Ophthalmoherpes is associated with the spread of herpes infection to the eyes. In this case, the patient’s cornea is damaged, which leads to the development of keratitis and decreased visual function. With ophthalmic herpes, it is very difficult to cope with the disease on your own, so it is highly advisable to contact a specialized center.
Among all corneal pathologies, ophthalmoherpes accounts for three quarters of cases. The infection tends to recur, and three to five episodes are often reported over the course of a year. If there are signs of herpes development, you should immediately consult a doctor, since if treatment is delayed, the virus will spread to the deeper tissues of the eye. This will adversely affect the patient's vision and can even lead to blindness.
Causes
Thanks to the tear fluid - it contains secretory immunoglobulins that reliably protect our eyes from various infections. Her strength, unfortunately, is not enough if the immune defense of the body as a whole weakens.
This happens for various reasons: after infectious diseases, surgery, stress, hypothermia.
In such circumstances, ophthalmoherpes quickly finds the “weak link” and manifests itself in all its “glory.”
The immediate impetus for the start of his hostilities is:
- eye injuries;
- contact with a sick person;
- using the same hygiene products with the patient;
- use of immunosuppressants.
An outbreak of the disease can occur in a pregnant woman, since during pregnancy the body undergoes dramatic changes and the immune system weakens.
Experts distinguish two methods of infection: endogenous (viral herpes, having entered the body, under favorable circumstances, manifests itself in various areas, including the cornea of the eye or the eyeball) and exogenous (the infection enters the mucous membrane of the eye from the outside).
The second option is more common in children than in adults, because children constantly violate the rules of hygiene, participate in general games and can easily catch some kind of infection.
According to medical statistics, 80 percent of infections in young patients occur through exogenous infection.
Reasons for appearance
After penetration into the body and spread of infection, symptoms of herpes may be absent for a long time, especially after a preliminary increase in immunity. This is explained by the fact that the harmful virus, penetrating the mucous membrane of the eye, does not multiply under the influence of the interferon produced. Own immunoglobulins contained in the tear fluid inhibit the inflammatory process, as if prolonging the incubation period.
If the immune system is weakened, the pathogenic virus equally affects the cornea and eyelids, accompanied by acute inflammation of the ocular structure of the apple and the optic nerves. Before proceeding to conservative therapy, it is important to study the etiology of the pathological process, identify and exclude factors that provoke ophthalmoherpes. This:
- prolonged hypothermia of the body;
- complicated infectious diseases;
- mechanical and chemical eye injuries;
- long-term use of medications;
- progressive pregnancy;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- complication of colds, viral diseases;
- stress, chronic fatigue.
Routes of infection
The causative agent of the disease is the pathogenic herpes virus, which is transmitted to a healthy person by airborne droplets or household contact. In addition, infection often occurs through unprotected sex. Pathogenic flora settles on the inner membranes and dermis, and may not manifest itself at first. With herpetic keratitis, the symptoms progress spontaneously and the pathological process can no longer be suppressed with one’s own interferon.
- Blepharoplasty of eyelids
- Recipes for green tomato salads for the winter: delicious preparations
- Homemade shortbread recipes
Causes
The herpes virus, once it enters the human body, remains there forever. Among the factors that provoke the growth and reproduction of pathogenic flora, the following should be highlighted:
- hypothermia of the body;
- experienced stressful situations;
- decreased immunity;
- long-term use of antibacterial medications;
- chronic infections;
- insufficient rest.
Blood test for herpes
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) types 1 and 2 cause genital infections and are the most common cause of genital ulcers.
Herpes is considered an infectious disease that is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. Infection occurs in several ways:
- when talking;
- with unprotected sexual intercourse;
- when using general personal hygiene products.
To catch the disease, it is enough to use the patient’s towel. For this reason, it is prohibited to give anyone personal items, especially cosmetics.
The pathology is transmitted to the child from the mother during childbirth. The cause of the appearance of herpes in the eyes can be infection of other parts of the body by the virus. Often the person himself, who does not follow the rules of hygiene, becomes the cause of the spread of infection to the organs of vision.
It often happens that when treating herpes on the lips with topical medications, a person forgets to wash their hands after treating the damaged areas. When scratching the eyes and applying makeup, viral particles enter the eyes, causing various damage to the structures of the organ of vision and the skin near it.
Symptoms of ophthalmoherpes
If a primary infection has occurred, the incubation period lasts from 2 to 7 days.
