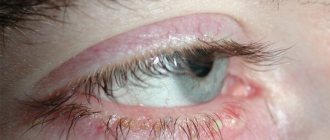
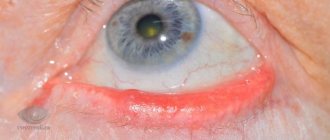
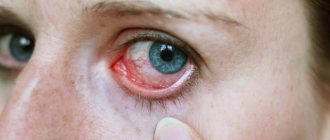
With scaly blepharitis in children, the edges of the eyelids become inflamed and swollen. The pathology received this name because of the exfoliating epithelium that forms scales. With scaly blepharitis, an inflammatory process appears in the affected area. If a child is left untreated for a long time, the disease can become chronic.
In this article
- What is scaly blepharitis?
- What types of blepharitis are there?
- Scaly blepharitis in children: symptoms
- What to do if a child gets blepharitis: treatment
- Prevention of scaly blepharitis
What is blepharitis and how does it develop?
Blepharitis affects the edges of the eyelids. Pathologies from this location belong to the group of ophthalmological diseases, as they affect the condition of the eyes and the quality of vision. However, inflammation of the eyelids does not always transfer from them to the eyeball. The inflammatory process begins in the meibomian glands after bacteria, mites, viruses and other pathogenic microorganisms enter their excretory ducts. The disease is polyetiological, that is, it can be caused by various reasons. In addition, it occurs in different forms, which determine the duration of the disease and the method of its treatment.
Direct causative agents of inflammation are microbes, mycoses, viruses, mites and chlamydia. Blepharitis often causes allergies. But, as a rule, the inflammatory process develops in the presence of predisposing factors. These include:
- avitaminosis;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diathesis;
- caries;
- anemia;
- allergy;
- parasitic diseases;
- viral pathologies;
- diabetes.
Blepharitis often worries people with eye diseases of non-infectious etiology:
- increased sensitivity of the cornea;
- refractive errors;
- spasm of accommodation;
- dry eye syndrome.
Causes
The main cause of the disease is an allergenic irritant for the body, in response to which the body develops a sensitization reaction. This leads to the destruction of the mast cell membrane and the release of inflammatory mediators.
Allergens that cause blepharitis may include:
- In medications - ointments, eye drops;
- In cosmetics - mascara, eyeliner, eye shadow, eye cream;
- In microparticles of plants, most often it is pollen during the flowering of trees, shrubs, and flowers;
- In house dust;
- In saliva, skin particles of domestic animals;
- In feather fillings for blankets and pillows;
- In household household chemicals.
In case of infectious and parasitic diseases, the development of allergic inflammation of the eyelids as a result of the toxic-allergic effect of pathogenic microorganisms on the body cannot be ruled out.
The disease occurs in isolation or against the background of other allergic pathologies - rhinitis, conjunctivitis, Quincke's edema, urticaria.
Causes of blepharitis in children
Inflammation of the eyelid margins is not a childhood disease. It is also diagnosed in adults, mainly in women aged 30-50 years. However, there are a number of factors due to which this disease is often detected in children. A child may develop blepharitis due to:
- physiologically unformed immunity;
- very thin eyelid skin;
- hormonal changes in adolescence;
- violations of hygiene rules;
- congenital vision pathologies - myopia, strabismus, astigmatism;
- frequent nasal infections;
- helminthic infestations;
- prevalence of food allergies in childhood;
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body.
Who else is at risk?
Based on the listed reasons and predisposing factors, we will highlight several population groups in whose representatives blepharitis occurs more often:
- women who use cosmetics;
- people whose work involves a lot of eye strain;
- patients with visual impairments;
- users of contact optics;
- allergy sufferers;
- diabetics;
- persons who have undergone eye surgery;
- aged people;
- HIV-infected people with tuberculosis.
Symptoms of blepharitis in children
The child may not immediately notice the first signs of inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. Typically, blepharitis begins with itching and redness. The patient rubs his eyes with his hands, hyperemia intensifies, and other symptoms of the disease occur:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- secretion and gluing of eyelashes;
- dry eye, feeling of “sand” on its surface;
- formation of compaction in the thickness of the eyelid, as with barley or chalazion.
