When a person observes sour eyes and a hot forehead in himself or his child, does he worry about whether there is a fever with conjunctivitis, or are these signs of a more serious pathology? Inflammation of the conjunctiva often occurs as a result of infection. To successfully fight germs, the body raises its temperature. This is a completely normal reaction of the immune system to an irritant.
Causes of fever with conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis with fever can occur as an independent disease or develop against the background of infectious inflammation of the respiratory tract: ARVI, rhinitis, bronchitis and others. Depending on the pathogen, the following types of conjunctivitis occur:
- Bacterial - appears due to infection with staphylococcus, streptococcus, pneumococcus, gonococcus. Transmitted through shared household items and close contact. Bacteria are often brought into the eyes by dirty hands or from stale towels or pillowcases. The spread of infection is likely due to sinusitis.
- Viral is the most common type of conjunctivitis. It is transmitted by airborne droplets and can develop against the background of acute respiratory viral infections or a runny nose.
- Adenoviral - characterized by simultaneous inflammation of the throat and conjunctiva. Another name is adenopharyngoconjunctival fever (AFCL). Infection occurs from an infected person. The peak of the disease occurs in the spring.
Can conjunctivitis cause fever? Of course, but only for children. In adults, this is a sign of the presence of pathogenic microbes in the body. You can identify the pathogen by knowing what pathological changes it causes in a person.
Causes of conjunctivitis
The main route of infection into the eye tissue is contact. In other words, the main reason is improper hygiene, especially when it comes to young patients. A child, without thinking, can play in the sandbox and then immediately rub his eyes. The sandbox is a real storehouse of bacteria, viruses and fungal pathogens. But you can also become infected at home, including in a kindergarten. In this case, transmission of germs occurs through toys, door handles, or directly, in the usual tactile way during play.
Also, the inflammatory process in the tissues of the eye can develop as a result of infection in the systemic bloodstream. This can most often be observed with colds, flu, and caries. Adults should not forget about chronic diseases such as prostatitis, cystitis, and nail fungi, when an infection in the bloodstream can also spread to other organs and tissues and become a source of new inflammation.
Finally, typical symptoms of conjunctivitis may actually be symptoms of allergies. Identifying an allergen (any component that led to an immune reaction) can be very difficult.
Do not forget about provoking factors:
- Eye fatigue. This is typical for adults in cases of prolonged work at the computer, but modern children are not far behind them. Computer, TV, telephone, gadgets - the visual image requires prolonged eye strain. It is especially fraught if such a situation is coupled with lack of sleep.
- Dry indoors. This, in turn, causes dry mucous membranes, including on the surface of the eyeball. The protective shell becomes weak, permeable, and the likelihood of pathogens settling on it increases significantly.
- Poor nutrition. Lack of intake of biologically active substances, minerals and vitamins into the body can cause the development of conjunctivitis.
Symptoms
A high temperature during conjunctivitis in adults and children indicates an acute course of the disease. When the conjunctiva is infected, the average incubation period lasts from 2 to 7 days. The following symptoms are observed:
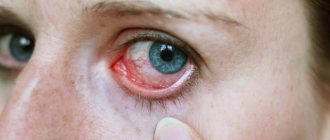
- Severe redness of the eyes, swelling of the eyelids. The phenomenon is accompanied by itching and a feeling of sand.
- Tear production increases. Discharge appears. The eyes turn sour during sleep, the patient has difficulty opening his eyelids in the morning. A viral infection produces clear, thick mucus, a bacterial infection produces pus, and an adenoviral infection produces pus with mucus.
- Increased sensitivity to light and wind.
- General malaise, loss of strength, loss of appetite.
- AFCL always occurs together with pharyngitis. The throat turns red and hurts, the voice becomes hoarse, and a dry cough appears. Adenovirus infection also provokes the formation of films on the eyes.
- The lymph nodes, usually the ones in the air, become enlarged.