The disease begins with the same symptoms as an allergy or bacterial infection (for example, conjunctivitis), and it looks very similar.
Here are some characteristic signs:
- the inflamed area itches;
- the eye is swollen;
- tears flow;
- the eye reacts painfully to bright light;
- Redness can be on the eyelids, on the skin around the eyes, and on the eyeball.
When the initial stage passes and the disease affects the retina, symptoms characteristic of ophthalmic herpes appear:
- sparks in the eyes, flashes of light;
- splitting of observed objects, visual changes in their shapes;
- loss of visual acuity;
- convulsive uncontrolled closing of the eyelids;
- headache.
If the herpetic lesion continues to develop, turning into neuritis, the following symptoms may be added to the listed symptoms:
- debilitating pain in the eyebrow area;
- narrowing of the field of view;
- blind spot in a person's vision.
Externally, the rashes resemble herpes simplex and herpes zoster . Fluid-filled blisters can be located on the upper eyelid or on the inside of the eyelid, but they are more painful than those that appear on the lips, for example. We talked about methods for quickly treating herpes on the lips in this article.
Complications of ophthalmoherpes
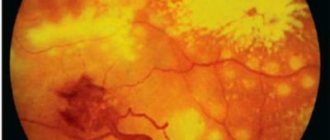
If treatment for herpetic eye lesions is started in time, the effectiveness of therapy is usually high, since the infection is located on the surface of the cornea. If the deep structures of the eye undergo changes, then clouding of the cornea and vitreous substance occurs, which leads to a decrease in visual acuity. Sometimes even corneal blindness occurs.
If the infection is chronic, symptoms of cataracts and glaucoma may appear. With necrotic changes in the retina, hemorrhages and detachment (complete or partial) occur.
Not in the eyebrow, but in the eye
| Attention | |
| In clinical practice, relapses of herpetic keratitis are often observed after topical use of corticosteroids. Experts warn: these drugs should be used with great caution and under the supervision of a doctor. | |
Most often, HSV affects the cornea, less often – the conjunctiva and inner membranes of the eye. At the same time, the virus, which is essentially an intracellular parasite, begins to capture more and more new cells, forcing them to produce similar ones. It is very difficult to dislodge an invader from his home. But if this is not done, it will bring a lot of trouble.
At the site of virus penetration, a creeping tree-like ulcer appears, which is essentially an entry gate for a bacterial infection. “Viruses pronounce the sentence, bacteria carry it out” - this medical saying very accurately reflects the destructive mechanism of action of HSV.
How to identify herpes
The symptoms of eye colds, as herpes is often called, are similar to those of other diseases. An ophthalmologist makes an accurate diagnosis
, who conducts an examination with a slit lamp, as a result of which ulcerations and
other lesions of the cornea
, as well as inflammation of the ocular vessels.
Also, in a hospital setting, cells are scraped from the affected mucous membrane or skin , which is studied using a fluorescent microscope.
Note Another diagnostic method is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, which can detect the presence of antibodies to the virus.
The listed diagnostic methods are required for damage to the cornea and blood vessels. As a rule, herpetic lesions of the mucous membrane of the eyes and skin of the eyelids are noticeable even without a medical examination. Herpes on the eyelid is characterized by multiple rashes in the form of small blisters with lymph - a liquid that gradually becomes cloudy. The blisters are painful and very itchy. If you scratch the sore, it spreads even more.
Types and clinical forms
There are clinical forms of ophthalmoherpes. Among them:
- eyelid dermatitis;
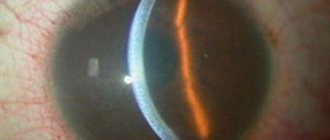
- keratitis (the cornea becomes inflamed and cloudy, the patient cannot open his eyes);
- stromal keratitis (vascular damage, displacement of the eyeball);
- trophic keratitis (cornea loses sensitivity);
- herpetic corneal ulcer;
- blepharoconjunctivitis (rash on the inside of the eyelids, along the edge and in the corner of the eye);
- herpetic uveitis (the vitreous body of the eye becomes cloudy);
- retinal necrosis (dangerous loss of vision).
There is also a species classification of ocular herpes. Among the most common types:
- epithelial (the disease does not penetrate deep inside);
- tree-like (areas damaged by the virus form convex lines, shaped like a tree);
- geographical (in contrast to the tree-like picture of the lesion is larger, reminiscent of a geographical map);
- disc-shaped (disc-shaped areas of deep infiltration are formed on the cornea).