If any of these signs are present, you should take your child to the doctor. The development of inflammation leads to an increase in its symptoms. They can be different and depend on the form of the pathology and its cause. Patients also complain of:
- increased sensitivity of the eyes to bright light;
- tearfulness;
- ghosting;
- accumulation of purulent exudate in the corner of the palpebral fissure;
- the appearance of yellowish crusts along the edges of the eyelids;
- graying, loss of eyelashes or abnormal growth.
Many of the signs indicate impaired blood supply to the eyelids and eyeballs. If no measures are taken, the inflammation spreads to the conjunctiva or cornea. The risk of sudden deterioration of vision increases.
If blepharitis appears in infants and newborns
Among the causes of blepharitis in newborns, experts identify two main ones:
- External. Redness of the baby's eyelids is a sure sign of a high concentration of dust, poor maternal hygiene and non-compliance with the pediatrician's instructions.
- Internal. The eyes of small children who do not yet speak instantly signal the penetration of staphylococcus, fungi or other microbes and bacteria into the body.
In the first months of life, it is important for a child to carefully observe personal hygiene, daily wet cleaning of the room. A weak immune system in children allows blepharitis to develop rapidly. Treatment must be started immediately if the initial symptoms are confirmed. If you miss a change in your child’s condition without taking action, you will encounter complications. Blepharitis without the necessary treatment quickly becomes chronic. The cornea of the eye becomes covered with microcracks, which opens the way for infection and ultimately leads to complete loss of vision. You cannot choose a treatment method on your own; only the advice of an ophthalmologist or an experienced pediatrician will help overcome the disease. Severe inflammation of the eye in a child leads to the formation of ulcers and scarring of the edges of the eyelids. This will prevent eyelashes from growing properly and will make them sparse and ugly.
The child's parents are required to immediately notify the pediatrician and ask for advice. To begin with, you can send a specialist e-mail with several photographs of the highest possible resolution. An experienced doctor will make a diagnosis without special tests. It is required to conduct a comprehensive study of the medical history, check for possible genetic abnormalities, predisposition to allergies, and much more. The cause of unexpected redness of the eyelid may be a banal draft or a change in diet. Blepharitis in formula-fed children is a signal of poor immune function. To make a correct diagnosis, in addition to a visual examination, the doctor will need:
- check the fundus and rule out other diseases. Make sure that visual acuity has not changed;
- taking a scraping, conduct laboratory tests of scaly deposits;
- consult with an infectious disease specialist and jointly select a treatment method;
- conduct microscopy of eyelashes to exclude the presence of mites;
- General tests of urine, feces and blood are taken from the child to identify possible pathogens;
- a color photograph is attached to the card, recording the appearance and condition at all stages of the disease;
- After starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct a complete blood and stool examination several times for the presence of viruses, bacteria and parasites.
While under the supervision of an experienced specialist and noticing the first symptoms of blepharitis, take a photograph as large as possible. Send it to your doctor and ask for advice. Quickly taken measures will help fight the disease more effectively and prevent it from becoming chronic. The child’s well-being will improve and it will help to wait for the pediatrician if:
- moisten the eyelid with a swab or clean cotton cloth. This will remove scaly layers and relieve irritation and itching;
- use a special ointment on the advice of a doctor. Apply a thin layer to the affected area;
- Apply the medicine before going to bed so that it does not get into your eyes.
Maximum efforts are required to identify the root causes and quickly eliminate them. The more effective the research, the easier it is to diagnose and fight scaly blepharitis. At each stage of the disease, take photographs and attach them to the archive. This will make it possible to monitor the treatment and avoid possible complications in the future.
Types of blepharitis
The method of treatment and the duration of the disease depend on the nature of the inflammatory process. The fastest way to treat is simple blepharitis, which is accompanied by slight redness of the eyelid, moderate itching and burning. If you consult a doctor in the first days of the disease, you will be able to overcome it in 7-10 days. But often blepharitis becomes chronic. Its symptoms can be eliminated in a week or two, but it will recur periodically. We'll talk about prevention methods later. Let's find out what other types of blepharitis exist.
