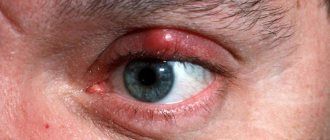
What is barley and why is it dangerous?
The correct medical name for an eye infection is hordeolum.
The disease is inflammatory and purulent; the sebaceous and sweat glands, as well as the hair follicles along the eyelash line, become infected. Barley can be internal or external, depending on location. Each type of ailment is treated in its own way, so to prescribe an ointment or drop, it is better to seek help from a doctor rather than try to make do with what you have in your medicine cabinet at home.
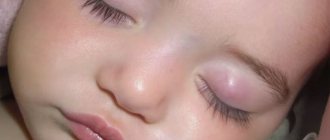
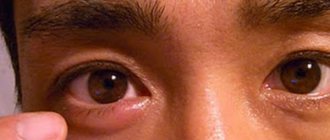
When the disease occurs, the eye swells, redness, itching and pain appear. After a few days, the “bump” acquires a yellow, purulent head. Continuing to swell, by the end of the week it opens on its own (if not, be sure to consult a surgeon!), after which the contents of the abscess come out, and the redness of the eye itself gradually disappears.
In children, eye inflammation is often accompanied by unpleasant side effects:
- elevated (up to 38 °C and above) temperature;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the eye;
- growth of lymph nodes under the jaw, behind the ears and on the back of the head;
- painful sensations (especially if inflammation occurs in the lower eyelid);
- intoxication of the body (in children under one year old).
It is worth remembering that the younger the child, the more severe the infection. In babies from birth to one year, it is several times more difficult to tolerate than in older children, and it cannot be treated at home without a doctor’s supervision!
Barley in a baby
Unfortunately, even such babies can develop eye inflammation. After all, their mucous membranes and organs of vision are very vulnerable. They are constantly exposed to negative influences from the outside. How to distinguish barley in the eyes of a baby from another disease? How to treat it. Let's look into the issue.
What causes stye to appear?
Young children are more susceptible to infectious diseases, because their immune system works for up to 6 months thanks to antibodies obtained from mother's milk. And only after this age does the baby begin to develop its own immunity.
Stye on a baby's eye is an inflammatory process. It begins on the eyelids due to a bacterial infection that is activated in the small body. The most common cause of barley is Staphylococcus aureus. It can get into a child's eyes with dust and dirty toys. Polluted city air and long walks in such conditions, hypothermia of the baby, colds, dysbacteriosis, and poor nutrition contribute to infection.
Signs of barley in infants
Before you start treating it, you should make sure that it is not another ophthalmological disease. After all, inflammatory processes are similar in their symptoms.
The main signs of barley eye disease in infants are as follows:
- Edema. In children of this age, the inflammatory process often occurs in the upper eyelid, and then can spread to the entire eye.
- Itching, burning. The child constantly reaches out with his hands to his eye, which itches, trying to help himself.
- Loss of appetite. irritability, poor sleep, moodiness, tears.
- Chemosis. This is the name for severe redness of the eyelid, which spreads to the entire conjunctiva.
- Swelling along the edge of the eyelid, turning over time into a dense tubercle, the formation of the head of an abscess. The latter usually appears on the 4-5th day, then opens. But sometimes there is no autopsy. The abscess simply resolves on its own.
Usually, after opening the stye, the redness of the skin decreases, soreness and itching disappear.
If the baby's stye is internal, which is rare, then it needs to be monitored very carefully. After all, it can break through the conjunctiva, and this will lead to a general infection of the orbit.
Whatever the symptoms of barley in infants, at this age you should not treat it yourself. You should contact a pediatric ophthalmologist. Only a specialist can accurately diagnose the disease and prescribe gentle and adequate therapy.
How is the disease treated in infants?
The main condition for treatment is its safety. The products used should not adversely affect the health of the baby. Ophthalmologists prescribe the following medications for children of this age:
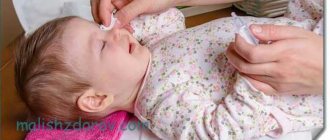
- Eye drops. This is the most convenient treatment for parents. Drops should be instilled into the conjunctival sac, one in each eye three times a day. Most often, patients of this age are advised to use Oftalmoferon. It is allowed for infants. Albucid is today considered an obsolete remedy. These drops cause a strong burning sensation, so it is better not to use them for such small children. The child will resist the burial in every possible way. Levomycetin eye drops are less stinging than Albucid. Still, it is better to give preference to the absolutely painless Tobrex. These antibacterial drops are very helpful in relieving the baby's condition. You don’t have to be afraid that your baby’s eyes will sting.
