Characteristics of central vision
With the help of central vision, the eye can perceive fine details of objects in view. Compared to peripheral vision, this type of vision is evolutionarily newer and is carried out by the fovea - the thinnest place on the retina. A large number of cones that perceive light stimulation are concentrated in this area. They convert them into electrical impulses, which reach the cerebral cortex through the conduction section. Each cone sends a signal along a separate nerve fiber, resulting in clear images of the smallest objects.
Formal vision disorders can be identified by assessing its acuity. This characteristic describes the eye's ability to see two points separately from each other. Assessment of acuity in ophthalmology is carried out using visometry, skiascopy, and in some cases by determining optokinetic nystagmus.
Golovin table
The Golovin table is a common table used to test visual acuity. The table is named after S. S. Golovin, a Soviet ophthalmologist (1866-1931).
This table contains rows of Landolt rings (12 rows in total), the size of which decreases from row to row in the direction from top to bottom. To the left of each line is the distance D (in meters) from which a person with normal vision should see them (5.0 meters for the top row; 2.5 meters for the bottom). To the right of each line is the value V (in conventional units) - this is visual acuity when reading signs from a distance of 5 meters (0.1 if the eye sees only the top row; 2.0 - if the bottom row is visible). Normal vision (1.0) - when a person sees the tenth line with each eye from a distance of 5 meters. To calculate the size of the rings on a certain line (with an error of approximately 1 millimeter), you need to divide 7 millimeters by the value V (the value on this line). So, the size of the rings on the top line (V = 0.1) will be 70 millimeters; on the bottom (V = 2.0) - 3.5 millimeters in size.
Visometry
Visometry is used to determine visual acuity. During the examination, the patient is shown tables that depict several objects. Tables consist of letters or numbers and are called optotypes.
Visometry is a universal diagnostic method that does not require special training or expensive equipment. But even this accessible method has its drawbacks. How to conduct research with young children who do not yet know letters and numbers? The answer to this question was found in the 20th century.
Sivtsev table
The Sivtsev table is the most common table in the former USSR used to test visual acuity.
The table is named after D. A. Sivtsev, a Soviet ophthalmologist (1875-1940). This table contains lines of printed letters (12 lines in total), the size of the letters decreases from line to line from top to bottom. On the left of each line is the distance D (in meters) from which a person with normal vision should see them (50 meters for the top row; 2.5 meters for the bottom). To the right of each line is the V value (in conventional units) - this is visual acuity when reading letters from a distance of 5 meters (0.1 if the eye sees only the top row; 2.0 - if the bottom row is visible). Normal vision (1.0) - when a person sees the tenth line with each eye from a distance of 5 meters.
To calculate the size of letters on a certain line (with an error of approximately 1 millimeter), you need to divide 7 millimeters by the value of V (the value on this line). So, the size of the letters on the top line (V = 0.1) will be 70 millimeters; on the bottom (V = 2.0) there are letters measuring 3.5 millimeters.
When examining visual acuity from a different distance (less than 0.1 - if a person does not recognize the letters of the top row from 5 meters), the person being tested is brought closer to the table and asked every 0.5 meters until he correctly names the letters of the top row. The value is calculated by the formula: V = d / D,
where V is visual acuity; d is the distance from which the study is carried out; D is the distance at which a normal eye sees a given row.
But it is better to use Polyak optotypes to determine visual acuity less than 0.1 s 5 meters. Ophthalmologists, as a rule, use this table in conjunction with the Golovin table.
Orlova table
An unusual idea to create a special table for children came to the mind of Natalya Sergeevna Orlova, a professor at the Department of Eye Diseases at Novosibirsk Medical University. Natalya Sergeevna devoted her entire life to working with children in medical practice and writing. Many kids know her wonderful poems from the collections “For Kids About Eyes”, “The Tale of Sickness and Health”, “About Eyes from A to Z”.
Natalya Sergeevna was a creative person. Her sincere love for her work helped her come up with a way to test visual acuity in preschool children. She replaced the usual images of letters and numbers with drawings of animals, cars and plants (Fig. 1). This is how the famous Orlova table turned out, which was named in honor of Natalya Sergeevna.
It contains 12 rows of pictures (some of the rows contain Landolt rings - optotypes, which are a ring with a gap), the size of which gradually decreases. To the right and left of the pictures there is a series of meanings. The left column characterizes the distance from which the child clearly sees the pictures in this line with normal visual acuity. The right column corresponds to the visual acuity value for each line.
When and how often do you get your eyes checked?
An eye test is necessary in the following cases:
- if, when working at the computer for a long time, watching TV, reading books, the eyes become red, watery, and pain in the head appears;
- circles periodically appear before your eyes;
- the color perception of objects changes;
- when reading, you move the text away or closer, whereas before you did not do this;
- the picture of what you see changes, it becomes not quite familiar;
- you stop recognizing your acquaintances from afar or up close.
