Our organs of vision are a unique system that provides the ability to see not only during the day, but also in low light. Of course, we do not have such visual acuity in the dark as our smaller brothers, but we are quite capable of distinguishing shapes and colors and navigating in a darkened space. How does the twilight vision mechanism work?
The concept of “twilight” in relation to an environment in which orientation is implied. It means the degree of illumination on the street at the moment when the sun begins to go below the horizon until the moment when the moon is in half phase in the sky. Indoors, this can be a small light source relative to the space, for example, a candle or a dim night light. Without a light source, our eyes cannot see.
Night, or mesopic vision (synonyms for the term “twilight”) is possible thanks to the coordinated work of rods and cones. Our eyes are quite sensitive, and the visual sensation appears due to light hitting the retina, which contains two types of receptors - rods and cones. Cones provide us with color vision, and rods contain the pigment rhodopsin, which reacts to light intensity. These two elements are responsible for night and day vision. During the day, cones are responsible for the brightness of vision, and at night, both types of cells work.
When the degree of illumination around changes (for example, when moving from a dark room to a light one or vice versa), an adaptation process occurs - the eyes adapt to a given brightness of light. At the same time, the area of the pupil changes, and adaptation from darkness to light occurs almost immediately, while the reverse process takes longer.
Definition of twilight vision
The human organ of vision has a fairly high degree of sensitivity. The visual sensation occurs when light hits the area of the retina (retina). This organ contains two types of perceptive elements: cones and rods. Cones function to provide the perception of color - color vision. Rods do not distinguish colors. But their sensitivity significantly exceeds that of cones.
These perceptive elements provide twilight and night vision (night blindness). Cones are elements of the light-sensitive apparatus for daytime vision. Thus, depending on the degree of illumination of the surrounding space, either the rods or cones of the retina function. This determines the difference between day, night and twilight vision.
Twilight vision is ensured by the “work” of both rods and cones simultaneously. If the degree of illumination brightness changes, the greater or lesser “contribution” to the mechanism of perception of rods and cones changes.
Twilight vision is black and white in quality. It gives only a feeling of darkness and light.
Symptoms of twilight vision
Suspicion of the development of night blindness arises when a person exhibits the following symptoms:
- incomplete visibility of objects in low light;
- feeling of discomfort when visible in the twilight;
- loss of spatial orientation in low light;
- the patient cannot distinguish between yellow and blue;
- narrowed fields of vision;
- in most cases, dry skin is noted, as well as the formation of dry flat spots within the palpebral fissure;
- the resulting softening of the cornea due to a lack of vitamin A.
Normal indicators
When the degree of illumination of the surrounding space changes, the eyes “reconfigure” to work in new conditions. Perceiving elements need a certain amount of time to begin to function effectively. The process of “tuning” is called darkness adaptation. The sensitivity of the organs of vision is directly related to the process of adaptation.
Light perception is the ability of the eye analyzer to perceive different degrees of brightness of light. Perceiving elements convert the energy of light radiation into physiological excitation.
The human eye is capable of perceiving light of fairly low intensity. The minimum amount of light flux that allows visual perception to occur is called the “threshold of irritation.” The limit of the minimum difference in light brightness between illuminated objects is the “discrimination threshold”.
The “threshold of irritation” can change and depends on the degree of brightness of the light that affected a person’s eyes at the previous point in time. After some time spent in a well-lit space, the eye will not be able to perceive its surroundings well. But after a while the objects become distinguishable.
Maximum visual perception during dark adaptation is achieved within the first 30-45 minutes. With longer exposure to limited lighting conditions, the eyes' light sensitivity continues to increase.
The functioning of twilight vision is ensured by both rods and cones, and receptors of both types are involved in the formation of the spectral dependence of photosensitivity. When studying the level of twilight vision, the ratio of the quantitative ratio of “rods” and “cones” in the perceptive system of the eye is taken into account. Normally, their ratio should be 18:1.
But a change in the brightness of the light flux causes a change in the ratio of the “contribution to work” of rods and cones. The spectral dependence of photosensitivity also changes: a decrease in illumination leads to a weakening of sensitivity to red light and increased perception of blue light. The maximum sensitivity in twilight lighting shifts towards the violet edge of the visible spectrum and is located at 510 nm.
Diagnosis and treatment of hemeralopia
Medicine distinguishes between congenital and acquired hemeralopia. Even modern treatment methods cannot cure the congenital form.
Methods for diagnosing hemeralopia:
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus, examination of the retina, optic nerve, blood vessels);
- biomicroscopy (examination of the eye using a slit lamp);
- tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure);
- visometry (determining visual acuity using a table);
- color vision research (the study of color perception based on color schemes).
It must be remembered that the treatment of hemeralopia is determined differently in each case, so you should not take any drugs uncontrollably. First, you need to find the cause of the disease, and the results of the examination will show what the body really lacks. Consultations from other specialists will not be superfluous.
If there is a cause for the defect, appropriate therapy is prescribed. Often these are vitamin complexes and treatment of pathologies of the visual system that provoke twilight vision disorders.
Pathologies of the visual system
When the cause of hemeralopia is myopia, therapy will consist of laser vision correction. Refractive surgeries (scleroplasty, lens replacement, etc.) can also be used.
Deviations and diseases
Impaired twilight vision is a disease that in ophthalmology is referred to as hemeralopia. The disease is not differentiated by degree of complexity or intensity. Hemeralopia, colloquially referred to as “night blindness,” is a vision disorder with the following symptoms:
- Weakened vision in conditions of significantly reduced lighting brightness.
- Poor spatial orientation in the dark or twilight.
- Changes occurring in the mechanism of light adaptation.
- Narrowing of visual fields.
- Problems associated with the perception of yellow and blue colors (quite rare).
An additional sign of night blindness is dryness and keratinization of the epidermis around the eye. In addition, the patient may also experience hair fragility. Hemeralopia is caused by damage to the retina and optic nerve due to various reasons. Twilight vision problems can be:
- Symptomatic. This type of pathology is caused by damage to photoreceptors, which is caused by glaucoma, neuritis, pigmentary degenerations and other organic diseases of the retina, optic nerve or choroid. In this case, the examination also reveals changes in the fundus and visual field.
- Functional. The disease occurs due to the development of hypovitaminosis A in the body. The patient also experiences the formation of xerotic plaques. Plaques appear on the conjunctiva, which is accompanied by exfoliation of the epithelium and hyperkeratosis.
- Congenital. The features of the development of this type of disease are still unclear. The disease is not accompanied by changes in the fundus.
The reasons for the development of acquired may be:
- Lack of vitamin A, B2, nicotinic acid in the body.
- Liver diseases.
- Physical exhaustion.
- Anemia.
- Eye diseases: glaucoma, retinal dystrophy, high degrees of myopia, retinal pigment pathologies, optic nerve atrophy, congestive disc.
- Childhood diseases (measles, chickenpox).
- Toxic poisoning.
- Alcohol abuse, drug addiction.
- Sunburn of the conjunctiva, exposure to excessively bright light on the organs of vision.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the visual part of the brain caused by head trauma.
Pregnancy can also cause night blindness.
Treatment of the disease
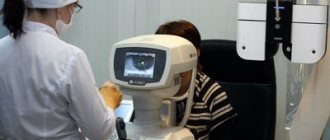
To choose a way to eliminate problems, you need a correct diagnosis. The search for the cause of deterioration of twilight vision is performed using the following methods:
- clarify visual acuity and color perception using standard tables in reduced light conditions;
- using perimetry, visual fields are determined for each eye;
- An ultrasound machine is used to check the functional state of organs;
- retinography monitors reactions to flashes of bright light;
- Tonometry determines the level of intraocular pressure.
A thorough examination of the retina can be done using a specialized CT scan.
If fatigue provokes night blindness, this deterioration in twilight vision is eliminated by correcting the load:
- organize work with regular breaks for rest (45 and 5 minutes, respectively);
- perform gymnastic exercises for the eyes;
- create optimal lighting for the workplace in accordance with current sanitary standards;
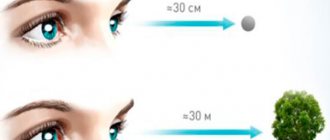
- maintain the recommended distance to the computer screen (35-45 cm).
Excessive light contrasts in the work area and the use of night lenses should be avoided. Separately, they check whether the display parameters comply with modern standards. The following negative factors (monitor characteristics) provide additional strain on the eyes:
- poor resolution with visible individual elements (pixels);
- distorted color scheme;
- excessively bright (dark) settings;
- low scan frequency.
If the deterioration of twilight vision is associated with a disease, the treatment method is chosen taking into account the corresponding cause:
- farsightedness (myopia) is corrected by ophthalmic surgery or corrected with glasses (contact lenses);
- laser coagulation restores the detached retina;
- eliminate the deterioration of twilight vision when replacing the lens with a lens if cataracts are detected;
- iridectomy in combination with drug therapy removes glaucoma.
To accelerate tissue recovery in the postoperative period, special medications, hardware technologies, diets and exercises are used. The exact procedure and restrictions are determined by the attending physician. As a rule, a mandatory period of load reduction is established.
Special treatment techniques are used if the deterioration of twilight vision is associated with a general disease. For hypertension, for example, blood pressure is normalized with medications to levels of 80/120.
Adding vitamins to your diet
A typical reason for the deterioration of twilight vision is a lack of nutrients that the light-sensitive elements of the retina need to function normally in the dark. Exact recommendations can be obtained from a specialist after studying a blood test.
To improve your vitamin A supply, your diet includes:
- blueberries;
- black currant;
- cottage cheese, kefir and other dairy products;
- eggs;
- carrots, green peas, corn;
- oranges, persimmons and apricots;
- parsley and other greens;
- fish, cod liver.
You can also use various specialized infusions. Dried blueberries, for example, can be poured with boiling water and left for 3-5 hours. This remedy is consumed daily 3-4 times, 100-120 g each. It is not difficult to prepare similar healing drinks yourself based on sea buckthorn berries and dried nettles. Fish oil contains many vitamins. Fruits and vegetables can be used to make fresh juices.
To speed up the elimination of night blindness, in addition to changes in diet, vitamins and specialized supplements are prescribed. In addition to the listed vitamins, suitable preparations contain selenium, zinc and other useful microelements.
conclusions
To determine the cause of the deterioration of twilight vision, contact a specialized doctor. You should not independently apply medical techniques without professional research. A narrowing of the visual field and other manifestations discussed may be signs of dangerous diseases. We should not forget that timely treatment is the most effective.
Preventive measures that reduce eye strain can be used without consulting a doctor. Periodic relaxation is recommended to be combined with training of the ciliary muscles. The purchase of high-quality computer and video equipment combined with good lighting will provide comfortable, healthy conditions for all family members. Characteristic signs of vitamin deficiency can be taken into account when developing an optimal diet.
To improve the functional state of the visual organs, professionals use hardware techniques. To eliminate visiting the treatment room and the associated costs, you can purchase Zevsonik. This device is well prepared for home use. Simple instructions can be studied in a few minutes. The operating mode is maintained automatically.
Zeusonic generates sound and electromagnetic vibrations, which accelerate the outflow of lymph and improve the conductivity of nerve tissue. Activated blood microcirculation ensures a good supply of tissues with nutrients. Techniques in this category can be used to improve vision at any age. Surgeries are used only in cases where preventive and medicinal methods are useless.
Prevention
Congenital night blindness cannot be treated. It is necessary to treat other types of hemeralopia, taking into account the underlying cause of the disease. Prevention of hemeralopia:
- A nutritious diet, including those foods that can provide sufficient amounts of essential vitamins.
- Retinal protection. Use of special glasses to protect against excessive exposure to sunlight, as well as when working in harmful radiation.
- Treatment of pathological processes causing hemeralopia.
If you have myopia, it is important to carry out timely vision correction. If twilight vision worsens, it is important to conduct an examination to determine the level of vitamin A, retinol and carotene in the blood. It is necessary to consult a gastroenterologist and endocrinologist.
What could be causing the deterioration of twilight vision?
Experts distinguish the following types of disease:
- congenital;
- essential;
- symptomatic;
- false.
The last item on the list is due to excessive fatigue of the visual organs. Negative reactions can be eliminated with sufficient rest and special eye exercises. By adjusting the operating mode, the problem is eliminated without much difficulty. Below we discuss in detail the reasons why deterioration of twilight vision and more complex situations may be associated.
conclusions
In cases where hemeralopia is not congenital, it can be caused by a number of reasons related to the functioning of the visual organs, as well as other diseases and the general condition of the body. The disease, caused by problems with the retina, manifests itself due to a lack of vitamins, as well as exhaustion, alcohol abuse, and diseases of the digestive system. Some forms of night blindness are explained by eye diseases: optic atrophy, glaucoma and even severe myopia.
With the development of hemeralopia, daytime vision remains normal. However, impaired twilight vision has a dangerous effect on the patient’s quality of life. This condition can have harmful consequences. For example, a person suffering from this disease practically does not see dangers on the road at dusk. This is extremely important for vehicle drivers. Also, patients suffering from hemeralopia may develop phobias associated with the dark. This causes obsessive states and other mental deformations.
Causes of twilight vision
Ophthalmologists distinguish acquired and congenital hemeralopia by origin. The cause of congenital night blindness lies in human genetics and no doctor or medicine can change anything.
If we talk about an acquired disease, then the reason for its development is a decrease in the number of rods in the retina, as well as a disruption in the process of restoration of the rhodopsin substance in the rods. The following situations provoke such conditions:
- eye diseases (high myopia, glaucoma, pigment pathologies or retinal dystrophy);
- unbalanced or inadequate nutrition, depleted in vitamins A and B2;
- head injury, which resulted in disruption of the visual center of the brain;
- excessive exhaustion of the body;
- liver disease, anemia;
- pregnancy;
- past infectious diseases (chickenpox, measles);
- chronic alcoholism;
- frequent and prolonged exposure to bright light on unprotected eyes;
- insufficient illumination of the workplace.
In most cases, the disease “night blindness” occurs, caused by hypovitaminosis. Vitamin A deficiency leads to dryness of the conjunctiva, its inflammation, thickening and, against this background, a decrease in the secretion of the lacrimal glands and clouding of the cornea.
How to improve twilight vision
Sunglasses
There are ways to improve dark adaptation. The first one goes back to the days of pirates. Not surprisingly, they are often depicted with an eye patch, but rarely did it cover up the missing eyeball. Pirates wore blindfolds to have one working eye when going down from the deck into the hold, where it was dangerous to use candles and lanterns.
Today, to improve dark adaptation, there is no need to wear bandages. It is enough to use sunglasses, the desired shade of gray. It has been proven that after being in the sun for 2-3 hours, it then takes 10 minutes more to fully adapt to the dark.
Don't look at the light
When in the dark, you don’t need to look at light sources. Such actions disrupt twilight vision, since rhodopsin will begin to rapidly decompose in the light. If it is not possible to avoid bright light, you need to cover one eye, maintaining dark adaptation at least in it. This way a person will not be completely disoriented if, for example, he is driving.
Red glasses
Another method is based on the fact that the rods are insensitive to red light. Previously, the army practiced this method of adaptation: soldiers wore red glasses before night guard, and the red did not interfere with the restoration of rhodopsin. Cones with red pigment did not interfere with orientation in the light, and thanks to the preservation of rhodopsin, the soldier could serve from the first minute of duty.
Today, red-tinted glasses can be purchased at any optical store. By putting them on 20-30 minutes before going out into the dark, a person ensures good adaptation. This method is used by pilots if they do not have the opportunity to be in the dark before flying into the night.
Eye exercise
Another feature of vision is actively used in special forces. Once in the dark, the soldiers close their eyes and press their eyelids on their eyes for 10 seconds. The method is effective, although medicine has not yet found an explanation for this.