On a note
The temperature for conjunctivitis varies from 37 to 39 degrees. A distinctive feature of adenoviral infection is its repeated rise a couple of days after the decline.
It is not difficult for an ophthalmologist to diagnose infectious conjunctivitis based on these signs. Sometimes, to select medications, it is necessary to do an analysis of pus and mucus from the eyes to accurately determine the pathogen. Additional consultation with a therapist or pediatrician is recommended to identify concomitant ailments.
Read in a separate article: What is conjunctivitis: types, signs and how to treat it
Conjunctivitis in a child and temperature 39 what to do
The conjunctiva of the eye reacts painfully to foreign bodies and microorganisms.
When particles enter, which are easily removed by ordinary eye washing, inflammation of the mucous membrane quickly passes, usually without a trace. Pathogens can cause a disease called conjunctivitis. What to do when it appears depends on the type of conjunctivitis. It can be allergic, viral and bacterial.
The temperature symptom manifests itself in different ways.
Inflammation of the eye
Why does the temperature rise in children with inflammation of the conjunctiva?
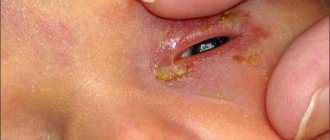
The baby returned from a walk, the parents noticed reddened eyes in the evening, while the child rubs them, becomes irritable and whiny. The next morning you can already observe an accumulation of mucus or pus in the eyelid area.
It happens that there is so much dried pus and mucus that children cannot even open their eyes on their own.
But not many parents know that the temperature when a child develops conjunctivitis in children is an absolutely normal phenomenon.
And this, on the contrary, indicates that the immune system is resisting. It is much worse if there is no temperature. In this case, it is easy to draw an appropriate conclusion about the state of the child’s immunity.
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the eye. It's called the conjunctiva. Hence, in fact, the name. With any inflammatory process, especially in children, body temperature rises. This process is a protective reaction of the body in response to the disease.
A distinctive sign of increased body temperature with conjunctivitis in children is cold hands and feet, as opposed to the body. There is one thing. Conjunctivitis should not be underestimated, especially in childhood.
Because the reasons why the pathology developed can be very different:
- The causative agent can be either a bacteria or a virus. And some of them are quite serious. For example, the herpes virus, which has settled in the nerve cells of a child’s body. It will be impossible to withdraw it in the future. And if it lives near the eyes, it means it can easily radiate to the brain. And this is a direct path to herpetic meningitis.
- In addition, it is very difficult for inexperienced mothers to distinguish conjunctivitis from influenza or acute respiratory infections. After all, the symptoms of respiratory pathologies are very similar to inflammation of the mucous membrane, especially in the initial stages of development. Therefore, self-medication of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes in children is strictly prohibited. First of all, you should find out which of the infections caused the increase in temperature and developing inflammation of the conjunctiva.
The temperature with conjunctivitis can rise, reaching 390 C. Therefore, antipyretics should always be present in the home medicine cabinet. But the main treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor.
We must not forget that, regardless of the form of conjunctivitis (except allergic), the pathology can be transmitted through direct contact.
Therefore, the baby should be provided with personal hygiene products and his communication with household members should be protected. Especially if the family has younger children.
Types of inflammation:
- Purulent discharge from the eyes, increased body temperature – bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Increased body temperature, absence of pus, but the presence of mucus - these are signs that develop with viral conjunctivitis.
- The eyes are red, irritated, there is no increase in body temperature and mucous, purulent discharge - signs of allergic conjunctivitis or other eye diseases.
- A red throat, elevated body temperature, and purulent discharge from the eyes are a sign of adenoviral conjunctivitis.
Another point is that bacterial therapy does not always help get rid of the disease “conjunctivitis”. This fact may mean that the treatment regimen was chosen incorrectly and the pathogen was not identified. Or the child has a flora that is resistant to the antibiotic used.
