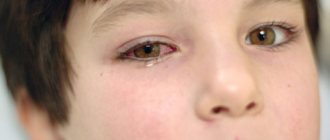
The only reason for getting a sunburn on the eye is prolonged exposure to direct sunlight without any protective equipment.. Even in the shade, ultraviolet rays can damage the eyeballs.
People get sunburns on their eyes not only on the sea coast in the summer, but also in the mountains against the backdrop of snow cover . And in this case, the pathological condition will be called snow blindness (snow burn). The explanation for an eye injury is simple: at high altitudes, the sun's rays are scattered very poorly, and their impact can be compared to a directed beam through a magnifying glass. Essentially, the mucous membrane is burned out.
Sunburn of the eyes can rarely occur in normal urban environments due to the constant scattering of ultraviolet rays onto many objects.
Symptoms of retinal damage:
- deterioration of vision - “blurred” images, flying golden “spots”, circles and a veil will appear;
- signs of conjunctival irritation - severe itching, redness of the inner corner of the eye;
- profuse lacrimation - in most cases the victim cannot even open his eyes completely.
1-2 hours after receiving a sunburn of the retina, a headache appears, which at first is mild in nature, but after a short time becomes unbearable.
A burn of the retina by the sun's rays is always accompanied by photophobia ; the patient cannot even tolerate ordinary daylight through windows. This symptom begins to develop literally immediately after receiving an injury - the person begins to actively squint and alternately close his eyes.
The presence of signs of sunburn of the eyes is a reason to visit an ophthalmologist.
Optical system of the eye
The retina and cornea of the eyes are extremely sensitive; in the absence of proper treatment, even minor damage to them can provoke the development of complete or partial blindness. But if you can’t see a doctor, then you should do the following:
- wash with cool water, but do not specifically rinse your eyes;
- apply cold compresses and change them as they warm up - at least every 10 minutes;
- Provide the victim with peace; he should be in a cool and darkened room.
Cold compress on eyes
Be sure to take an antihistamine , which will not only quickly “calm” the mucous membranes of the visual organs, but also relieve swelling, redness, and relieve itching. The optimal choice would be Tavegil, Suprastin, Claritin, Ceterizin and other antiallergic drugs .
If the patient is bothered by severe pain in the eyes or heaviness/noise in the head, then ordinary analgesics can alleviate the condition . It is highly advisable to measure the victim’s blood pressure before taking painkillers and, if necessary, take medications that lower it - often the classic symptoms of sunburn appear precisely against the background of such a condition.
It is recommended to make cold compresses from a decoction of medicinal plants that have anti-inflammatory properties : chamomile flowers, calendula, linden blossom, sage. Recipe: 1 tbsp. l. vegetable raw materials must be brewed with hot water (300 ml) and left for 10 minutes (or heated in a water bath for 2 minutes), cooled.
It is strictly forbidden to use antibiotics in the form of drops or ointments, or any anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate the condition . If a visit to the doctor is postponed for 2-3 days, then sodium sulfacyl (Albucid) can be instilled into the eyes twice a day, 2 drops.
This drug quickly relieves inflammation and irritation, normalizes the condition of blood vessels and relieves redness and swelling.
Precautions against sunburn:
- when relaxing on the beach, visiting the mountains or going out into the open sea, you must wear sunglasses;
- if a person constantly wears corrective glasses or contact lenses, then before going out into direct sunlight they need to be replaced with regular ones with tinted glasses;
Photochromic sunglasses
- regularly use sunscreen, applying it to the skin around the eyes;
- do not let the mucous membrane of the eye dry out, periodically wash your face with cool water;
- if necessary, use hats with wide brims or a visor;
- When getting a natural tan, do not expose your face to direct sunlight, even if your eyes are tightly closed at this moment.
The sun becomes most aggressive between 11:00 and 16:00. During this period, it is highly advisable to avoid appearing on the street altogether.
Read more in our article about sunburn of the eyes.
First aid
If you receive a retinal burn, you must call an ambulance. Before the arrival of doctors, you can perform first aid measures. They are to:
- Stop eye contact with ultraviolet rays and other light sources. To do this, you need to close the curtains tightly, turn off the bright lamps;
- Wear sunglasses to give the affected eye rest;
- apply a cold compress to the damaged eye for sunburn;
- rinse the eye with a weak solution of citric or acetic acid (a few drops per 500 ml of water). This should be done if the retina has been damaged by alkali;
- treat the affected organ of vision with a weak soda solution. This method is suitable if acid gets into the eye.
If the lesion is accompanied by severe pain in the eyes, then you can drip a solution of Novocaine or Lidocaine (2%).
To prevent the possibility of tissue infection, instill an antibacterial agent (Levomycetin, Ciprofloxacin).