Inflammation of the edges of the eyelids can be unilateral or bilateral, that is, affecting one or both eyes. Most often the upper eyelids become inflamed, less often the lower ones. Also, according to the localization of the inflammatory process, blepharitis is divided into 3 types:
- Front edge. Damage to the ciliary margin of the eyelids is observed. Severe dryness develops in the eye. This occurs due to the formation of a compaction in the area of the meibomian glands, which are responsible for the wettability of the conjunctiva. The production of secretions is disrupted, which causes the connective membrane to dry out. It may cause lacrimation.
- Posterior marginal, in which the meibomian glands directly become inflamed, resulting in dry mucous membranes becoming even more pronounced. A person complains of the constant presence of a foreign body on the conjunctiva.
- Angular, or angular. This type of blepharitis is characterized by the development of inflammation in the corner of the eye.
Symptoms are determined by the causes of the disease, its location and a number of other factors. We list the types of blepharitis that determine the choice of medications:
- meibomian;
- seborrheic;
- ulcerative;
- demodectic;
- allergic.
These are the most common types of pathology. There are other forms of it, more rare, but severe, for example, blepharitis with damage to the eyelids by molluscum contagiosum or inflammation of the edges of the eyelids with systemic allergies. Let's characterize these diseases, find out how they manifest themselves and how long it takes to cure them in a child.
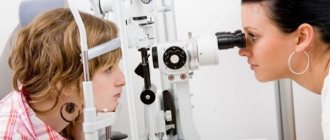
Diagnostics
Diagnostics Source: o-krohe.ru
In order to find out what kind of infection provoked the occurrence of blepharitis, the doctor makes a scraping from the conjunctiva of the eyelashes and eyes. Laboratory testing will reveal the cause of the disease.
If the pathology is the result of an allergy, then an additional test is prescribed to identify the provoking factor.
To clarify the etiology of blepharitis, microscopy of a preparation prepared from 4-6 epilated eyelashes should be performed. Usually, the presence of one or two mites is detected on 16 eyelashes (4 eyelashes are taken from each eyelid).
Meibomian blepharitis
It is also called marginal and blepharoconjunctivitis. The disease develops due to hypersecretion and inflammation of the meibomian glands.
The following symptoms are of concern:
- itching of the eyelids;
- foamy discharge in the corner of the palpebral fissure;
- fullness of the excretory ducts of the glands with yellowish-gray contents;
- redness of the conjunctiva and skin around the eyes;
- thickening and hyperemia of the eyelid margin.
When pressing on the cartilage, a cloudy pasty secretion comes out of the excretory ducts. In case of severe leakage, squeezing it out is impossible due to its very thick consistency. The contents of the glands become so dense that they cannot exit through the ducts. Subsequently they expand. This leads to the formation of cysts in the thickness of the eyelid. Dysfunction of the meibomian glands often causes stagnation of lipid secretions, which can result in the formation of scars and deformation of the edge of the affected eyelid.
Symptoms of the disease
With blepharitis, the baby suffers greatly from itching, sometimes it can be simply unbearable. The eyelid turns red, a burning sensation appears, there is a feeling that something has got into the eye, and the child suffers from severe lacrimation. Upon examination, you may find that the edges of the eyelids are thickened.
- With scaly blepharitis, there are small scales near the eyelashes, and the skin underneath is red and thin.
- In the ulcerative form of the disease, purulent crusts are characteristic; if you try to remove them yourself, they are removed along with the eyelashes, and in place of the crust a small ulcer appears, in most cases it bleeds.
- With demodectic blepharitis, the symptoms are very similar to the symptoms of scaly blepharitis. The eyelash bulbs enlarge, transparent muffs appear at their roots, pigmentation may change and a large number of papillomas may appear.
- With meibomian blepharitis, the symptoms are similar to other forms of the disease, a characteristic feature is small blisters on the upper part of the eyelid, they cause inflammation of the meibomian glands, these blisters break over time and small scars form in their place. If blepharitis is not treated, it becomes chronic and can severely impair the child’s vision. At the same time, the child feels unwell, his activity decreases sharply.
How is meibomian blepharitis treated?
87% of patients with this disease develop dry eye syndrome. Therefore, tear replacement therapy is carried out. Systane drops are prescribed, which help restore the fatty layer of the tear film, and VitA-POS eye ointment. These drugs must be used 2-3 times a day for 2 weeks. Then these medications are replaced with Optiv or Hilabak, which will have to be instilled for 3-6 weeks, 2 times a day.