Treatment for herpetic eye lesions
Procedures to eliminate ophthalmoherpes are dictated by diagnostic results. If the anterior zone of the visual organ and surrounding areas are affected, then a complex of drugs is used. Posterior eye pathology may require surgery along with medications.
Drug therapy
Treatment includes:
- Antispasmodics and decongestants.
- Immunomodulators.
- Antiviral drugs.
- Vaccination against herpes virus.
Immunomodulatory drugs are aimed at increasing the body's resistance to viruses. These include interferon inducers (Amiksin, Cycloferon) and immunoglobulins (Interlock). Amiksin (price from 600 rubles) and Cycloferon are prescribed in tablets and injections; they have a minimum number of contraindications. Interlock for eyes comes in drops. It restores the cell membrane and builds protection against the virus.
Antiviral agents for external use are creams, ointments and drops. Acyclovir ointment (price from 20 to 100 rubles) is recommended with a 3% content of the active substance, which is safe if it comes into contact with the mucous membrane. Fenistil Pencivir cream copes better with relapses, unlike Acyclovir, and is strictly applied to the eyelid. Oftalmoferon drops are prescribed in combination with ointments to prevent damage to the corneal layer of the eye. Viferon in the form of suppositories is prescribed to children.
Trifluorothymidine drops are safe and non-toxic. Ophthalmologists recommend them for their gentle and targeted action. Apply every hour, but in dosage due to possible damage to the retina. The price is within 300 rubles.
The tablet form of antiviral drugs is represented by Valtrex, Valvir, Zovirax (price about 500 rubles). Valvir is used to treat childhood herpes.
If necessary, symptomatic medications are added to the main treatment.
- Painkillers are based on lidocaine, novocaine, atropine and reduce the unpleasant symptoms of herpes: burning, itching, pain, and also suppress swelling.
- In case of acute damage with a possible bacterial nature, antibiotics are used.
- Necrosis of tissue of the visual organ is treated with glucocorticosteroids, which are responsible for the regeneration of the epithelium.
- Ocular herpes, accompanied by intraocular pressure, is treated with antihypertensive medications.
- An integrated approach requires excluding possible allergies, so antihistamines Suprastin, Tavegil, Zyrtec are added.
Vaccination is carried out in the absence of complicated herpes 2 times a year.
How to get rid of eye herpes using folk remedies?
Traditional medicine recipes can be combined either in combination with drug therapy or independently.
Effective infusions for the eyes:
- From lungwort. 2 tbsp. l. herbs are brewed in 500 ml of boiling water and left for 2 hours. The resulting infusion is used to wash the eyes for 2 weeks.
- From arnica. Take 1 arnica inflorescence per glass of boiling water and brew for 2 hours. Make compresses from the resulting product and wash the eyes every 2 hours.
To increase overall immunity, drink chamomile and rosehip teas, add honey and lemon.
In addition to medicinal treatments, physiotherapy in the form of UHF is used to heal sores.
Diagnostic methods
For an accurate diagnosis and selection of appropriate treatment for the disease, a visual examination, various tests (visometry - for visual acuity, perimetry - for the width of the visual field), laboratory methods, as well as psychosomatics - a technique for studying the impact of psychological factors on the patient's condition are used.
The main role is still given to laboratory methods using special equipment.
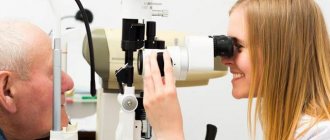
Slit lamp inspection
An examination using this device helps to determine the nature of the corneal lesion and detect symptoms typical of a herpes infection.
Immunofluorescence analysis (RIF)
Experts consider this type of diagnosis to be the most accurate. Material taken from an infected area is examined under a microscope.
After exposure to ultraviolet radiation, the sample gives (or does not give, then the diagnosis is not confirmed) a special glow.
Linked immunosorbent assay
The method is used in the most difficult cases, when other studies and analyzes give conflicting results.
The method is based on the fact that in case of ophthalmoherpes, immunoglobulins M must be present in samples taken from infected areas.
In this article we will answer the question and explain in detail: GCS - what is it in medicine, what are the indications for their use.
Methods for treating oral dermatitis on the face are discussed in this material.
