According to alternative medicine, certain parts of the body reflect the state of our health. Popular methods include examination of the surface of the skin, organs of hearing, vision and smell.
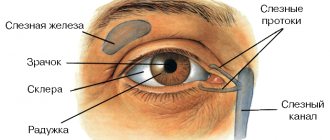
The iris of the human eye is interconnected with the work of internal organs by a large number of nerve connections. Visual diagnostics of the visual organs allows us to identify the slightest deviations in health and promptly prevent the development of complications. This type of study is called iridology. The practice originated in ancient India and China. Today, iridology is practiced in research centers around the world.
Iridology: how is it carried out?
- The essence of iridology is to project the pattern of the iris onto the internal organs of a person. In this technique, the iris of the eyes is a mirror image of vital processes. Any anomaly in the body manifests itself in the form of pigmentation on the iris.
- Iridology of the eyes is carried out using a bright light source. The examination lamp dazzles the patient's eyes, but is absolutely safe.
- Expensive optical equipment works effectively with the right technical equipment. A slit lamp microscope allows you to make an image three-dimensional, magnifying the image several tens of times.
What is iridology?
There are two types of research - iridoscopy and iridography. Iridoscopy involves illuminating the eye shell using incandescent lamps. Iridography allows you to take black and white and color photographs.
- The main objective of the examination is to characterize the color gamut of the iris and the uniformity of its distribution, to identify inclusions and darkening.
What is the essence of the technique
To understand what the essence of this method of research on the iris of the human eye is and why it is needed at all, you should familiarize yourself a little with the structure of the human visual organs. Translated from Greek, often used in medical terminology, iris or “iris” means “iris”. Its structure is similar to a diaphragm that transmits the sun's rays to the retina of the eye.
The iris is somehow connected and connected not only with all elements of the visual organs, but also with other internal organs. For medical researchers, it is a kind of screen that reflects almost everything that happens in the human body. All pathological processes are projected onto the iris. If something changes in the condition and functions of the internal organs, this is reflected in the distribution of pigment in the iris. Using iris diagnostics using this method, you can create a detailed diagram that will show the presence of pathologies in the patient.
In some ways, iridology is very similar to acupuncture. By means of a needle injection into certain areas of a person’s skin, specific internal organs can be affected. By changes in the color and structure of a certain area of the iris, the doctor will be able to determine how certain systems work.
This is interesting: modern medicine has established five projection zones on the human body. These are his skin, the auricle, the surface of the tongue, the nasal mucosa and the iris. Each zone has its own schemes. By comparing them with the resulting picture, you can find out how the heart, liver, and spleen function.
Iridology: criteria for assessing the iris
Comparative characteristics of the results of iridodiagnosis and the iris diagram allow us to make a preliminary diagnosis. The assessment scheme contains more than 80 points interconnected with internal organs. Projection zones characterize the functioning of the genitourinary system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, and gastrointestinal tract.
Why is the membrane of the eye examined?
When assessing the iris, several parameters are important:
- Direction and structure of fibers.
- Condition of the vessels of the iris.
- Size and shape of the pupil, reaction to light.
Pathological processes in the body are automatically accompanied by reflex impulses to the iris of the eye, which change the state of the above parameters. Iris signs can be either local or general in nature - characterizing the work of a specific organ or the general condition of the body.
- A special computer program that processes the data obtained from a visual examination of the iris and generates the examination result.
In addition to diseases, iridology determines heredity, reserve capabilities of the body, metabolic processes, and the state of the nervous system
A little about the history of iridology
Iridology today is considered to be a relatively new research method, and at the same time it was used by ancient healers. Information about this was preserved, for example, in ancient Egyptian papyri, which were found during excavations in Giza of the tomb of the famous pharaoh Tutankhamun. In ancient India and China, healers also used the study of the condition of the iris of human eyes in the practice of identifying diseases of the body.
At the moment, iridology is a fairly popular diagnostic method, which is used by specialists from many of the world's leading medical centers, as well as research institutes. The first medical research institution in Russia to begin using iridology methods was the center created in Moscow at the Faculty of Medicine of Peoples' Friendship University, which was headed by the famous specialist in the field of reflexology E.S. Wellkhover. The center's staff developed special computer programs, the use of which made it possible to effectively diagnose various diseases (stomach ulcer, kidney stones, etc.).
