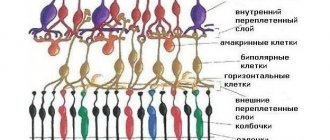
The laser coagulation procedure of the retina is performed with the aim of delimiting the areas of the retina affected by dystrophy to reduce the risk of retinal detachment. It is prescribed for prevention or performed for therapeutic purposes in case of existing local flat retinal detachment. In addition, laser coagulation is performed in the area of retinal rupture after surgery for retinal detachment.
Laser treatment aims to create adhesions between the retina and the underlying vascular tissue. This is achieved by exposing tissue to a laser beam of a certain power. Laser exposure causes the formation of local microburns on the retina - coagulates. They form a reliable adhesion with the underlying tissues, but the tension (traction) of the altered retina from the vitreous body is not eliminated. Therefore, even after the procedure, patients may notice sparks in the eyes, lightning, and flashes. Laser coagulation does not affect visual acuity.
Causes and symptoms of retinal tear
Laser coagulation is most often performed for thinning and rupture of the retina. Every person should be able to distinguish the symptoms of pathology from eye fatigue in order to seek help in time.
Causes of retinal pathologies:
- refractive errors (myopia, farsightedness);
- circulatory defects;
- age-related disorders;
- cataract;
- negative impact (injuries, excessive stress);
- diseases of other body systems (stress, neurological disorders, sharp increase in blood pressure).
The danger of a retinal tear lies in the fact that the pathology is mild and sometimes does not manifest itself at all. The patient simply cannot recognize the presence of a problem and seek help in time. Therefore, it is very important to undergo regular preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist.
Symptoms of a retinal tear:
- the appearance of flashes of light and glare before the eyes (the symptom worsens in the dark);
- decreased visual acuity;
- blurred image;
- narrowing of visual fields;
- distorted perception of objects.
Retinal tears often result in detachment. Only an experienced doctor who has special equipment can identify the violation. If retinal tears are detected, it is recommended to undergo a laser coagulation procedure. In these cases, preventive or limiting operations are prescribed.
If left untreated, a retinal tear will certainly cause serious complications. The most common - retinal detachment - can deprive a person of vision forever. If there is a sudden and sharp deterioration in vision, it will be very difficult to help the patient. Doctors are not always able to return a detached retina to its place, but even after successful operations, vision is often not completely restored.
Postoperative period and restrictions
In the postoperative period for two weeks (and especially during the first 2-3 days), you should completely limit:
- alcohol consumption;
- any movements or actions accompanied by shaking, vibration or physical stress;
- car driving;
- watching TV, reading and using a computer or other electronic gadgets;
- bending forward and staying in an upright position for long periods of time.
Over the next few weeks, the patient will need to undergo several follow-up examinations at the same clinic where the operation was performed.
During this period, it will be necessary to instill several types of ophthalmic drops for different purposes (painkillers, antiseptics, keratoprotectors).
Stay up to date! Recommendations on dosage and duration of use are given by the attending physician based on the characteristics of the rehabilitation period and the presence or absence of complications.
It is better to avoid walking outside for 2-3 weeks, especially if the operation was performed in the cold season.
This can be fraught with the development of colds, and inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eye that occurs against this background can slow down the healing process or lead to additional negative consequences.
This also applies to infectious eye diseases, especially conjunctivitis, which are easily transmitted from person to person.
Therefore, during recovery after coagulation, it is better to refrain from visiting crowded places.
Features of laser coagulation for retinal pathologies
Most often, degenerative processes in the retina develop against the background of high and moderate degrees of myopia, when the shape of the eyeball changes, as well as when the membrane is stretched and cellular nutrition is disrupted. Laser retinal strengthening is one of the few procedures that can eliminate such disorders.
The purpose of laser surgery for retinal detachment is to create a fusion (fusion) between the retina and the adjacent choroid. This effect can be achieved using a laser coagulator, which increases the temperature in the tissues and creates local microburns of the retina.
Laser coagulation allows limiting flat detachment in people who have contraindications to radical surgery. The operation is also indicated as an additional measure after surgical correction of detachment.
Types of laser coagulation
- Restrictive preventative. This procedure is considered therapeutic and prophylactic. The laser causes dosed burns, creating a barrier around the area of retinal dystrophy, which helps stop the process and helps prevent complications.
