transition to the second stage may take 10-20 years or not occur at all.
- Immature cataracts are characterized by significant visual impairment. The lens becomes heterogeneous, and pressure inside the eye leads to glaucoma with subsequent atrophy of the optic nerve. At this stage, cataract treatment with surgery is considered the most effective.
- Mature cataracts manifest as weak vision, when a person already sees contours poorly and has difficulty distinguishing colors. In this case, cataract surgery must be performed as soon as possible to restore vision.
- Overmature (Morgani) cataract is characterized by complete disintegration of the lens, which may, for some moments, partially restore the ability to see the outlines of objects. However, the destruction of the so-called lens can lead to the release of contents and complete destruction of the entire eye.
Functions and structure of the eye lens
The human visual organs are a complex optical system in which the lens of the eye is endowed with the most important function.
In this article
- Functions and structure of the eye lens
- What happens to the lens during cataracts?
- Surgery is the only solution to the problem of cataracts
- Laser and ultrasound phacoemulsification - advantages of progressive techniques
- Choosing an eye lens for cataracts
- What should an artificial lens be like?
Absolutely transparent, it has a high refractive index and does not contain nerve fibers or blood vessels.
In structure, this organ resembles a lens convex on both sides, the front and rear surfaces of which have different curvatures. The lens is located in a capsule and consists of water, proteins, and lipids. The capsule is dense, prevents the passage of bacteria, and is constantly in an elastic state. Modern methods of treating cataracts by replacing the natural lens with an artificial one involve preserving the capsule, since this is the most physiological place for the lens.
High transparency, elasticity and the special structure of the lens allow it to effectively perform the functions of a natural lens. Depending on the distance at which a person needs to focus his gaze, it can change its curvature. Unfortunately, due to the natural processes of aging, the lens loses its transparency and elasticity. The loss of accommodative properties of the lens leads to presbyopia, age-related farsightedness, and its clouding affects the optical zone, which affects the quality of vision. Treatment of such a problem is possible only by replacing the lens of the eye.
Patient preparation
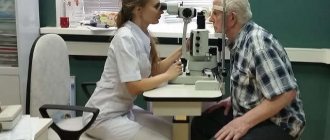
First you need to carry out a diagnosis, which includes the following:
The doctor may also prescribe a number of special procedures, for example, refractometry, ophthalmometry, or use electrophysiological methods for determining pathology.
A few days before cataract surgery, it is necessary to obtain the results of laboratory tests of urine and blood. If the urine test is quite general, then blood should be donated:
The patient should know that the results of these studies are valid from ten days to one month. In addition, it is necessary to do an electrocardiogram no earlier than two weeks before cataract surgery. To be admitted to a hospital, you must have fluorography on your hands.
It is also necessary to visit a therapist, who will give an opinion on the general condition of the patient and the possibility of surgical intervention. It is advisable to visit doctors such as a dentist, gynecologist, urologist, or otolaryngologist to identify possible infections in the body that could cause complications after cataract surgery.
What should you not do before surgery? Here the requirements are standard and apply to any operations:
- It is unacceptable to exert yourself physically.
- Do not consume alcoholic beverages or drugs.
- From the evening of the day preceding the intervention, you should refuse to eat.
- Liquids should be consumed to a minimum.
- Taking medications for chronic diseases must be coordinated with the surgeon and anesthesiologist.
Procedures on the day of surgery
You may be interested in: Normal eye pressure in adults. Device for measuring intraocular pressure
When a patient enters the clinic, he must be examined by an ophthalmologist. In some medical institutions, blood is taken from the patient to separate plasma. After surgical manipulations, it is administered to the patient to speed up the recovery of the body. Usually the patient is given a sedative several hours before the operation. Also, before entering the operating room, drops are instilled in him to dilate the pupil.
The patient is offered a sterile set of clothes, which he puts on. After changing, he goes into the operating room, where he is placed on the table. As mentioned above, the entire procedure will last from 15 to 40 minutes. The time depends on the lens replacement method.