Iridology: diagram of the iris
A schematic representation of the iris of the eye is divided into 12 zones similar to a watch dial.
- The central part characterizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- The projection of the head is located in the upper zones of the iris.
- The work of the limbs is superimposed on the lower parts of the iris.
- The work of the internal organs - the respiratory system, thyroid gland, back muscles - is projected from top to bottom on the sides.
Iridology: photo with interpretation
In view of the individual characteristics of a person, icons of symbols often have controversial meaning. The indicators of neighboring organs can adjust to each other. Changes in the size, shape and location of internal organs also distort the results of iridology.
REDUCTION OF RESERVE FORCES OF THE ORGANISM IN MICROELEMENTS
— 320 — types of PARASITES in humans — Boxes must be full
• Helps identify the main causes of ailments • Determines the level of toxic damage to organs and tissues • Reveals microelement imbalance. • Deficiency of such vital microelements: Molybdenum, Zinc, Selenium, Iron, Iodine, Manganese, Copper, Chromium, Fluorine. • Shows the level of parasitic intoxication • Selects an individual health program
Advantages of iridology
- Iridology is carried out at any time without prior preparation.
- The absence of mechanical contact with the eyes encourages patients to undergo examination.
Absolutely any patient can have their iris examined. The procedure has no contraindications.
- Highly accurate examination results allow you to identify the problem at an early stage and get ahead of traditional diagnostics.
- Iridology effectively diagnoses diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, pathologies of the genital organs, and cardiovascular disorders.
- An unconventional type of diagnosis is carried out by qualified specialists.
The procedure has both advantages and disadvantages
Software for iridology
Naturally, the speed of diagnosis and its accuracy will increase significantly with the use of modern computers. To do this, it is necessary to “translate” the information and make it available for machine processing. This can be done using special programs, which are a recording of an algorithm for solving a problem in a special conventional machine language. The essence of these languages is the automatic programming of tasks. Their use greatly simplifies the programming process, making it universal and manageable. There is a wide variety of programming languages. For service terms, English is predominantly used. It is believed that every algorithmic language is quite universal. What does it mean? To solve any problem on any computer, you can use any of the existing languages.
Continued below
⇓
Methods of medical and laboratory diagnostics
Overdiagnosis is
the diagnosis of
a “disease” that will never cause symptoms or death during the patient's lifetime. She is a problem because...
Read more…
everything on this topic
The most widely used languages for programming are Algol-60, Fortran-IV, Cobol, Pascal, and BASIC. At the same time, the large number of languages indicates that each of them has certain advantages and disadvantages, which necessitates their further improvement. As a result, more and more new algorithmic languages are being developed. Among the already existing ones, Algol and Fortran turned out to be better suited for solving computational problems; economic ones - Cobol, PL/1.
The development of computer technology places high demands on the language, which can only be satisfied by the capabilities of an ideal algorithmic one. Such a language should allow full use of the machine's power and economical (compressed) writing of a task, work on any existing computer, and be close to the natural language for describing the task itself.
A committee was created by ABC (1963) which concluded that to meet these demands and make better use of the increasing power of computing systems, it was necessary to develop a high-level programming language. This new language, called PL/1 (programming language - one), has absorbed the best features of existing ones and allows you to fully realize the capabilities of modern computing systems. In 1977, the Russian edition of the book by R. Scott and I. Sondak “PL/1 for Programmers” was published. Reflecting the many advantages of this language, the authors draw attention to an interesting fact. One of the most stringent tests of a language is its ability to serve as the basis for the creation of another. PL/1 became the basis of the new language.
Now this algorithmic language is used to compile a variety of programs for computers of any class. R. Scott and N. Sondak write: “A person engaged in the humanities and arts can use the PL/1 language as an excellent tool for analyzing and studying works of literature, music and the fine arts. A programmer involved in solving scientific problems will find in PL/1 a powerful tool for solving analytical and modeling problems.”
