Vision problems are no longer uncommon. According to statistics, the number of young people who suffer from eye diseases that impair vision is gradually increasing. Although until a certain time it was believed that vision problems were more typical for older people. However, every year more and more people under the age of 40 come to the clinic with complaints of sudden deterioration in vision. And the most common disorder is astigmatism. In most cases, this disease is congenital, but its first signs can be observed from the age of 7 years.
General clinical picture
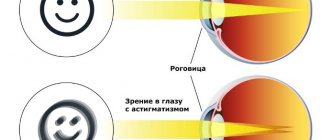
First of all, it is necessary to mention that this disorder is indeed widespread. It affects the cornea. As a result of this, negative changes occur in her. As a result, the shape of the cornea itself changes. Due to the changes that have occurred, focus is lost. How many people think about how important it is to see the world clearly? In fact, there are practically no such people. After all, most people think that the most terrible disease is blindness.
However, loss of focus can be compared to blindness. The patient who has been diagnosed with this disease does not see clear forms. He can easily confuse a dot with a dash. This happens precisely because of the lack of focus. It is worth noting that this disease progresses very quickly. And ultimately, it is this that causes vision loss.
But what exactly can cause the development of the disease? Surprisingly, doctors have not yet been able to establish the exact causes of this disease. Although there is a list of so-called risk factors. They significantly increase a person's chances of getting sick. Let's take a closer look at them.
- Corneal injuries.
- Eye surgeries.
- Dystrophic processes in the cornea.
- Inflammatory process.
All of the above factors can not only provoke the appearance of the disease. They also contribute to its faster development.
Course of astigmatism
With astigmatism, disturbances in the optical system of the visual organs are observed. In this case, the refraction or reflection of rays in different sections of the light beam is not the same. Due to this, the astigmatist does not see a clear picture; all objects visible to him seem to be blurred and have a convex shape. The picture seen by the patient resembles looking at a “distorting mirror”. A person complains of blurriness of visible objects, deterioration of distance vision and doubling of objects.
Visual impairment of this type can be regular or irregular; this is what further treatment tactics depend on:
- Regular. In this case, there are two zones where the cornea has different levels of refraction. This defect can be easily corrected with the help of special glasses or contact lenses.
- Irregular. In such a case, many axes exist simultaneously. This phenomenon usually occurs with serious eye injuries, when a lot of scar tissue forms at once. A similar disorder may also be due to uneven convexity of the cornea.
Astigmatism can be myopic and hypermetropic. Sometimes a mixed form of visual impairment occurs. In such a case, part of the image falls on the area in front of the retina, and the second - behind it.
Symptoms
Before listing the symptoms characteristic of the disease, it is necessary to clarify that it has congenital and acquired forms. But the most common form is the congenital form. In other words, a person can be born with this disorder. And if this happens, then the disease behaves less aggressively. The symptoms remain not too pronounced. Especially at the initial stage of the disease. Children may not even realize that they have astigmatism. And therefore he does not complain to his parents about strange sensations or blurred vision.
But as soon as the child reaches school age, the clinical picture changes dramatically. Gradually, vision begins to deteriorate. The deterioration manifests itself in the fact that it becomes difficult for the baby to distinguish between letters and symbols when sitting far from the board. More serious symptoms are also possible. For example, when the letters in the eyes seem to change places. It is at this stage that the main signs appear that the disease has begun to actively progress:
- the child may complain of a constant headache, which intensifies when trying to recognize the outline of letters and symbols;
- fatigue increases, so when a child comes home from school, he or she may feel “broken”;
- visual acuity begins to fluctuate during the day (decreases noticeably in poor lighting);
- the sensitivity of the eyes to light increases, which manifests itself as a pronounced pain syndrome when looking at the light;
- an unpleasant sensation appears, as if sand had gotten into the eyes.
But as for adults, their signs of the disease are somewhat different: show jumping becomes more blurred, and the objects themselves become a little blurry. However, in some cases, these symptoms may be accompanied by others:
- burning sensation;
- pain;
- double vision
In addition, a person begins to experience difficulty determining the distance to an object. This is why people who have been diagnosed with this disease often crash into objects. Although they see all these objects, due to the inability to determine the exact distance, it seems to them that they are all further away than they actually are. This article will tell you about astigmatic contact lenses.
Causes
The main reason why astigmatism develops is heredity. If parents have such a deviation, the child is likely to develop it. Congenital pathology is most often detected in both eyes at once, so vision is much worse than with the acquired form.
Acquired astigmatism develops for numerous reasons:
- Eye infection involving the cornea.
- Injuries to the corneal layer, as a result of which scars appear on it, changing the shape of the transparent medium of the eye.
- An open bite, in which the teeth of the upper and lower rows do not connect when the jaws close. Because of this, a person has to constantly squint or tilt his head to the side to look at objects. As a result, the cornea begins to deform.
- Thinning and dystrophy of the corneal layer.
The pathology may be associated with a change in the sphericity of not only the cornea, but also the lens. Lens astigmatism is a rare phenomenon associated with overstrain of the ciliary muscle; it cannot be corrected.
Signs of disease progression
We already mentioned above in the article that the disease does not manifest itself immediately. And this is the main danger. After all, some people tend to attribute mild symptoms to a temporary phenomenon that does not require special treatment. And therefore they do not even realize that they have astigmatism. Find out about complex myopic astigmatism here.
Many people mistake blurry vision for fatigue and are in no hurry to see a doctor.