Find photos of herpes zoster at the initial stage here: https://udermatologa.com/zabol/gerp/opoyasyvayushhiy-lishay-foto-simptomy-lechenie/.
Diagnosis of viral eye infection
80% of eye diseases have the same symptoms, which makes it difficult to quickly diagnose them and create a treatment plan. To identify the disease, the doctor must:
- examine the skin of the eyelids for herpetic rashes;
- check visual acuity (often it is greatly reduced);
- test the patient's visual boundaries;
- check the sensitivity of the cornea;
- examine the posterior/anterior parts of the eyeball;
- examine the fundus to identify existing infections.
A number of laboratory tests are also carried out. Only after them the diagnosis is determined. A general blood test, a scraping from inflammation, and a smear from the cornea are taken from the patient.
This is required in order to identify the type of virus, the activity of the immune system, and the number of antibodies produced by the body.
Treatment of herpes on the eyelid and eyebrows
Depending on the form and severity of the disease, the doctor selects etiotropic and symptomatic therapy: the first is aimed at combating the causative agent of the disease, the second helps to get rid of unpleasant symptoms when the eyelids swell, become inflamed, and itch.
Drugs
A large group of antiviral drugs used to treat ophthalmoherpes includes:
- Acyclovir (tablets and ointment);
- Valacyclovir (tablets);
- Famvir (tablets);
- Oftan-IDU and TFT (eye drops);
- Vidarabine (gel).
The patient is prescribed immunomodulators made from donor blood and modifying cell membranes in such a way as to protect them from the penetration of the virus: Interlock, Reaferon, Cycloferon.
These drugs are used for injection, as well as in the form of tablets and eye drops.
To relieve the symptoms of the disease, Atropine and Irifrin are used - they relieve spasms that often accompany eye infections.
Opatanol drops help with allergic reactions. For burning and itching, you can apply tetracycline or erythromycin ointments to the areas of inflammation.
If healing of wounds takes a long time and causes pain, the doctor prescribes physical treatment (UV, UHF).
How to treat with folk remedies
Let's start with a taboo: on some forums on the Internet, garlic is recommended as a cure for ocular herpes, but in no case should it be used to treat sores on the eye or even under the eye.
The body's reaction to such a radical remedy can be unpredictably severe.
Here are some traditional medicines that professional doctors approve of:
- infusion of marshmallow flowers or rose hips (you can wash your eyes with them);
- drops of 1 part honey and 2 parts water;
- fresh dill juice (compresses are made from it that help relieve swelling);
- grated fresh potatoes (lotions using it relieve burning and pain).
Any folk remedy is only a help, and not the main medicine, but they must be used to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Vaccine use
Vaccines are used in cases where the patient suffers from relapses of the disease. The most commonly used domestic drugs are “Gerpovax” and “Vitagerpevac”, as well as the Belgian “Gerpevac”.
Vaccination is carried out when the patient's exacerbation period ends. It is allowed to repeat it no earlier than after 6 months.
The vaccination course consists of 5 injections, which must be given with a one-week break.
Antiherpetic interferon has a vaccine-like effect on the body (it is produced in the form of an ointment). It blocks the activity of the virus and prevents it from reaching healthy cells of the body.
Many people are interested in whether pets (for example, kittens) can have herpes and how to protect their health. It turns out that the problem of herpes also affects our smaller brothers, and the infection selects the smallest, weakest animals.
Fortunately, vaccination is also provided for them - in the clinic it will be carried out by a veterinarian for pets from 3 months to 3 years.
Herpes on a child's eye
In childhood, herpes near the eye resembles an allergic reaction, since it affects the conjunctiva of the eyeball and is visualized by visible redness, burst blood vessels and a feeling of severe itching. If the eye is damaged, the child is at risk; a secondary infection cannot be ruled out. At all stages of the disease, childhood symptoms are presented below:
- sore eyes;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- loss of visual acuity with retinal damage;
- visible bubble around the eye contour;
- disturbed sleep phase;
- increased irritability;
- sensation of itching, burning in the eye.
Treatment
How to treat eye herpes is directly related to the form of the disease. That is why it is necessary to consult a doctor who can carry out the necessary diagnostics. If you have herpes under the eye, treatment is no different from treatment for simple herpes on the skin around the lips. Usually, to treat herpes in the tissues surrounding the eyes, drugs are used to relieve symptoms and agents that suppress the activity of the virus.