To process information on a computer, the created algorithm for solving a problem using the selected language must be translated into a set of commands for the machine, that is, a program must be written. Composing computer programs is a creative process. Like works of art, literature, programs can be good and bad. True, there may be conflicting assessments about the content and merits of the former. After all, there is no arguing about tastes. The advantages of computer programs when solving similar problems are clearly evident.
Let us recall that the program itself is a sequence of commands that determine the actions of the computer at each period of time, which together ensures the transformation of the source data into the final result.
All programs used in the operation of computers, machines, both large and small, can be divided into two groups. The first is the so-called system programs. They are used to control the computer itself and are, as it were, its integral part. It is customary to say about such programs that they are “hardwired” into the computer. System programs are usually entered into the computer's circuitry or memory.
The second is programs that are compiled according to the instructions of the computer user. They are called applied. They are able to configure the computer to perform a specific task.
Is programming an art, a science, or a craft? After all, there is an opinion that large programs are the most complex objects that man has ever created.
The software and mathematical support of modern computers is the most expensive and expensive component. According to global data, the cost of mathematical software is now about half the total cost of the machines themselves. The price of the software is even higher. According to experts, today the cost of software for computer networks is commensurate with the cost of their hardware. This includes computers, communication channels and terminals. By 2000, it will account for up to 80–90% of the total cost of any information processing system built on the network. For example, it took more than 10 years and about a billion dollars to create software for one of the first computer networks in the United States, AR PA.
Computer software is a well-established business in developed countries. In the USA alone, about 10 thousand different companies and companies are developing it. The numbers are quite eloquent: turnover from the sale of programs jumped from $5 billion in 1982 to $25 billion in 1985.
Should we expect everyone to be able to write computer programs? Here are some interesting opinions on this issue, expressed by participants in the Moscow club of computer general education “Interface”. According to A. N. Kushnarev, who took part in one of the discussions, computer literacy is, first of all, knowledge of the techniques and rules for using computer technology, that is, a person is literate if he knows how to work with a computer. A competent user must first of all know about the specific ready-made software tools he needs and be able to work with them. The words “can work” mean that he can use a computer in a way that will allow him to do some work more quickly, efficiently, and efficiently. In his opinion, in this regard, programming - as the ability to compose computer programs - is probably not related to computer literacy. Programming becomes necessary only at a sufficiently high level of interaction with a computer, and if you start training the user with the construction of various algorithms, then the matter may simply not reach practical useful skills.
An interesting metamorphosis has occurred with the concept of “computer literacy” in the United States. In the 60s, it was associated primarily with knowledge of one or more algorithmic languages and the ability to program in them. “Now,” says G. B. Kochetkov, another participant in the discussion, “a person who is able to transmit or receive the necessary information through numerous information processing systems is considered literate. It should be emphasized that more and more Americans feel an urgent need for this. After all, those who do not know how to handle information transmission devices find themselves in some way thrown out of the social system. The American example, according to G. B. Kochetkov, demonstrates, on the one hand, the historical relativity of the concept of computer literacy (today it is one thing, tomorrow it is completely different), on the other hand, a very utilitarian approach to determining the criteria for computer literacy. To make it more convincing, he gives a well-known example about a child who knew only one number, 7. “What is 35 minus 28,” adults ask him. “Seven,” the child answers. “And 18 minus 11.” “Seven,” he answers again. Can such answers, despite their arithmetic correctness, be considered literate? Most likely no. Literacy must necessarily include an understanding of the results obtained. In this sense, the use of computers will be “computer literate” only if you understand the things that happen during this process.”
In the mid-1970s, Science magazine published a review: “80% of physiologists believe that all students in this specialty should take an introductory computer science course and write at least one computer program. It is now available to any organization for $400-$800 per month. With modern technical and economic capabilities, it is possible to achieve this level of training in the American secondary education system in a year. At a time when most American youth are entering college, we can expect that most of the next generation will master computers in the same way that the previous generation mastered electricity, and the current generation mastered airplanes and televisions.”