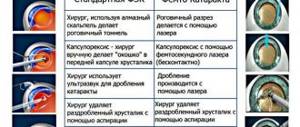
Types of surgery
There are several methods of surgical treatment of cataracts. We will find out further which operations are the most popular and less traumatic today by studying each type separately. The general list of types of operations includes:
The main opinion of doctors and patients, to put it briefly, is that the first method is the most accessible in terms of financial costs, and the latter is considered the most gentle, but expensive.
Extracapsular extraction
It is performed in patients with particularly dense lens tissue and retinal angiopathy. This operation preserves the posterior part of the lens capsule. Experts call the advantage of the method the remaining natural barrier between the front of the eye and the vitreous substitute. However, the disadvantage of this method is that it is highly traumatic to the cornea of the eye, since the incision is the largest. As a result of the operation, an artificial lens is installed to replace the natural one. Cataract surgery in this case is performed as follows:
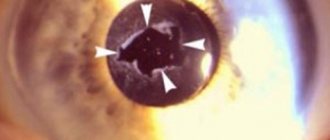
After an intervention of this kind, inflammation of the remaining posterior part of the capsule or the development of film cataracts is possible.
Intracapsular extraction
The method is based on the complete removal of the capsule with the lens inside, which relieves the patient of cataracts. Reviews about this type of operation are different. There are both positive and negative opinions posted on the Internet. Doctors don't really like this method. Despite the fact that complications in the form of film cataracts are excluded with this method, there is a risk of loss of the lens with a bag, which can lead to vascular damage, retinal detachment and hemorrhages.
Let us outline the main stages of surgical intervention:
In modern ophthalmology, this method is rarely used, usually in cases of damage to the lens, and is not used at all until the patient’s 18th birthday.
Surgery is the only solution to the problem of cataracts
In the 21st century, cataract surgery is not associated with serious risks to the patient's eye health. Surgical intervention techniques are well established, and new technologies have made it possible to significantly reduce the number of postoperative complications. Increasingly, the choice of specialists falls on less traumatic methods of replacing the lens, through laser and ultrasound phacoemulsification, which, although they are somewhat more expensive than simple operations, can quickly restore vision and reduce rehabilitation time. The essence of cataract surgery is to remove the clouded lens through an incision in the cornea and replace it with an artificial one. What are the ways to replace the lens for cataracts:
- Intracapsular extraction - currently this method is used infrequently, since it involves the removal of not only the lens itself, but also the capsule, which is associated with a high degree of trauma and great difficulties during engraftment.
- Extracapsular extraction - during this traditional lens replacement operation, its posterior capsule is preserved, which acts as a kind of barrier between the anterior part of the eye and its posterior part.
- Laser phacoemulsification is a seamless laser operation, the incision is made no more than 2.5 mm, all lens replacement processes are displayed on the monitor and controlled by specialists.
- Ultrasonic phacoemulsification is an effective method of getting rid of cataracts of any density; the puncture can be even 1.7 mm if new generation lenses are implanted.
Lens replacement operations, which created a large incision that required long-term healing, were also associated with the development of various complications: retinal detachment, lens displacement, the appearance of secondary cataracts, macular edema, increased intraocular pressure, hemorrhage in the anterior chamber or vitreous body. Secondary cataracts are quite common and are the most common complication that occurs after cataract removal. In most cases, the processes of capsule opacification are associated with fibrosis and excessive regeneration of the epithelium (more often in younger patients).
Now, with the advent of progressive technologies, methods such as extracapsular and intracapsular extraction are practically not used. Increasingly, preference is given to sutureless methods of intraocular lens implantation. Such methods have many advantages, including: a short rehabilitation period, a self-sealing incision, and the use of modern types of lenses.
Ultrasound phacoemulsification
This is the preferred option and provides excellent results and good reviews. Cataract surgeries of this level are considered the gold standard. The first three stages are carried out in the same way as with other interventions. Then a small incision is made, which does not exceed 3 mm. Afterwards, a hole is made in the anterior capsule of the lens and a special liquid is injected through it. The next step is crushing the vitreous body using ultrasound. Small fragments are removed through a phacoemulsifier, and the doctor removes the remaining tissue. After this, a new lens is installed in place of the lens, and the incision is closed using sutureless technology.
This method has a lot of advantages. After cataract surgery using ultrasound, complications are observed in only 1% of cases and they most often consist of retinal detachment.