If you can see distant objects perfectly, read books without problems, and you have no apparent reason to worry about your vision, then even in such cases you should regularly undergo annual examinations with an ophthalmologist. As a rule, at such appointments pathological vision problems are identified and treatment is prescribed in a timely manner.
Doctors recommend that teenagers have their eyes checked twice a year. People under 40 years of age can visit a doctor once every 2 years. If a person is over 40 years old, it is better to visit an ophthalmologist annually. Also, every year you need to bring young children to the doctor in order to promptly identify congenital problems with the organ of vision.
How is visometry done in children?
Before testing, it is important to find out whether the child knows the pictures that make up the table. To do this, the child is brought to the optotype and asked to name the objects depicted on it. So the optometrist notes for himself how the child is used to calling the depicted objects.
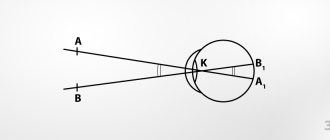
When checking visual acuity, the child should sit at a distance of 5 meters from the table. This is explained by the fact that with emmetropia (normal refraction of the eye, in which the image is focused exactly on the retina), the eye can clearly see objects at a distance of infinity. For our eyes, such “infinity” begins at a distance of 5 meters. It is from this distance that the light rays form an image that is focused on the retina.
The child takes turns naming the pictures shown on the table. At the same time, you cannot make mistakes from the first to the third line, from the fourth to the sixth - 1 mistake is allowed, from the seventh to the tenth - 2 mistakes. If a child makes mistakes, they move up one line. This happens until all the images in the line are named correctly.
Orlova’s table is remarkable because it helps check visual acuity even in the youngest patients. Thanks to this table, you can quickly and painlessly identify refractive errors in preschool children, which will help to avoid negative consequences in the future.
SVITSEVA-ORLOV tables (set of 5 pieces for ROTTA apparatus)
DESCRIPTION
Attention! When sending Sivtsev's table to regions of Russia, there is a possibility of creasing and damage. To avoid this, we recommend using a tube for transportation.
Sivtsev-Orlova tables for testing vision - a set of 5 tables for determining visual acuity (Sivtsev-Golovin, Orlova-children, Landolt rings, table for near)
There are several types of tables. Let's get acquainted with the main ones:
1. Determination of visual acuity using the Sivtsev table.
Presented in the form of a large white sheet with letters printed on it. The letters of the alphabet are arranged in twelve lines. The top line contains the largest size letters, the bottom line the smallest.
To the left of the letters there is a “D” designation, which determines the distance at which a person with one hundred percent vision can recognize the letters.
This distance is: for the top row, m - 5; for the bottom row, m - 2.5.
On the right is the designation “V” - this is the definition of visual acuity.
Vision is one hundred percent when a person is able to recognize the tenth line in order with each eye separately at a distance of five meters.
2. Orlova’s table or table for determining visual acuity in children.
How to check the eyesight of a child who cannot read? For this purpose, specialists use the presented tool. Outwardly, it is also a white sheet with various images printed on it instead of letters (horse, star, mushroom, duck, car, etc.). Also, as you decrease, the sizes of the patterns in the lines gradually decrease. A child with 100% vision will be able to discern what is shown in the tenth line from a distance of five meters.
3. It is also available today to buy a table for determining Golovin’s visual acuity.
The external presentation of this instrument is similar to those described above, the difference is the symbols depicted. This table shows rings of the same size that have gaps. The location of the break in each ring is different.
The total number of lines in this table is 15. The character size of the first ten lines decreases in increments of 0.1 as it decreases, the eleventh and twelfth lines - in increments of 0.5 and from the thirteenth to fifteenth - in increments of 1.0
This table can be used both in conjunction with Sivtsev’s table and independently.
4. The table is designed to determine visual acuity from a distance of 30 cm.
Visual acuity equal to 1.0 is considered normal (text No. 1 of the table, from a distance of 30 cm from the eyes). If you read text No. 1 without difficulty (from a distance of 33-35 cm), then you can see well up close.
The set includes 5 tables:
- Golovin-Sivtsev table with letters of the Russian alphabet;
- Table with Landolt rings;
- Table with W-shaped optotypes;
- Orlova table (children's);
- Table for determining visual acuity near (from a distance of 30 cm).
The size of the tables for distance is 450 x 300 mm; for close-up 300 x 200 mm
NOTE: The technical specifications indicated on the website are for informational purposes only.
The manufacturer reserves the right to make changes to the design, appearance, technical parameters, and packaging of the goods without prior notice to the seller and buyer!
The Sivtsev-Golovin table has two parts. The right one has an image of rings with slots, the left one - letters of the alphabet. There are only two characters on the top line, but they are the largest. The first line corresponds to 10% of vision or 0.1 vision.