- Peripheral preventive. The procedure consists of preventive strengthening of the periphery of the retina to avoid its detachment. The laser treats thinned areas, soldering them to the choroid and creating adhesions around existing gaps.
- Panretinal. The method involves applying microscopic burns to the entire area of the retina (except for the center). Usually the procedure is carried out in several stages and at intervals of 2-4 months to reduce the load on the eyeball. The number of these stages will depend on the stage of the pathology (3-5 sessions). At each stage, 500-800 point burns are applied, which takes an hour.
Laser coagulation is common because it improves vision, restores blood supply, and effectively prevents detachment and related complications, including complete blindness. Laser coagulation is considered one of the best ways to treat retinal pathologies.
Advantages of laser coagulation:
- efficiency (the procedure takes 10-20 minutes without the need to hospitalize the patient);
- bloodlessness;
- seamlessness;
- high efficiency (studies show that the procedure gives good results in 70% of cases).
It is noteworthy that laser coagulation is well tolerated by patients of all ages. Even a child can undergo the operation, since the process uses light and safe local anesthesia.
Useful video
Laser coagulation of the retina is performed according to indications and does not require serious preparation, and the rehabilitation period is quite short and in most cases patients do not develop complications.
In some cases, the operation may be repeated, but this does not occur against the background of medical errors.
More often this is due to the insufficient effectiveness of the primary procedure, which is easily corrected at the next corrective stage.
dear, there are a lot of restrictions after it, it can be painful, after it your eyes and head hurt for several days
Good day!
I want to tell you why I haven’t been here for a whole week.
In order. In May, I was examined in Yekaterinburg at Eye Microsurgery regarding the possibility of laser vision correction. As a result of this examination, I was given the go-ahead for surgery, but before that it was necessary to carry out, as the doctor put it, treatment of the retina.
Before this, I had no problems with the retina (at least, microsurgery doctors in our city did not diagnose anything like this). And here, during the last examination with a contact lens, the doctor discovered changes in the retina that had begun, which could lead to its detachment.
Why do such changes occur? A healthy eye has the shape of a ball, but with high myopia (like mine), the eyes are constantly under tension and the eye is flattened, and this is what the retina suffers from. That's it in short.
The date was set for me a month after the appointment. There was no need to prepare in any special way. Those who wear contact lenses must come without them on the day of surgery. But I don’t wear contact lenses or glasses, so this wasn’t relevant to me.
Before the procedure itself, some manipulations with the eyes were carried out in a separate room, and the vision was checked again. After this, they sent me to instill dilating drops twice with an interval of 15 minutes. After the second instillation, I was immediately called into the office for this operation.
The surgeon I came across was simply wonderful - K. G. Naumov. Calm, attentive, I really liked him.
First, he gave me anesthetic drops, after which he thoroughly washed his hands, put on and handled rubber gloves, and processed the lens. He promised that it wouldn’t hurt, but I didn’t believe it and for good reason)
The device is very similar to the one used for the lens examination. There is also a small table, on one side there is a place for the patient, on the other for the doctor.
The most difficult thing for me was maintaining the correct head position during the laser “shots”. You need to relax as much as possible without lifting your forehead and chin from the stand. And breathe evenly.
We suggest you read: Red eyes in a child: causes, treatment, what to do?
The operation began in the right eye and lasted several minutes. But it seemed to me that it was longer than later with the left one. As I understand it, each shot repairs one point in the retina.
Personally, with my high sensitivity, it was quite painful. The doctor was surprised at first, but when I told him about increased sensitivity, he said that this could be the case and that we should be patient. The pain felt like a blow from the inside.
When the right eye was finished, the doctor gave me a few minutes to come to my senses to rest and to restore color vision, which became somewhat different after exposure to the laser. During this time, sensitivity began to return to my left eye (which should not happen to average people, but it always happens to me), so I asked for another drop of anesthetic.
The doctor generously dropped 3 drops). The operation on the left eye was easier and faster, and there was almost no pain. But I still couldn’t relax, so at the end I felt dizzy and the doctor revived me with ammonia. Also typical for me, after the mole was removed I completely fainted)
After removing the lens, the doctor gave me drops.
You can wash your face immediately after this procedure (this made me very happy). After the procedure, it is advisable to rest all day, or even better, sleep. I was also offered sick leave, but I didn’t take it because I was still caring for the child anyway.