Hygienic treatment of the edges of the eyelids is carried out using special gels. In case of severe inflammation, you need to massage the eyelid with a glass rod. Anti-infective therapy is carried out with antibiotics. The patient is also prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. They become necessary when the disease lasts for a long time.
Features of the treatment of childhood blepharitis
Treatment of blepharitis in infants involves a conservative approach. In most cases, it is carried out under the supervision of a qualified eye doctor, however, parents can perform some procedures aimed at reducing the symptoms of the disease and improving the baby’s well-being.
Important! We are talking about treating the child’s inflamed eyelids with special solutions and medicinal ointments. This is done to remove crusts, scales and dried secretions.
Speaking about how to treat childhood blepharitis, I note that ointments that have antibacterial properties are used for this: furacilin, tetracycline, sulfonamide and hydrocortisone. By the way, many parents are worried about the fact that hydrocortisone-based ointment is hormonal.
However, as reviews show, it is successfully used to treat blepharitis in children. This drug effectively relieves redness, swelling and itching.
Ophthalmologists also prescribe antimicrobial drops that help relieve inflammation (Levomycetin, Miromistin, Sulfacyl sodium).
In more severe cases, they resort to physiotherapeutic procedures, during which UV irradiation, ultra-high frequency therapy (UHF) and electrophoresis are used (simultaneous exposure of the body to electric current and medications, in particular vitamins and antibiotics). This allows you to speed up the healing process.
Here’s what Dr. Komarovsky recommends doing to eliminate this disease in young patients:
- To wash your hair and wash your face, use a special medicinal shampoo that has a healing effect.
- Wipe your eyelids daily with a cotton swab dipped in warm soapy water (after waking up and before going to bed).
- To remove scales from the eyelids, use a cotton swab (the procedure should be carried out 2 times daily).
Seborrheic blepharitis
Seborrheic, or scaly blepharitis occurs when inflammation develops in the eyelash follicles and glands of Zeiss and Moll. Often this disease is combined with seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, behind-the-ear areas, eyebrows and sternum. The ophthalmological symptoms of the pathology are as follows:
- small grayish greasy scales on the eyelashes, reminiscent of dandruff;
- itching and burning;
- heaviness, thickening, hyperemia of the eyelids;
- rapid eye fatigue.
These are the primary signs of the disease. As it progresses, the skin of the eyelid becomes wrinkled and hypertrophied. Conjunctivitis often develops, and sometimes marginal keratitis occurs. The last two ailments can be both the cause and the consequence of seborrheic blepharitis.
Treatment of scaly blepharitis
Inflammation is treated according to the following algorithm:
- Cleaning the eyelids is carried out using “Theagel”, it is performed several times a day - in the morning, before bed and each time before instilling medicinal drops into the eyes;
- for infection, Vitabact is prescribed 2-3 times a day for 2-3 weeks; if the infection is severe, stronger drugs are used;
- inflammation is eliminated with the help of Oftalmoferon, which is taken for 1-2 weeks.
Medicines that mimic tear fluid are used for almost any type of blepharitis. But the duration of treatment with tear substitutes may vary. For seborrheic inflammation, Systane and other similar drugs are used for 6-8 weeks.
Traditional recipes for the treatment of blepharitis
Despite the fact that traditional recipes are considered safe, they should not be used without consulting a doctor. Many medicinal herbs are poisonous and, if they get into the eye, can greatly aggravate the course of the disease.
They are quite suitable for enhancing the effectiveness of drug therapy.
- You can use eucalyptus leaves, sage, calendula or chamomile to wash your eyes. Both infusions and decoctions can be made from these herbs. It is recommended to do 3-5 washes per day.
- Rose oil will help get rid of scaly blepharitis. They lubricate the child's eyelids to make it easier to remove scales. You can also brew rose petals and wash your eyes with this infusion.
- For the treatment of demodectic blepharitis, clover inflorescences are used; they relieve inflammation well. Collect, wash and chop the clover flowers, then squeeze the juice out of them. 3 drops should be instilled into each eye of the child once a day. It is recommended to make eyelid lotions from the remaining pulp.