In any case, herpes on the eye must be treated comprehensively. To do this, use the following means:
Symptoms of herpes zoster during pregnancy and its treatment
- Symptomatic therapy is carried out using decongestants and painkillers;
- Immunomodulators are required;
- Patients must take specific antiviral agents;
- Sometimes an antiherpetic vaccine is used for treatment.
If the causative agent of the disease has penetrated into the deep tissues of the ocular apparatus, the ophthalmologist may prescribe surgical treatment, namely:
- laser coagulation;
- removal of virus-affected tissues.
What are the symptoms and types of colds on the eye?
A cold on the eye is familiar to many people firsthand. The inflammatory process can affect not only the eyelids, but also the mucous membrane. There are many reasons that cause inflammation in the eye area. As a rule, such discomfort is a consequence of the activity of bacteria and viruses. It is preceded by the following factors:
- Avitaminosis;
- Hypothermia or overheating;
- Weakening of the immune system;
- Various inflammatory or infectious diseases;
- Hypovitaminosis;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Stress, depression, chronic fatigue;
- Hormonal disorders, fatigue.
There are no difficulties in determining the form of a cold on the organs of vision during diagnosis. Often an initial examination is enough for the doctor to recognize a viral infection, but sometimes the patient requires additional consultation with specialists such as a therapist, allergist, immunologist and dermatologist.
If the doctor has suspicions about making the correct diagnosis for a cold of the eye, the patient is prescribed additional tests - ultrasound of the visual apparatus, biomicroscopy, non-contact tonometry, visometry, ophthalmoscopy and/or gonioscopy.
The doctor may also resort to laboratory analysis, after first taking the necessary samples from the mucous membrane (this can be a scraping or a smear).
A cold can be expressed as an acute form of inflammation, localized in the area of the sebaceous gland of the eyelid. Along with adults, children often suffer from this type of disease. These ophthalmopathologies can manifest themselves in the form of barley, herpes rashes or conjunctivitis. The appearance of these diseases is provoked by specific pathogens. Pathogenic bacteria and viruses are regularly present in the human body, but their numbers and activity are regulated by the immune system. When the natural protective functions of the body decrease, a favorable time comes for microorganisms that are instantly activated.
Lack of hygiene, the habit of rubbing your eyes with dirty hands, diseases of the digestive tract (for example, gastritis), diabetes mellitus - these factors also contribute to the appearance of inflammatory processes.
Eye viruses can attack a person unexpectedly, but a cold under the eye is not a reason to panic, since there are many medications that can quickly get rid of unwanted manifestations.
Perhaps the most common eye disease is conjunctivitis, i.e. an inflammatory process localized in the mucous membrane or in the inner parts of the eyelids. Most often, this disorder occurs on an infectious basis, but often the cause of its occurrence is mechanical damage to the eye or allergies. Conjunctivitis is caused by adenovirus, herpes, various fungi and bacteria of different groups. In the acute phase of the inflammatory process, the patient complains of pain, discomfort, purulent discharge, deterioration of health (headache, fever). There are two ways to become infected with this disease: contact or airborne transmission. Therefore, quarantine is recommended for patients (isolation is especially necessary if an adult is in contact with children). The active phase of inflammation can last up to three weeks.
Stye, or hordeolum, is another common manifestation of a cold on the eyelid, implying inflammation of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle, appearing in the form of a purulent formation. Unlike conjunctivitis, stye is not contagious. It occurs due to the active proliferation of Staphylococcus aureus, which the body fights, resulting in tissue inflammation. Swelling and redness occur at the site of infection. Often, when treating gordeloma, ophthalmologists are faced with a situation where the patient’s eye is severely swollen and due to deformations on the eyelid, the view is partially or completely blocked. With barley, the patient complains of itching, accompanied by pain at the site of the rash. 2-4 days after infection, an abscess appears at the site of infection, which in most cases breaks out spontaneously after 3-7 days.
If the pus does not come out naturally for a long time, the stye turns into a so-called chalazion - a hard formation that can retain its shape for up to 2 months.
The herpes simplex virus can cause ophthalmoherpes. The symptoms of this disease are similar to those described above: the eye turns red during a cold, swelling occurs, a sensation of a foreign body, increased temperature and lacrimation, itching, etc. Such rashes can be localized not only on the eyelids or in the area of the lacrimal canal, but also on the cornea, causing clouding and damaging its surface. Ocular herpes is dangerous because it easily spreads to other unaffected areas. It is especially difficult in children.