The following recommendations were given to me.
- wear lenses,
-go to the bathhouse and sauna,
-drink alcohol
(the first three points are basically irrelevant)
-limit eye strain to 3 hours (computer, TV, reading, etc.).
This turned out to be the most difficult thing, because I was used to always doing something. So I got a little vacation for my eyes, including from needlework.
They didn’t tell me anything about physical activity, and I forgot to ask right away, so I had to write an email. I received the following answer: “According to the recommendations of your doctor NAUMOV K. G.
And this is even more difficult than living without handicrafts)
I would like to dwell in more detail on the sensations after this procedure.
All that day my eyes continued to hurt. Simply closing the eyelids did not save or provide relief. It became easier for a short time after sleep. Luckily, I was able to take a couple of naps in the car on the way home. By evening, severe headaches and dizziness arose. So rest was simply necessary.
The next day (June 16), my eyes hurt less, but by the evening I also felt headaches and dizziness at the same time.
On June 17, in the morning my eyes didn’t hurt, but in the afternoon the child was playing around for a walk and hung with all his weight in my arms, his eyes hurt instantly and hurt until the end of the day. By evening, my head ached again and I started feeling dizzy. Already less, but still.
It is not in vain that it is recommended to reduce the load; when you try to read something, your eyes instantly get tired and begin to hurt. So these restrictions cannot be neglected.
In the following days, June 18, 19 and 20, my eyes felt much easier, the discomfort became weaker, and evening headaches no longer visited me.
All week, lifting bags weighing more than 1 kg immediately began to hurt my eyes. So I would also classify this point as a limitation.
Today I feel almost as usual, only my eyes get tired a little faster. I even tried working out on an elliptical trainer with minimal load. Luckily, I didn’t notice any unpleasant sensations in my eyes.
So, although the operation is not complicated, it turned out to be very painful for me during the procedure, as well as for several days after it. Now I’m even afraid to imagine how painful it is to have laser correction.
To summarize, I want to say that the procedure is still necessary, although you cannot check the result yourself.
So by all means do it if prescribed, but be prepared for restrictions after it. I had a week, but this is not a standard for other people. In each specific case, these terms should be determined by the doctor.
Of the minuses, I would also like to note the high cost - 4600 for one eye. but vision is more expensive in any case.
anonymous, Woman, 34 years old
Good afternoon On January 4, laser coagulation of the retina of the right eye (periphery) was performed. The eye hurt for the first 2 days, then the pain subsided. A week later there was a plane flight. Now, over the last week, a dull pain has been felt in the eye (as in the first 2 days after the procedure), which practically does not go away, but intensifies with a temperature change (for example, when I go outside the temperature is -30), as well as with tension.
The pain is relieved by analgesic tablets, but is not relieved by Diclofenac and Tobradex eye drops. 14 days have passed since the intervention. I can’t see the doctor who performed the coagulation, because... it was held in another city.
Laser coagulation of the retina is a bloodless surgical intervention on the retina, which involves creating adhesions between the retina and the underlying choroid. Due to its low morbidity, the intervention is performed on an outpatient basis for patients of any age, including those with cardiovascular pathologies.
Indications and contraindications
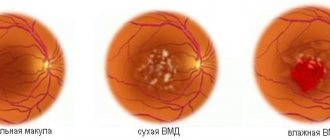
Laser photocoagulation of the retina is the best and almost the only method for treating angiomatosis, diabetic retinopathy, thrombosis of the central retinal vein, age-related changes in the macula and other pathologies of this part of the eye.
Indications for laser coagulation of the retina:
- dystrophy of this element;
- vascular changes, including angiomatosis (proliferation of blood vessels in the eye);
- retinal rupture and detachment;
- central vein thrombosis;
- obstruction of the central artery;
- diabetic retinopathy;
- benign and malignant retinal tumors.
Preventive laser coagulation is recommended for men before undergoing laser vision correction. Laser coagulation is also used to eliminate vascular defects of the retina and some types of tumors. The operation is recommended for retinal pathologies in patients with diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension.