- If blepharitis is of an allergic nature, then the first thing, of course, is to exclude the allergen that affects the child. If, after eliminating the allergen, there is still discomfort in the eyes, then they can be washed with a solution of boric acid; Lotions made from fresh cottage cheese help relieve inflammation from the eyes. To do this, you need to put a spoonful of cottage cheese in gauze and apply it to your eyelids.
- To cure meibomian blepharitis, traditional medicine recommends the following recipe: take a medium onion, boil it in half a liter of water, add 1 tbsp. l. honey and mix well. Rinse your eyes with this solution at least 5 times a day.
- To cope with chronic blepharitis, you will need thyme. You need to prepare a decoction from this plant and wash your eyes. For 1 tbsp. l. herbs you need to take a glass of boiling water.
- Burdock oil helps with seborrheic form. They need to remove crusts from their eyelids and lubricate them before going to bed.
- If you mix half a glass of black and green tea and add a dessert spoon of dry grape wine, you will get a solution that is very useful for washing your eyes with blepharitis.
Massage is also very useful for blepharitis. Buy a special stick at the pharmacy. There is a spatula at one end and a ball at the other. The end with the spatula massages the eyelid, and the side with the ball is convenient for applying ointment. You need to massage the eyelid from the outer edge to the inner.
- home
- Other diseases
Good day, friends! Due to the fact that the children's body is very vulnerable due to an incompletely developed immune system, many children become carriers of various eye diseases, which often lead to deterioration of visual functions. Such diseases include barley, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, demodicosis, etc.
Today I would like to tell you about the features of such an ophthalmological pathology as blepharitis in children. You will learn about the most common types of this disease, as well as effective methods of combating it.
Ulcerative blepharitis
It is the result of a chronic infection of the hair follicles of the eyelashes, most often staphylococcal, which leads to ulceration and destruction of the eyelid margin. The following symptoms are typical for ulcerative blepharitis:
- sticking of eyelashes at the base;
- formation of yellowish crusts;
- ulcers on the skin of the eyelids and subsequent scarring of wounds;
- madarosis and trichiasis - loss and abnormal growth of eyelashes.
If they grow towards the eyeball and begin to come into contact with the cornea, erosion occurs. Due to infection of the cornea, an ulcer develops, which leads to deterioration of vision and even its complete loss. This happens with severe ulcerative blepharitis. But other complications arise not so rarely. Thus, inflammation of the eyelid margin caused by staphylococcal infection can cause chronic follicular or papillary conjunctivitis, toxic corneal epitheliopathy, marginal keratitis, etc.
How long does it take to treat ulcerative blepharitis?
Twice a day, the patient should wash the eyelids with an antiseptic solution and treat them with a special gel or ointment.
The course of treatment lasts 2-3 weeks. Drops based on natural tears - “Artificial tears”, “Systane” - are taken for 6-8 weeks. In severe cases of the disease, strong antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Ulcerative blepharitis lasts longer than simple and meibomian blepharitis. It is dangerous to interrupt therapy even if symptoms disappear, since this pathology can lead to deterioration of vision.
Demodectic blepharitis
It develops due to damage to the edges of the eyelids by mites of the genus Demodex folliculorum after they enter the ciliary follicles or the genus Demodex brevis, which penetrate the Zeiss glands and meibomian glands. Parasites are clearly visible under a microscope at the roots of the eyelashes. During inflammation, the mite population increases sharply. At the same time, there must be quite a lot of them for the development of the inflammatory process, since asymptomatic carriage of up to 1-2 individuals on 4 examined eyelashes is possible. The diagnosis is confirmed after the detection of at least 4-6 ticks, as well as their eggs and larvae. At the very beginning of the disease, the patient is bothered by unbearable itching, especially in the morning. Later symptoms such as:
- feeling of stinging in the eyes;
- discharge of sticky consistency;
- severe inflammation of the edge of the eyelid, its thickening and redness;
- accumulation of dried secretion in the form of scales between the eyelashes;
- formation of honey-colored crusts.
Prolonged course leads to damage to other structures of the eyeball - the conjunctiva and cornea. Against the background of blepharitis, keratitis, corneal ulcer, and conjunctivitis develop.
Prevention
You can prevent the development of an inflammatory process in the eyelids in a child if you are taught to carry out simple preventive measures and monitor it:
- Dirty hands are the first source of infection; you should not allow your eyes to rub with dirty hands;
- teach not to use other people’s towels and hygiene products;
- put a few handkerchiefs so that the child does not ask a friend;
- avoid contact with sick people and animals;
- This also applies to eye drops; you cannot use someone else’s.
Strengthening the body is important for the prevention of eye diseases. Vitamin complexes and hardening help strengthen the immune system. Vitamins are prescribed by an ophthalmologist or pediatrician. The child should be hardened gradually, lowering the water temperature slowly. Otherwise, flu or pneumonia cannot be avoided.
It is important to eliminate factors and causes that can provoke inflammation. Any manifestation of chronic diseases should be treated promptly. The pathological condition must be treated in the early stages of development, preventing them from developing.
The main goal of prevention is to prevent the development of chronic inflammation.
Treatment of demodectic blepharitis
The morning begins with cleansing the affected areas of the skin from crusts and washing the eyes with antiseptic agents. It is also recommended to massage the eyelids once a day. Glass rods used to perform the procedure can be purchased at the pharmacy. Before going to bed, the edges of the eyelids should be lubricated with Vaseline or VitA-POS ointment.
The main treatment is carried out with the help of antibacterial drops and ointments, anti-inflammatory drugs and tear substitutes. Its duration ranges from 2 to 4 weeks.
How to diagnose the disease?
Knowing the symptoms, parents themselves can identify the presence of the disease in their child, but to make a final diagnosis, a professional diagnosis by a specialist is necessary, so contact a specialized doctor. But what the doctor will do is to carefully collect anamnesis, carefully examine the site of the inflammatory process, check visual acuity, take eyelashes for microscopic examination to establish the cause of the disease, and refer you for general clinical examinations in the form of a general blood test and a general urinalysis. After all the research, knowing the cause, the doctor will prescribe treatment for the child.
- It is important to maintain personal hygiene. Change the pillowcase on which your child sleeps every day. Make your child wash their hands constantly. Pets that have fur will have to be removed from the apartment during treatment.
- The doctor may also prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures, this is an important component of the treatment of blepharitis. This is mainly UHF, ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis with the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, antibacterial agents with groups of vitamins that act locally, darsonvalization.
- Diet. It is important to exclude the consumption of foods that most often cause allergies.
- Etiotropic treatment. This is when the drug acts on the cause that causes this process. Antibacterial therapy is usually prescribed. Using ointments or eye drops.
Drops:
- "Tobrex".
- "Floxal".
- "Tsipromed".
- "Alomid" (for allergic reactions).
- "Okomistin" (for purulent form).
- "Maxidex".
- "Lofox."
Blepharitis in children is not uncommon. The pathology represents an inflammatory process of the eyelid margin, which can manifest itself in 3 main forms - simple, scaly and ulcerative. There are other forms of the disease, but they are less common.
Allergic blepharitis
Blepharitis can be allergic, which occurs after exposure to an allergen on the eyelids, pseudo-allergic as a toxic reaction to a drug, and infectious-allergic, which is a consequence of an infection of bacterial or viral etiology entering the body. Allergic blepharitis is often combined with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye - allergic blepharoconjunctivitis.
Allergies can occur to dust, pollen, pet hair, feathers, fluff, insects, household chemicals, etc. Allergic blepharitis occurs acutely and is accompanied by:
- severe itching;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- pain in the eyes;
- photophobia.
Almost always the disease is bilateral. In addition, it can be complicated by an infectious disease. A child rubbing his eyes with his hands introduces bacteria to the conjunctiva, resulting in bacterial conjunctivitis.
Don't forget about prevention!
The prognosis for blepharitis in childhood is almost always favorable, even if complications arise during the course of the disease in the form of conjunctivitis, barley, keratitis, etc. The most important thing is that treatment is timely and adequate.
We should not forget about preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of eye pathology. Prevention of blepharitis involves the following:
- Avoid contact with the eyes of chemicals that cause inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Avoid contact with allergens (in case of predisposition to allergies).
- Timely treat infectious ophthalmological diseases and correct visual disturbances.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
Blepharitis when the eyelids are affected by molluscum contagiosum
This disease is viral. Molluscum contagiosum virus is transmitted by contact. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- rashes on the skin of the neck, face, arms and legs;
- formation of nodules on the skin;
- when they are localized on the eyelids, conjunctivitis develops.
With this blepharitis, the follicles gather in folds, usually on the lower eyelid. Papillary hyperplasia of the connective membrane of the eye often develops. In rare cases, corneal damage is observed. The disease takes a very long time to cure. Sometimes its symptoms do not go away for years, periodically subside and worsen.
To combat this type of pathology, electrocoagulation of the nodules or scraping them with a sharp spoon followed by cauterization with iodine is prescribed. Blepharitis and conjunctivitis are treated with ointments and eye drops.
Blepharitis with systemic allergies
Allergosis is not a specific disease, but a collective concept for various pathologies of an allergic nature. Thus, with atopic dermatitis, blepharitis develops in almost all patients and it is quite severe with frequent relapses. It is usually combined with keratitis and conjunctivitis. In this case, bilateral eye damage occurs. Patients complain of symptoms such as:
- itching of the eyelids and skin around the orbit;
- dry skin, appearance of scales;
- dry eye syndrome;
- inflammation and redness of the edges of the eyelids;
- swelling of the conjunctiva.
In addition, there is a tendency to develop secondary infections - fungal, bacterial, herpetic. With this disease, it is necessary to prescribe antibiotics, but with great caution, as allergies may worsen. This form of blepharitis is treated not only by an ophthalmologist, but also by a dermatologist and allergist. For allergies, steroid medications may be prescribed. They are rarely prescribed to children, only in extreme cases, since such medications have many side effects.
How long does blepharitis last in a child?
Children suffer from simple blepharitis for 7-10 days. If the disease is chronic, a longer course of treatment may be required - from 2 to 4 weeks. The duration of the disease depends on several factors:
- causes of inflammation;
- flow forms;
- patient's age;
- the state of the patient’s immune system;
- the presence or absence of other eye pathologies.
It is important to begin treating blepharitis after the first signs appear. Do not delay your visit to the doctor and do not try to get rid of redness of the eyelids, itching and other symptoms using lotions and compresses. Folk remedies only temporarily relieve the symptoms of the disease, but they do not affect its cause. A few days of delay can cause the inflammatory process to become chronic.
What it is
Inflammatory processes of the eyelids that appear with blepharitis mainly spread on its front part, on the outer side. Some forms of the disease may also affect the inside of the eyelid.
, which is in contact with the eyeball.
The pathology does not have pronounced symptoms and is often invisible during its acute course. This leads to the fact that in many patients it is diagnosed in a chronic form.
Blepharitis does not affect the quality of vision and does not lead to irreversible consequences if treatment is started in a timely manner.
How to protect your child from blepharitis?
As noted earlier, children suffer from blepharitis quite often. However, following a few rules will help you avoid the disease:
- When using contact optics for scheduled replacement, take good care of it and treat it with special solutions each time after removal;
- wear only correctly selected optical products;
- take vitamins and eat right;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- Treat all eye diseases in a timely manner.
Explain to children how important it is to adhere to hygiene, wash their hands with soap after going outside and contacting animals. Blepharitis can lead to various complications, some of which have to be treated surgically, for example, entropion, trichiasis, chalazion. In addition, inflammation of the eyelids, when prolonged, spreads to other structures of the eyeball. When the conjunctiva and cornea are damaged, vision decreases. Complicated blepharitis may not go away for a long time with frequent relapses.
Video: Eyelid hygiene for blepharitis
I recommend watching a video in which I will tell you in detail about eyelid hygiene. Caring for our eyelids should become as commonplace for each of us as brushing our teeth. It is hygiene that occupies a leading place in the prevention of various diseases of the eyelids.
Dear parents, despite the fact that blepharitis is not considered a dangerous disease, it cannot be ignored. Otherwise, it will become chronic and then it will be much more difficult to get rid of it.
To prevent such problems from arising, be attentive to your children and take care of their health. See you again!
I will be glad to see your comments and questions! Sincerely, Olga Morozova.