- Ointments. Compared to drops, they last longer. Ointments must be placed under the lower eyelid, which is not very convenient in treating a child. However, the advantage of ointments is that they practically do not irritate the mucous membrane of the eyes. For the treatment of barley, ophthalmologists most often prescribe Tobrex and Floxal ointments for infants.
As for the treatment of such crumbs with folk remedies, with the permission of the doctor, you can apply dry heat to the eye at the stage of barley ripening, make lotions from calendula, chamomile, plantain, string - these herbs soothe and have excellent anti-inflammatory properties.
Professional examination of stye in a child
So, the first manifestation of barley in a child should be a reason for an early visit to a pediatrician or ophthalmologist. Do not be mistaken that successfully getting rid of barley in the past will allow you to overcome it now, but without the participation of a doctor, for example, using the same medications.
A professional examination of a sick baby is necessary for the following reasons:
- As part of the initial examination, it would not be superfluous to conduct an analysis to identify a bacterial agent;
- if after the first barley the next ones are formed, it means that the infectious microflora has not been overcome, which means that there is a need to revise treatment tactics;
- if barley is accompanied by fever or other symptoms complicating its course, then it is unlikely that it will be possible to avoid the use of antibiotics, and they should only be prescribed by a doctor for both children and adults;
- some cases of stye can be overcome only with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures in combination with medications, which means a visit to a medical facility cannot be avoided;
- frequent relapses will allow the doctor to suspect a deeper and more fundamental cause of the disease and then identify it.
The main rule for parents, which should not be questioned, is the advisability of seeing a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease. Diagnosis of barley in a child usually involves collecting a history of the disease, as well as a visual examination. To exclude other infectious diseases, a laboratory test may be performed as prescribed by a doctor.
Disease prevention
Stye is not contagious. Women are more susceptible to it than men. The explanation is quite simple. Women touch their eyes much more often, for example when applying makeup. Therefore, you should choose only high-quality and proven cosmetics. Makeup applicators and brushes should be washed regularly. It is a good idea to wash your hands with soap before applying cosmetics.
You should definitely take vitamins, especially in the autumn and spring, spend more time outdoors and eat right.
Other more dangerous diseases can be hidden under the guise of barley. For example, chalazion. This disease can only be treated surgically. Therefore, consult a doctor immediately to make a correct diagnosis.
Stye on the eye is a common disease among the population, accounting for 80% of people experiencing it throughout their lives. Stye is a serious disease characterized by purulent inflammation at the edge of the upper or lower eyelid. Self-medication of an abscess can lead to unpleasant complications, such as inflammation of the ocular cornea (keratitis), chalazion, the appearance of stye in another area of the eye, spreading it when squeezing out the pus on your own, which is strongly not recommended by doctors. Under the guise of barley, a cyst or tumor may appear, without realizing it in the absence of knowledge about the symptoms of the disease. Then the question is: “A stye popped up on the eye, which doctor should I contact?” Therefore, you need to consult a doctor, namely an ophthalmologist, who will help solve the problem with stye on the eye.
If you suspect a stye, it is important to immediately contact a specialist
Features of treatment of barley in adults
https://youtube.com/watch?v=SxfjJGrVlrc
If you are tormented by barley, you should not self-medicate, but should consult a specialist. If you treat barley correctly, you can prevent the disease at the initial stage and avoid relapse and complications. Modern medicine offers a wide selection of medicines that promote the complete restoration of damaged tissues, which leads to a quick recovery. First of all, drugs containing levomycin or gentomycin are prescribed, which perfectly suppress pathogenic microflora.
When treating barley, products produced in the form of ointments are convenient to use. They allow you to apply the medicine locally, directly to the affected area. “Hydrocortisone” and “Erythromycin ointment” have excellent properties. A minimal set of side effects and the absence of contraindications allow the use of hydrocortisone ointment in the treatment of eye inflammation in children.
What will the doctor prescribe for a child with stye?
No matter how confident you are in the effectiveness of home methods for treating barley, it is pharmaceutical preparations that demonstrate maximum effectiveness. They neutralize pathogenic microflora and produce an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
If the disease is moderate, then drug treatment will consist of taking sulfonamides in a dosage appropriate for the child’s age (determined by the attending physician). Drugs in this group are similar in their action to antibiotics, but the latter cannot be abandoned if the barley ripens poorly, there is a fever and there is an obvious infection. Sulfonamides and antibiotics destroy systemic infection and are therefore taken orally.
