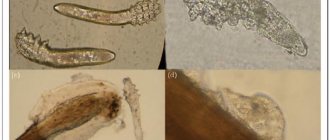
Demodectic mange – disease caused by mites of the genus Demodex (Demodex), which can hit or facial skin, or spread over the eyelids and especially - in the ciliary hair follicles, concentrating on the eyelash follicles.
Unlike cutaneous demodicosis, which is relatively easy to treat by treating with various external preparations, the treatment of demodicosis of the eyelids must be approached with caution.
It is necessary that large quantities of medications do not come into contact with the eyes (this can cause irritation).
Note! The main treatment for such cases is ointments against demodicosis.
The main symptoms of demodectic blepharitis
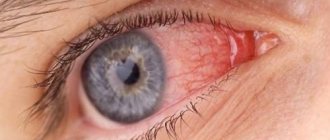
With this eye disease, pronounced symptoms are observed. Signs of the disease are usually noticed by the patient himself, but this does not eliminate the need to consult an ophthalmologist
to make a final diagnosis.
The most characteristic symptoms of this disorder include:
- Swelling and itching of the eyes and eyelids;
- Sticky eyelashes;
- A specific plaque, as well as small, but noticeable upon close examination, scales located along the edges of the eyelids and at the roots of the eyelashes.
If you have any of these signs, you should contact a specialist! This is necessary not only to confirm the diagnosis, but also to alleviate your condition.
Risk factors and causes
The parasite that causes demodectic blepharitis and other diseases is present in approximately 60% of adults. However, according to some data, these numbers are even higher - up to 90% of adults are carriers of the Demodex folliculorum mite, which is localized in the ducts of the sebaceous and meibomian glands. Although the statistics include adults, children are also exposed to glandular acne.
We have already said earlier that this mite is of a conditionally pathogenic nature, that is, a person can live his whole life and never encounter the negative effects of the acne gland.
Demodicosis can occur against the background of a number of diseases and decreased immunity
However, against the background of decreased immunity, chronic diseases and other negative factors, various diseases can develop in the body, affecting not only the eyes, but also the skin. In this case, the actual pathogen will not be the tick itself, but its metabolic products.
At risk are:
- Aged people;
- Patients with metabolic disorders;
- People who have reduced immunity;
- Children with diseases of the digestive system and lungs.
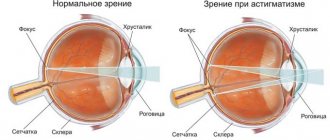
Sometimes signs are observed in people with visual impairments - myopia, farsightedness or astigmatism. However, this only happens in cases where the patient does not use vision correction.
Sign up for a free vision test
Factors that increase the risk of developing demodicosis include:
- Using cosmetics with hormonal components;
- Regular use of a solarium;
- Excessive consumption of caffeinated drinks;
- Stress;
- General fatigue of the body;
- Chronic lack of sleep;
- Chronic infections;
- Avitaminosis;
- Eye surgeries.
Diagnosis of demodectic blepharitis
If the disease is in its early stages, the patient is referred for laboratory testing to make a diagnosis. This allows you to exclude other factors that could cause blepharitis.
The laboratory test does not require any preparation: a few eyelashes are simply taken from both eyes of the patient for analysis. Next, the eyelashes are placed under a microscope, exposed to glycerin, and examined for the presence of mites or their metabolic products.
If demodicosis has become chronic, the doctor
can detect it during normal visual inspection. The presence of an inflammatory process is indicated by swelling of the eyes and hyperemia of the eyelids, that is, a condition in which the vessels of the eyelids are filled with blood and stand out against the background of the skin as a pronounced “cobweb”. But the most characteristic sign for making a diagnosis is the scales that are found near the line where the eyelashes grow.
Chronic demodicosis can be diagnosed by visual examination.
The need for additional laboratory testing in this case remains at the discretion of the doctor; often it is not necessary.