Temperature with bacterial conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis is characterized by the presence of purulent discharge from the eyes. This disease occurs under the influence of various bacteria that release toxins into the patient's blood.
Bacterial conjunctivitis can be diagnosed even in newborns. This is due to the presence of a bacterial infection in a woman during pregnancy. Infection of the baby can occur in utero or during passage through the birth canal.
This type of conjunctivitis is accompanied by high body temperature. It should be noted that hyperthermia in bacterial conjunctivitis is higher than in viral conjunctivitis (the exception is the film form of adenoviral conjunctivitis).
During bacterial inflammation of the conjunctiva, the body temperature remains at 39 degrees. In rare, severe cases, pyretic fever is observed, that is, the readings range from 39 to 41 degrees.
Hyperthermia with bacterial conjunctivitis is quite persistent and is poorly controlled by antipyretics. To reduce body temperature, it is necessary to eliminate the cause, that is, carry out antibacterial treatment as prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
Fever lasts in this case for at least 4 days.
Source: https://mcvdh.ru/zabolevaniya/konyunktivit-temperatura-37.html
Treatment of conjunctivitis with fever
For adults, concomitant infections should be treated to make a full recovery. The following drugs are prescribed locally:
- For a bacterial infection, apply ointments under the lower eyelid at night, and antibacterial drops during the day.
- At temperatures above 38.5, antipyretics based on paracetamol and ibufen are used. Adults can take Aspirin. It will not only reduce the temperature, but also improve tissue nutrition by thinning the blood.
- Anti-inflammatory drops are used to reduce hyperemia and relieve itching. When the mucous membrane is dry, artificial tears are recommended.
- Local and general vitamin therapy is prescribed, including calciferol, ascorbic acid and B vitamins.
It is useful to wipe pus from your eyes during the day with diluted aloe juice, chamomile and calendula decoctions.
If all the doctor’s recommendations are followed and the disease progresses well, treatment takes from 7 to 15 days.
What is infectious conjunctivitis?
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, or mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelid. It usually affects both eyes at the same time, although it may start in one and spread to the other within a day or two. In the first eye, the inflammation usually goes away more severely. Conjunctivitis caused by an infectious agent (bacteria or viruses) manifests itself acutely. There are many factors and it is a very common condition that usually resolves without complications, but can be very unpleasant for people.
Features of the disease in children
If a child has a fever and his eyes are purulent, he needs to be seen urgently by a doctor, especially when the baby is less than a year old. In children, the spread of infection occurs much faster and the likelihood of complications is higher.
As first aid, the eyes are washed from pus with a swab of sterile gauze moistened with chamomile infusion or boiled water.
If the temperature is above 38.5 degrees, it is brought down with Efferalgan, Paracetamol, Panadol. Albucid can be used topically. All other medications are used only as prescribed by a doctor .
Conjunctivitis and fever are common companions in children under 7 years of age. Often, every cold in a child occurs with inflammation of the conjunctiva, which goes away on its own after recovery. In this case, the eyes do not require separate treatment.
Features of treatment
Treatment of conjunctivitis in childhood has some peculiarities; when providing first aid to a child, the main thing is not to harm him. When the first symptoms of the disease occur, as well as subsequent treatment, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- do not self-medicate before visiting an ophthalmologist;
- if an immediate visit to a doctor is not possible for any reason, then it is allowed to drop Albucid into the eyes;
- if an allergic form of the disease is suspected, it is recommended to give the baby an antihistamine;
- viral and bacterial types require washing the eyes with furatsilin or chamomile decoction every 2 hours;
- rinsing is carried out with movements from the temple to the nose;
- crusts formed near the eyes are removed using sterile wipes;
- in case of an allergic form, the washing procedure is not carried out;
- if there is inflammation of one eye, both should be treated;
- It is permissible to use drops only with a doctor’s prescription;
- maintain bed rest;
- ointments should be applied to the lower eyelid.