G. A. Aleksakov (MEPhI), in the polemical article “Question for everyone: why do we need computers,” published in the brochure “Informatics in Technology,” expresses his opinions about computerization and computer literacy:
“Let’s agree,” he argues, “let computer literacy be the professional virtue of those computer specialists (system and circuit engineers, programmers, technologists, adjusters, repairmen, etc.) who create their professional computers for other professionals, that is, practically carries out computerization without talking about computer literacy. Just as plumbing literacy will continue to be the valor of plumbers, medical literacy - of doctors, pedagogy - of teachers, television - of TV studio workers, automotive - of car service workers. These different literacies will never be replaced by any universal computer..."
“And there is no need to once again destroy the education system that has been developing for centuries,” writes G. N. Aleksakov, “by teaching everyone to “write down the algorithms they invent in a familiar language, so that later...”. The laws of nature cannot be invented. Everyone should discover them personally, just like Archimedes, Newton, Einstein and other smart people of the pre-computer era. And we need to help schoolchildren and students with this now, not later. It is well known what came out of attempts to hastily modernize school textbooks. And let's trust practicing teachers more than theoretical teachers and correspondence teachers. And let the programmers do their thing - programming.
Everything will be better if schoolchildren from a young age can widely become involved - try themselves - both in “rough” technology, and in the fine arts, and in programming - whatever their heart is in. For this we need “personal” machines, instruments, tools, workshops, studios and personal computers. But not everyone, but only those who find it interesting.”
© Authors and reviewers: the editorial team of the health portal “To your health!” All rights reserved.
Find out more about diagnostics:
Methods of medical and laboratory diagnostics
Early ultrasound diagnosis
pregnancy (ultrasound examination)
Diagnosis - without a doctor?
MRI diagnostics
Diagnostic methods
: pulse
diagnostics
The art of recognizing diseases in Tibetan medicine
Diagnostic techniques
diagnostics has started in Russia
GERD
Breast mammography
Modern concept of organizing express diagnostics
emergency conditions
all articles on the topic
Disadvantages of iridology
- The ease of conducting the survey raises many doubts about the reliability of the results.
- Scientific studies of iridology completely discount the results of the study, calling the exact results a mere coincidence.
- Making a diagnosis without a comprehensive examination of the body casts doubt on the result obtained.
- The iris has a stable texture from birth and throughout life, which makes iris diagnostics not a completely accurate test.
- An erroneous diagnosis brings psychological discomfort and unexpected financial expenses to the patient.
- Iridology is ineffective for diabetes and malignant tumors.
The effectiveness of iridology in diseases
There are a number of diseases for which iridology is an alternative type of diagnosis.
Reviews from doctors about iridodiagnosis are quite positive, but still the diagnosis is not always accurate.
In traditional medicine, the iris of the eye is a reliable reflection of the following chronic pathologies:
- Different colors of the right and left visual organs - heterochromia .
- The absence of the iris from birth is aniridia .
- Pathological or physical dilation of the pupil - mydriasis .
- Incorrect arrangement of the muscles of the iris - polycoria.
- Weak pigmentation of the iris - albinism .
- Genetic diseases leading to changes in appearance.
Iridology of the eyes: signs of pathological changes in the body
- In older patients with chronic illnesses, the pigment layer of the iris is depleted, which visually creates the effect of dull eyes.
- In a healthy organism with a strong immune system, the structure of the iris is dense and clean. Exhaustion of the body leads to looseness.
- pinpoint pigmentation of brown or white shades appears on the iris
- Disruption of chemical reactions in the body is reflected in the form of dark rays on the iris of the eye. As soon as the health condition improves, the rays disappear.
- In a healthy person, the pupillary border has a thickened, clearly visible structure.
- As the disease progresses in the body, the edge of the iris becomes halo-like.
- In case of cancer, the pigment fringe may completely disappear.
- By nature, brown-eyed people have a larger number of nerve rings in the iris, which indicates greater activity than blue-eyed people.
- An incomplete ring indicates a disease of a specific organ.
Certain ailments are detected quite accurately
According to statistics, urban residents have more rings in their irises than people from rural areas.