Local treatment of stye in a child involves the use of eye drops or ointments. These are usually Albucid, Sofradex or Ciprofloxacin drops, Tetracycline or Hydrocortisone ointments.
If the process spreads - increased pain, redness, swelling, increased body temperature, enlarged lymph nodes - more powerful anti-inflammatory therapy with the use of antibiotics and sulfonamide drugs is recommended.
Causes of barley
A stye can appear on a child’s eyelid at any moment, which means that an inflammatory process has begun and a bacterial infection has become active. In frequent cases, this occurs due to the fault of Staphylococcus aureus.
A microbe appears for the following reasons:
- children do not always wash their hands after going outside or going to the toilet and may rub their eyes;
- severe hypothermia of the body;
- immune system failure and weakening;
- entry of a foreign body into the eyes (eyelash, dust, speck, etc.);
- Once wet feet can cause stye;
- getting into the eyes of wind, smoke, gas, air spoiled by chemicals;
- diabetes;
- heredity;
- anemia;
- poor quality contact lenses;
- improper or monotonous diet, poor appetite;
- some chronic diseases (for example, gastrointestinal tract);
- the use of certain medications (antibiotics, etc.);
- infrequent exposure to fresh air;
- lack of sleep, fatigue, stress, mental and physical stress;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
If a child has a stye on his eye, it is necessary to find out the reason for its appearance. Knowing it, you can avoid this inconvenient, unpleasant, serious disease next time.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=SxfjJGrVlrc
What are the symptoms of the disease
With external and internal barley, the main and characteristic symptom is the presence of painful swelling of the eyelid. But if with external stye we subsequently see the formation of a cone-shaped formation containing pus, then with internal barley this picture is not visualized. An increase in temperature, as well as disturbances in visual acuity, usually does not occur. The painful sensations subside as soon as a purulent core is formed and the disease resolves. Barley in infants can occur more rapidly with an increase in body temperature and a deterioration in general condition. If a one-year-old baby has enough gestures, he will try to show what is bothering the eye
A very young child can only try to attract attention by crying and trying to rub the already red eyelid, which greatly complicates the diagnosis and increases the area of the lesion. With internal barley, pus along with the secretion of the gland accumulates in the thickness of the eyelid under the conjunctiva. If examining the lower eyelid is not difficult, since it is enough to simply pull it back, then in order to turn out the upper eyelid without causing harm, certain medical experience is required.
Do not attempt this procedure at home; consult a doctor.
Frequent internal styes change the structure of the gland and its function, leading to the formation of a chalazion.
Treatment of barley in children at home
As soon as the first symptoms of the ill-fated barley appear, it is necessary to take action immediately. It would be good to immediately contact an ophthalmologist. And if there are no deteriorations such as high fever or a large number of styes, then the doctor will prescribe home treatment.
If it is still not possible to see a doctor on the same day, then you need to do the following:
- Soak a cotton swab in 70% alcohol, brilliant green or iodine and cauterize the inflammation;
- Apply dry heat to the sore eye. It can be a boiled chicken egg, a warm tea bag, sea salt, preheated in a frying pan and wrapped in a cloth bag. Such procedures will help relieve pain and improve outflow in the sebaceous gland;
- Place the drops listed above into the eyes;
- At night, put ointment under the lower eyelid. If the child does not allow this, you can wait until he falls asleep and spread the ointment along the eyelashes;
- When the stye is opened, pus is released, which can stick together the baby’s eyelashes. To remove pus, you need to moisten a cotton swab in furatsilin solution, tea leaves or boiled water and rub it over the eye;
- It’s good to make sure that the baby doesn’t put his hands in his eyes or rub them. This may spread the infection to other areas of the eye;
- After opening, you need to wash the eye with herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula) for 1-2 days. This will promote rapid healing of the wound and also protect the eye from recurrent infection.
Folk recipes
You can resort to folk recipes, but you should not give them complete preference:
- For eyelid lotions, you can use an infusion of calendula or chamomile. To do this, pour 1 tablespoon of dry herb into 200 ml of boiling water. Let it brew for about half an hour. Cool slightly and apply to the eyelid.
- Aloe juice lotion has a good bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effect. For preparation you will need 1 part squeezed aloe juice and 10 parts boiled water. The lotion should be applied 3 times a day.
- A simple decoction, accessible to everyone, can be made from birch leaves. To prepare it, you need 1-2 tablespoons of dry crushed birch leaves, pour 200 ml of boiling water, let it brew for half an hour. Rinse the baby's sore eye with warm broth 3 times a day.
Treatment of barley in a child at home
If a visit to a doctor cannot be made on the same day, then emergency measures are proposed, which, however, do not involve taking medications, but only some relief of the general condition. Completing these does not exclude the need to seek an in-person consultation in the near future.
Apply dry heat. This is only permissible if the baby does not have a fever. It is suggested to use warm compresses, which stimulates the ripening of barley in a child . The duration of the compress is 10-15 minutes, and the number of applications per day is 4-6 times. This ensures blood flow to the inflammation. and hence its speedy rupture and maturation.
A compress is a dry, warm or hot object, like a boiled egg in everyday life. An alternative option is to wrap a container of hot water in a clean towel. The compress should be applied exclusively to the closed eye, without trying to act directly on the source of inflammation.
Apply a dry bandage to your eye. Before going to the doctor, parents can apply a sterile dry bandage to the eye. This will localize the process and not aggravate it. It is clear that not every child will want to wear it, but parental imagination can help here - for girls, decorate it with interesting patterns, and for boys, the role of a pirate will suit them.
Traditional methods of treating barley in a child
Traditional medicine offers several effective methods for treating stye, but each of them is best used in addition to traditional ways to overcome the disease. Phytotherapy methods can also be prescribed by the attending physician. If this does not happen, ask him about the appropriateness of the following recipes:
- combine chamomile, St. John's wort and calendula herbs in equal proportions, 2 tbsp. Brew the collection with a glass of boiling water, and when it cools down, strain; add a few drops of alcoholic propolis; use for compresses at night;
- Chop 1 cabbage leaf and combine with egg white, wrap the resulting pulp in clean gauze and use as compresses;
- Pour 200 ml of boiling water over 10-15 dried flowers, leave for about 40 minutes, strain and use as compresses and lotions;
- combine 2 parts of calamus root and birch buds, 3 parts of violet herb, 4 parts each of wild rosemary and string, it is better to grind the herbs in a coffee grinder; 2 tbsp. pour the resulting mixture with a liter of boiling water, simmer for 10 minutes, remove from heat, leave for 12 hours, strain; use for oral administration (can be flavored with honey) half a glass half an hour before meals or for compresses;
- Brew a handful of dry figs with a glass of milk, after 10-15 minutes grind the figs in milk and take half a glass orally 2-3 times a day half an hour before meals.
Non-surgical treatment of stye on the eye
The first signs of immediately contacting a doctor when an abscess appears are:
- blurred vision;
- swelling of the eyelids that does not go away for more than 2-3 weeks;
- increased tearfulness;
- painful sensations.
During the initial examination by an ophthalmologist, having taken the necessary tests, he will be able to determine the severity of the inflammation and prescribe the appropriate procedures and treatment. If this is barley at the initial stage, accompanied by redness of the eyelids, itching, swelling at the edge of the eye, then doctors recommend cauterization with an alcohol solution, brilliant green or iodine to prevent its maturation. In the absence of fever, you can carry out thermal procedures every 20 minutes during the day with tea bags of black tea, boiled eggs, salt in a bag, and make lotions from herbal infusions of chamomile, calendula, and aloe.
In case of severe inflammation of stye, which can develop into a chronic form - chalazion, the ophthalmologist will prescribe:
- Antibacterial therapy. It is known that the main cause of an abscess is a bacterial infection, namely staphylococcus, streptococcus. Based on this, the patient should undergo a bacterial test to culture the contents of the eyelid to determine the sensitivity of the infectious agent to a particular antibiotic.
- Drug therapy. It is also recommended to use the following in combination:
- eye drops containing sulfacetamide, ciprofloxacin (albucid, tobrex, fluxal, chloramphenicol), which should be instilled 3-4 times a day;
- antibacterial ointments with antibacterial action (levomycin, gentamicin, erythromycin, hydrocortisone, tetracycline), which should be carefully applied 3-4 times a day without damaging the mucous membrane of the eye. When applying any ointment, vision may be blurred for a short time.