Contraindications to laser coagulation of the retina:
- pathological proliferation of blood vessels in the iris area (iris neovascularization);
- severe hemorrhagic syndrome (hemorrhage in the eyeball or a high predisposition to it);
- pathological clouding of the eye environment (or before laser coagulation, cryopexy must be performed through the conjunctiva);
- epiretinal gliosis, accompanied by traction syndrome (grade 3-4 vitreous detachment, which provokes retinal detachment);
- severe retinal detachment (increases the risk of maculopathy, choroidal detachment and pathologies in the macular area);
- retinal vein thrombosis (in certain cases);
- central serous chorioretinopathy (sometimes);
- severe rubeosis of the retina;
- pronounced changes in the fundus elements;
- severe mental and somatic illnesses.
Also, the procedure is not recommended for patients with visual acuity below 0.1 diopter. In this case, the advisability of the operation should be discussed with the doctor, since laser coagulation can negatively affect the patient’s health.
What is the operation
Restrictive LKS is a surgical method in which the retina is “welded” exclusively at the edges using a laser. In this case, adhesive areas are created between the retina and choroid. This effect is achieved by applying a laser to microscopic burns, which form adhesions as they heal.
IMPORTANT! The purpose of the operation is preventive attachment of the retinal layer, and not vision correction. Therefore, this procedure does not affect its quality.
Preoperative examination
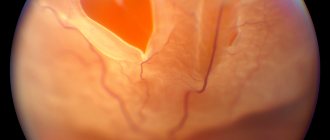
In case of retinal rupture and detachment, laser coagulation makes it possible to limit the focus of dystrophy. The defect can be identified only by careful examination of the periphery of the fundus with maximum pupil dilation. If there is an increased risk of developing detachment, you need to undergo such an examination at least twice a year. Patients with myopia, a family history of retinal detachment, and those who have undergone surgery on the visual system should be registered with an ophthalmologist.
The examination before laser coagulation should include the following procedures:
- tonometry (checking intraocular pressure);
- visometry (determining visual acuity);
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye);
- Ultrasound;
- retinal tomography.
If there are concomitant pathologies, other studies may be prescribed. It is important to visit a therapist, otolaryngologist and dentist before surgery to exclude the presence of contraindications from other body systems. Immediately before surgery, you need to have your blood and urine tested, be tested for HIV, syphilis and hepatitis, and have an X-ray of your chest and face.
Rehabilitation
To avoid postoperative complications, it is imperative to follow medical recommendations.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with eye bruise and retinal concussion
On the first day after coagulation, do not strain your eyes, do not use contact lenses or glasses.
Over the course of two weeks:
- eliminate salt from the diet;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- minimize the amount of liquid you drink;
- wear sunglasses;
- Apply drops prescribed by your doctor to your eyes.
For a month, all types of physical activity, sports associated with sudden movements and bending are excluded. Also during this period you need to avoid visiting saunas, baths, and the beach.
After coagulation, it is necessary to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist, first every month, then every three months, then every six months.
Laser photocoagulation of the retina
The advantage of laser coagulation of the retina is its simplicity. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis using local drip anesthesia. Since the retina is operated with a laser, there is no blood loss and the traumatic effect on the eye is minimized. This reduces the risk of infection to zero.
Before the operation, special drops are instilled into the patient's eyes: some dilate the pupil, while others numb the pain. During the procedure, the patient can be in a sitting position. During laser coagulation, a three-mirror Goldmann lens is installed on the eye, which allows laser radiation to be focused in certain areas of the fundus of the eye. A low-frequency laser affects the retina for up to 20 minutes. The patient may see flashes of light and feel the lens, but there is no discomfort or pain.
The surgeon monitors the procedure through a stereomicroscope (provides volumetric perception). Depending on the characteristics of the pathology, the laser can affect limited areas or pass along the periphery. When a retinal tear occurs, the laser is directed along the edge to heal the defect. Bonding with the underlying membranes guarantees inhibition of the degenerative process and prevention of detachment in this place.
Laser photocoagulation causes a sharp increase in temperature in the operated area. This phenomenon stops bleeding and forms adhesions at the site of pathology. If the retina is torn, the laser helps to glue the damaged areas together. Laser coagulation occurs without cutting the membranes of the eye.
After the operation, the patient must remain in the clinic for several hours. When the doctor is convinced of the successful outcome of the procedure, the patient is sent home.
Specifics of laser coagulation:
- The area of ruptures or local detachment is limited to several rows of adhesions.
- It takes up to two weeks for strong adhesions to form.