An eye with a burned retina should not be rubbed with your hands. It is also prohibited:
- wipe your eyes with dry wipes, a towel or clothing;
- apply a hot compress to the affected area;
- Continue contact with the source of the burn.
Until paramedics arrive, the victim must be in a horizontal position.
Causes of sunburn of the eyes
The only reason for getting a sunburn on the eye is prolonged exposure to direct sunlight without any protective equipment. To do this, it is not at all necessary to peer closely at the celestial body, because even in the shadows, damage to the eyeballs by ultraviolet rays is possible.
People get sunburns on their eyes not only on the sea coast in the summer, but also in the mountains against the backdrop of snow cover. And in this case, the pathological condition will be called snow blindness (snow burn).
Snow blindness
The explanation for an eye injury is simple: at high altitudes, the sun's rays are scattered very poorly and their impact can be compared to a directed beam through a magnifying glass. Essentially, the mucous membrane is burned out.
Degree of damage
Depending on the severity of the burn, the following degrees of retinal damage are distinguished:
- first. Features: redness of the skin around the eyelids, swelling of the cornea, burning sensation in the eye. At this stage, only the superficial part of the organ of vision is damaged;
- second. The cornea becomes cloudy, and white areas—dead cells—form on the surface of the mucous membrane. Colored spots flash in front of the affected organs of vision. This degree is characterized by damage to the deep tissues of the eye;
- third. A dense gray-white film forms on the surface of the burned eye. The victim feels severe pain. The conjunctiva becomes dirty yellow, the cornea loses its transparency;
- the fourth, the most difficult. Necrosis of all tissues occurs, the cornea is damaged or completely destroyed. Vision deteriorates significantly. Injury to the vitreous body and lens occurs.
First degree injuries can be treated safely. More severe injuries entail consequences that affect the victim’s ability to fully see.
Retinal burn (welding, sun, laser) - symptoms and treatment
A retinal burn can result from various causes, but it must be distinguished from damage to other tissues of the eyeball. In particular, the cornea is damaged when various chemical agents come into contact with it, for example, alkalis, acids, and perfumes. Ammonia, ethyl alcohol, caustic potassium, and slaked lime can also cause serious damage. With this type of injury, there is destruction of eye tissue, as well as some other changes. According to statistics, such corneal injuries occur in the majority of cases (68%), while injuries at home occur much less frequently.
A retinal burn is usually associated with exposure to bright light, laser radiation, or welding. Retinal burns often occur due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. This type of injury is called a sunburn. Compared to chemical, it causes less damage, but also leads to adverse consequences. In case of sunburn, among all the structures of the eye, it is the retina that is most damaged. If you stay in the bright sun for a long time without using personal protective equipment, you can get a similar burn. The sun can also affect the eyes indirectly, for example, when reflected from water or snow. This is why the visual impairment is called snow blindness. This pathology occurs due to exposure to a large amount of sunlight reflected from pure snow on the retina. Therefore, when traveling in the mountains, you should wear special protective glasses that help reduce the amount of ultraviolet radiation reaching the retina.
The laser beam also has a detrimental effect on the retina. Most often, people who work with laser devices are exposed to such effects. In this case, the radiation has high energy, therefore, when it hits the retina, it causes serious damage. Sometimes there are cases of occupational injury when acetic or sulfuric acid, as well as lime, get on the retina and lead to a burn.
Symptoms of a retinal burn
When the retina of the eye is burned, cells of the damaged tissues die, the blood circulation process is disrupted, and intoxication develops as a result of tissue breakdown.
As a result of eye damage from rays, chemicals or high temperatures, the following symptoms occur:
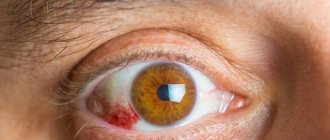
- redness of the eyeball;
- headache;
- inflammation of the choroid;
- burning, cutting pain in the organs of vision;
- intolerance to bright light;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye;
- decreased visual acuity;
- profuse lacrimation;
- change in field of view;
- red-green spots before the eyes;
- redness or swelling of the skin of the eyelids;
- the appearance of yellow and white spots on the cornea.
The danger of an eye injury such as a burn is that its symptoms may not appear immediately. Sometimes this occurs only 8-10 hours after the lesion.
Symptoms
Having been exposed to the radiation of a quartz lamp and getting a burn to the eyes, a person experiences painful symptoms. Their intensity is affected by the scale of the lesion. Doctors distinguish three degrees of injury, each of which has individual characteristics.
- A mild degree develops with short-term exposure to quartz radiation. The mucous membrane of the visual organ turns red, profuse lacrimation and burning pain are observed. The eyelids swell slightly. Such damage does not affect the deep layers of the eye and does not cause complications. With proper treatment, symptoms disappear within a few days.