Prevention of conjunctivitis
In order not to guess whether conjunctivitis can cause a fever, you need to reduce the likelihood of the disease. This is done using simple recommendations:
- treat infectious diseases in a timely manner;
- during epidemics, appear less often in public places;
- replace contact lenses on time and keep them clean;
- touch eyes only with clean hands and tools;
- do not use other people’s hygiene items;
- monitor the cleanliness of towels and bed linen;
- when sick, sneeze and cough into your elbow or tissue;
- foreign bodies must be removed from the eyes with clean hands using a sterile bandage;
- wash your hands more often.
Important! Delayed or incorrect treatment can lead to the spread of inflammation to other eye tissues and cause a decrease in visual acuity.
Author of the article: Mager Irina Yuryevna, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
Symptoms of infectious conjunctivitis
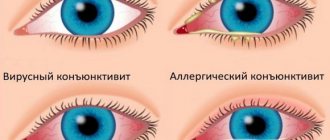
Viral conjunctivitis
- Redness of the eyes, sometimes with hemorrhages in the conjunctiva.
- Symptoms and signs are usually similar to those of bacterial conjunctivitis, usually like a cold.
- There may be enlarged lymph nodes, which can cause pain near the ears or at neck level.
- This type of conjunctivitis can also spread to the cornea (keratitis), resulting in decreased vision and more severe symptoms that increase the disease process.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
It usually affects both eyes. Symptoms are mild and, if there are no complications, include:
- Discomfort in the eyelids
- Redness of the eyes
- Feeling of itching or foreign body (feeling of sand in the eyes)
- Discharge from the eyes, usually mucous, which can blind the eyelids during sleep.
- Does not cause significant pain. Possible blurred vision due to discharge.
- If there is significant pain or a noticeable decrease in vision, the diagnosis should be compared with other pathologies.
How is conjunctivitis treated?
Viral conjunctivitis
- There is no effective treatment for viral conjunctivitis.
- Moisturizing drops are commonly used to relieve discomfort (eye drops, ointments, saline rinses). Anti-inflammatory drugs may be used to improve symptoms, and broad-spectrum antibiotics in eye drops or ophthalmic ointment can be used to prevent bacterial infection, although these do not reduce the rapid spread of the disease or the duration of symptoms.
- It is highly contagious, so strict hygiene practices must be followed in terms of washing hands, face and all objects that may come into contact with the virus.
- When the cause is a herpes virus, specific antiviral treatment is required.
- In any case, if glucocorticoids are prescribed, they can only be prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
- It is usually treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics in the form of eye drops or ointments.
- In addition, crusts and discharge should be removed by rinsing with saline.
How does conjunctivitis usually develop?
The vast majority of conjunctivitis improves spontaneously after a few weeks. Even with treatment, there may be worsening in the first few days, and the possibility of infection in the other eye. Treatment does not shorten the duration of viral conjunctivitis. Viral conjunctivitis follows a clinical course (usually 2 to 4 weeks), and medications help reduce symptoms but do not shorten the time it takes for symptoms to resolve.
As a follow-up, you may experience a foreign body sensation in your eyes (such as sand) or unexpected redness of your eyes for several months. Over time, this usually goes away. For these cases, it is advisable to use moisturizing eye drops and evaluate the evolution of the disease. In the most severe cases, between the 3rd and 4th week, small spots may appear on the cornea, which can cause decreased vision. This complication lasts longer than the previous ones, up to several months, and there is a possibility of scars and marks on the cornea, so it is necessary to undergo periodic check-ups with an ophthalmologist until the process is completely completed.
Inflammation of the conjunctiva can be associated both with an allergic reaction of the body and with exposure to viruses and bacteria on the mucous membrane of the eye. If conjunctivitis in children occurs with hyperthermia, this indicates activation of immune defense against the background of a viral or bacterial infection. The causes of the disease and methods of treatment are in the article.