- The absence of progression of the defect (spread beyond the coagulation boundary) is considered a sign of a successful outcome of the operation.
If the laser is overly aggressive on a large area of the retina, exudative detachment is possible, as well as defects in the choroid and changes in the macular area. With timely treatment, complications can be stopped in a matter of days.
How is laser coagulation performed?
After installing a three-mirror lens on the eye, a laser beam is applied through it to the retina and its vessels.
In this case, the patient extremely rarely experiences painful sensations that are more similar to tingling.
The visual system perceives the laser as bright flashes of light.
The direction of the laser beam is controlled by a doctor who sits opposite the patient.
It can take up to 15 minutes for one eye, after which the lens is removed and installed on the other eye.
Important! If the patient does not tolerate the operation very well, before working on the second eye, the doctor may take a break of a few minutes or additionally drop an anesthetic into the second eye if the person’s visual organs are highly sensitive.
At the end of the operation, the patient can get used to the new optical sensations and relax in specially designated rooms.
Or he can immediately go home, since a further rehabilitation period in the hospital after such operations is not provided.
Laser photocoagulation of the retina during pregnancy
Laser coagulation of the retina during pregnancy is acceptable. Typically, surgery is prescribed in cases where significant changes in the retina and a high risk of retinal detachment during natural childbirth are detected against the background of myopia.
Peripheral retinal dystrophy is included in the list of reasons for prohibiting natural childbirth. For such patients, it is strongly recommended that a cesarean section be performed, since childbirth places great strain on the visual system. Therefore, if you have eye pathologies, even before conception you need to undergo an examination and, if necessary, strengthen the retina. Preventive laser coagulation can be performed up to 35 weeks of pregnancy.
Negative consequences of laser eye coagulation
In most cases, laser coagulation of the retina is successful. Complications, as a rule, indicate inexperience or carelessness of the surgeon, or insufficient preoperative diagnosis. Before surgery, it is important to check all contraindications and evaluate the possibility of an allergic reaction to medications. However, even if these conditions are met, there are chances of complications developing, since laser coagulation is a surgical procedure. And surgery is always a risk.
Possible consequences of retinal laser coagulation:
- development of inflammation in the conjunctiva (conjunctivitis is an unpleasant complication, but it can always be cured with drops in 4-5 days);
- clouding of the membranes of the eyeball.
It is also very important after surgery to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and protect your eyes. So, after laser coagulation, patients should not endure strong physical activity, otherwise the eye membranes may rupture. It is noteworthy that moderate activity should be limited after surgery for life.
After laser coagulation, you must visit an ophthalmologist every six months (regardless of the presence of discomfort or symptoms). If necessary, the operation can be repeated.
Stages of the operation
First, the patient is given cycloplegia. This is the dilation of the pupil, which occurs with the help of special drops to dilate the pupil. To make the operation more comfortable, drops with an anesthetic effect may be prescribed. After completing the preparation of the patient, he is placed on the table.
Cyclomed eye drops allow you to dilate the pupil of the eye
During this operation, the patient should not move his eyes. Otherwise, the effect may not be fully achieved.
Cost of laser surgery
You can strengthen your retina with laser at different prices. Depending on the clinic, doctors’ experience and technical equipment, the figure varies from 3 to 50 thousand rubles. The cost of panretinal laser coagulation is 6-15 thousand rubles per session. When calculating the cost, the doctor will also take into account the complexity of the procedure and the area of the retina that needs to be operated on. The price may also depend on whether the service package includes a full examination and annual postoperative follow-up.
Modern eye microsurgery has reached such a development that with the help of laser coagulation it is possible to cure not only ruptures and thinning of the retina, but even complex cases of detachment. To avoid retinal pathologies, it is necessary to carry out early diagnosis and treatment of pathologies of the visual system, undergo examinations twice a year, especially in the presence of retinal pathologies and risk factors (myopia), and also check the condition of the retina at the beginning and end of pregnancy.
Sources used:
- Implantation of artificial lens / S.N. Fedorov. - M.: Medicine, 1977.
- Microsurgery of the vitreous body and retina: monograph. / Steve Charles, Jorge Calzada, Byron Wood. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2012.
- Revelations of a surgeon. How I did the world's first eye transplant / E. Muldashev. - Moscow
- “Eye Microsurgery” named after Academician S.N. Fedorov" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation