According to WHO, almost half of blindness worldwide is due to cataracts. At the age of 50-60 years, cataracts are detected in 15% of the population, 70-80 years - in 26%-46%, over 80 years - in almost everyone. The high prevalence and consequences of the disease make cataract one of the most difficult problems of human vision. You will find everything about this disease in this section.
Popular materials
- How to treat cataracts with folk remedies
- Secrets of the development of nuclear cataracts
- 5 best remedies for immature cataracts
Cataract surgery with a scalpel (phacoemulsification)
This is the surgical removal of the lens and its replacement with an artificial lens. Through very small incisions at the edge of the cornea, a special instrument is inserted into the eye, which, once opened through a small puncture in the lens capsule, uses ultrasound to crush the hardened and cloudy lens into tiny particles and wash out the resulting liquid.
Then a foldable (multifocal) soft artificial lens is implanted into the eye. It also lasts a lifetime and no longer needs to be replaced.
The advantages of this approach include an individual approach to each patient, thanks to which the risk of complications, despite the frightening description of the technology, tends to zero.
The lens of the eye is a lifelong UV filter
: 03.02.2021
We cannot, like salamanders, grow new limbs, but many of our tissues and organs, such as skin or liver, successfully regenerate. But there is an organ that plays a huge role in our lives, but is not able to renew itself throughout a person’s life - this is the lens, the main optical element of the eye. And considering that the lens also serves as a light filter, blocking harmful ultraviolet radiation, the question arises: how is its natural protection structured and how does it change with age? And how to save it? The answer is in an article by specialists from the Novosibirsk International Tomography Center SB RAS
Lens of the eye
transmits sunlight and focuses it on the retina, while absorbing radiation in the near ultraviolet range - the main UV radiation on the Earth's surface. This “ultraviolet” passes through clouds and window glass and can damage the photosensitive cells of the retina.
The danger of ultraviolet radiation is that when light is absorbed, one of the electrons of an organic molecule (for example, a protein) moves to a higher energy level. This process itself is not dangerous - it’s all about the path along which the molecule will return from this extremely unstable state to the ground state. If the excess energy is emitted in the form of a quantum of light or heat, everything is in order. But there is a third way, depending on the total projection of the spins
a high-energy electron and its unpaired “partner”.
The quantum concept of “spin” refers to the angular momentum that is inherent in elementary particles, not related to their real movement (rotation) in space and therefore has no analogy in classical mechanics.
Due to its quantum nature, spin can only take discrete, strictly defined values: for example, the spin of an electron is ½. In the latter case, an excited molecule can go into the so-called triplet state
(T-state), which can exist for a long time.
This creates dangerous particles with excess energy that can react with a large number of their neighbors. As a rule, these photochemical
reactions are irreversible, and the accumulation of defective molecules can, over time, cause the development of pathologies such as skin cancer and
cataracts
- clouding of the lens of the eye.
The lens has an unusual structure. Its cells, not at all similar to ordinary ones, are filled with long transparent fibers of proteins called crystallins.
, tightly adjacent to each other in the manner of onion scales. They have neither cell nuclei nor other organelles that could scatter light. Accordingly, the synthesis, restoration and utilization of proteins does not take place in them, so throughout our lives we live practically with the lens with which we were born.
It is not surprising that with age, under the influence of light, crystallins accumulate numerous chemical modifications, which leads to an increase in rigidity, the appearance of a yellow color and an increase in light scattering of the lens. On the other hand, many people's lenses remain transparent even into very old age. What kind of mechanism keeps our “apple of our eye” in good health?
kynurenine serves as a molecular UV filter for the lens.
(an intermediate product of the enzymatic breakdown of the amino acid
tryptophan
) and its derivatives. However, the mechanism of its “work” remained unknown until recently.
Researchers from the ITC SB RAS (Novosibirsk) found that in aqueous solutions under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, the kynurenine molecule glows weakly and produces an extremely small number of reactive triplet states. This means that it very quickly and efficiently gets rid of excess energy, converting it into heat. In this case, an environment saturated with hydrogen bonds is required, otherwise the UV filter turns into its opposite - a photosensitizer
.
With age, the content of kynurenines in the human lens decreases significantly, primarily due to attachment to crystallin proteins. And the larger the attached particle, the worse the molecular UV filter will work.
Being in a dangerous triplet state, kynurenine molecules can react with lens proteins to form radicals, which leads to “cross-linking” of protein molecules, which at some stage can precipitate - this is how light-scattering areas appear in the lens. But even in this case, photodamage to proteins is usually small, including due to the action of antioxidants - ascorbic
and
glutathione
. The first of them effectively “quenches” the triplet states of kynurenines, the second intercepts free radicals, preventing protein binding.
Thanks to such mechanisms, our eyes are effectively protected from harmful solar radiation in young and middle age. Over the years, the efficiency of transport of small molecules in the lens decreases, which leads to the accumulation of breakdown products and a slowdown in the supply of necessary substances, including antioxidants. Therefore, the best prevention of cataracts is a healthy lifestyle that maintains protective systems in good condition, as well as sufficient consumption of ascorbic acid, which the human body cannot synthesize itself. And, of course, the use of sunglasses to compensate for the reduction in natural UV filters in the lens of the eye.
Read more in the magazine “SCIENCE First Hand” in the article by P. S. Sherin and Yu. P. Tsentalovich “Crystal: solar eclipse”
Photo: https://www.flickr.com
: 03.02.2021
About the functions of the eye lens
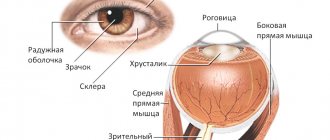
The eye is a complex visual organ, and one of its most important components is the lens. This element performs the main visual functions, and this is what it does:
- focuses the gaze on objects located near and far;
- refracts light rays;
- due to its transparency, it ensures that light enters the eye onto its retina, thereby providing the ability to see;
- separates different parts of the eye.
Due to the enormous role of the lens, its clouding and other pathologies can provoke partial loss of vision or even complete blindness. That is why, in case of severe ophthalmological diseases, it is recommended to replace this element of the eye with an artificial lens, that is, an intraocular lens (common abbreviation - IOL).
Choosing an artificial lens
All prostheses are made from biologically compatible materials, and rejection by the body is almost impossible. There are several types of IOLs that are used most often.
Accommodating lenses
Under the action of the ciliary muscle, implants can move in the eye and change focus, imitating the work of the lens. They have one optical zone, so among the disadvantages there is insufficient quality of vision in twilight conditions. Reading glasses are often required after accommodating IOLs are placed.
Important! These are the cheapest lenses, often presented by domestic manufacturers for quota lens replacement.
Among the highest quality manufacturers, Alcon lenses (USA) stand out, the price of which starts from 19,000 rubles and reaches 48,000. IOLs are also produced by Rumex with a price of 9,000 (Britain), B&L (USA) with a price of 15,000 and Silco (USA) – 5,000 rubles.
Aspheric IOLs
Designed to correct spherical distortions that often occur after IOL implantation. Previously, spherical elements were used, but they led to severe distortion.
The most popular manufacturers and prices:
- ACRYSOF IQ NATURAL (USA, Alcon) – 22,000 rubles;
- CT ASPHINA 509M – (“Carl Zeiss”, Germany) – 25,000 rubles;
- HOYA ISERT 251 – (“Hoya”, Japan) – 32,000 rubles;
- TECNIS 1 ZCB00 – (“Abbot”, USA) – 25,000 rubles;
- ASPIRA -AAY - (Human Optics, Germany) - 24,000 rubles.
These lenses are often used in younger patients and for a wide range of conditions. But for complex forms of cataracts with additional pathologies, they are not always suitable.
Toric IOLs
Used for cataracts complicated by astigmatism. Prices and manufacturers:
- AcrySof Toric (Alcon, USA) – from 32,000 rubles;
- At Lisa Toric 909 M – (“Carl Zeiss”, Germany) – from 50,000 rubles;
- Rayner T-Flex (Britain) – from 15,000 rubles.
IOLs are distinguished by greater refractive power in some areas, due to which distance vision is corrected.
Multifocal IOLs
Used for lens correction in patients over 40 years of age. They perfectly imitate the work of the lens and can focus far and near. Prices and manufacturers:
- ACRYSOF RESTOR (“Alkon”, USA) – from 48,000 rubles;
- M-FLEX (Rainer, UK) – from 38,000 rubles;
- ATLIS ATRI 839 MP (“Carl Zeiss”, Germany) – from 66,500 rubles.
After implantation of these IOLs, 80% of patients no longer need glasses.
Phakic IOLs
Used for implantation without removing the lens for myopia or farsightedness. The procedure is relevant when laser vision correction is prohibited. The cost of phakic IOLs starts from 20,000 rubles.
When surgery is contraindicated
Contraindications to eye lens replacement for cataracts or other reasons are divided into permanent (irremovable) and temporary. The operation is contraindicated for:
- inflammatory processes in the organs of vision (all inflammation is stopped before replacement);
- recent stroke or heart attack;
- excessively small sizes of the anterior eye chamber - a space filled with transparent liquid contents and located between the iris and cornea;
- detachment or significant damage to the retina;
- decompensated glaucoma (with a significant increase in eye pressure and visual impairment);
- reduction in the size of the eyeball caused by farsightedness;
- various eye infections;
- periods of lactation and pregnancy.
If the contraindications are temporary, lens replacement is prescribed after they are eliminated.
Operation methods
You can change the eye lens in different ways, and in ophthalmology the following surgical methods are used:
- Extracapsular replacement of the eye lens (extraction) is carried out with surgical removal of the damaged or pathologically altered element of the visual organ, leaving only the posterior capsule.
- Intracapsular extraction. The lens is removed through an incision made in the cornea, and the capsule is also removed.
- Phacoemulsification using ultrasound. Ultrasound waves destroy the lens, and it is removed through a tube, preserving the posterior capsule. Next, the remaining camera is cleaned (polished), after which the lens is installed, vision is restored, and the cataract is eliminated.
- Replacement by phacoemulsification using a femtolaser. The lens is destroyed not by ultrasound, but by a special laser. After removal and cleaning of the preserved posterior capsule, vision is restored through implantation of an artificial IOL, and the cataract is successfully eliminated.
Each method is accompanied by a postoperative period. But rehabilitation after exposure to ultrasound or laser will last less, since the integrity of the tissue is minimally damaged. Vision is restored quite quickly, cataracts disappear without a trace, but restriction of the usual lifestyle is necessary.
After surgical interventions, according to reviews from doctors and patients, the postoperative period lasts longer, and visual acuity recovers more slowly due to prolonged regeneration. Some special restrictions must also be observed.
Restrictions
After surgery, you will need to follow a number of measures aimed at speeding up your recovery. There are restrictions on some activities and activities. Such restrictions include:
Avoid sharp and long tilts of the head downwards. Shaking increases the risk of dislocation of the intraocular lens, so you should not run, ride a horse or ride an exercise bike. Do not dye your hair or do a perm. Avoid drinking alcohol, strong tea and coffee. Avoid using nicotine until healing. Men are advised to stop drinking. using electric razors that create vibration. During the first 7 days, it is recommended to avoid any visual stress. Do not drink carbonated and alcoholic drinks. No physical activity for 14 days. Avoid challenging exercises and heavy lifting. This also applies to special gymnastics. Do not lift more than 5 kilograms, as exertion causes an increase in fluid pressure inside the eye. Stay away from dusty places. After the procedure, the eyes are sensitive to airborne allergens such as dust
It is important that the house is cleaned before the person undergoing surgery arrives. Don't rub
Friction is a quick way to develop an infection. Avoid large temperature changes, do not visit the sauna and swimming pool. Avoid exposure to cold and wind. If you need to go out to the store, wear a headband and sunglasses. Women are prohibited from wearing cosmetics. When to resume its use a few weeks after surgery. When washing your hair, do not lean forward. Tilt it back so that water and soap do not get into the operated organ. Sleep on your back or the side opposite to the operated organ of vision.
Questions and answers
Patients have many questions. The answers to them are discussed below.
Will the lens be replaced for free?
Yes, a replacement is possible within the compulsory medical insurance if there is a quota, but you will have to stand in line, and a lot of time may pass from the appointment to the day of the operation.
How long does the operation take?
From 15-20 minutes to 2 hours in severe cases. Average duration is 30-40 minutes.
How much does the operation cost?
If there is no quota, then the patient pays the price of the lens, which will stand in place of the natural lens, as well as the surgeon’s work. In large cities (Moscow, St. Petersburg), the cost of surgical intervention ranges from 35-40 thousand. The price depends on the complexity of the operation and the condition of the organ of vision, sometimes reaching 100-120 thousand. Taking into account the cost of the prosthesis, treatment can cost 60-200 thousand.
From what age and until what age do lenses need to be replaced?
The boundaries are set depending on the condition of the patient and his visual organs. Thus, even an infant may need to replace the eye lens, and older people need it very often.
How many days does the postoperative period last?
It all depends on the complexity of the operation, the speed of tissue regeneration, the person’s health and compliance with the ophthalmologist’s recommendations. Typically, from the moment of intervention until complete recovery, it takes from 2 to 4 weeks. After this time interval, vision is completely normalized.
Are patients satisfied?
Yes, almost every review is positive. Everyone notes the effect, minimal risks of consequences and recovery, which is quite quick and easy. A negative review may contain dissatisfaction with the cost and quality of service.
Why does the eye see dimly?
Usually the turbidity goes away on its own within a day or two. If it lasts longer, consult a doctor. Most likely, complications arose.
Treatment of secondary cataracts using YAG laser
Until recently, the beginning of opacification of the posterior wall of the lens capsule required repeated surgery. The latest laser technologies have eliminated this need. In modern ophthalmology, the problem is solved “in one day” using a YAG laser. Laser treatment of secondary cataracts is completely painless, minimally traumatic and produces lasting results. This procedure is called “laser posterior capsule dissection.” The effect of laser treatment is achieved by removing the back wall of the lens sac with overgrown epithelium, which prevents light from penetrating the retina. Treatment is performed under local drip anesthesia; the patient does not need to stay in the hospital. Laser correction with a YAG laser for secondary cataracts eliminates interference on the optical axis and significantly restores visual functions.
Choosing a cataract treatment method
The main factors that influence the quality of vision are the choice of surgical method and the lens used. Therefore, before the operation, everyone is asked to make 2 decisions.
Selecting the type of operation: laser or scalpel
Most people nowadays choose the laser method. It costs the same as a standard operation at the dentist. But, unlike her, the result is guaranteed to last until the end of life.
Selecting the type and quality of the lens (artificial lens)
Here, everyone chooses for themselves, since everyone’s financial capabilities (or medical insurance options) are different. But please do not save on your health, the difference in the cost of lenses is not as great as the richness and beauty of the world that surrounds you.
Regime restrictions
Although the person undergoing surgery does not necessarily have to remain in bed, some restrictions regarding his lifestyle should still be taken into account. So, during the first month you should not turn on your stomach while sleeping.
For the first two weeks, you cannot watch TV, knit, sew, read or spend time at the computer. After a month, the doctor may allow you to do your favorite activities, but not longer than 1-2 hours a day. Reading is allowed no more than 2 hours a day.
It is not recommended to wash your hair for the first 3-4 days so that dirty water does not get into the operated eye. You are not allowed to visit public saunas and swimming pools. It is also prohibited to take a hot bath for 10-15 days after surgery.
Smoking and drinking alcohol is prohibited. You should also avoid being near people who smoke, since passive smoking is no less dangerous than active smoking.