- Physiotherapy. To avoid surgical intervention, doctors strongly recommend physiotherapeutic procedures:
- electrophoresis - improves blood circulation at the site of the abscess;
- warming - effective use of ultraviolet lamps, high frequency currents (UHF therapy). If accumulated mucus is released, rinse the eye with a solution of furatsilin. Wet compresses for ripened barley are strictly prohibited.
- massage of the inflamed eyelid helps remove the sebaceous accumulation of the meibomian glands from the eyelid with special instruments used by an ophthalmologist. It is recommended by your doctor to carry out this procedure as a preventative measure 2 times a year.
What is the difference between stye in children and adults?
Barley is a disease characteristic of both children and adults. However, treatment, and partly prevention, and diagnosis of barley in a child differ from that in adults. The differences are as follows:
- barley usually develops due to a staphylococcal infection, but the child’s body is more defenseless against it, and therefore the presence of staphylococci in an adult is reflected in isolated cases of barley or ENT diseases, while the child suffers chronic forms of diseases and frequent relapses of barley; Staphylococcus cannot be ignored in either adults or children, but children are the most vulnerable;
- recurrent barley in a child is not only a suspicion of staphylococcus, but also of gastrointestinal diseases, hypovitaminosis, weak immunity, and this requires immediate correction, otherwise it will cause chronic diseases for many years;
- adults who have stye on the eye are advised to seek diagnosis and prescription of medications from a doctor, however, this is not such a complex disease that you can overcome it yourself by choosing a medication from a pharmacy network; you cannot avoid visiting a doctor if the stye lasts more than 3-4 days; barley in a child is a mandatory reason to consult a doctor;
- During the course of the disease, it is recommended to adhere to certain rules, including, for adults, avoiding makeup and wearing contact lenses; for children, this is only compliance with the rules of hygiene and cleanliness of hands, as well as rest for the eyes (refusal of computer games and TV cartoons, good sleep).
How to treat barley in a child
What to do if barley appears in a one-year-old child? How to treat stye on the eye of a two-year-old child? This question often arises among parents of young children.
Since the inflammation is bacterial in nature (bacterial infection), treatment is aimed at strengthening the body's immunity and using antibacterial drugs.
As soon as the first signs of barley appear in a child, the fight against this inflammatory process must immediately begin.
Folk remedies for treating stye in a child: warm compresses
They are aimed at a local increase in temperature at the site of infection, so that our immune system more actively fights the infection. Compresses help well in the first stage of the disease. Depending on the moment at which the use of compresses began, the barley can either completely disappear without forming a purulent head, or, on the contrary, quickly form a purulent head (rod) and break through.
For children of any age, warm (not hot) compresses are an excellent treatment for inflammation. They are applied to the affected eye 3-4 times a day. You can apply compresses when the child is sleeping. With this treatment, barley goes away in 7-8 days.
A popular remedy is a compress made from chamomile infusion. It is very convenient to use chamomile in special tea bags for these purposes. Pour boiling water over the bag and wait until the infusion becomes warm. Squeeze the bag and apply to the affected eye for 10-15 minutes.
Regular tea bags with black tea without additives are also suitable for compresses; pour a cup of boiling water over the bag, wait until the water cools down but remains warm enough, squeeze out the bag and apply to the affected eye for 10-15 minutes.
Ordinary warm boiled water is also suitable for compresses. Take a clean gauze or cotton napkin. Soak in warm, boiled water and apply to the affected eye for 10-15 minutes.
To warm up, many people use a warm, hard-boiled egg. The egg is wrapped in gauze or a napkin and held near the affected eye for 10 minutes. Next time you can use the same egg, after boiling it in water for 10 minutes.
Sometimes, it is recommended to lubricate the external barley with brilliant green, fucorcin, iodine solution or medical alcohol. However, we do not recommend doing this; these drugs can get into the mucous membrane of the eye and cause serious damage to it.
Preparations for the treatment of barley
If first aid is provided at an early stage of the disease, the stye is usually cured within a few days. However, in the later stages of the disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will examine the child and prescribe treatment. Barley is treated locally. Along with eye drops and ointments, medications are prescribed to increase the child’s immunity, especially if the child develops stye frequently.
A child who is 1 year old can carefully drip Albucid (Sodium Sulfacyl) drops onto the affected eyelid, in a dosage appropriate for their age (indicated in the instructions for the drug), 3 times a day. These eye drops are effective in treating stye; they eliminate the inflammatory process that caused the appearance of the abscess
The active substance sulfacetamide will quickly destroy bacteria.; Eye drops based on chloramphenicol are also widely used to treat the disease. This well-known antimicrobial agent is used quite often; Tobrex drops are a new generation drug. It contains an antibiotic that effectively fights Staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria. Tobrex for barley is instilled into the baby’s eye 3 times a day, 1 drop; For enlarged lymph nodes, elevated temperature, and severe pain in the eye, oral antibiotics and sulfonamide drugs are prescribed.
Ointments are also used to treat stye. These drugs are less common, especially for young children. However, ointments are very effective and quickly help cure stye. They are usually prescribed to school-age children.
Basic ointments for treating the disease:
- Erythromycin;
- Tetracycline;
- Gentomycin;
- Hydrocortisone (hormonal ointment);
- Levomykoleva.
If the stye breaks out on its own, you need to rinse the eye with warm water using a cotton swab.
Treatment of barley in a child
The number of “folk methods for barley” practiced by parents is truly enormous. But if we discard everything that does not have the slightest effect on bacterial invasion (ritual-magical, religious and, excuse me, frankly delusional mapipulations), two main approaches remain: heat and rinsing. Here it is necessary to emphasize several critically important points that, without exaggeration and unnecessary pathos, every parent should remember by heart.
First: instilling, infusing, smearing anything, applying it in the form of lotions or compresses, or giving it orally is CONTRAINDICATED without a doctor’s prescription. Dear adults: well, you can’t, that’s all. You and only you bear full responsibility for the health and life of your child, remember? If yes, then you CAN wash your eyes with aseptic herbal infusions (chamomile, birch buds, calendula, sage, St. John's wort, regular tea leaves); this can be done quite often, several times a day, using only disposable cotton pads, and if styes grow in two eyes at the same time, then a separate swab for each eye. Such procedures really alleviate symptoms and help flush out purulent discharge, which is infested with pathogens.
Second: without the prescription and supervision of an ophthalmologist, any thermal procedures are CONTRAINDICATED, no matter what coolants are used (salt, chicken eggs, bread, seeds, stones, etc., etc.). Let us clarify especially for the most distrustful and “seeing through medicine”: the point is not at all that they are trying to force you to see a doctor at any cost in order to receive stable fees... however, even if you really think so, go anyway - go for free , go off with a scandal - but be sure to show the child to the doctor. The fact is that in the early stages, before the deployment of a full-fledged immune response, additional heat can give pathogenic bacteria such an advantage that no immunity can cope with their lightning-fast spread.
As a rule, the doctor does prescribe warming, but only from a certain point, and this is best done using a household UV reflector (“blue lamp” if you have one), or in a physiotherapy room at a clinic where UV or UHF is used. There is, of course, a point in taking such a course: it accelerates the ripening (already controlled by immune forces), opening and healing of barley, and ultraviolet light also has a bactericidal effect.
Just in case, let’s stipulate one more point: please, there is no need to “cauterize” the hordeolum with anything, okay? The ophthalmologist may prescribe, depending on a number of obvious nuances of the clinical picture and dynamics, wiping with ethyl alcohol in one concentration or another, applying brilliant green, antibiotic eye drops and/or ointments.
And again: well, if you don’t believe this particular doctor, take the child to another, and if this one doesn’t inspire confidence or, say, you don’t like his appearance, then to a third one. But if you are prescribed medications containing an antibiotic, and if you have already started using them, do it - for the sake of your child and for the sake of all of us, sinners and those suffering from bacterial infections! - in such doses, for as many days and in combination with those auxiliary medications as PRESCRIBED for you (for example, under antifungal or antiallergic cover).
Finally, the third point, which is also the last and most important:
- under no circumstances (“The child is exhausted”, “We’ve been treating for the second hour, but nothing helps”, “It’s impossible to watch him cry”);
- in no way (“I’ll just touch”, “I’ll press a little”, etc.);
- and do not try to squeeze out the barley for any purpose (“Easy”, “Accelerate”). This is CATEGORICALLY CONTRAINDICATED, since it is already truly dangerous, and the level of risk is up to fatal. Penetration of the pathogen into surrounding tissues, the circulatory or lymphatic system, given the proximity of the brain and other vital organs, can lead to general sepsis, meningitis, panophthalmitis, thrombosis and other severe complications.
If it comes to the need for surgical intervention - and sometimes it does - let it be done under sterile conditions; quickly, correctly and painlessly; a qualified person who has been taught this for many years and who has done it with success many times.
Why does it appear
The causative agent of the inflammatory process is Staphylococcus aureus.
This bacterium lives on the skin and hair of every person, but becomes dangerous only under favorable conditions. The main reason for the development of a purulent infection in the eye is a weakening of the body's protective function.
This condition is provoked by:
- hypothermia of the body;
- previous diseases of a viral or bacterial nature;
- avitaminosis;
- changes in hormonal levels (in adolescents, the endocrine system is reconstructed, which is why sweat becomes more viscous and clogs the jelly ducts);
- inflammatory diseases occurring in a chronic form;
- worms;
- disorders of the intestines and/or stomach.
To avoid wasting valuable time, find out the symptoms of retinal cancer.
Worms can cause frequent stye in a child.
Let's make life easier - learn about the causes and treatment of pain in the eyes from.
Stye on a child's eye
Treatment of barley is local. An eye disease characterized by severe pain is stye on the eye, the treatment of which requires a serious approach. First, let's try to figure out how barley appears on a child's eye. If you notice symptoms of stye in children, do not panic. Stye on a child’s eye is a common occurrence that can occur at any age. Dr. Komarovsky believes that the only microbe that causes barley is Staphylococcus aureus.
Therefore, if you have the first symptoms of barley, you should consult a doctor. Treatment should be carried out by an ophthalmologist. Barley is an acute inflammatory process in the hair follicle or sebaceous gland at the edge of the eyelid. Inflammation can also be localized in the lobule of the meibomian gland, such barley is called internal.
A contributing factor in the development of barley is reduced immunity. The main factor contributing to the development of barley is considered to be a violation of hygiene rules. Do not be intimidated by this list and immediately look for signs of a serious pathology in your child. Barley against the background of these diseases does not appear sporadically, but is recurrent in nature (frequent barley). In young children, the swelling can be so massive that it is difficult to open the eye.
In children, inflammation may be accompanied by eyelid twitching, headache, and a slight increase in temperature. If this does not happen, consult a doctor who will examine the child and tell you how to treat a specific case of illness. If barley appears against the background of another pathology, the underlying disease is treated. I myself have barley, I don’t know how to fight it.
Barley is a rather painful phenomenon. It appears unexpectedly and can affect the eyes of both adults and children. While playing on the playground and being in the company of other children, the child is constantly exposed to pathogenic bacteria. Children often neglect basic hygiene rules and do not wash their hands regularly, and the infection gets into the eye through their palms. This is where the causes of the disease lie.
An even greater danger of infection appears when the child’s immune system is weakened. Then it is necessary first of all to treat these internal diseases. After 3 or 4 days, the stye ripens and pus comes out of it, although in some cases, especially when treatment begins on time, it may simply pass without opening.
You should also seek medical help if you are faced with a form of the disease such as internal stye. The doctor himself opens the internal stye and carries out disinfection. In order to get rid of stye, eye drops and ointments are usually used. The most popular drops that are most often used to treat styes in front of a child’s eyes are Albucid.
But for children, tetracycline ointment can be used only in consultation with a doctor. It is usually used to treat children over the age of eight, and for babies under one year old it is used in very rare cases. I always talked barley into my children. It sounds strange in the 21st century, but this method really works. The child's eyes must be protected. Barley on the eye is an infectious process accompanied by unpleasant symptoms.
The disease is not contagious; with the right therapeutic approach, it can be treated quickly and effectively. Barley is an inflammatory disease, for the treatment of the external form of which conservative methods of therapy are used. A small nodule that visually resembles a small tumor is a stye on the eye, the treatment of which often involves surgery. Do not confuse the cold form with ordinary barley, the treatment of which in some cases is significantly different.
A small lump inside the eyelid is an internal stye on the eye, the treatment of which requires the use of special ointments, for example, hydrocortisone. Often the nodule transforms into a compacted formation, flowing into the form of cold barley. Stye on the eyelid, usually the upper one, manifests itself in the form of a small tumor, upon which pressure appears unpleasant painful sensations. Treatment of stye on the eye during pregnancy involves therapy without the use of antibiotics.
To treat barley as quickly and easily as possible, you need to recognize this disease in a child at the very first stage of development. Such an unpleasant phenomenon as a stye on a child’s eye certainly causes concern among young parents.
Barley in a child: how to recognize?
Caring parents should carefully monitor the health of their little child so as not to miss the first symptoms of any disease. Children are most susceptible to infectious diseases due to fragile immunity and imperfect compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards. It is these two groups of factors that provoke stye on the eye.
When can a child develop stye?
It is often argued that barley in a child is the result of hypothermia, to which the child’s body is so sensitive. This is only partly true, because in most cases, susceptibility to low temperatures is determined by underdeveloped immune mechanisms. Barley in a child , especially a constantly recurring one, indicates a malfunction of the immune defense, which may be hereditary in nature, or may be artificially created. Analyze or seek professional diagnostics to see if your baby has:
- hypovitaminosis - lack of vitamins A, C, group B;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and helminthic infestations, which serves as a source of infection in the body and weakens general immunity;
- any infections in a chronic form - if your baby often flares up tonsillitis or sinusitis, suspect the presence of a stable pathogenic microflora, which determines the risk of stye.
Barley belongs to the category of infectious diseases, the frequent causative agent of which is latent staphylococcal infection. Adults can be carriers of a staphylococcal infection for a long time, which will manifest itself in a not too long and severe course of otolaryngological diseases. In a child, staphylococcus acts more aggressively, outbreaks of provoked diseases occur much more often, barley is one of them. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the causative agent of barley is Staphylococcus aureus in combination with a weakened immune system.
How to protect your baby from staphylococcus? If there is anything that can be done, it is to carefully observe hygiene, which also does not completely eliminate risks. Parents are recommended to instill in their child from an early age the habit of washing their hands (after a walk, going to the toilet, before eating) and to wean them from the desire to contact their hands with their mouth, nose, eyes without apparent need (that is, rubbing their eyes, licking their fingers, etc.) . It is recommended to observe cleanliness even more carefully for a baby already sick with stye - it is strictly forbidden to scratch the eyes or touch the inflamed eyelid.
Symptoms of barley in a child
Barley is an acute inflammatory process in the hair follicle of the eyelash or in the sebaceous gland located next to the eyelash bulb; in addition, inflammation can be localized in the meibomian gland lobule, then we will be talking about internal barley. Barley is certainly a process of suppuration, the causative agent of which is usually a staphylococcal infection.
With barley, a hyperemic “grain” appears on the child’s eye, accompanied by redness, inflammation and swelling of the eyelid margin, as well as pain. The baby’s pain is traditionally accompanied by itching and burning.
Often, barley in a child takes on a complicated form, which means the following develop:
- headache,
- increase in body temperature,
- tremor of the eyelid,
- swelling so severe that the eyelid stops opening,
- spread of styes to both eyes.
If the barley proceeds without complications, then on the 3-4th day of illness, a light yellow patch forms at the top of the swelling, which opens on its own, followed by the release of pus. Under no circumstances should barley be squeezed out! Any treatment tactic comes down to stimulating the self-opening of the abscess, but without mechanical participation in that.
How to recognize the danger of barley in a child?
Barley in a child is perceived by parents without excessive concern, which is quite fair, however, there are situations when a seemingly harmless barley poses a serious threat to health:
- barley opened by mechanical movement - unripe barley cannot be squeezed out, this contributes to the spread of infection up to a purulent abscess of the eyelid and even meningitis; successful treatment leads to the fact that the abscess will open on its own and all further actions are reduced only to eliminating the fluid flowing from it, because getting it into the eye also does not bode well;
- chronic course of barley - determined by constant relapses of the disease, usually with any cold or hypothermia, indicates serious problems with the immune system or the presence of a stable infectious microflora, which cannot be ignored and only barley should be treated as a consequence, and not the cause;
- chalazion, eyelid cyst - a disease visually similar to styes, but characterized by a slower progression; Another difference is the rigidity of the neoplasm; it looks like a bone under the eyelid; treatment of this requires specific diagnosis with the determination of a further strategy (this can be conservative treatment and restoration of normal function of the gland, or surgical elimination of the defect).
Prevention of relapse
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat
It is important for parents to carefully monitor the health of their child throughout the year and do everything possible to ensure that their immune system works effectively. Personal hygiene plays an important role
The child should always have clean hands so that he does not introduce an infection into his eyes, which can subsequently provoke the appearance of chiria.
Children should also eat a balanced diet and receive the full range of vitamins and minerals. If you know that your baby is prone to infectious diseases, carry out preventive therapy every year during the season of mass influenza and acute respiratory viral infections. You can give your child prophylactic antiviral drops to boost immunity. They should be prescribed by a pediatrician. Don't forget to do frequent wet cleaning and ventilation in the children's room.