- Barley in a child: how to recognize? When can a child develop stye?
- Symptoms of barley in a child
- How to recognize the danger of barley in a child?
- Traditional methods of treating barley in a child
| Barley is an unpleasant disease in aesthetic and physiological aspects. Its course cannot be missed, but treatment must be timely, and sometimes requires some specificity. For example, barley in a child is a common occurrence, but it baffles many parents, because once it appears, it can often recur. |
What is hordeolum?
The scientific name of barley is hordeolum. This is a disease of the eyelid, which is accompanied by inflammation or suppuration of the eyelash follicle or nearby glands.
Hordeolum is divided into types according to localization: stye of the upper eyelid, lower eyelid or internal (located on the inside of the eyelid). As a rule, the focus of inflammation forms on the upper eyelid, although lesions in the area under the eye are not uncommon. Depending on the strength of the immune system and the intensity of inflammation, lesions can be single or multiple, and located on one or two eyes at once.
Causes of the disease
Those who have encountered this problem always ask the question: is it possible to infect someone or become infected with stye? Can this disease spread to the second eye?
Remember, stye is not contagious. But the infection can affect the other eye. This occurs because the immune system has not yet recovered from the previous inflammation.
There are many reasons for the appearance of barley in a child.
First of all, this is not observing the most basic rules of hygiene:
- rub your eyes with dirty, unwashed hands;
- ingress of foreign objects;
- dust that gets into the eyes;
- hypothermia.
And also the inflammatory process in the eye can be provoked by:
- Reduced and weak immunity. Strong immunity prevents bacteria and viruses from multiplying, and when it is weak, all viruses freely enter the body.
- Hypothermia. When hypothermia occurs, the protective reaction of the immune system decreases.
- Diabetes. Due to damaged blood vessels, blood circulation worsens.
- Hereditary predisposition. There are programs in our DNA system that carry a predisposition to diseases.
- Hormonal imbalances, during which the viscosity of secretions in the glands increases.
- Contact lenses. When taking them off and putting them on, the chances of infection increases significantly, plus, the service life of the lenses is often not respected.
It is impossible to become infected with barley, but it can form again, even in the shortest possible time. This may happen because the baby’s body was unable to resist microbes, that is, his immunity was weak.
Stye appears on the upper and lower eyelids for one reason. But on the upper eyelid it can be not only external, but also internal, maturing inside the eyelid. In this case, it is formed in one day. With barley below, part of the face swells, swells, and the inflamed area turns red.
Barley often appears when the simplest hygiene rules are not followed:
- The child rubbed his eyes with unwashed hands and caused an infection;
- A speck got into the eye and caused a stye, especially if they tried to get it out with a dirty handkerchief;
- Dust gets into the eye, this often happens on the street, especially in windy weather;
- The infection could have ended up on someone else's towel or handkerchief, which the child could have used;
- Hypothermia could also be the cause of barley.
However, parents should be aware that barley can also appear as a consequence of serious diseases.
When the reasons for the frequent appearance of barley in a child are not clear, you need to undergo an examination
Causes of occurrence in a newborn
The main reason for the appearance of barley is the inflammatory process caused by bacterial infections. As a rule, pathogenic microorganisms enter the eye mucosa through touching with dirty hands.
But there are other provoking factors:
- The baby's immune system is not yet mature enough to resist infections.
- Insufficient hygiene, in particular, improper or infrequent hand washing, leads to pathogenic microorganisms entering the mucous membrane from the outside and causing inflammation.
- Severe hypothermia and being in a draft.
- The presence of chronic infections (sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc.) can also provoke the appearance of barley as a complication.
In children older than infancy, the appearance of a focus of inflammation is also provoked by insufficient nutrition or a diet that does not contain sufficient vitamins and microelements.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy procedures are recommended at the infiltration stage in the absence of body temperature. They increase the body's resistance to infection and have anti-inflammatory, bactericidal and analgesic effects.
The main procedure is UHF therapy with a low-thermal dose with a duration of 8 minutes, 4-6 procedures.
For individual indications the following may be used:
- microwave therapy;
- UV irradiation;
- electrophoresis with penicillin or sodium sulfacyl;
- infrared irradiation of the eyelids.
Patients with a recurrent form of the disease will benefit from spa therapy: swimming in sea water, air and sun baths.
First symptoms
In infants, the disease occurs suddenly. The first symptom is redness of the eyelid, which quickly turns into swelling. After 2-3 days, an abscess appears in this area.
In young children, the swelling can be quite large, to the point that the eyelid covers the entire eye. The inflammatory process is accompanied by severe itching and burning. Because of this, the baby becomes capricious, often cries and appetite worsens. In rare cases, headaches and a slight increase in temperature are observed.
Expert opinion
Nosova Yulia Vladimirovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
As a rule, the abscess opens on its own 4-5 days after the first symptoms appear. After this, the swelling and discomfort disappear. However, it is necessary to seek the help of a doctor at the first manifestations of the disease. This will help speed up the recovery process, avoid complications and ease the course of the disease.
Symptoms
Knowing the first signs of barley, you can identify the disease at the initial stage. To cure the pathology, it is important to make sure that the diagnosis is correct, and for this it is better to consult a doctor.
Note! A doctor's advice is required, since abscesses may differ, and different treatment methods are used at different stages of the disease.
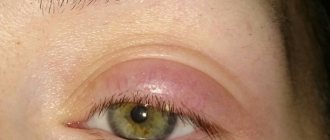
A stye on a child’s eye causes the following complaints:
- local swelling;
- burning in the affected area;
- severe itching;
- pain;
- severe redness of the eyelid;
- restlessness and crying;
- decreased appetite;
- restless night's rest;
- at first there is slight swelling, and then the formation of an abscess.
Children in infancy often cannot explain what hurts them. They simply stretch their hands to the sore eye and often cry.
Redness lasts the longest. For some, the abscess never breaks through, but simply resolves on its own.
Important! A cold stye that remains motionless for a long time and does not go away requires only medical treatment.
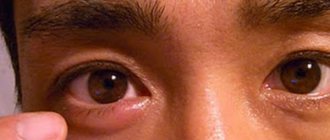
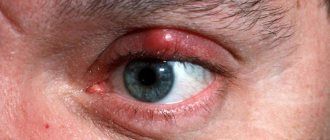
If the eye is inflamed and it is clear that it is an internal stye (you can see what it looks like in the photo), you should be especially careful. The abscess can rupture inside the conjunctiva, causing a general infection of the orbit.
Advice! For any type of barley, it is better not to treat at home, but to consult a doctor.
Approved drugs for newborns
Medicines for the treatment of stye in newborns are selected especially carefully, since most conventional medicines are not suitable for infants.
Modern drug manufacturers provide a wide selection of medications intended specifically for the treatment of infants. Despite this, these drugs should not be used independently, without first consulting a doctor.
Fucithalmic
These eye drops are topical antibiotics. They are used in ophthalmology to treat barley and other diseases of bacterial origin. The drug has a viscous consistency, which ensures long-term contact with the conjunctiva.
The drug is suitable for the treatment of newborns, children and adults. Used for the treatment of barley, conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis and dacryocystitis.
Fucithalmic is instilled 1 drop 2 times a day for 7 days. Longer therapy is prohibited, since use may cause bacterial resistance to the active components of the drug.
Vitabact
Eye drops made in France. They are a colorless or slightly yellowish liquid. According to the medical classification, the drug belongs to antiseptics for local use in ophthalmology.
Vitabact is recommended for patients of all ages, including newborns, for the treatment of bacterial infections of the anterior eye and the prevention of infectious complications after ophthalmological operations.
To treat barley in infants, the drug is instilled into the conjunctival sac, 1 drop 2-6 times a day. The duration of treatment is 10 days. Longer use, as well as the exact dosage, is determined by the doctor during an individual examination.
Phloxal
This drug is available in the form of eye drops and ointment. Both medications are classified as local antibiotics. Used to treat infectious and inflammatory processes in the anterior part of the eye.
Stye on a child’s eye – causes and how to treat
The natural protection of the eye, the eyelid, consists of five main elements: the anterior (external) skin, muscle fibers, cartilage tissue, the posterior (internal) mucous membrane-conjunctiva and the ciliary row along the edge.
In addition, evolution has provided a system of small glands, which are located partly in the conjunctiva (additional lacrimal glands), partly in the inner space of the eyelid (sweat and sebaceous glands). Moll's sweat glands and Zeiss' sebaceous glands emerge between the eyelashes or communicate with each other; Meibom's sebaceous glands are located deeper and open from the conjunctiva. In general, the secretion of the glands serves to hydroregulate the skin and ciliary roots, as well as to reduce friction during blinking.
Despite the fairly simple structure of the eyelid, each of its structural elements is susceptible to many pathological processes and conditions. Most of them are infectious and inflammatory in nature and are caused by viral, bacterial or fungal pathogens, as well as a skin parasite - the smallest Demodex mite, which settles at the base of the eyelashes, in the hair follicles and glands.
Thus, patients constantly turn to ophthalmologists with all kinds of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, dermatitis, as well as various combinations thereof. Such inflammations occur with varying frequencies, which depend on many factors - regional, age, etc. However, among these diseases there are undisputed leaders: conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane) and hordeolum, or barley.
Both diseases are so widespread that, probably, any earthling will encounter them at least once during his life - if not in himself, then in his closest relatives. And when a child with barley appears at the reception, one can often only be surprised at how little parents know about the causes and patterns of this “national” pathology, and what strange and sometimes dangerous methods they try to cope with it.
Why is barley dangerous for babies?
Barley is considered a relatively safe ophthalmological disease, since with proper therapy the abscess is eliminated on its own in 5-7 days.
But with improper treatment or its absence, the inflammatory process can provoke serious consequences:
- An internal stye can develop into a chalazion, which can only be treated with surgery.
- Attempting to open an abscess on your own can lead to meningitis or blood poisoning.
- The lack of correct treatment for barley in infants provokes phlegmon of the orbit and keratitis.
Important! If frequent relapses of the disease are observed, it makes sense to undergo a full examination, since frequent inflammatory processes in the eye can be symptoms of serious pathologies of internal organs or weakened immunity.
Prevention of stye
To prevent inflammation of the eyes and eyelids, it is recommended:
- wash your hands before touching your face;
- strengthen the immune system through hardening, proper nutrition and exercise;
- promptly treat any infectious processes in the body.
Ophthalmologists warn that if signs suspicious of stye appear, do not self-medicate and, moreover, do not heat the source of inflammation (with a warm egg, a bag of salt). The most correct decision is to show the child to a pediatric ophthalmologist. Doctors at the SM-Doctor clinic for children and adolescents practice both conservative and surgical treatment of stye. High-tech diagnostic and surgical equipment, professional staff and an individual approach to each patient allow us to achieve high results in the treatment of ophthalmological diseases.
Preventive measures
Since the causative agent of the disease most often enters the mucous membrane through dirty hands, the following preventive measures should be observed:
- Teach your child to wash their hands more often and not rub their eyes with them.
- The baby must be provided with his own towel and bed linen.
- The house is also kept clean and wet cleaning is carried out regularly, since in dusty rooms the risk of inflammation increases.
In addition, it is important to strengthen the newborn’s immunity: adhere to a nutritious diet, toughen up, and, if necessary, give the baby vitamins. If inflammation often recurs, it is necessary to take a blood test.
Possible complications
Barley disease has a favorable prognosis in most cases. Complications develop after neglecting the rules of treatment and hygiene:
- spread of infection over large areas with the formation of multiple foci of abscess;
- chronicity of an untreated disease;
- development of eye phlegmon (purulent inflammation of the orbital tissue);
- formation of chalazion (compaction in the thickness of the eyelid);
- thrombophlebitis of the orbital eyelids.
In extremely severe cases, when pathogens enter the bloodstream, purulent meningitis and a systemic inflammatory reaction may develop.