Most people experience pathological changes in the lens over the years. They are also called age-related. Although it is difficult to avoid disorders, this does not mean that they do not need to be treated. Many people don't pay attention to their eyes. In this age of technological advancement, when phones and computers make up a large part of life, the eyes suffer the most. One of the most unpleasant vision pathologies is phacosclerosis - age-related hardening of the lens nucleus.
Features of the lens
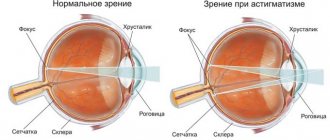
The lens tends to change throughout a person's life. In infants, the lens is colorless and soft, it has a spherical shape. In children, it becomes a flat lens at the front of the eyeball. In adults, crystals turn from transparent to yellowish.
By the age of forty, a person’s lens begins to lose its elasticity, and presbyopia develops (a defect that leads to the inability to distinguish small print up close). At sixty, most people are diagnosed with sclerosis of the lens nucleus. The pathology is fraught with deterioration in the perception of objects near.
Stages of lens opacification
It is customary to distinguish 4 stages of cataract development, in which a minor defect transforms into a serious pathology:
- Initial stage. At this stage, the changes are invisible from the outside, there is not even a hint of a slight nebula. However, microscopic locations along the periphery of the biological lens already exist. And they can make themselves known with unfavorable symptoms. Since there is a frequent violation of the refractive power, it becomes difficult to choose glasses for vision correction. Often, difficult-to-choose glasses require replacement soon after purchase.
- Immature cataract. This stage of clouding of the lens gives signs that are noticeable even to a layman. The deterioration in the quality of vision is explained by the slow movement of “fog” from the edge to the central part. The structure of the lens changes, the tissue swells, causing an increase in intraocular pressure. This, in turn, provokes the development of concomitant eye diseases such as glaucoma.
- Mature cataract. Vision is seriously deteriorating. A person does not see objects at a distance, catching only what is located in the immediate vicinity. He may only have light perception
- Overripe form. The structure of the lens is significantly deformed. The natural lens shrinks, its fibers disintegrate, and the substance liquefies, forming a milky stain.
Only in the initial stages of clouding of the eye lens is it possible to use drops and other pharmacology. Then the effect can only be obtained from surgical intervention.
Hardening of the lens with age
Another feature of the eye is the hardening of the lens. According to research, in a fourteen-year-old teenager, the core is just beginning to harden and changes 450 times over time. In some cases, 1000 times hardening occurs. To determine the degree of hardening, a mechanical analyzer is used, which allows one to study different points and parts of the eye. This is how the stiffness of the eyeball is measured.
In parallel with the nucleus, the cortical parts of the eye also harden. They change 20 times during life. Until the age of 30, the cortical parts are normally harder than the nucleus of the eye, but by the age of 35 the parameters are equal.
After 35 years, hardening of the core predominates. The reasons for these phenomena have not yet been studied, but there are several opinions. Some scientists argue that the hardness of the lens increases due to the compaction of its constituent substances. However, such a process is always accompanied by dehydration of the eye, but this does not happen with phacosclerosis. With age, the amount of fluid in the lens does not change.
Complications after eye lens replacement
They arise due to the fault of the patient himself, who does not follow the doctor’s instructions, due to a surgeon’s error, from which no one is insured, and due to the individual characteristics of the body. Complications are as follows:
- corneal edema, which is more of a side effect rather than a complication, and goes away on its own after a few days;
- secondary cataract, which affects the posterior chamber;
- retinal detachment;
- infectious eye diseases;
- increased intraocular pressure, which is caused by displacement of the IOL or insufficient flushing of the chamber after removal of the lens from the eye.
Secondary cataracts are eliminated using laser dissection. The pressure is reduced with eye drops. Infectious eye diseases must be treated with antibiotics. When the retina is detached, laser coagulation is prescribed. All these complications should not frighten the patient. Firstly, they rarely occur, and secondly, prosthetics are the only way to restore vision to a person with lens atrophy.