The second line is ten percent higher, which means 20% or 0.2. If a person sees the lowest line, the tenth, then it can be said that vision is 100% or 1 (unit). Modified tables have also been developed, which have 11 and 12 rows: 1.5 and 2.0, respectively.
Tables can be displayed on a monitor, they can be plotted on paper, or they can be displayed on a wall using a spotlight. To obtain the most accurate results, it is necessary to provide the most effective lighting. The distance between the table and the person being examined should be five meters. This is the distance from which the eye, if healthy, should see the lowest line of the table.
If the room cannot be five meters long, then it is necessary to adjust the scale of the table. There are other research methods that can be used to determine the nature of the disorders and choose the optimal treatment method.
Indications for visometry
Visometry is prescribed in different cases. Among them are:
- Impaired visual acuity when the cause is not established.
- Checking how the disease progresses in a dynamic state.
- Preparatory procedures before eye surgery.
- Checking over time how high-quality the treatment was.
- Inspections for preventive purposes at various enterprises.
- Inspection of conscripts at military registration and enlistment offices.
Contraindications for visometry
There are also cases of contraindications for visometry: nIn case of drug or alcohol intoxication of the patient. In case of inappropriate behavior of a patient, if he suffers from mental disorders, especially during times of exacerbation, when the patient can cause harm to both himself and the ophthalmologist. All other cases require visometry.
The essence of the procedure
Special tables with pictures, rings with slots, and numbers are used to carry out visometry. They are called optotypes. Other optotypes, letters and drawings are arranged as rows in tables.
The size of the image differentiates each line from the previous one. The tables used by ophthalmologists should be proportionally reduced according to the distance that the specialist has.
A special paddle is used to close one eye and test the vision of the other. The line that the patient sees with an open eye, he names and reads the letters, voices the symbols depicted on it. A similar procedure is performed with the second eye.
Based on the results, the ophthalmologist selects corrective lenses.
The patient is put on a metal device that resembles glasses and glasses with different optical powers are inserted into it one after another. When the patient sees the last line normally, testing of the second eye begins. There are also diseases in which it is impossible to achieve one hundred percent vision, then you need to write down the result that was achieved with maximum correction and record it.
You should not lose sight of cases when each eye requires different vision correction. This happens quite often and, given modern capabilities, is not something extremely difficult.
Types of vision test tables
Sivtsev-Golovin table
In Russia, the Sivtsev-Golovin table has been used to test vision for almost a hundred years.
On it, in 12 lines, optotypes of various sizes are placed - letters of the Russian alphabet and Landolt rings. The lower the patient sees the line, the higher the level of visual acuity. In this case, the letters are used as similar to each other as possible, so that there is no intuitive recognition.
Snellen chart
The most common one in the world is the Snellen chart. The operating principle remains similar to the previous diagnostic system.
This table consists of 11 lines of optotypes - capital letters of the Latin alphabet. Each of the subsequent lines decreases, but the level of difficulty in recognizing signs remains the same.
Bailey-Lovey Table (ETDRS)
The most accurate system for testing vision is considered to be the Bailey-Lovey table (ETDRS). Today, this technique is the gold standard for measuring visual acuity throughout the world. Scientists Bailey and Lowey calculated the necessary spaces between letters and lines in such a way as not to create unnecessary strain on the eyes when reading the smallest lower lines and to more correctly determine the patient’s visual acuity. In our country, some clinics use a modified version of this table with letters of the Russian alphabet.
Orlova table
Lastly, we present Orlova’s table for checking vision in children. It is designed for young patients, since the emphasis is on their ignorance of the alphabet and numbers, so the tables contain only easily recognizable symbols of objects and Landolt rings.
Regardless of the chosen vision testing system, the order of its implementation remains the same: first, monocular vision is determined, then binocular vision. Experts note that usually the vision in both eyes is about 20% higher than in one. Therefore, after the check, you may see the following entries in your medical record or extract: Vis OD and Vis OS with values of 1.0, as well as below or above this indicator. In this case, Vis OD is the visual acuity of the right eye, and Vis OS is the visual acuity of the left eye. Most often, their indicators differ. If they are below 1.0, then vision correction is required, if above, then congratulations, your vision is excellent.
For patients with myopia Myopia (nearsightedness)
- a refractive error that makes it difficult to visually perceive objects in the distance., hypermetropia
Hypermetropia (farsightedness)
is a refractive error that makes it difficult to visually perceive objects near and leads to deterioration of distance vision.
and astigmatism Astigmatism
is a vision defect associated with uneven curvature of the cornea or a violation of the shape of the lens. As a result, the rays of light falling on the retina are refracted unevenly, and instead of a clear picture, a person sees a blurry double image. we have good news. Given the knowledge that visual acuity depends on many factors, accordingly, if you are predisposed to the possibility of having vision above 100%, for example, 120%, then after laser correction you will get it. A preliminary prognosis of the result can be discussed with an ophthalmic surgeon before surgery.
Read us on Yandex.Zen