Indications for the use of ointments and gels for demodicosis of the eyelids
Ointments for demodicosis should be used at the first symptoms of this disease, namely the following signs:
- swelling of the edges of the eyelids;
- eye fatigue against the background of developing inflammatory infectious processes;
- loss of eyelashes that lose their strength;
- redness of the eyelids.
Such inflammatory reactions can be noticed already in the first days of the development of the disease.
And if inflammation affects only the eyelids and practically does not spread to the conjunctival membrane, it is necessary to use ointments and gels for demodicosis.
Treatment of demodectic blepharitis
The course of treatment is drawn up by an ophthalmologist
. Only a specialist can select and combine medications correctly; self-medication is unacceptable!
Drug therapy
The doctor selects medications based on several factors, including the degree of the disease and the patient’s age. The following types of drugs may be prescribed to treat blepharitis:
- Antimicrobial agents, mainly in the form of ointments;
- Antiseptics (selected by a doctor);
- Tear replacement therapy - the patient may experience discomfort in the eyes in addition to itching. To eliminate them, the specialist prescribes lipid-containing moisturizing preparations of high or medium viscosity;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, usually hormonal ointments with corticosteroids;
- Antibiotics in drops or ointments. Antibiotic therapy is prescribed in rare cases when inflammation of the eyelids has reached a high degree of development and is no longer amenable to other types of treatment.
Non-drug therapy
At the discretion of the specialist, additional non-drug therapeutic procedures may be prescribed, including eyelid massage. As a rule, eyelid massage is accompanied by special warm compresses. The patient can perform these procedures independently, at home.
After compresses and eyelid massage, the patient can treat certain areas of the skin with an antiseptic and antiparasitic agent.
As an additional effect on demodicosis, magnetic or ozone therapy can be prescribed, which is carried out in the clinic.
How long does it take to treat demodicosis?
Although the first signs of improvement, as a rule, occur within a few days from the start of therapy, treatment lasts quite a long time - from two weeks to a month.
Treatment of demodicosis can last up to a month
If the patient follows all the doctor’s instructions, but the condition of the eyes and eyelids does not improve within a week, it is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist
to select more effective therapy.
Treatment of demodicosis with antibiotics
Antibiotics help get rid of demodex. Such drugs act as heavy artillery and are used in cases of complex forms of the disease. The most popular drugs in this group include:
- Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum drug that performs a bacteriostatic function. The duration of treatment and dosage is calculated individually for each patient. Treatment should be stopped no earlier than 24-48 hours after the disappearance of the main symptoms of the disease.
- Zinerit combines antibiotic and zinc in its composition. This drug does not act as quickly as other antibiotics, but has virtually no side effects. Taking the drug will be relevant if demodicosis has caused acne.
- Metronidazole is an effective remedy for demodicosis, capable of fighting a variety of protozoal infections. The drug must be taken strictly according to the treatment regimen. One missed dose of medication may increase your risk of developing an infection.
Treatment with antibiotics gives quick results, but it must be prescribed by a doctor and strictly according to the prescribed regimen. This is due to the fact that most of these drugs have many side effects and contraindications for use. Self-medication is strictly prohibited here and can lead to the most undesirable consequences.
Recommendations for the prevention of demodectic blepharitis
Prevention of the disease begins with eliminating risk factors that influence the reappearance of demodicosis. The patient needs to receive therapy aimed at improving immunity and eliminating vitamin deficiency, as well as treating chronic diseases.
In addition, it is important to undergo a vision test and ensure the necessary correction with glasses and contact lenses.
Regular eye exams are an important part of preventing demodectic blepharitis.
For preventive purposes, it is also recommended to be observed by a dermatologist, especially if the patient has acne - in this case it is important to control the inflammatory process.
Sign up for a free vision test
Hygiene measures
A patient with a history of demodicosis is recommended to have his own set of bed linen, towels, and handkerchiefs. All personal hygiene items must be kept clean.
Touching your eyes and face with dirty hands is unacceptable; before each touch, you must thoroughly wash your hands with antibacterial soap. During the period of exacerbation, you should abandon contact lenses in favor of glasses.
It is recommended to continue independent procedures - warm compresses and eyelid massage.
Lifestyle
Women should limit their use of cosmetics. Avoiding oily creams for the face and eyelids also reduces the likelihood of clinical manifestations of demodicosis.
It is important to use antiseptics in cases where it is impossible to wash your hands with soap.
Diet
As such, a diet for demodectic blepharitis is not necessary. However, experts recommend reducing the percentage of allergenic products. These include citrus fruits and some seafood.
At the same time, it is recommended to take an OMEGA-3 supplement due to its positive effect on eyelid inflammation. However, before this, you need to consult with a specialist; self-prescription of medications and active supplements is unacceptable!
Other means of combating demodicosis
In addition to the above-described methods of treating demodicosis, there are other means of combating this disease that work well in complex therapy. One such remedy is iodine, which can be included in masks. You can make a mask by diluting cosmetic clay with water and adding a little iodine to the resulting mixture. This product should be applied to the affected areas of the skin and left until dry.
A variety of creams can relieve itching, burning and irritation of the skin. The cream must be as moisturizing as possible. Only in this case will it protect the affected areas from external irritants.
The following agents can be used as additional methods of treating demodicosis:
- Roaccutane is a drug in tablet form that reduces the activity of the sebaceous glands and reduces inflammation of the skin. This drug is recommended to be used under the supervision of a doctor.
- Dimexide is applied to the skin only a few times a week. This remedy has an analgesic effect and promotes the penetration of acaricidal drugs into the epidermis.
- Baziron is available in the form of a gel and a cleanser. The drug has an antibacterial effect and is available without a prescription.
Drops for demodicosis
For demodicosis of the eyelids, it would be appropriate to use eye drops, of which there are several types:
- Acaricidal drops must be applied to the eyelids and the skin around them. The product paralyzes the limbs of ticks and immobilizes them. The most effective include Carbachol and Phosphacol.
- Antibacterial drops are used for re-infection or complications. This type of drug causes changes in the DNA structure of the subcutaneous mite. Levomycytin and Tobrex deserve special attention.
- Antihistamine drops weaken allergic reactions and have an anti-inflammatory effect. “Acular” and “Okumetil” give good results.
Gels for demodicosis
According to medical research statistics, about 90% of those examined are carriers of subcutaneous mites, and 5% of them exhibit an active form of demodicosis. This is due to the widespread use of gel products for the treatment of this disease.
Dermatological gel for demodex negatively affects pathogens, reduces their population, and cleanses the skin. In addition to this, the product effectively moisturizes the skin, gives it a healthy color and elasticity, and promotes regeneration. Gels such as Blefarogel 2 and Metrogyl enjoy well-deserved attention among doctors and patients.
Effective traditional methods of treatment at home
Along with traditional methods of treating demodicosis, folk remedies are used. This is especially true during pregnancy and lactation.
In folk medicine, decoctions, tinctures, and compresses based on medicinal plants are used. Such drugs have anti-inflammatory properties and are used for skin diseases in combination with drug therapy.
According to patients who have tried traditional methods of combating demodicosis, the leaders are:
- Tincture of calendula. It has a good antiseptic effect, so regular use gives good results. Rubbing the diseased areas of the skin with the prepared solution should continue for a month.
- Birch tar is mixed with sulfur ointment in equal parts. The product helps remove redness, acne and numb the affected skin.
- Tar soap can be used as a cleanser. It has an antibacterial effect, but you should only use it a few times a week so as not to dry out your skin.
Any folk remedy for demodicosis can give maximum results only in combination with drug treatment.
conclusions
- Demodectic blepharitis is the most common eye reaction of the body to waste products of a parasite that lives on the skin of the face;
- The disease is more susceptible to the elderly, children with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and lungs, as well as patients with systemic diseases;
- In some cases, the cause of inflammation of the eyelids may also be a visual disturbance that cannot be corrected with glasses or contact lenses;
- The course of treatment takes from two weeks to a month. Therapy is prescribed by an ophthalmologist
; - For preventive purposes, it is recommended to carefully monitor personal hygiene, see a dermatologist, and, if possible, eliminate all risk factors.