Specifics of phacosclerosis
Phakosclerosis is a thickening of the lens fibers, which is provoked by changes in the metabolism of this part of the eye. The functionality of the lens directly depends on its softness. There is a Helmholtz theory: tuning the optical system of the eye to perceive objects nearby occurs by increasing the curvature of the surface of the lens. In this case, the lens takes on a more spherical shape due to the contraction of the ciliary muscle.
To ensure constant mobility of the lens, it must be soft and elastic. With age, the lens thickens, making it harder for it to change shape to perceive nearby objects. For this reason, people begin to use glasses and special corrective lenses.
Types of cataracts
Depending on the moment when the clouding of the lens began, the disease is divided into the following categories:
- congenital - clouding forms immediately after the birth of a child or during the first year of life;
- acquired - cataracts develop in people who have reached 60 years of age or more.
Depending on the location on the lens where the clouding began to form, the disease is divided into several categories:
- anterior – formed on the anterior surface of the capsule;
- posterior – opacification on the posterior surface of the capsule;
- pyramidal deposits;
- fusiform deposit;
- layered deposit;
- zonal deposits;
- cup-shaped deposit;
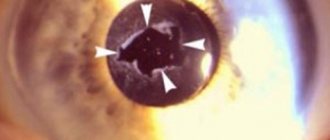
- nuclear cataract - the concentration of insoluble protein fractions in the center of the lens in the form of a circle;
- cortical formations.
Depending on the degree of progression, the disease is divided into several forms:
- partial;
- total.
Depending on the root cause of senile cataracts, formation can be divided into several forms:
- primary cataract, associated with the accumulation of insoluble protein fractions, slowing down metabolism;
- secondary cataract caused by systemic diseases, accumulation of toxins in the body, damage to the lens.
The doctor needs to classify the cataract. This is based on diagnostic tests.
How to recognize phacosclerosis
In order to take timely measures to alleviate phacosclerosis (usually the selection of corrective glasses), you need to note all minor symptoms. You should not hesitate to visit an ophthalmologist if you experience discomfort in the eyes due to overexertion and working at the computer. The first sign of phacosclerosis is visual strain when focusing on objects that are close.
With a timely visit to an ophthalmologist, it is possible to prescribe prophylaxis in a timely manner to slow down the development of pathology. Phakosclerosis can develop against the background of other pathologies, which do not always directly indicate ophthalmological abnormalities.
Symptoms of disorders
Changes occur gradually. The earlier it is possible to detect lens opacities , the more favorable the prognosis. There are a number of symptoms that serve as indicators in determining eye diseases:
- visual acuity is lost, the adaptive capabilities of the eyes in twilight and darkness are reduced;
- blurry contours of objects appear, even at a short distance they seem unclear;
- when looking to the side, interference occurs, which is popularly called “veil before the eyes”;
- Sensitivity to light appears; solar and electric light sources cause lacrimation;
- when looking at a lamp, car headlights in the dark, or a TV screen, halos appear around these objects;
- color contrast disappears.
Patients note a temporary refractive error when the shift goes towards myopia. Some patients find it more comfortable to read without glasses, although this was previously impossible. However, the most important change when the lens becomes cloudy is a “haze” in the center of the eye. It characterizes the late stage of cataract development.
Causes and symptoms of lens pathology
Phacosclerosis is the result of changes in the lens. Complications of this condition are farsightedness, clouding of the lens, imaginary myopia, deterioration of metabolism, and decreased hyperopia (perception of distant objects).
The characteristic signs for this pathology are:
- decreased visual acuity;
- myopia;
- dryness or tearing;
- eye fatigue (with severe overstrain);
- photophobia;
- pain;
- loss of ability to distinguish colors;
- decreased clarity of text when reading (letters seem to blur).
Possible causes of phacosclerosis:
- age-related changes in the visual system;
- myopia;
- ulcer on the cornea;
- glaucoma;
- complications of cataracts;
- iridocyclitis (inflammation of the iris and ciliary body);
- diabetes;
- heredity.