Scientific research
In 1979, Bernard Jensen and two other proponents of iridology failed a trial in which they evaluated photographs of the eyes of 143 people in an attempt to determine which of them had kidney disease. (48 were diagnosed with the disease by a standard kidney function test; the rest had normal kidney function.) All three showed no statistically significant ability to determine which patients had kidney disease and which did not. One iridologist, for example, decided that 88% of healthy people were sick, and another found that 74% of patients requiring hemodialysis were healthy. [3] Click here to see an example of a Jensen chart.
In 1980, an experienced Australian iridologist took part in two trials. In the first, he studied photographs of the irises of 15 patients who underwent medical examination and, according to the results, had a total of 33 diseases. The iridologist was unable to correctly identify any of these diseases. On three occasions he correctly identified the affected body part (for example, he said “a lesion in the throat area” to a patient whose tonsils were removed as a child), but completely missed another 30 problem areas and made 60 incorrect diagnoses. In the second trial, pictures were taken of four people's eyes when they were in good health and taken again when they reported being sick. The iridologist made a large number of (incorrect) diagnoses from the initial photographs and was unable to accurately identify any of the organs in which pathological changes had developed. He was also asked to compare photographs of the iris of another healthy person taken two minutes apart. He made five different misdiagnoses from the first photo and four different misdiagnoses from the second. [4]
In the late 1980s, five leading Dutch iridologists failed a similar test. They were given images of the right iris of 78 people, half of whom had gallbladder disease. None of the five could distinguish sick people from healthy ones. On top of this, they disagreed. [5] These negative results are, of course, not surprising, since there is no known mechanism by which the organs of the body could have representations at certain locations in the iris and transmit information about their condition to them.
In another study, researchers took color photographs of the eyes of 30 patients with ulcerative colitis, 25 with coronary heart disease, 30 with asthma, 30 with psoriasis, and age- and sex-matched controls. The images were coded and analyzed by the researcher, both manually and using a computer program, in accordance with the criteria proposed by leading iridologist. Neither of the two methods distinguished patients from healthy people better than random guessing. The authors concluded that “iridological analysis cannot facilitate the diagnosis of these diseases.” [6]
In 1998, Eugene Emery, a science columnist for the Providence Journal, tested two iridologists who assessed his health and compared photographs he prepared of the irises of 8 people with an established diagnosis. Both iridology tests showed very poor results. [7]
In 2000, Dr. Edzard Ernst prepared a thorough review of published research. Noting that none of the studies with “positive” results were properly designed, he concluded:
“Does iridology cause harm? Wasting money and time are two obvious undesirable consequences. More serious is the possibility of making a false-positive diagnosis, that is, the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of conditions that the patient does not have. The real problem, however, can be false negative diagnoses: a person may feel ill, go to an iridologist and receive a report of complete health. He may subsequently be diagnosed with a serious illness. In such cases, iridology leads to the loss of precious time for early treatment (and life itself).” [8]
A study published in 2005 tested whether iridology could be useful in diagnosing common forms of cancer. An experienced practitioner studied the eyes of 68 patients with breast, ovarian, uterine, prostate or colon cancer and 42 healthy people. The practitioner, who did not know their gender or details of their medical history, was given a choice of up to five diagnoses for each person, and his findings were compared with each patient's known diagnosis. The iridologist correctly identified cancer in only 3 out of 68 cases. [9]
Iridology: reviews
- Elena, Russia. Previously, I didn’t know what iridology was, but I decided to try it. The result of iridology did not coincide with my expectations. The result of the examination was printed in the form of a list with the percentage load on various organs, which is understandable only to a specialist. For the average patient, the results remain a mystery. The diagram of the iris of the eye has been compiled for several dozen internal organs - the brain, heart, lungs, spine, uterus, etc. Too many abnormalities have been identified in my body, which raises even greater doubts.
- Natalia, Nizhny Novgorod. I would like to recommend iridology as a very effective examination method. Iridology helped identify the cause of my long-standing gynecological problems. I was diagnosed with improper functioning of the thyroid gland and a lack of a number of microelements - the causes of my hormonal imbalances and constant loss of strength. It was established that the hearing organs were damaged by a fungus, which was later confirmed in laboratory tests. At the clinic I purchased several dietary supplements, which within a month significantly improved my health.