Moreover, over time, patients begin to take the “blurry” world for granted. In other words, they simply get used to the fact that they do not see clear boundaries. But it is during this period of addiction that the disease progresses. The disease develops faster if the patient initially suffers from either myopia or farsightedness. Find out how a person with astigmatism sees here.
These two defects can significantly accelerate the course of the disease.
It is noteworthy that astigmatism may not manifest itself at all for a long time. But this does not mean that it is absolutely harmless during this period. This is not entirely true. It is also necessary to remember that various diseases and injuries of the eyes are provoking factors. This link will tell you how the Amsler test is performed and what it is.
This is why people who have been diagnosed with astigmatism need to be especially careful.
The main signs that the disease has begun to actively progress is the appearance of additional symptoms. We have already examined the main signs of developing astigmatism. But they rarely appear all at once. Often the patient is bothered by the inability to focus on the boundaries of an object, its blurriness. Intensification of symptoms indicates that the disease has begun to progress.
Symptoms
With a small degree of refractive error, not exceeding 3 diopters, a person may not notice the changes. Vivid symptoms appear if vision impairment is more than 3 diopters.
The following symptoms are observed:
- increased eye fatigue;
- rapid decrease in vision;
- incorrect perception of the shape of surrounding objects (to understand how people with astigmatism see, just look at your reflection in a shiny spoon);
- pain and discomfort in the eyes.
In addition to impaired visual acuity, astigmatism leads to headaches, since the eyeball is constantly in a tense state, trying to focus the gaze, and the brain works hard, trying to process information received from the diseased eye in a distorted form.
Diagnostic methods
Everyone knows that a disease that is detected at an early stage is much more treatable. That is why the question arises about the correct method for diagnosing the disease. Today there are many effective methods. However, ophthalmologists always insist on a comprehensive examination. And the most popular and in demand comprehensive examination is visometry.
The patient is asked to undergo a simple visual test. The doctor uses two different charts to perform this test. It is with their help that visual acuity is determined. Despite the relative simplicity of the technique, it is indeed one of the most effective, which allows you to determine the degree of astigmatism. Moreover, it can be used even in the early stages of the disease.
Shadow testing is also used. Because it is with its help that the degree of refraction can be determined. In order to check the level of refraction, the ophthalmologist uses two types of lenses. The first type is spherical, the second is cylindrical. And among hardware methods, doctors prefer to use refractometry. With its help, it is possible to obtain data on whether there are any pathologies of the visual system. This material will tell you about complex astigmatism in both eyes.
Types and types of farsighted astigmatism
Depending on the meridian of the eye in which there are defects, hyperopic (far-sighted) astigmatism is divided into the following types and types:
- Simple farsighted astigmatism . With it, normal vision (emmetropia) is observed in one of the main eye meridians, while farsightedness is determined in the other. In other words, part of the light rays in this meridian, after refraction, are focused behind the retina, and another part of the light rays are focused on it.
- Complex farsighted astigmatism . It accompanies different amounts of hypermetropia in the main meridians of the eye, in which focal points formed by the refraction of light rays appear behind the retina.
The cause of both simple and complex farsighted astigmatism, as a rule, is a violation of the sphericity of the shape of the cornea of the eye. Although, this pathology in rare cases is caused by improper curvature of the lens.
The severity of astigmatism is divided according to the degree of anomaly. Moreover, the degree of astigmatism up to 0.5 diopters is the norm and occurs quite often. It does not impair the quality of vision and does not cause any visual discomfort.
Diagnostics
The final diagnosis is made by an ophthalmologist based on comprehensive studies of the state of visual functions of the eye. Modern techniques are used to identify the disease, its type and stage.
- Visometry. The most common type of diagnosis to check visual acuity. The person being tested is fitted with a diagnostic frame in which one eyepiece is covered with a light-blocking material. Cylindrical lenses of different refractive powers are placed opposite the open eye, and the one at which vision will be as sharp as possible is selected.
- Shadow test or skiascopy. A method for determining the degree of refraction using cylindrical and spherical lenses, illuminating the pupil and studying the light reflex on it.
- Refractometry. Accurate measurements of the refractive power of the eye and refractive errors with an automatic computer refractometer.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye. It makes it possible to identify pathologies of a dystrophic, inflammatory and post-traumatic nature.
- Ophthalmoscopy. Examination of the fundus in detail, making it possible to visually assess the degree of transparency of the optical components of the eye.
- Ultrasound of the organs of vision. It is carried out using devices with high-frequency sound waves. Allows you to identify pathologies and neoplasms.
- Computer keratotopography. Determines the presence and degree of corneal astigmatism and keratoconus.
Based on the examinations of the patient, the doctor determines what exactly caused the disease, makes a final diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Features of vision with astigmatism
The quality of vision depends on the degree and type of optical deviation. With a weak degree of astigmatism, visual acuity is normal or reduced to 90-80%. At this stage, many patients do not even notice the presence of a defect.
Average astigmatism can reduce visual acuity by ⅓ and requires optical correction. More advanced stages significantly affect vision. In this case, the performance of the visual organs decreases, color and binocular vision deteriorates. As the pathological condition develops, visual acuity gradually decreases.
A person suffering from astigmatism sees objects a little blurry and distorted.
The quality of perception does not depend on the plant. In everyday life, discomfort may occur when reading near or recognizing objects in the distance. As a result, the patient is in constant tension to focus on the text or object.