Phakosclerosis and its signs
Sclerosis of the lens (phacosclerosis) is an age-related thickening of its fibers, accompanied by metabolic disorders of functional elements. When phacosclerosis occurs, patients often note the onset of slight imaginary myopia (up to 0.5-0.75 D) or a decrease in existing hypermetropia. Other, most common manifestations of this pathology include:
- Lacrimation and photophobia.
- Tension or dull pain in the eyeballs and temples.
- Asthenopia.
- The occurrence of presbyopia.
Provoking factors for the occurrence of lens sclerosis may include:
- Corneal ulcers and iridocyclitis.
- Myopia of varying degrees.
- Cataract with complications.
- Diabetes.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Age-related changes.
Diagnosis of phacosclerosis
Methods for diagnosing phacosclerosis:
- extended ophthalmological examination;
- ultrasound echobiometry;
- biomicroscopy.
Phacosclerosis can be detected using an ophthalmological examination with side lighting. For this, the doctor uses a 20 D lens. Diagnosis of lens hardening is also carried out using transmitted light. This method shows the change in the shape of the lens.
Biomicroscopy using a slit lamp reveals small changes in the shape, position and color of the lens in phacosclerosis. Ultrasound A-scanning or echobiometry can detect areas of lens compaction and areas of opacification.
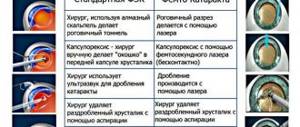
Nuclear cataract - treatment options
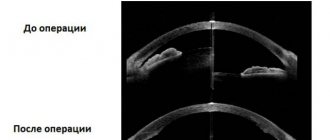
In an ophthalmology clinic, doctors can remove cataracts using suture technology and a seamless method. To select a technique, you need to visit a doctor, undergo an examination, and determine the stage of development of the disease. Immature nuclear cataract requires treatment without suturing, like the initial form of the changes. This type of surgical intervention is considered a low-traumatic correction method and is performed on an outpatient basis without placing the patient in a clinic. The operation allows you to restore visual acuity. The period of complete recovery is no more than a month.
In surgical practice, the method of laser extraction (LEC) of nuclear cataract is used. The treatment is performed using a precisely targeted beam of high energy intensity. The use of this technique is permissible for any form of cataract maturation, as well as at different levels of core density. However, in Russian practice this method is used infrequently.
Phacoemulsification technology (PEC) has become widely used . The method is effective until the disease reaches an advanced stage. In this case, phacoemulsification cannot be used because the high-density core is impervious to ultrasound energy. Its crushing is complicated, and the doctor is forced to use the incision method to remove the natural lens and replace it with an intraocular element (IOL). Using this technique, the surgeon places stitches at the end of the procedure.
For high density nuclear cataracts, ophthalmic surgery uses treatment with intra- or extracapsular extraction techniques . The specialist manually removes the cloudy lens. The technology is imperfect. It involves a deep effect on the eyeball, retrobulbar anesthesia and a long period of rehabilitation. The quality of vision after such operations is worse than when using sutureless techniques. This is due to postoperative astigmatism or distortion of the upper layer of the cornea caused by sutures.
Dr. Trubilin's clinic uses modern methods of vision restoration . Here they take on the most difficult cases, showing good results. High professionalism of doctors and new equipment contribute to comfortable treatment of nuclear cataracts in a medical institution. High-quality diagnostics allows you to accurately identify the disease in the early stages. Once the diagnosis is made, we recommend not delaying the date of surgery. Remember that the faster the treatment is completed, the better the result and the shorter the rehabilitation period.
Treatment of phacosclerosis
Compared to many other eye diseases, phacosclerosis does not cause vision impairment. Therefore, ophthalmologists do not recommend the use of any medications to treat pathology. Glasses are enough for correction.
When treating phacosclerosis, drugs effective for cataracts are not prescribed, since they do not have any beneficial effect. Drops with vitamins do not affect the metabolism in the lens, so they are also not used. Drops do not improve metabolism and tissue respiration in the eye.
There are no special measures that could help a person with age-related changes in the visual system, in particular, with hardening of the lens. Phacosclerosis rarely causes overall vision deterioration, but even in this case, spectacle correction is sufficient.
Why phacosclerosis is not curable:
- the disease does not lead to a significant deterioration in visual function; correction with glasses is sufficient;
- anti-catarrhal drugs do not affect the lens;
- Vitamin eye drops do not affect metabolism;
- age-related vision deformities do not require additional therapy.
Since the causes of phacosclerosis are not fully understood, there is no complete and effective therapy for this condition. It is recommended throughout your life to follow the recommendations of specialists who help slow down the process of hardening of the lens. To do this, you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, eat a balanced diet and take additional vitamin supplements.
It wouldn't hurt to eat carrots, blueberries and honey every day. These products have a beneficial effect on the quality of vision and functionality of the visual system. The main way to avoid phacosclerosis is to maintain the functionality of the body. If there is a sufficient amount of nutrients, the body is able to maintain the softness of the lens at the proper level.
Complications
Hardening of the lens of the eye can lead to the development of certain diseases. The onset of biconvex lens sclerosis causes the following complications:
- farsightedness (hypermetropia);
- reduction of farsightedness;
- clouding of the lens of the eye;
- deterioration of metabolism in the tissues of the visual analyzer;
- imaginary myopia.
To prevent the disease from leading to complications, you must go to the hospital in a timely manner and follow doctors’ recommendations, do not self-medicate and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Prevention of phacosclerosis
Doctors offer a set of therapeutic measures that help avoid or slow down the development of phacosclerosis.
Prevention of phacosclerosis comes down to the following measures:
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- moderate physical activity;
- rejection of bad habits;
- use of vitamin complexes.
There are also no traditional methods for treating phacosclerosis. There are only general recommendations for strengthening visual function. Both doctors and herbalists recommend that people eat more foods that can preserve vision even into adulthood.
Products to preserve vision:
- carrots (vitamin A, B, C, E, D, antioxidant beta-carotene, sodium, calcium, phosphorus, iron, potassium, zinc, copper);
- spinach (vitamins A, C, E, K, B2, B6, phosphorus, protein, fatty acids);
- onion, garlic (sulfur);
- eggs (vitamins A, B1, B2, glycine, copper, iron);
- blueberries (vitamins A, B, C, PP, lutein, which help maintain visual acuity, relieve fatigue, and improve night vision);
- fish (omega fatty acids);
- fruits (vitamin C, beta-carotene, which contribute to normal blood circulation in the visual system, antioxidants and beta-carotene, which are involved in the synthesis of vitamin A);
- soy (fatty acids, vitamin E);
- broccoli (lutein, zeaxanthin, carotenes);
- dark chocolate (flavonoids that strengthen blood vessels and the cornea).
Persistent decline in visual function throughout life usually only manifests itself with age. With an inappropriate standard of living, poor nutrition and passive existence, there is a negative impact on the body as a whole.
Sources used:
- Gorban, A. I. Microsurgery of the eye. Guide for doctors / A.I. Gorban, O.A. Jaliashvili. - M.: Medicine, 1982.
- Vodovozov, A.M. Study of the fundus of the eye in transformed light / A.M. Vodovozov. - M.: Medicine, 1986.
- Belyaev, V.S. Operations on the cornea and sclera / V.S. Belyaev. - M.: Medicine, 1984.
- Wikipedia article
Gymnastics for eyes with farsightedness
- Rotate your eyes clockwise and counterclockwise. After rotating several times in one direction and then in the other, you need to close your eyes and relax them.
- Touch the tip of your nose with your index finger and concentrate your gaze on it. Slowly move your finger forward, continue to focus your gaze on the finger.
- Look alternately left and right.
- Draw a figure eight in front of your eyes for several minutes. Do not make yourself dizzy; movements should be smooth and not cause discomfort.