Did you know that diseases can also be detected by the tongue? If not, then we recommend reading the article - “Diagnosis of diseases by language”
We also recommend useful articles about the disease:
- Goffa
- Perthes
- Schlatter
- Koenig
- Alzheimer's
- home
- »
- Development and Training Center
- »
- Timetable of classes
Author's educational seminars and courses of Doctor of Medical Sciences Alla Mikhailovna Lugova
Lugova A.M. For 26 years she has been engaged in scientific and pedagogical activities in iridology, developed her own methods of teaching and iridological testing and correction of health levels (RF patent for invention No. 2348346). Author of distance learning in iridology based on a patent for topography of iridograms (RF utility model patent No. 130212). In 2012, she prepared the “Atlas of Iridograms” for publication, and in 2013, an educational and methodological manual on iridology. For 19 years Lugova A.M. conducts scientific and pedagogical work on light therapy and color therapy, color pulse therapy. He is the author of the patented effective method “Anti-stress color correction” (RF invention patent No. 2313282, RF industrial design patents No. 64493 and No. 67829). He has about 40 publications, 7 teaching aids, 6 monographs, 6 patents. Author of a number of techniques for iridology, light therapy and color therapy.
Lugova Alla Mikhailovna conducts her own educational seminars and courses: “Fundamentals of iridology”, “Practical iridology”, “Color pulse therapy”, “Anti-stress color correction using the method of Dr. A.M. Lugovoi."
Iridology
– a method for studying the state of the body using the iris of the eyes. It allows you to assess the heredity, resistance and adaptive capabilities of the body. Iridology reveals signs of emotional overstrain, neurotic and psychosomatic disorders, metabolic and toxic disorders. The method reveals iridological signs: - predisposition to diseases (the so-called “target organs”); — changes in the projection zones of organs; - various diseases. Iridodiagnostics can be used for differential diagnosis between somatic and psychosomatic pathologies, visceral and musculoskeletal pathologies in vertebrogenic visceropathies, identifying the source of pain, including in the presence of referred pain. This method is used to assess the state of the body and further individual selection of the most optimal methods of prevention, treatment and rehabilitation: reflexology, manual therapy, homeopathy, color pulse therapy, anti-stress color correction, herbal medicine, psychotherapy, etc. Currently, computer iridology is being developed using special hardware complexes and portable devices.
Anti-stress color correction according to the method of Dr. A.M. Lugovoi
– a method for correcting a psycho-emotional state, which includes an assessment of the current psycho-emotional state, individual personality characteristics and stress resistance;
situational, typological choice of color and complex color therapy. Complex influence of color through a visual analyzer is color pulse therapy
with special devices and
color correction ranges
(tonic, relaxation and mixed) for visual influence.
Color pulse therapy
– an effective drug-free method of prevention, treatment and rehabilitation, combining color therapy and biorhythm therapy. The impact is carried out by pulses of electromagnetic radiation in the visible region of the spectrum on the human body through the visual analyzer and the central nervous system. The method is most effective for visual, neurotic and psychosomatic disorders.
Anti-stress color correction
can be widely used in the prevention and correction of neurotic and psychosomatic disorders, visual impairments, for harmonizing personality and interpersonal relationships, increasing stress resistance and adaptive capabilities of the body.
Course and seminar programs
Training seminar “Anti-stress color correction using the method of Dr. A.M. Lugovoi"
23.04 – 24.04.2014
Duration 10 hours (2 lessons), cost 8,000 rubles.
Training program
1. Concept of the method “Anti-stress color correction according to the method of Dr. A.M. Lugovoi." 2. Psychological testing and the M. Luscher color test in assessing the current psycho-emotional state, individual personality characteristics and stress resistance. Methodology for conducting and interpreting the M. Luscher test. 3. Color pulse therapy. Design of color pulse therapy devices. Indications and contraindications. Technique of color pulse therapy. 4. Application of color pulse therapy in medicine and psychology. The significance of the method in the prevention and correction of visual, psychoemotional and psychosomatic disorders. 5. The relationship between color and emotions. Methodology for situational and typological color selection in anti-stress color correction. The phenomenon of color preference. The use of anti-stress color correction tables in color selection. 6. Color correction scales: principles of construction. Selection technique and practical application in the “Anti-stress color correction” method.