Preparing for surgery
In preparation for the operation, additional examinations will be prescribed, which may include blood tests, urine tests, ECG, and fluorography. They are valid for a certain period.
On the eve of surgery, the patient is advised to take a sedative. The doctor will advise the means with which you will need to care for your eyes in the postoperative period.
It should be remembered. that in order to avoid complications in the postoperative period, you should not eat for at least eight hours before surgery. A full stomach can cause bouts of nausea, which will lead to increased eye pressure.
How is the operation performed?
Before cataract removal is performed, anesthesia is selected for the patient according to individual indications. These can be either special drops or an anesthetic drug that is administered by injection.
The operation is carried out by a team of medical workers, each of whom performs specific functions. The stages of work depend on the chosen method.
- Phacoemulsification. After anesthesia, an incision is made at the base of the cornea, and an ultrasound probe is inserted into the lens chamber. Under the influence of the waves emitted by it, the lens is destroyed, after which it can be easily removed from the eye. The chamber is cleaned, then the lens (implant) is installed. It unfolds on its own inside. Then the lens chamber is treated with a special preparation.
- Extracapsular removal of the lens is somewhat more traumatic. After the lens is inserted, sutures are placed, which will dissolve on their own after some time. But this method is characterized by the complexity of rehabilitation; vision does not return immediately.
- Intracapsular removal is performed using a cryoextractor. The lens freezes to it, then is carefully removed. An implant is inserted into the empty space, rinsed, and sutured.
- The use of a laser beam is less traumatic. No stitches are required after lens removal. The recovery period proceeds, as a rule, without complications.
The entire operation to remove the lens takes approximately 15-20 minutes. After the doctors complete the operation, the patient does not experience pain. Sometimes unpleasant sensations do occur; sedatives are used to alleviate them. The patient is then transferred to a ward for observation and can go home after a few hours.
Additional consultations
Before a decision is made on the method of surgical intervention, additional consultations with certain specialists (endocrinologist, therapist, cardiologist) may be required.
Contraindications for surgery
Cataract removal is prohibited in the following cases:
- the patient has an infectious lesion of the organs of vision;
- acute infectious-inflammatory process;
- oncological formation located next to the eyes.
Relative contraindications for surgery:
- the patient’s childhood or adolescence (during this period the eyes have not yet fully formed, and vision may improve);
- glaucoma;
- high blood pressure.
It is in the patient’s interests, even at the stage of making a decision about cataract removal, to warn the doctor about any existing health problems, the presence of allergic diseases, or taking medications.
Laser phacoemulsification
This is the most modern method of performing cataract surgery. The replacement of the lens here occurs in the same way as in the previous version, but the removal of the damaged body is done in a different way. First, the surgical field is treated, anesthesia is administered, and the necessary fluids are administered. Next, an incision and a hole are made, after which parts of the fiber-optic system are inserted into it. Using a laser beam, the natural lens is destroyed, the tissue of which is removed in the form of an emulsion through special tubes. After polishing the back of the capsule, a new artificial vitreous is installed in place of the old lens. The incision is also closed without using sutures.
This method cannot be used on overripe cataracts and when the cornea is clouded.
Choosing an eye lens for cataracts
After cataract removal, an intraocular lens is implanted into the capsule. Its choice is not easy and requires the participation of a highly qualified specialist who, after carrying out a set of diagnostic measures, will select a lens that best suits the patient’s needs. During diagnostics, the following studies are carried out to correctly select the artificial lens model:
- examination of the fundus with a dilated pupil;
- visual field examination;
- The condition of the retina, cornea, and the integrity of the lens ligaments are checked;
- ultrasound biometrics;
- scanning of the vitreous body and retina;
- coherence tomography and keratotopography of the cornea.
When choosing an intraocular lens, priority should be given to the latest lens models. The most in demand are lenses produced by European and American companies. The modern techniques used by clinics make it possible to make micro-incisions in the eye, and if the lens is of an outdated type, a larger puncture will have to be made, which will significantly affect the recovery time. Specialized clinics offer a large selection of lenses from leading optical manufacturers. The cost of replacing a lens for cataracts depends on the surgical technique and the optical characteristics of the lens.