Before going out into the dark, you need to close your eyes and massage your eyeballs, pressing with your palms. After a few seconds, the field of vision will brighten. This is a signal that vision has been rebooted. You should wait for the black to return and open your eyes. Twilight vision will be better.
| Mix the crushed ingredients. Brew a large spoonful of the resulting mixture in 250 ml of boiling water and leave for 180 minutes. Filter. | Drink half a cup three times a day before breakfast, lunch and dinner. | |
| Blue cornflower flowers | Brew a small spoon of plant material in a cup of boiling water and wait 60 minutes. Filter. | Drink a quarter cup three times a day 30 minutes before meals. |
| blueberries | Brew a large spoonful of dried fruits in a cup of boiling water and let it brew for four hours. Filter. | Drink half a glass three times a day, at any time. |
| Sea buckthorn berries | Three large spoons of fresh fruits are infused in boiling water (250 ml) for 30 minutes, then filtered. If desired, you can sweeten the drink with honey or jam. | Drink twice a day, an hour after meals. |
| Nettle | Crushed leaves of a medicinal plant (two large spoons) are steamed in a cup of boiling water for 60 minutes, filtered. | Drink a third of a cup three times a day 30 minutes before breakfast, lunch and dinner. |
Light perception is characterized by a threshold of irritation (perception of the minimum light flux) and a threshold of discrimination (discrimination of the minimum difference in
Lighting). Daytime (photopic) vision (cones work) is carried out when the external illumination of surrounding objects is 30 lux or more; it is characterized by high visual acuity and color perception. At illumination from 25 to 0.3 lux, the eye moves from phototopic to mesopic vision (both cones and rods function). At illumination of 0.3-0.1 lux, rods function predominantly. When illumination is below 0.01 lux, only scotopic vision (rods only) is possible.
Twilight Vision Features:
1. Colorlessness. Since cones do not function at low light levels, colors are not perceived at night. Therefore, twilight and night vision are achromatic.
17
2. Changing the brightness (lightness) of colors. This is a phenomenon
This is called the Purkinje phenomenon: “warm” color tones (red, orange, yellow) appear darker at dusk, and “cold” colors (blue, indigo, green) appear lighter. In low light conditions, blue, blue-green, yellow and purple-crimson colors are perceived the longest.
3. Peripheral nature. At dusk it is not functional
They activate the cones that provide central vision, so when lighting decreases, vision becomes peripheral. The place of greatest sensitivity of the peripheral retina to light is 10-12° from the center.
Adaptation of the eye to changes in lighting,
its violations
- the process of adapting vision to different lighting conditions by changing the light sensitivity of the visual analyzer. It is caused by a reversible photochemical reaction (disintegration of rhodopsin molecules in the light and their restoration in the dark).
There is adaptation to light, i.e. adaptation to higher illumination (occurs within 5—
7 minutes), and to darkness, i.e. adaptation to work in low light conditions (occurs within approximately an hour).
Variants of light adaptation disorders. Nyctalo-
Piya - impaired light adaptation, vision at dusk
Better than in the light (sometimes happens in children with
Congenital
Complete color blindness).
Hemeralopia is a disorder of dark adaptation. Severe hemeralopia leads to loss of spatial orientation in patients under twilight lighting conditions.
Symptomatic hemeralopia occurs when
Various diseases of the eyes and body - retinal pigmentary degeneration, retinal detachment, inflammatory lesions of the retina, optic nerve, choroid, glaucoma, high degrees of myopia. There may be false hemeralopia due to opacities of the refractive media of the eye.
Functional or essential hemeralopia
It occurs due to the absence or deficiency of vitamin A, which leads to a change in the normal structure of epithelial cells, in particular the pigment epithelium and light-sensitive elements of the retina.
Congenital hemeralopia may be familial in nature. Arises from childhood in the complete absence of diseases of the eyes and the body as a whole.
Determination of the value of light sensitivity and the course of its change under conditions of adaptation of the eye to darkness is carried out using special devices - adaptometers. An accelerated study of adaptation to darkness, which is carried out on an adaptometer, consists of determining the time of discrimination of a test object after dosed adaptation to light. First, the subject looks at a bright light for 2 minutes. Then set the device’s aperture with a diameter of 1.1 (with the light turned off) and present the subject for identification with one of the test objects - a circle, a square or a cross. The moment of identification of the test object is noted using a stopwatch. Normally, during binocular examination, this time does not exceed 45 seconds.
The device is also used to measure the time required to restore vision after illuminating the retina with very bright light (a similar phenomenon is often observed when moving to a dark place after being in a sunlit space or when a driver is temporarily “blinded” at night by the headlights of an oncoming car).
39