Course participants will be able to purchase special glasses for studying the rhythms of the visual analyzer, a color pulse therapy apparatus with an additional set of light filters of different colors and shades, an educational and methodological set on anti-stress color correction, which includes the educational and methodological manual “Anti-stress color correction in medicine and psychology”, “Atlas” anti-stress color correction tables" A.M. Lugovoy, M. Luscher color test.
PROMOTION FOR COURSE PARTICIPANTS!
04/23 and 24/2014 10% discount on a color pulse therapy device with an educational and methodological kit and on glasses for studying the rhythms of the visual analyzer.
Calendar and thematic plan of the seminar
“Anti-stress color correction according to the method of Dr. A.M. Lugovoi"
Teacher: Lugova Alla Mikhailovna
Seminar length 10 hours
| date | Lesson plan | Total hours | Type of activity |
| 04/23/2014 Wednesday 10..00 — 15.00 | The concept of the method “Anti-stress color correction according to the method of Dr. A.M. Lugovoi." Color pulse therapy. Design of color pulse therapy devices. Indications and contraindications. Technique of color pulse therapy. | 5 | Lesson No. 1 |
| 04/24/2014 Thursday 10.00 -15.00 | M. Luscher color test: methodology, interpretation of results, practical application in combination with color pulse therapy. Methodology for situational and typological color selection in anti-stress color correction. The phenomenon of color preference. The use of anti-stress color correction scales in combination with color pulse therapy. | 5 | Lesson No. 2 |
Training course
Practical iridology
25.04 – 27.04.2014
Duration 18 hours (3 lessons), cost 15,000 rubles.
Training program
1. Structure of the iris. Iridological assessment of heredity. 2. Classification of iridological signs. Pupil diagnostics, pupillary border, autonomous ring. 3. Adaptation rings and arcs. Iridological assessment of emotional overstrain, predisposition to neurotic and psychosomatic disorders. 4. Toxic-dystrophic signs. Iridological signs of metabolic and toxic disorders. 5. Structural and chromatic signs. 6. Iridology of diseases of the digestive system. 7. Iridology of diseases of the cardiovascular system and kidneys. 8. Iridology of respiratory and ENT diseases. 9. Iridology of the state of the endocrine and nervous systems. 10. Modern methods of iridology. The use of an iridoscope, a portable device for computer iridology. 11. Iridology in the selection and further application of the most optimal comprehensive treatment and preventive programs. The importance of a holistic (integral) approach to the application of iridology in medicine and psychology.
Course participants will be able to purchase a portable device for computer iridology, a special magnifying glass with LED illumination (six LEDs), a portable iridoscope, educational literature, including the “Atlas of Iridograms” and teaching aids on iridology by A.M. Lugovoy.
Calendar and thematic plan of the course
"Practical iridology"
Teacher: Lugova Alla Mikhailovna
Course length: 18 hours
| date | Lesson plan | Total hours | Type of activity |
| 25.04.2014 Friday 16:00 – 20:00 | Structure of the iris. Heredity assessment. Pupillodiagnostics. Pupillary border. Autonomous ring. Adaptation rings and arcs. Toxic-dystrophic signs. | 4 | Lesson No. 1 |
| 26.04.2014 Saturday 10:00 – 17:00 | Structural and chromatic signs. Practical lesson. Methodology for identifying iridological signs. Iridodiagnosis of diseases of the digestive system | 7 | Lesson No. 2 |
| 27.04.2014 Sunday 10:00 – 17:00 | Iridodiagnosis of diseases of the cardiovascular system and kidneys. Iridodiagnosis of respiratory and ENT diseases. Iridology diagnostics of the endocrine and nervous systems. Practical lesson. Methods of iridology. The use of an iridoscope, a portable device for computer iridology. | 7 | Lesson No. 3 |