Features of ocular herpes in children
The causes of the development of the disease are almost the same in children and adults, but the symptoms are somewhat different, which means that the treatment required is different.
In addition to the classic symptoms of ophthalmoherpes, the child develops a cold on the lips.
This, on the one hand, makes it possible to quickly make an accurate diagnosis, and on the other, complicates treatment. Therefore, trying to cope with the disease without medical support is strictly prohibited.
But you can provide first aid to your baby before going to the doctor: drop Ophthalmoferon drops into the sore eye.
The doctor will most likely recommend several medications for treatment: Acyclovir ointment (3 percent is used for small children), the already mentioned drops and Viferon suppositories.
By the way, ocular herpes often occurs in children who are being treated for chickenpox. Parents need to keep this in mind and monitor the condition of their baby's eyes.
What is ocular herpes?
Ophthalmoherpes is a type of simple herpes virus (HSV) that affects the skin and mucous membranes around the eyes, eyeballs and appendages of the visual organ.
The infectious focus is localized in the tissues of the cornea, with its rapid development it emerges from a latent state, affecting nearby cells, destroying the structures of the visual organ.
According to its course, ocular herpes is classified:
- Primary. Diagnosed in people who do not have developed immunity against the virus. Infection occurs between the ages of 6 months and 5 years.
- Chronic. It develops when there are antibodies to HSV in the body and occurs periodically during the active phase of the virus.
There are several forms of infection, depending on the degree of damage:
- Superficial: conjunctivitis;
- blepharoconjunctivitis;
- dendritic keratitis;
- vesicular keratitis;
- marginal keratitis;
- episcleritis;
- Landkart-like keratitis.
- iridocyclitis;
How to distinguish ophthalmoherpes from barley?
Visually, ocular herpesvirus can easily be confused with an allergy, chalazion, or infection of another origin.
The main differences between herpes and barley:
- Chalazion. It forms on the edge of the eyelid in the form of a small red bump.
- Herpes. It manifests itself as a blistering rash, accompanied by redness, severe itching in the eyelid area and elevated body temperature.
Complications and possible consequences
The most dangerous complications occur in cases where herpes is localized not near the eye, but directly in its tissues. This may cause:
- partial or even complete loss of vision;
- corneal clouding;
- detachment and death of fiber;
- eye diseases - glaucoma, cataracts.
This development of events can be expected if the patient did not attach due importance to the disease, tried to self-medicate at home, and the method he chose turned out to be insufficiently developed for this disease and is not supported by official medicine (for example, homeopathy).
Complications
If treatment for eye herpes is started on time and, after correct diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed, then complications are unlikely. But if the eye infection with herpes was in the deep tissues, then this can affect vision up to the point of blindness.
Incorrect diagnosis, and accordingly incorrectly selected treatment, as well as untimely consultation with a doctor, can lead to the following complications:
- Decreased clarity of vision;
- Constant feeling of dryness in the cornea area;
- Poor eyesight;
- Cyclic eye pain;
- An eye affected by herpes may eventually stop seeing altogether.
With a long course of the disease, the virus can provoke cataracts or glaucoma. Retinal detachment is also possible due to hemorrhages that are typical when it is damaged.
Prevention
Any type of virus (herpes zoster, ocular) is dangerous for relapses, so the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs to recovered patients as a preventive measure.
They help avoid frequent re-outbreaks, but they cannot completely defeat the disease.
Here's what else you can do to stay healthy:
- reduce close contacts with the sick person to a minimum, since the virus is contagious;
- use only your own hygiene items;
- do not overheat in the sun and do not overcool the body in winter;
- eat right, not forgetting about vitamins;
- improve health (hardening and physical therapy will help).
People often ask: corticosteroids - what are these drugs? How do they work and when are they used? Our publication will provide answers to these and other questions.
The main symptoms and treatment of cytomegalovirus infection in women are discussed in detail in this article.
Prevention of ophthalmoherpes
Preventive measures for herpetic disease in the eye area mean:
- timely treatment of herpes of other localization;
- strengthening the body's protective capabilities;
- avoiding direct contact with a person with herpes;
- treatment of other infectious diseases.
Eye herpes manifests itself in various forms and, if left untreated, leads to other serious ophthalmological diseases. Treatment of pathology is carried out only with those drugs prescribed by the doctor.
Prevention and control of relapses
To reduce the risk of contracting herpes and to prevent relapses, you should follow simple rules:
- Dress appropriately for the weather to prevent hypothermia.
- Avoid stress and worry.
- Use individual towels, dishes, and cosmetics.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Do not contact sick people.
- Play sports, lead a healthy lifestyle.
To maintain immunity, hardening, walking in the fresh air, taking multivitamins, and proper nutrition are useful. If you notice the first signs of herpes in your eyes, you should contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible and begin treatment.
Forms of herpes
Ophthalmoherpes differs from other types of herpes in a large number of manifestations, and symptoms during relapses can vary greatly. Depending on the damage to the tissues of the eye, the following main forms of herpes on the eyes are distinguished:
Herpetic conjunctivitis is a lesion of the conjunctiva, that is, a thin film of epithelium covering the eyeball and the inside of the eyelids. Herpetic lesion is manifested by redness of the eye;Blepharo-conjunctivitis - inflammation and the formation of herpetic blisters on the eyelids or along the eyelash line are added to the damage to the conjunctiva. Bubbles may also appear on the inner surface of the eyelids, in this case severe lacrimation and sharp pain in the eye appear;
Keratitis - affects the cornea, on which blisters appear
Keratoiridocyclitis is an inflammation of the cornea with damage to blood vessels in the eye. This is the most severe form of herpes and is difficult to cure. Such herpes can recur again and again.
Reviews
Galina Ts.: “Ocular herpes is very difficult to cure once and for all. My son contracted it in kindergarten when he was 3 years old. I remember: my eye was swollen, my cheek was swollen, it was very itchy. Then there were a couple more cases. The last time, the symptoms did not seem very pronounced, but the son rubbed his eyes and brought the infection deeper. Now he has swelling and clouding of the cornea. Vision has become worse. We are being treated at home, and, according to the doctor, we are getting better.”
Daria I.: “The other day I did powder eyebrows. Many of my friends didn’t even know what it was (it turns out it was a new type of tattoo), but they were delighted with the result. The effect of well-groomed, beautifully colored eyebrows, as they promised me, will last for several years. I liked that the specialists take the procedure very seriously - so that after tattooing no sores appear on the face, and especially on the eyes, people who have had herpes (and I just had it three years ago, and it was an eye one) are offered for 2 the day before the procedure, take preventive antiviral drugs.”
Lyudmila D.: “All eye diseases are very dangerous, and herpes also differs from stye in the duration of treatment. When a sore appeared on the mucous membrane of my eye, on the lower eyelid, I thought it was a stye and it would go away in a week at most. It turned out to be herpes. Doctors prescribed various medications, but it is impossible to quickly cure this type of herpes; it will take several months. I read reviews from ophthalmologists on the Internet about new methods of treating ocular herpes, they claim that modern medicine can provide the patient with a stable (up to several years) remission.”
Symptoms
Herpes on the mucous membrane of the eye is not only an internal disease, but also provokes an aesthetic defect. Externally, the eye turns red, small vessels burst, ulcers appear on the soft tissues, and the functions of the lacrimal glands are disrupted. Herpes on the mucous membrane of the eye has general symptoms, which are described below:
- redness of foci of pathology, which are accompanied by pain, itching;
- increased sensitivity of the cornea;
- progressive conjunctivitis, blepharitis;
- severe itching with skin rashes;
- visible swelling of the eye tissues;
- the formation of blisters on the mucous membrane or eyelid with relapses of eye diseases;
- disruption of the structure of the mucous membrane;
- signs of vision impairment;
- local compaction of the upper or lower eyelid;
- formation of scars if the vesicle is forcibly opened.
No relapses!
There was a time when treating herpetic keratitis was a big problem. Antiviral drugs were initially imperfect and caused severe complications, but with the advent of interferon inducers (in drops and injections) that stimulate the immune system, the situation changed. Along with modern antiviral and anti-inflammatory drops and ointments, the drug, which was jointly developed by the Research Institute of Eye Diseases and the Institute of Virology, is still one of the main ones in the treatment of this disease.
– We cannot make sure that the patient does not have herpes in his body. But in the vast majority of cases, we succeed in ensuring that it does not relapse, and if it does recur, then in a mild form, says Professor Kasparov.
Vaccination against HSV, which doctors carry out after the end of antiviral therapy, has also become a great help in this. Five injections intradermally - and you can forget about exacerbations of the disease.