- The average degree changes the shade of the mucous membrane. It becomes bright red and swells. The victim experiences acute pain, photophobia and blepharospasm develop. When the eyelids open, they immediately close involuntarily. A moderate burn is dangerous: it destroys the cornea, which is manifested by a decrease in its sensitivity .
- A severe degree occurs when a person looks at the source of radiation for a long time. The conjunctiva, cornea and eyeball are affected. A yellowish or gray scab forms on the eyelids, small blisters appear, severe swelling, lacrimation and pain are tormented.
Signs of superficial injuries appear after a few hours. Severe damage can be noticed immediately after exposure to quartz.
If your eyes are exposed to ultraviolet radiation from a lamp, you should not hesitate. You need to urgently seek medical help.
Improper treatment can lead to irreversible consequences, the worst of which is loss of vision.
Diagnostics
To confirm the fact of a burn and establish the degree of its complexity, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- visual inspection;
- perimetry to determine the boundaries of vision;
- assessment of visual acuity using ophthalmological tables;
- assessment of intraocular pressure level;
- biomicroscopy to assess the extent of the lesion;
- fundus examination.
After obtaining a complete picture of the eye condition, the specialist will prescribe the appropriate course of treatment.
Diagnostic measures
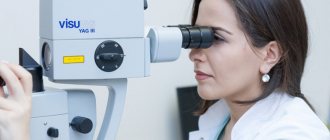
An ophthalmologist can detect sunburn on the retina or with a laser. The doctor finds out the cause of the pathology, conducts a visual examination and prescribes diagnostic procedures, such as:
Such organ damage is clearly visualized using ophthalmoscopy.
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- biomicroscopy using a contrast agent;
- visual field test (perimetry);
- Ultrasound of the eye;
- electrophysiological study to identify the functionality of the retina and optic nerve.
Burn treatment
Patients with damaged retina are prescribed the following groups of medications:
| Group and purpose | Names |
| Mydriatics (dilators for dilating the pupil, used for inflammatory processes, treatment of injuries and blockage of blood vessels in the eye) |
|
| Antioxidant drops (preparations for restoring visual function, improving the functions of the lacrimal gland and protecting the visual organs from adverse external factors) |
|
| Local antibiotics (to combat the infectious-inflammatory process and prevent the addition of a bacterial infection) |
|
| Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal and steroidal (relieve the inflammatory process of non-infectious nature) |
|
| Metabolic (improves metabolic processes in the affected tissues of the eye and accelerates the process of their recovery). Such drugs are produced in the form of eye gel and drops. |
|
| Preventing dry mucous membranes |
|
At home, for first-degree burns and only with the permission of a doctor, you can use the following treatment methods:
- compress of grated raw potatoes. You need to apply the mass to the affected areas for 10-15 minutes;
- decoctions of chamomile or calendula. To prepare, pour a teaspoon of dry raw material into a glass of boiling water and let it brew. Use for rinsing affected organs of vision only when cooled down;
- lotions with aloe juice. Squeeze out the juice from large aloe leaves. Dilute a teaspoon of juice in a tablespoon of water. Soak a cotton pad in the resulting mixture and apply to the affected area for 10-15 minutes.
Surgical intervention for burn lesions of the retina is required in especially severe cases. Thus, a fourth-degree chemical burn requires removal of areas of necrosis.
Patients, depending on the degree of tissue damage to the organ of vision, are indicated for keratotomy (incisions on the cornea to restore visual function) or penetrating keratoplasty (transplantation of a healthy donor cornea in place of the damaged cornea).
Urgent Care
It is important to provide first aid correctly.
- It is necessary to turn off the radiation source and take the person to a dark room. A damaged retina reacts painfully to any light sources.
- Then you should rinse your eyelids with cool water and place a damp cloth over your closed eyes. This will reduce pain.
- Manipulations should be carried out with latex gloves to avoid infection.
- If the victim complains of a persistent burning sensation, you can take Analgin or Ibuprofen.
When providing assistance, do not put medications in your eyes or use ointments . They can cause the burn to deepen. In addition, it is prohibited:
- open blisters if they appear on the eyelids;
- rub your eyes;
- apply a tight bandage that interferes with the access of oxygen to the tissues.
If symptoms appear immediately after exposure to the lamp, then the burn is serious and an ambulance must be called. If the injury is minor, you can go to the hospital yourself, wearing dark glasses to protect your eyes.
Possible consequences
Chemical, radiation, thermal damage to the retina can cause:
- irreversible loss of visual function;
- cataract;
- secondary glaucoma;
- death of the eyeball;
- cicatricial changes in the eyelids;
- corneal clouding;
- retinal detachment;
- dry eye syndrome;
- addition of a secondary infection;
- fusion of the mucous membrane of the eye with the eyelids;
- obstruction of the lacrimal ducts.
Some complications can be corrected surgically, but treatment can begin no earlier than a year after receiving the burn.