Possible complications
You may be interested in: Fundus ophthalmoscopy: types, indications, how it is performed
After cataract surgery, the reviews given by patients are accompanied by a description of unpleasant symptoms and problems encountered. Let's look at each state separately:
How to behave after lens replacement?
Any surgical intervention requires a subsequent rehabilitation period. What should not be done after cataract surgery, and what manipulations should be performed, we will consider further. The recommendations doctors give to patients are as follows:
Should I have surgery?
Cataract is a complex disease leading to unpleasant consequences. If left untreated, the person is guaranteed blindness in the future. However, the decision to undergo surgery is not easy for many. Experts say that you should definitely undergo a comprehensive study. And if the results alarm you, you need to contact another specialist. Perhaps you will be convinced of the correctness of the diagnosis and the need for surgery in the first minutes of your visit, or the doctor will suggest an alternative method of therapy.
In any case, seeing a doctor is the first step towards treatment. Modern medical equipment makes it possible to identify the problem and deal with it in the early stages.
If all the doctors you consulted diagnosed cataracts, then you should immediately begin treatment or prepare for surgery. Listen to the opinion of the ophthalmologist and find out what way out of this situation he suggests.
The patient should keep in mind that lens clouding is an irreversible process that requires medical intervention. The consequences of the development of the disease are not only the loss of transparency of the vitreous body, but also its increase in size, which complicates the outflow of intraocular fluid. This leads to increased blood pressure and the development of glaucoma.
Indications and contraindications for cataract surgery – who should not have surgery?
The need for surgical intervention for cataracts is determined by medical and professional indications .
Medical indications are common to all patients. The operation, if present, is performed to preserve the normal morphology and function of the organ of vision.
Medical indications:
- Overripe cataract.
- Inflammatory form of cataract.
- Secondary glaucoma.
- Dislocation or subluxation of the lens.
- Abnormal shapes of the lens.
- The need for fundus examination in case of concomitant diseases (diabetic retinopathy, hypertension, retinal detachment).
- The need for partial excision of the vitreous body with an opaque lens.
- Drug-resistant lens block.
Professional and everyday indications take into account the individual needs of the patient at home and at work. The same indicators may or may not be a reason for surgical intervention in different patients.
Some professions place particularly high demands on vision. For example, vehicle drivers, navigators, pilots, and operators often need surgery with visual acuity of 0.4-0.5.
Professional indications:
- Insufficient visual acuity for the patient to carry out usual activities.
- Narrowing of visual fields, preventing the patient from performing usual activities.
- Low degree of binocular vision, which prevents the patient from carrying out his usual activities.
Contraindications for cataract extraction:
- Oncological disease in the eye area.
- Inflammatory process in the eye area.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- Infectious diseases.
- Decompensation of diabetes mellitus.
- Uncorrected arterial hypertension.
- Coronary heart disease in the stage of decompensation.
- Condition up to 6 months after myocardial infarction.
- Hemophilia.
In children, the decision to surgically treat congenital cataracts is made depending on visual acuity.
- An absolute indication is a sharp decrease in objective vision . The operation is performed at the age of 12-24 months for bilateral diffuse, membranous and zonular cataracts with visual acuity of 0.1-0.005 or lower.
- A relative indication for surgical treatment of cataracts is considered to be local opacities of the lens of medium intensity , with visual acuity from 0.2 to 0.1. The operation is usually performed at the age of 2-6 years.
Surgery for congenital cataracts is not performed if visual acuity is not lower than 0.3 under normal conditions. Typically in these cases, lens opacities are polar, cortical, nuclear or polymorphic.
Doctors' opinion
Doctors are inclined towards surgical intervention, explaining their choice as follows. The process of lens clouding cannot be reversed. Therefore, the only way is surgery. Domestic specialists already have extensive experience in providing radical treatment. The operation does not last long and is usually performed using local anesthesia, which reduces the load on the heart. Improvement in vision occurs immediately after surgery. It should be noted that the result depends not only on the skillful hands of ophthalmologists and equipment, but also on the implanted lens.
The choice of vitreous is important. This is usually done by a specialist, but he can take into account your wishes. Be sure to tell the doctor your current type of work. This will help the doctor make the right choice, and you will not be disappointed after installing the lens. Cataract surgery can significantly change vision and improve the clinical picture.
Source